././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692426889.039503
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/LICENSE.txt�������������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000104515�00000000000�012212� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
Version 3, 29 June 2007
Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
Preamble
The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
software and other kinds of works.
The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee your freedom to
share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
software for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the
GNU General Public License for most of our software; it applies also to
any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
your programs, too.
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you
these rights or asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have
certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the software, or if
you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
gratis or for a fee, you must pass on to the recipients the same
freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive
or can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they
know their rights.
Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps:
(1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License
giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains
that there is no warranty for this free software. For both users' and
authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked as
changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to
authors of previous versions.
Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run
modified versions of the software inside them, although the manufacturer
can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic
pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for individuals to
use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those
products. If such problems arise substantially in other domains, we
stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in future versions
of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents.
States should not allow patents to restrict development and use of
software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we wish to
avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could
make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that
patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
modification follow.
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
0. Definitions.
"This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
"Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
works, such as semiconductor masks.
"The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
"recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
on the Program.
To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
public, and in some countries other activities as well.
To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
1. Source Code.
The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
form of a work.
A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
is widely used among developers working in that language.
The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
"Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
(kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
(if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
includes interface definition files associated with source files for
the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
subprograms and other parts of the work.
The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
Source.
The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
same work.
2. Basic Permissions.
All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
makes it unnecessary.
3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
measures.
When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
technological measures.
4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
it, and giving a relevant date.
b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
released under this License and any conditions added under section
7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
"keep intact all notices".
c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
work need not make them do so.
A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
"aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
parts of the aggregate.
6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
in one of these ways:
a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
customarily used for software interchange.
b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
with subsection 6b.
d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
charge under subsection 6d.
A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
included in conveying the object code work.
A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
the only significant mode of use of the product.
"Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
modification has been made.
If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
been installed in ROM).
The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
protocols for communication across the network.
Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
source code form), and must require no special password or key for
unpacking, reading or copying.
7. Additional Terms.
"Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
this License without regard to the additional permissions.
When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
Notices displayed by works containing it; or
c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
authors of the material; or
e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
those licensors and authors.
All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
governed by this License along with a term that is a further
restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
not survive such relicensing or conveying.
If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
where to find the applicable terms.
Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
the above requirements apply either way.
8. Termination.
You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
paragraph of section 11).
However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
prior to 60 days after the cessation.
Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
your receipt of the notice.
Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
material under section 10.
9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
(including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
11. Patents.
A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
this License.
Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
propagate the contents of its contributor version.
In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
(such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
patent against the party.
If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
country that you have reason to believe are valid.
If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
work and works based on it.
A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a single
combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License,
section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the
combination as such.
14. Revised Versions of this License.
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
the GNU General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
address new problems or concerns.
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU General
Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
version or of any later version published by the Free Software
Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
by the Free Software Foundation.
If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
versions of the GNU General Public License can be used, that proxy's
public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
to choose that version for the Program.
Later license versions may give you additional or different
permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
later version.
15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
16. Limitation of Liability.
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES.
17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
copy of the Program in return for a fee.
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
Copyright (C)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program. If not, see .
Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
If the program does terminal interaction, make it output a short
notice like this when it starts in an interactive mode:
Copyright (C)
This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
parts of the General Public License. Of course, your program's commands
might be different; for a GUI interface, you would use an "about box".
You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU GPL, see
.
The GNU General Public License does not permit incorporating your program
into proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you
may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with
the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
Public License instead of this License. But first, please read
.�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692427122.946598
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/README.md���������������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000006501�00000000000�011642� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������# OpenCV Playground
The OpenCV Playground is a Qt6 application that brings together improved documentation alongside OpenCV functions with the ability to explore the effects of function parameters on an image in real time.
It also comes with a custom `Pipeline Launcher` that allows you to build and interact with your own sequence of image transformations along with custom build functions.
Full documentation can be found on [Read the Docs](https://opencv-pg.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
## Demo
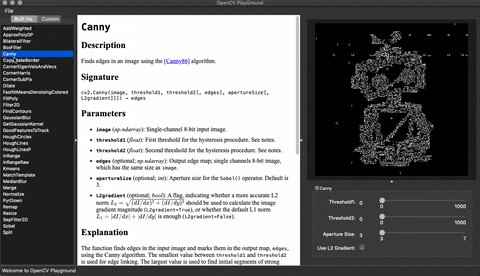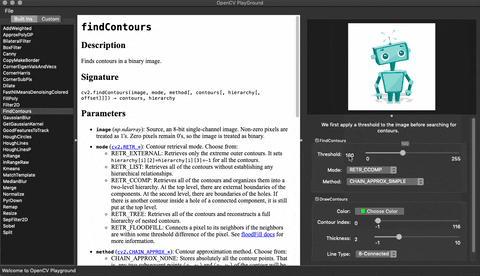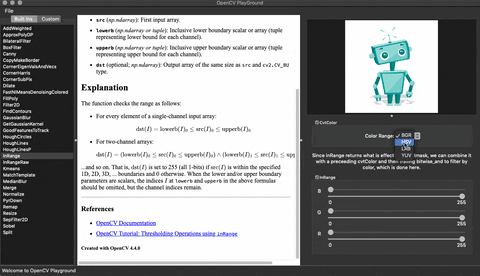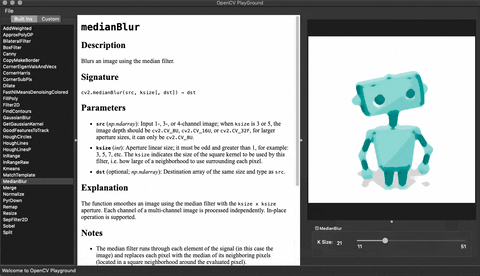 ## Installation
Currently tested with python 3.8.10/3.10.0 and opencv-contrib-python-headless 4.8.0.76 on an M1 Mac.
From PyPi:
```shell
pip install opencv-pg
```
From Github Repo:
```shell
pip install git+https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
```
### Note for Linux Users
**NOTE:** I no longer have access to anything but a Mac (as of `1.0.2`), so I can't confirm if the below still stands. It did in `1.0.1`.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (others currently untested), there may be missing links to xcb related shared objects.
tldr;
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
------
**Digging Deeper**
If you see errors about xcb, you can perform the following to help troubleshoot. In your terminal, make the following export:
```shell
export QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS=1
```
Run opencvpg again and validate the output. The final lines will likely mention details about files not found. Likely `libxcb-xinerama.so.0`.
Run the following:
```shell
cd your_venv/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/PySide2/Qt/plugins/platforms/
ldd libqxcb.so | grep "not found"
```
This will print any missing links. In our case, `libxcb-xinerama.so.0` showed up a couple times. Reinstalling the package as follows resolved the issue:
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
Once it’s working, you may want to disable that `QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS` env variable so it doesn’t throw extra garbage in your output.
## Usage
### Playground
To launch the OpenCV Playground with:
* The built-in image:
```shell
opencvpg
```
* An image of your choice:
```shell
opencvpg --image
```
* Without the documentation window:
```shell
opencvpg --no-docs
```
### Custom Pipeline
The following is an example of building a custom Pipeline.
```python
from opencv_pg import Pipeline, Window, launch_pipeline
from opencv_pg import support_transforms as supt
from opencv_pg import transforms as tf
if __name__ == '__main__':
my_image = '/path/to/image.png'
# Creates two windows
pipeline = Pipeline([
Window([
supt.LoadImage(my_image),
supt.CvtColor(),
tf.InRange(),
supt.BitwiseAnd(),
]),
Window([
tf.Canny(),
]),
])
launch_pipeline(pipeline)
```
Then run the file.
## Development
### Installation
To install in development mode:
```shell
git clone https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
pip install -e opencv-pg/[dev]
```
### Running Tests
```shell
cd tests
pytest
```
### Generating Docs
* Go into the top level `docs` directory
* run `sphinx-apidoc -f -o source/ ../src/opencv_pg`
* run `make html`
Output will be in the `docs/build/html/` directory.
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692427051.7198155
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/pyproject.toml����������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000001657�00000000000�013306� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������[build-system]
build-backend = "flit_core.buildapi"
requires = ["flit_core >=3.2,<4"]
[project]
name = "opencv-pg"
description = "Qt6 GUI Application for realtime exploration of OpenCV functions"
version = "1.0.2"
readme = "README.md"
authors = []
requires-python = ">=3.7"
license = { file = "LICENSE.txt" }
dependencies = [
"pyside6==6.5.2",
"qtpy==2.3.1",
"opencv-contrib-python-headless==4.8.0.76",
"jinja2==3.1.2",
]
keywords = ["opencv", "cv2", "cv", "computer vision"]
[project.optional-dependencies]
dev = ["pytest==6.0.1", "flake8", "sphinx==3.2.1"]
[project.urls]
Homepage = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg"
Documentation = "https://opencv-pg.readthedocs.io/en/latest/"
Repository = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg"
Changelog = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md"
[project.scripts]
opencvpg = "opencv_pg.launcher:main"
opencvpg_docview = "opencv_pg.launcher:docview"
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692379427.5699644
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/.DS_Store�������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�014612� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������������������������������������������������������������������������bwspblob���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������d�o�c�sbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������d�o�c�svSrnlong���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1640369016.170552
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/__init__.py�����������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000001062�00000000000�015240� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������from opencv_pg.pipeline_launcher import launch_pipeline
from jinja2 import Environment, PackageLoader, select_autoescape
env = Environment(
loader=PackageLoader("opencv_pg", "docs/source_docs"),
autoescape=select_autoescape(["html"]),
)
from opencv_pg.models.pipeline import Pipeline
from opencv_pg.models.window import Window
from opencv_pg.models.base_transform import BaseTransform
from opencv_pg.models import params
from opencv_pg.models.params import Param
from opencv_pg.models import transforms
from opencv_pg.models import support_transforms
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1706455
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/doc_viewer.py���������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000004227�00000000000�015635� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������from pathlib import Path
from qtpy.QtCore import Slot, QUrl
from qtpy.QtGui import QKeySequence
from qtpy.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QAction
from qtpy.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView
from opencv_pg.docs import doc_writer
# Make sure rendered_docs folder exists
doc_writer._create_rendered_docs()
class MyWebView(QWebEngineView):
def contextMenuEvent(self, event):
self.parent().reload()
super().contextMenuEvent(event)
class DocWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, template_name):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("OpenCV DocViewer")
self._setup_window_dims()
self._add_statusbar(template_name)
self._add_menus()
self._load_webview(template_name)
self._template_name = template_name
def _load_webview(self, template_name):
"""Return a WebView widget"""
view = MyWebView(self)
doc_writer.render_local_doc(doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR, template_name)
doc_name = doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR.joinpath(template_name)
url = QUrl.fromLocalFile(str(doc_name))
view.load(url)
self.setCentralWidget(view)
view.show()
def reload(self):
print("RELOAD")
doc_writer.render_local_doc(doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR, self._template_name)
doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR.joinpath(self._template_name)
def _setup_window_dims(self):
"""Setup default window dimensions"""
# TODO: Figure out how to get screen geometry
# screen = QScreen()
# geometry = screen.availableGeometry()
width = 800
height = 600
self.resize(width, height)
def _add_statusbar(self, fname):
"""Create and add a status bar"""
self.status = self.statusBar()
self.status.showMessage(fname)
def _add_menus(self):
"""Create and add menubars"""
self.menu = self.menuBar()
self.menu.setNativeMenuBar(False)
self.file_menu = self.menu.addMenu("File")
exit_action = QAction("Exit", self)
exit_action.setShortcut(QKeySequence.Quit)
exit_action.triggered.connect(self.close)
self.file_menu.addAction(exit_action)
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692379427.5692556
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/.DS_Store��������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�015542� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������� ����������������������������������������������������������������blob����bpli���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������j�sbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������j�svSrnlong�������
�r�e�n�d�e�r�e�d�_�d�o�c�svSrnlong�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E��� ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1707227
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/__init__.py������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000000000�00000000000�016157� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1708918
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/css/styles.css���������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000000471�00000000000�016707� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������body {
margin: 10px;
}
h1 {
font-weight: bold;
font-family: monospace;
}
refli {
margin: 0px 0;
}
li {
margin: 10px 0;
}
li ul li {
margin: 0px 0;
}
pre {
white-space: pre-wrap;
}
prmtr {
font-weight: bold;
font-family: monospace;
}
ptype {
font-style: italic;
}�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0401392
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/doc_writer.py����������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000002270�00000000000�016574� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������import logging
from pathlib import Path
from opencv_pg import env
from jinja2.exceptions import TemplateNotFound
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
ROOT = Path(__file__)
RENDERED_DIR = ROOT.parent.joinpath("rendered_docs/")
def _create_rendered_docs():
"""Create rendered_docs folder if it doesn't exist"""
if not RENDERED_DIR.exists():
RENDERED_DIR.mkdir()
log.info("Created %s", RENDERED_DIR)
def render_local_doc(folder, doc_fname):
"""Renders template into a local file
Normally we would render content in the webview with `setHtml`, but there
seems to be a bug which doesn't load local resources when that method is
used. It works properly when loaded from a local file.
"""
try:
template = env.get_template(doc_fname)
html = template.render()
except TemplateNotFound:
template = env.get_template("error.html")
html = template.render(error=f"Template: {doc_fname} not found :(")
path = folder.joinpath(doc_fname)
with open(path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(html)
log.debug("Wrote Doc: %s", path)
# Create rendered docs folder if it doesn't exist
_create_rendered_docs()
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692389906.8380182
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/.DS_Store�����������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�016156� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������� �����������������������������������������������������������������j�a�xbwspbl���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������m�a�t�h�j�a�xbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������m�a�t�h�j�a�xlg1Scomp�����p�������m�a�t�h�j�a�xmoDDblob����p�@��G�A�����m�a�t�h�j�a�xmodDblob����p�@��G�A�����m�a�t�h�j�a�xph1Scomp�����s0������m�a�t�h�j�a�xvSrnlong������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E��� ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692389906.8391132
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/.DS_Store���������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�017612� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1���������������
����������������������������������������������������������������lg1Scomp���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������a�1�1�ylg1Scomp������1������a�1�1�ymoDDblob�����n&��G�A�����a�1�1�ymodDblob�����n&��G�A�����a�1�1�yph1Scomp������P������a�d�a�p�t�o�r�slg1Scomp������Y������a�d�a�p�t�o�r�smoDDblob�����C���G�A�����a�d�a�p�t�o�r�smodDblob�����C���G�A�����a�d�a�p�t�o�r�sph1Scomp������`������i�n�p�u�tlg1Scomp������������i�n�p�u�tmoDDblob���������G�A�����i�n�p�u�tmodDblob���������G�A�����i�n�p�u�tph1Scomp�������������o�u�t�p�u�tlg1Scomp�������]�����o�u�t�p�u�tmoDDblob����2J���G�A�����o�u�t�p�u�tmodDblob����2J���G�A�����o�u�t�p�u�tph1Scomp�������������s�r�elg1Scomp�����<�������s�r�emoDDblob�����(A��G�A�����s�r�emodDblob�����(A��G�A�����s�r�eph1Scomp�����=`������u�ilg1Scomp�������������u�imoDDblob������,��G�A�����u�imodDblob������,��G�A�����u�iph1Scomp��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E���
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000032�00000000000�010210� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������26 mtime=1692426889.04051
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/a11y/assistive-mml.js���������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014474�00000000000�022050� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,i,o={62:function(t,e,i){var o,s=this&&this.__extends||(o=function(t,e){return o=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var i in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,i)&&(t[i]=e[i])},o(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function i(){this.constructor=t}o(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(i.prototype=e.prototype,new i)}),n=this&&this.__assign||function(){return n=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,i=1,o=arguments.length;i0)&&!(o=n.next()).done;)r.push(o.value)}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(i=n.return)&&i.call(n)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}return r},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,i){if(i||2===arguments.length)for(var o,s=0,n=e.length;s=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[o++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AssistiveMmlHandler=e.AssistiveMmlMathDocumentMixin=e.AssistiveMmlMathItemMixin=e.LimitedMmlVisitor=void 0;var p=i(769),c=i(433),u=i(77),h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return s(e,t),e.prototype.getAttributes=function(e){return t.prototype.getAttributes.call(this,e).replace(/ ?id=".*?"/,"")},e}(c.SerializedMmlVisitor);function m(t){return function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return s(e,t),e.prototype.assistiveMml=function(t,e){if(void 0===e&&(e=!1),!(this.state()>=p.STATE.ASSISTIVEMML)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableAssistiveMml||e)){var i=t.adaptor,o=t.toMML(this.root).replace(/\n */g,"").replace(//g,""),s=i.firstChild(i.body(i.parse(o,"text/html"))),n=i.node("mjx-assistive-mml",{unselectable:"on",display:this.display?"block":"inline"},[s]);i.setAttribute(i.firstChild(this.typesetRoot),"aria-hidden","true"),i.setStyle(this.typesetRoot,"position","relative"),i.append(this.typesetRoot,n)}this.state(p.STATE.ASSISTIVEMML)}},e}(t)}function M(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],i=0;i0)&&!(i=n.next()).done;)l.push(i.value)}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(o=n.return)&&o.call(n)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return l},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var i,r=0,n=e.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.ComplexityHandler=e.ComplexityMathDocumentMixin=e.ComplexityMathItemMixin=void 0;var p=o(769),c=o(511),u=o(175),h=o(77);function y(t,e){return function(t){function o(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return r(o,t),o.prototype.complexity=function(t,o){void 0===o&&(o=!1),this.state()>=p.STATE.COMPLEXITY||(this.isEscaped||!t.options.enableComplexity&&!o||(this.enrich(t,!0),e(this.root)),this.state(p.STATE.COMPLEXITY))},o}(t)}function d(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Collapse=void 0;var i=function(){function t(e){var o=this;this.cutoff={identifier:3,number:3,text:10,infixop:15,relseq:15,multirel:15,fenced:18,bigop:20,integral:20,fraction:12,sqrt:9,root:12,vector:15,matrix:15,cases:15,superscript:9,subscript:9,subsup:9,punctuated:{endpunct:t.NOCOLLAPSE,startpunct:t.NOCOLLAPSE,value:12}},this.marker={identifier:"x",number:"#",text:"...",appl:{"limit function":"lim",value:"f()"},fraction:"/",sqrt:"\u221a",root:"\u221a",superscript:"\u25fd\u02d9",subscript:"\u25fd.",subsup:"\u25fd:",vector:{binomial:"(:)",determinant:"|:|",value:"\u27e8:\u27e9"},matrix:{squarematrix:"[::]",rowvector:"\u27e8\u22ef\u27e9",columnvector:"\u27e8\u22ee\u27e9",determinant:"|::|",value:"(::)"},cases:"{:",infixop:{addition:"+",subtraction:"\u2212",multiplication:"\u22c5",implicit:"\u22c5",value:"+"},punctuated:{text:"...",value:","}},this.collapse=new Map([["fenced",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,1))>o.cutoff.fenced&&"leftright"===t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role")&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.getText(t.childNodes[0])+o.getText(t.childNodes[t.childNodes.length-1]))),e}],["appl",function(t,e){if(o.canUncollapse(t,2,2)){e=o.complexity.visitNode(t,!1);var i=o.marker.appl,r=i[t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role")]||i.value;e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["sqrt",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0))>o.cutoff.sqrt&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.sqrt)),e}],["root",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.sqrt&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.sqrt)),e}],["enclose",function(t,e){if(1===o.splitAttribute(t,"children").length){var i=o.canUncollapse(t,1);if(i){var r=i.getProperty("collapse-marker");o.unrecordCollapse(i),e=o.recordCollapse(t,o.complexity.visitNode(t,!1),r)}}return e}],["bigop",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.bigop||!t.isKind("mo")){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content").pop(),r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["integral",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.integral||!t.isKind("mo")){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content").pop(),r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["relseq",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.relseq){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content")[0],r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["multirel",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.relseq){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content")[0],r=o.findChildText(t,i)+"\u22ef";e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["superscript",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.superscript&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.superscript)),e}],["subscript",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.subscript&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.subscript)),e}],["subsup",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,3))>o.cutoff.subsup&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.subsup)),e}]]),this.idCount=0,this.complexity=e}return t.prototype.check=function(t,e){var o=t.attributes.get("data-semantic-type");return this.collapse.has(o)?this.collapse.get(o).call(this,t,e):this.cutoff.hasOwnProperty(o)?this.defaultCheck(t,e,o):e},t.prototype.defaultCheck=function(t,e,o){var i=t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role"),r=this.cutoff[o];if(e>("number"==typeof r?r:r[i]||r.value)){var n=this.marker[o]||"??",l="string"==typeof n?n:n[i]||n.value;e=this.recordCollapse(t,e,l)}return e},t.prototype.recordCollapse=function(t,e,o){return o="\u25c2"+o+"\u25b8",t.setProperty("collapse-marker",o),t.setProperty("collapse-complexity",e),o.length*this.complexity.complexity.text},t.prototype.unrecordCollapse=function(t){var e=t.getProperty("collapse-complexity");null!=e&&(t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",e),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"))},t.prototype.canUncollapse=function(t,e,o){if(void 0===o&&(o=1),this.splitAttribute(t,"children").length===o){var i=1===t.childNodes.length&&t.childNodes[0].isInferred?t.childNodes[0]:t;if(i&&i.childNodes[e]){var r=i.childNodes[e];if(r.getProperty("collapse-marker"))return r}}return null},t.prototype.uncollapseChild=function(t,e,o,i){void 0===i&&(i=1);var r=this.canUncollapse(e,o,i);return r&&(this.unrecordCollapse(r),r.parent!==e&&r.parent.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",void 0),t=this.complexity.visitNode(e,!1)),t},t.prototype.splitAttribute=function(t,e){return(t.attributes.get("data-semantic-"+e)||"").split(/,/)},t.prototype.getText=function(t){var e=this;return t.isToken?t.getText():t.childNodes.map((function(t){return e.getText(t)})).join("")},t.prototype.findChildText=function(t,e){var o=this.findChild(t,e);return this.getText(o.coreMO()||o)},t.prototype.findChild=function(t,e){var i,r;if(!t||t.attributes.get("data-semantic-id")===e)return t;if(!t.isToken)try{for(var n=o(t.childNodes),l=n.next();!l.done;l=n.next()){var s=l.value,a=this.findChild(s,e);if(a)return a}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}return null},t.prototype.makeCollapse=function(t){var e=[];t.walkTree((function(t){t.getProperty("collapse-marker")&&e.push(t)})),this.makeActions(e)},t.prototype.makeActions=function(t){var e,i;try{for(var r=o(t),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){var l=n.value;this.makeAction(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=r.return)&&i.call(r)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},t.prototype.makeId=function(){return"mjx-collapse-"+this.idCount++},t.prototype.makeAction=function(t){t.isKind("math")&&(t=this.addMrow(t));var e=this.complexity.factory,o=t.getProperty("collapse-marker"),i=t.parent,r=e.create("maction",{actiontype:"toggle",selection:2,"data-collapsible":!0,id:this.makeId(),"data-semantic-complexity":t.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity")},[e.create("mtext",{mathcolor:"blue"},[e.create("text").setText(o)])]);r.inheritAttributesFrom(t),t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",t.getProperty("collapse-complexity")),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),i.replaceChild(r,t),r.appendChild(t)},t.prototype.addMrow=function(t){var e,i,r=this.complexity.factory.create("mrow",null,t.childNodes[0].childNodes);t.childNodes[0].setChildren([r]);var n=t.attributes.getAllAttributes();try{for(var l=o(Object.keys(n)),s=l.next();!s.done;s=l.next()){var a=s.value;"data-semantic-"===a.substr(0,14)&&(r.attributes.set(a,n[a]),delete n[a])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return r.setProperty("collapse-marker",t.getProperty("collapse-marker")),r.setProperty("collapse-complexity",t.getProperty("collapse-complexity")),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),r},t.NOCOLLAPSE=1e7,t}();e.Collapse=i},175:function(t,e,o){var i,r=this&&this.__extends||(i=function(t,e){return i=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},i(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}i(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)}),n=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,o=e&&t[e],i=0;if(o)return o.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&i>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.ComplexityVisitor=void 0;var l=o(176),s=o(850),a=o(77),p=function(t){function e(e,o){var i=t.call(this,e)||this;i.complexity={text:.5,token:.5,child:1,script:.8,sqrt:2,subsup:2,underover:2,fraction:2,enclose:2,action:2,phantom:0,xml:2,glyph:2};var r=i.constructor;return i.options=(0,a.userOptions)((0,a.defaultOptions)({},r.OPTIONS),o),i.collapse=new i.options.Collapse(i),i.factory=e,i}return r(e,t),e.prototype.visitTree=function(e){t.prototype.visitTree.call(this,e,!0),this.options.makeCollapsible&&this.collapse.makeCollapse(e)},e.prototype.visitNode=function(e,o){if(!e.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity"))return t.prototype.visitNode.call(this,e,o)},e.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var o;if(t.isToken){var i=t.getText();o=this.complexity.text*i.length+this.complexity.token}else o=this.childrenComplexity(t);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMfracNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)*this.complexity.script+this.complexity.fraction;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsqrtNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.sqrt;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMrootNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.sqrt-(1-this.complexity.script)*this.getComplexity(t.childNodes[1]);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMphantomNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.phantom,e)},e.prototype.visitMsNode=function(t,e){var o=(t.attributes.get("lquote")+t.getText()+t.attributes.get("rquote")).length*this.complexity.text;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsubsupNode=function(e,o){t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var i=e.childNodes[e.sub],r=e.childNodes[e.sup],n=e.childNodes[e.base],l=Math.max(i?this.getComplexity(i):0,r?this.getComplexity(r):0)*this.complexity.script;return l+=this.complexity.child*((i?1:0)+(r?1:0)),l+=n?this.getComplexity(n)+this.complexity.child:0,l+=this.complexity.subsup,this.setComplexity(e,l,o)},e.prototype.visitMsubNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMsubsupNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMsupNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMsubsupNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMunderoverNode=function(e,o){t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var i=e.childNodes[e.under],r=e.childNodes[e.over],n=e.childNodes[e.base],l=Math.max(i?this.getComplexity(i):0,r?this.getComplexity(r):0)*this.complexity.script;return n&&(l=Math.max(this.getComplexity(n),l)),l+=this.complexity.child*((i?1:0)+(r?1:0)+(n?1:0)),l+=this.complexity.underover,this.setComplexity(e,l,o)},e.prototype.visitMunderNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMunderoverNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMoverNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMunderoverNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMencloseNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.enclose;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMactionNode=function(t,e){this.childrenComplexity(t);var o=this.getComplexity(t.selected);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsemanticsNode=function(t,e){var o=t.childNodes[0],i=0;return o&&(this.visitNode(o,!0),i=this.getComplexity(o)),this.setComplexity(t,i,e)},e.prototype.visitAnnotationNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.xml,e)},e.prototype.visitAnnotation_xmlNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.xml,e)},e.prototype.visitMglyphNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.glyph,e)},e.prototype.getComplexity=function(t){var e=t.getProperty("collapsedComplexity");return null!=e?e:t.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity")},e.prototype.setComplexity=function(t,e,o){return o&&(this.options.identifyCollapsible&&(e=this.collapse.check(t,e)),t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",e)),e},e.prototype.childrenComplexity=function(e){var o,i;t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var r=0;try{for(var l=n(e.childNodes),s=l.next();!s.done;s=l.next()){var a=s.value;r+=this.getComplexity(a)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return e.childNodes.length>1&&(r+=e.childNodes.length*this.complexity.child),r},e.OPTIONS={identifyCollapsible:!0,makeCollapsible:!0,Collapse:s.Collapse},e}(l.MmlVisitor);e.ComplexityVisitor=p},306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},511:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.EnrichedMathItemMixin=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichedMathItemMixin,e.EnrichedMathDocumentMixin=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichedMathDocumentMixin,e.EnrichHandler=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichHandler},723:function(t,e){MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,e.PV=MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},769:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.protoItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.protoItem,e.AbstractMathItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.AbstractMathItem,e.STATE=MathJax._.core.MathItem.STATE,e.newState=MathJax._.core.MathItem.newState},176:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlVisitor=MathJax._.core.MmlTree.MmlVisitor.MmlVisitor},77:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup}},s={};function a(t){var e=s[t];if(void 0!==e)return e.exports;var o=s[t]={exports:{}};return l[t].call(o.exports,o,o.exports,a),o.exports}t=a(723),e=a(306),o=a(589),i=a(850),r=a(175),n=a(511),MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("a11y/complexity",e.q,"a11y"),(0,t.r8)({_:{a11y:{complexity_ts:o,complexity:{collapse:i,visitor:r},"semantic-enrich":n}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.extendHandler((function(t){return(0,o.ComplexityHandler)(t)})),(0,t.PV)(MathJax.config,"options",MathJax.config["a11y/complexity"]||{}))}();��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0411465
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/a11y/explorer.js��������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000106731�00000000000�021111� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,o,r,n,i,a,s,l={18:function(t,e,o){var r,n=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,o=1,r=arguments.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},u=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var o="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!o)return t;var r,n,i=o.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},h=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var r,n=0,i=e.length;n=f.STATE.EXPLORER)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableExplorer||o)){var r=this.typesetRoot,n=e(this.root);this.savedId&&(this.typesetRoot.setAttribute("sre-explorer-id",this.savedId),this.savedId=null),this.explorers=function(t,e,o){var r,n,i={};try{for(var a=c(Object.keys(S)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;i[l]=S[l](t,e,o)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return i}(t,r,n),this.attachExplorers(t)}this.state(f.STATE.EXPLORER)}},o.prototype.attachExplorers=function(t){var e,o,r,n;this.attached=[];var i=[];try{for(var a=c(Object.keys(this.explorers)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;(p=this.explorers[l])instanceof m.AbstractKeyExplorer&&(p.AddEvents(),p.stoppable=!1,i.unshift(p)),t.options.a11y[l]?(p.Attach(),this.attached.push(l)):p.Detach()}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}try{for(var u=c(i),h=u.next();!h.done;h=u.next()){var p;if((p=h.value).attached){p.stoppable=!0;break}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(n=u.return)&&n.call(u)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},o.prototype.rerender=function(e,o){var r,n;void 0===o&&(o=f.STATE.RERENDER),this.savedId=this.typesetRoot.getAttribute("sre-explorer-id"),this.refocus=window.document.activeElement===this.typesetRoot;try{for(var i=c(this.attached),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.explorers[s];l.active&&(this.restart.push(s),l.Stop())}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}t.prototype.rerender.call(this,e,o)},o.prototype.updateDocument=function(e){var o=this;t.prototype.updateDocument.call(this,e),this.refocus&&this.typesetRoot.focus(),this.restart.forEach((function(t){return o.explorers[t].Start()})),this.restart=[],this.refocus=!1},o}(t)}function O(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],o=0;o0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},n=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var r,n=0,i=e.length;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__importDefault||function(t){return t&&t.__esModule?t:{default:t}};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractExplorer=void 0;var s=a(o(712)),l=function(){function t(t,e,o){for(var r=[],n=3;n0&&n[n.length-1])||6!==i[0]&&2!==i[0])){a=0;continue}if(3===i[0]&&(!n||i[1]>n[0]&&i[1]0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.FlameHoverer=e.ContentHoverer=e.ValueHoverer=e.Hoverer=e.AbstractMouseExplorer=void 0;var a=o(367),s=o(724);o(712);var l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.events=t.prototype.Events.call(e).concat([["mouseover",e.MouseOver.bind(e)],["mouseout",e.MouseOut.bind(e)]]),e}return n(e,t),e.prototype.MouseOver=function(t){this.Start()},e.prototype.MouseOut=function(t){this.Stop()},e}(s.AbstractExplorer);e.AbstractMouseExplorer=l;var c=function(t){function e(e,o,r,n,i){var a=t.call(this,e,o,r)||this;return a.document=e,a.region=o,a.node=r,a.nodeQuery=n,a.nodeAccess=i,a}return n(e,t),e.prototype.MouseOut=function(e){e.clientX===this.coord[0]&&e.clientY===this.coord[1]||(this.highlighter.unhighlight(),this.region.Hide(),t.prototype.MouseOut.call(this,e))},e.prototype.MouseOver=function(e){t.prototype.MouseOver.call(this,e);var o=e.target;this.coord=[e.clientX,e.clientY];var r=i(this.getNode(o),2),n=r[0],a=r[1];n&&(this.highlighter.unhighlight(),this.highlighter.highlight([n]),this.region.Update(a),this.region.Show(n,this.highlighter))},e.prototype.getNode=function(t){for(var e=t;t&&t!==this.node;){if(this.nodeQuery(t))return[t,this.nodeAccess(t)];t=t.parentNode}for(t=e;t;){if(this.nodeQuery(t))return[t,this.nodeAccess(t)];var o=t.childNodes[0];t=o&&"defs"===o.tagName?t.childNodes[1]:o}return[null,null]},e}(l);e.Hoverer=c;var u=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.ValueHoverer=u;var h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.ContentHoverer=h;var p=function(t){function e(e,o,r){var n=t.call(this,e,new a.DummyRegion(e),r,(function(t){return n.highlighter.isMactionNode(t)}),(function(){}))||this;return n.document=e,n.node=r,n}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.FlameHoverer=p},367:function(t,e,o){var r,n,i,a,s=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HoverRegion=e.LiveRegion=e.ToolTip=e.StringRegion=e.DummyRegion=e.AbstractRegion=void 0;var l=o(888),c=function(){function t(t){this.document=t,this.CLASS=this.constructor,this.AddStyles(),this.AddElement()}return t.prototype.AddStyles=function(){if(!this.CLASS.styleAdded){var t=this.document.adaptor.node("style");t.innerHTML=this.CLASS.style.cssText,this.document.adaptor.head(this.document.adaptor.document).appendChild(t),this.CLASS.styleAdded=!0}},t.prototype.AddElement=function(){var t=this.document.adaptor.node("div");t.classList.add(this.CLASS.className),t.style.backgroundColor="white",this.div=t,this.inner=this.document.adaptor.node("div"),this.div.appendChild(this.inner),this.document.adaptor.body(this.document.adaptor.document).appendChild(this.div)},t.prototype.Show=function(t,e){this.position(t),this.highlight(e),this.div.classList.add(this.CLASS.className+"_Show")},t.prototype.Hide=function(){this.div.classList.remove(this.CLASS.className+"_Show")},t.prototype.stackRegions=function(t){for(var e=t.getBoundingClientRect(),o=0,r=Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,n=this.document.adaptor.document.getElementsByClassName(this.CLASS.className+"_Show"),i=0,a=void 0;a=n[i];i++)a!==this.div&&(o=Math.max(a.getBoundingClientRect().bottom,o),r=Math.min(a.getBoundingClientRect().left,r));var s=(o||e.bottom+10)+window.pageYOffset,l=(r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,a,i=r.call(t),o=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)o.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return o},c=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,a=0,i=e.length;a=u.STATE.ENRICHED)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableEnrichment||n)){t.options.sre.speech!==y&&(y=t.options.sre.speech,h.mathjax.retryAfter(d.default.setupEngine(t.options.sre).then((function(){return d.default.sreReady()}))));var a=new t.options.MathItem("",e);try{var i=this.inputData.originalMml=r(this.root);a.math=this.serializeMml(d.default.toEnriched(i)),a.display=this.display,a.compile(t),this.root=a.root,this.inputData.enrichedMml=a.math}catch(e){t.options.enrichError(t,this,e)}}this.state(u.STATE.ENRICHED)}},n.prototype.attachSpeech=function(t){var e,r;if(!(this.state()>=u.STATE.ATTACHSPEECH)){var n=this.root.attributes.get("aria-label")||this.getSpeech(this.root);if(n){var a=t.adaptor,i=this.typesetRoot;a.setAttribute(i,"aria-label",n);try{for(var s=o(a.childNodes(i)),c=s.next();!c.done;c=s.next()){var l=c.value;a.setAttribute(l,"aria-hidden","true")}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(r=s.return)&&r.call(s)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}this.state(u.STATE.ATTACHSPEECH)}},n.prototype.getSpeech=function(t){var e,r,n=t.attributes;if(!n)return"";var a=n.getExplicit("data-semantic-speech");if(!n.getExplicit("data-semantic-parent")&&a)return a;try{for(var i=o(t.childNodes),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var c=s.value,l=this.getSpeech(c);if(null!=l)return l}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return""},n}(t)}function m(t,e){var r;return r=function(t){function r(){for(var r=[],n=0;n0&&i[i.length-1])||6!==o[0]&&2!==o[0])){s=0;continue}if(3===o[0]&&(!i||o[1]>i[0]&&o[1]delete e[t])),t.open.forEach((n=>e[n]=t[n]));const n=Object.keys(e);e.open=n},t.sortClose=function(e,t){if(e.length<=1)return e;const n=[];for(let r,i=0;r=t[i],e.length;i++)r.close&&r.close.length&&r.close.forEach((function(t){const r=e.indexOf(t);-1!==r&&(n.unshift(t),e.splice(r,1))}));return n};let a={},c=[];function l(e,t){const n=e[e.length-1];if(n){if(p(t)&&p(n)){if(void 0===n.join)return void(n.span=n.span.concat(t.span));const e=n.span.pop(),r=t.span.shift();return n.span.push(e+n.join+r),n.span=n.span.concat(t.span),void(n.join=t.join)}h(t)&&h(n)?n.pause=s(n.pause,t.pause):e.push(t)}else e.push(t)}function u(e,t){e.rate&&(t.rate=e.rate),e.pitch&&(t.pitch=e.pitch),e.volume&&(t.volume=e.volume)}function d(e){return"object"==typeof e&&e.open}function h(e){return"object"==typeof e&&1===Object.keys(e).length&&Object.keys(e)[0]===i.personalityProps.PAUSE}function p(e){const t=Object.keys(e);return"object"==typeof e&&(1===t.length&&"span"===t[0]||2===t.length&&("span"===t[0]&&"join"===t[1]||"span"===t[1]&&"join"===t[0]))}function f(e,t,n,r,a,c=!1){if(c){const c=e[e.length-1];let l;if(c&&(l=c[i.personalityProps.JOIN]),c&&!t.speech&&a&&h(c)){const e=i.personalityProps.PAUSE;c[e]=s(c[e],a[e]),a=null}if(c&&t.speech&&0===Object.keys(n).length&&p(c)){if(void 0!==l){const e=c.span.pop();t=new o.Span(e.speech+l+t.speech,e.attributes)}c.span.push(t),t=new o.Span("",{}),c[i.personalityProps.JOIN]=r}}0!==Object.keys(n).length&&e.push(n),t.speech&&e.push({span:[t],join:r}),a&&e.push(a)}function m(e,t){if(!t)return e;const n={};for(const r of i.personalityPropList){const i=e[r],o=t[r];if(!i&&!o||i&&o&&i===o)continue;const s=i||0;d(n)||(n.open=[],n.close=[]),i||n.close.push(r),o||n.open.push(r),o&&i&&(n.close.push(r),n.open.push(r)),t[r]=s,n[r]=s,a[r]?a[r].push(s):a[r]=[s]}if(d(n)){let e=n.close.slice();for(;e.length>0;){let i=c.pop();const o=(0,r.setdifference)(i,e);if(e=(0,r.setdifference)(e,i),i=o,0!==e.length){if(0!==i.length){n.close=n.close.concat(i),n.open=n.open.concat(i);for(let e,r=0;e=i[r];r++)n[e]=t[e]}}else 0!==i.length&&c.push(i)}c.push(n.open)}return n}t.personalityMarkup=function(e){a={},c=[];let t=[];const n={};for(let r,o=0;r=e[o];o++){let e=null;const o=r.descriptionSpan(),s=r.personality,a=s[i.personalityProps.JOIN];delete s[i.personalityProps.JOIN],void 0!==s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]&&(e={[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]:s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]},delete s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]);f(t,o,m(s,n),a,e,!0)}return t=t.concat(function(){const e=[];for(let t=c.length-1;t>=0;t--){const n=c[t];if(n.length){const t={open:[],close:[]};for(let e=0;e"string"==typeof e?new l.Span(e,{}):e)),n=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return n?n.merge(t):e.join()},t.finalize=function(e){const t=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return t?t.finalize(e):e},t.error=function(e){const t=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return t?t.error(e):""},t.registerRenderer=function(e,t){m.set(e,t)},t.isXml=function(){return m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup)instanceof p.XmlRenderer}},1292:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.LayoutRenderer=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4998),s=n(2599),a=n(4708);class c extends a.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return function(e){l="";const t=i.parseInput(`${e}`);return r.Debugger.getInstance().output(i.formatXml(t.toString())),l=p(t),l}(e)}pause(e){return""}prosodyElement(e,t){return e===o.personalityProps.LAYOUT?`<${t}>`:""}closeTag(e){return``}markup(e){const t=[];let n=[];for(const r of e){if(!r.layout){n.push(r);continue}t.push(this.processContent(n)),n=[];const e=r.layout;e.match(/^begin/)?t.push("<"+e.replace(/^begin/,"")+">"):e.match(/^end/)?t.push(""):console.warn("Something went wrong with layout markup: "+e)}return t.push(this.processContent(n)),t.join("")}processContent(e){const t=[],n=s.personalityMarkup(e);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)e.span?t.push(this.merge(e.span)):s.isPauseElement(e);return t.join("")}}t.LayoutRenderer=c;let l="";const u={TABLE:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(1).slice(0,-1)}));const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CASES:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(0,-1)}));const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CAYLEY:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.sep=e.sep+e.sep}));const[n,r]=b(t),i={lfence:"",rfence:"",cells:r.map((e=>"\u2810"+new Array(e).join("\u2812"))),width:r,height:1,sep:t[0].sep};return t.splice(1,0,i),t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},MATRIX:function(e){let t=S(e);const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CELL:p,FENCE:p,ROW:p,FRACTION:function(e){const[t,n,,r,i]=Array.from(e.childNodes),o=d(n),s=d(r),a=m(o),c=m(s);let l=Math.max(a,c);const u=t+new Array(l+1).join("\u2812")+i;return l=u.length,`${C(o,l)}\n${u}\n${C(s,l)}`},NUMERATOR:T,DENOMINATOR:T};function d(e){const t=i.tagName(e),n=u[t];return n?n(e):e.textContent}function h(e,t){if(!e||!t)return e+t;const n=f(e),r=f(t),i=n-r;e=i<0?g(e,r,m(e)):e,t=i>0?g(t,n,m(t)):t;const o=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),s=t.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),a=[];for(let e=0;eMath.max(t.length,e)),0)}function g(e,t,n){return e=function(e,t){const n=t-f(e);return e+(n>0?new Array(n+1).join("\n"):"")}(e,t),function(e,t){const n=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),r=[];for(const e of n){const n=t-e.length;r.push(e+(n>0?new Array(n+1).join("\u2800"):""))}return r.join("\n")}(e,n)}function S(e){const t=Array.from(e.childNodes),n=[];for(const e of t)e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&n.push(_(e));return n}function b(e){const t=e.reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(t.height,e)),0),n=[];for(let t=0;te.width[t])).reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(e,t)),0));return[t,n]}function N(e,t){const n=[];for(const r of e){if(0===r.height)continue;const e=[];for(let n=0;ne.lfence+e.cells.join(e.sep)+e.rfence)).join("\n");const n=[];for(const t of e){const e=y(t.sep,t.height);let r=t.cells.shift();for(;t.cells.length;)r=h(r,e),r=h(r,t.cells.shift());r=h(y(t.lfence,t.height),r),r=h(r,y(t.rfence,t.height)),n.push(r),n.push(t.lfence+new Array(m(r)-3).join(t.sep)+t.rfence)}return n.slice(0,-1).join("\n")}function y(e,t){let n="";for(;t;)n+=e+"\n",t--;return n.slice(0,-1)}function A(e){return e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&"FENCE"===i.tagName(e)?d(e):""}function _(e){const t=Array.from(e.childNodes),n=A(t[0]),r=A(t[t.length-1]);n&&t.shift(),r&&t.pop();let o="";const s=[];for(const e of t){if(e.nodeType===i.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){o=e.textContent;continue}const t=d(e);s.push(t)}return{lfence:n,rfence:r,sep:o,cells:s,height:s.reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(f(t),e)),0),width:s.map(m)}}function C(e,t){const n=(t-m(e))/2,[r,i]=Math.floor(n)===n?[n,n]:[Math.floor(n),Math.ceil(n)],o=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),s=[],[a,c]=[new Array(r+1).join("\u2800"),new Array(i+1).join("\u2800")];for(const e of o)s.push(a+e+c);return s.join("\n")}function T(e){const t=e.firstChild,n=p(e);if(t&&t.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE){if("ENGLISH"===i.tagName(t))return"\u2830"+n;if("NUMBER"===i.tagName(t))return"\u283c"+n}return n}},9610:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MarkupRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(7086);class o extends i.AbstractAudioRenderer{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.ignoreElements=[r.personalityProps.LAYOUT],this.scaleFunction=null}setScaleFunction(e,t,n,r,i=0){this.scaleFunction=o=>{const s=(o-e)/(t-e),a=n*(1-s)+r*s;return+(Math.round(a+"e+"+i)+"e-"+i)}}applyScaleFunction(e){return this.scaleFunction?this.scaleFunction(e):e}ignoreElement(e){return-1!==this.ignoreElements.indexOf(e)}}t.MarkupRenderer=o},1674:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.PunctuationRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(7086),o=n(2599);class s extends i.AbstractAudioRenderer{markup(e){const t=o.personalityMarkup(e);let n="",i=null,s=!1;for(let e,a=0;e=t[a];a++)o.isMarkupElement(e)||(o.isPauseElement(e)?s&&(i=o.mergePause(i,e,Math.max)):(i&&(n+=this.pause(i[r.personalityProps.PAUSE]),i=null),n+=(s?this.getSeparator():"")+this.merge(e.span),s=!0));return n}pause(e){let t;return t="number"==typeof e?e<=250?"short":e<=500?"medium":"long":e,s.PAUSE_PUNCTUATION.get(t)||""}}t.PunctuationRenderer=s,s.PAUSE_PUNCTUATION=new Map([["short",","],["medium",";"],["long","."]])},8078:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SableRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(4708);class o extends i.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return''+this.getSeparator()+e+this.getSeparator()+""}pause(e){return''}prosodyElement(e,t){switch(t=this.applyScaleFunction(t),e){case r.personalityProps.PITCH:return'';case r.personalityProps.RATE:return'';case r.personalityProps.VOLUME:return'';default:return"<"+e.toUpperCase()+' VALUE="'+t+'">'}}closeTag(e){return""}}t.SableRenderer=o},1930:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Span=void 0;t.Span=class{constructor(e,t){this.speech=e,this.attributes=t}}},4115:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SsmlRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4708);class s extends o.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return''+this.getSeparator()+e+this.getSeparator()+""}pause(e){return''}prosodyElement(e,t){const n=(t=Math.floor(this.applyScaleFunction(t)))<0?t.toString():"+"+t.toString();return"":'%">')}closeTag(e){return""}}t.SsmlRenderer=s},6123:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SsmlStepRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4115);class i extends r.SsmlRenderer{markup(e){return i.MARKS={},super.markup(e)}merge(e){const t=[];for(let n=0;n'),i.MARKS[o]=!0),1===r.speech.length&&r.speech.match(/[a-zA-Z]/)?t.push(''+r.speech+""):t.push(r.speech)}return t.join(this.getSeparator())}}t.SsmlStepRenderer=i,i.CHARACTER_ATTR="character",i.MARKS={}},8244:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.StringRenderer=void 0;const r=n(7086),i=n(2599);class o extends r.AbstractAudioRenderer{markup(e){let t="";const n=(0,i.personalityMarkup)(e).filter((e=>e.span));if(!n.length)return t;const r=n.length-1;for(let e,i=0;e=n[i];i++){if(e.span&&(t+=this.merge(e.span)),i>=r)continue;const n=e.join;t+=void 0===n?this.getSeparator():n}return t}}t.StringRenderer=o},4708:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.XmlRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(2599),o=n(9610);class s extends o.MarkupRenderer{markup(e){this.setScaleFunction(-2,2,-100,100,2);const t=i.personalityMarkup(e),n=[],o=[];for(let e,s=0;e=t[s];s++)if(e.span)n.push(this.merge(e.span));else if(i.isPauseElement(e))n.push(this.pause(e));else{if(e.close.length)for(let t=0;t{n.push(this.prosodyElement(t,e[t])),o.push(t)}))}}return n.join(" ")}}t.XmlRenderer=s},1426:function(e,t){function n(e,t){return e?t?e.filter((e=>t.indexOf(e)<0)):e:[]}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.union=t.setdifference=t.interleaveLists=t.removeEmpty=void 0,t.removeEmpty=function(e){return e.filter((e=>e))},t.interleaveLists=function(e,t){const n=[];for(;e.length||t.length;)e.length&&n.push(e.shift()),t.length&&n.push(t.shift());return n},t.setdifference=n,t.union=function(e,t){return e&&t?e.concat(n(t,e)):e||t||[]}},9501:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.loadScript=t.loadMapsForIE_=t.installWGXpath_=t.loadWGXpath_=t.mapsForIE=t.detectEdge=t.detectIE=void 0;const r=n(4755),i=n(5024);function o(e){c(r.default.WGXpath),s(e)}function s(e,t){let n=t||1;"undefined"==typeof wgxpath&&n<10?setTimeout((function(){s(e,n++)}),200):n>=10||(r.default.wgxpath=wgxpath,e?r.default.wgxpath.install({document:document}):r.default.wgxpath.install(),i.xpath.evaluate=document.evaluate,i.xpath.result=XPathResult,i.xpath.createNSResolver=document.createNSResolver)}function a(){c(r.default.mathmapsIePath)}function c(e){const t=r.default.document.createElement("script");t.type="text/javascript",t.src=e,r.default.document.head?r.default.document.head.appendChild(t):r.default.document.body.appendChild(t)}t.detectIE=function(){return"undefined"!=typeof window&&"ActiveXObject"in window&&"clipboardData"in window&&(a(),o(),!0)},t.detectEdge=function(){var e;return"undefined"!=typeof window&&"MSGestureEvent"in window&&null===(null===(e=window.chrome)||void 0===e?void 0:e.loadTimes)&&(document.evaluate=null,o(!0),!0)},t.mapsForIE=null,t.loadWGXpath_=o,t.installWGXpath_=s,t.loadMapsForIE_=a,t.loadScript=c},1984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Debugger=void 0;const r=n(4755);class i{constructor(){this.isActive_=!1,this.outputFunction_=console.info,this.stream_=null}static getInstance(){return i.instance=i.instance||new i,i.instance}init(e){e&&this.startDebugFile_(e),this.isActive_=!0}output(...e){this.isActive_&&this.output_(e)}generateOutput(e){this.isActive_&&this.output_(e.apply(e,[]))}exit(e=(()=>{})){this.isActive_&&this.stream_&&this.stream_.end("","",e)}startDebugFile_(e){this.stream_=r.default.fs.createWriteStream(e),this.outputFunction_=function(...e){this.stream_.write(e.join(" ")),this.stream_.write("\n")}.bind(this),this.stream_.on("error",function(e){console.info("Invalid log file. Debug information sent to console."),this.outputFunction_=console.info}.bind(this)),this.stream_.on("finish",(function(){console.info("Finalizing debug file.")}))}output_(e){this.outputFunction_.apply(console.info===this.outputFunction_?console:this.outputFunction_,["Speech Rule Engine Debugger:"].concat(e))}}t.Debugger=i},6671:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.serializeXml=t.cloneNode=t.tagName=t.querySelectorAll=t.querySelectorAllByAttrValue=t.querySelectorAllByAttr=t.formatXml=t.createTextNode=t.createElementNS=t.createElement=t.replaceNode=t.NodeType=t.parseInput=t.XML_ENTITIES=t.trimInput_=t.toArray=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4755),s=n(5024);function a(e){const t=[];for(let n=0,r=e.length;n[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]+<").trim()}function l(e,t){if(!t)return[!1,""];const n=e.match(/^<([^> ]+).*>/),r=t.match(/^<\/([^>]+)>(.*)/);return n&&r&&n[1]===r[1]?[!0,r[2]]:[!1,""]}t.toArray=a,t.trimInput_=c,t.XML_ENTITIES={"<":!0,">":!0,"&":!0,""":!0,"'":!0},t.parseInput=function(e){const t=new o.default.xmldom.DOMParser,n=c(e),a=!!n.match(/&(?!lt|gt|amp|quot|apos)\w+;/g);if(!n)throw new Error("Empty input!");try{const e=t.parseFromString(n,a?"text/html":"text/xml");return r.default.getInstance().mode===i.Mode.HTTP?(s.xpath.currentDocument=e,a?e.body.childNodes[0]:e.documentElement):e.documentElement}catch(e){throw new r.SREError("Illegal input: "+e.message)}},function(e){e[e.ELEMENT_NODE=1]="ELEMENT_NODE",e[e.ATTRIBUTE_NODE=2]="ATTRIBUTE_NODE",e[e.TEXT_NODE=3]="TEXT_NODE",e[e.CDATA_SECTION_NODE=4]="CDATA_SECTION_NODE",e[e.ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE=5]="ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE",e[e.ENTITY_NODE=6]="ENTITY_NODE",e[e.PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE=7]="PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE",e[e.COMMENT_NODE=8]="COMMENT_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_NODE=9]="DOCUMENT_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE=10]="DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE=11]="DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE",e[e.NOTATION_NODE=12]="NOTATION_NODE"}(t.NodeType||(t.NodeType={})),t.replaceNode=function(e,t){e.parentNode&&(e.parentNode.insertBefore(t,e),e.parentNode.removeChild(e))},t.createElement=function(e){return o.default.document.createElement(e)},t.createElementNS=function(e,t){return o.default.document.createElementNS(e,t)},t.createTextNode=function(e){return o.default.document.createTextNode(e)},t.formatXml=function(e){let t="",n=/(>)(<)(\/*)/g,r=0,i=(e=e.replace(n,"$1\r\n$2$3")).split("\r\n");for(n=/(\.)*(<)(\/*)/g,i=i.map((e=>e.replace(n,"$1\r\n$2$3").split("\r\n"))).reduce(((e,t)=>e.concat(t)),[]);i.length;){let e=i.shift();if(!e)continue;let n=0;if(e.match(/^<\w[^>/]*>[^>]+$/)){const t=l(e,i[0]);t[0]?t[1]?(e+=i.shift().slice(0,-t[1].length),t[1].trim()&&i.unshift(t[1])):e+=i.shift():n=1}else if(e.match(/^<\/\w/))0!==r&&(r-=1);else if(e.match(/^<\w[^>]*[^/]>.*$/))n=1;else if(e.match(/^<\w[^>]*\/>.+$/)){const t=e.indexOf(">")+1;e.slice(t).trim()&&i.unshift(),e=e.slice(0,t)}else n=0;t+=new Array(r+1).join(" ")+e+"\r\n",r+=n}return t},t.querySelectorAllByAttr=function(e,t){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(`[${t}]`)):s.evalXPath(`.//*[@${t}]`,e)},t.querySelectorAllByAttrValue=function(e,t,n){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(`[${t}="${n}"]`)):s.evalXPath(`.//*[@${t}="${n}"]`,e)},t.querySelectorAll=function(e,t){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(t)):s.evalXPath(`.//${t}`,e)},t.tagName=function(e){return e.tagName.toUpperCase()},t.cloneNode=function(e){return e.cloneNode(!0)},t.serializeXml=function(e){return(new o.default.xmldom.XMLSerializer).serializeToString(e)}},4886:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.EnginePromise=t.SREError=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(4998),o=n(1984),s=n(4513);class a extends Error{constructor(e=""){super(),this.message=e,this.name="SRE Error"}}t.SREError=a;class c{constructor(){this.customLoader=null,this.parsers={},this.comparator=null,this.mode=i.Mode.SYNC,this.init=!0,this.delay=!1,this.comparators={},this.domain="mathspeak",this.style=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.STYLE],this._defaultLocale=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE],this.locale=this.defaultLocale,this.subiso="",this.modality=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.MODALITY],this.speech=i.Speech.NONE,this.markup=i.Markup.NONE,this.walker="Table",this.structure=!1,this.ruleSets=[],this.strict=!1,this.isIE=!1,this.isEdge=!1,this.rate="100",this.pprint=!1,this.config=!1,this.rules="",this.prune="",this.evaluator=c.defaultEvaluator,this.defaultParser=new r.DynamicCstrParser(r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_ORDER),this.parser=this.defaultParser,this.dynamicCstr=r.DynamicCstr.defaultCstr()}set defaultLocale(e){this._defaultLocale=s.Variables.ensureLocale(e,this._defaultLocale)}get defaultLocale(){return this._defaultLocale}static getInstance(){return c.instance=c.instance||new c,c.instance}static defaultEvaluator(e,t){return e}static evaluateNode(e){return c.nodeEvaluator(e)}getRate(){const e=parseInt(this.rate,10);return isNaN(e)?100:e}setDynamicCstr(e){if(this.defaultLocale&&(r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE]=this.defaultLocale),e){const t=Object.keys(e);for(let n=0;n{void 0!==e[n]&&(t[n]=e[n])};return n("mode"),t.configurate(e),a.default.BINARY_FEATURES.forEach((n=>{void 0!==e[n]&&(t[n]=!!e[n])})),a.default.STRING_FEATURES.forEach(n),e.json&&(l.default.jsonPath=c.makePath(e.json)),e.xpath&&(l.default.WGXpath=e.xpath),t.setCustomLoader(e.custom),function(e){e.isIE=s.detectIE(),e.isEdge=s.detectEdge()}(t),i.setLocale(),t.setDynamicCstr(),t.init?(a.EnginePromise.promises.init=new Promise(((e,t)=>{setTimeout((()=>{e("init")}),10)})),t.init=!1,a.EnginePromise.get()):t.delay?(t.delay=!1,a.EnginePromise.get()):o.loadLocale()}))}},6988:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Event=t.EventType=t.Move=t.KeyCode=void 0,function(e){e[e.ENTER=13]="ENTER",e[e.ESC=27]="ESC",e[e.SPACE=32]="SPACE",e[e.PAGE_UP=33]="PAGE_UP",e[e.PAGE_DOWN=34]="PAGE_DOWN",e[e.END=35]="END",e[e.HOME=36]="HOME",e[e.LEFT=37]="LEFT",e[e.UP=38]="UP",e[e.RIGHT=39]="RIGHT",e[e.DOWN=40]="DOWN",e[e.TAB=9]="TAB",e[e.LESS=188]="LESS",e[e.GREATER=190]="GREATER",e[e.DASH=189]="DASH",e[e.ZERO=48]="ZERO",e[e.ONE=49]="ONE",e[e.TWO=50]="TWO",e[e.THREE=51]="THREE",e[e.FOUR=52]="FOUR",e[e.FIVE=53]="FIVE",e[e.SIX=54]="SIX",e[e.SEVEN=55]="SEVEN",e[e.EIGHT=56]="EIGHT",e[e.NINE=57]="NINE",e[e.A=65]="A",e[e.B=66]="B",e[e.C=67]="C",e[e.D=68]="D",e[e.E=69]="E",e[e.F=70]="F",e[e.G=71]="G",e[e.H=72]="H",e[e.I=73]="I",e[e.J=74]="J",e[e.K=75]="K",e[e.L=76]="L",e[e.M=77]="M",e[e.N=78]="N",e[e.O=79]="O",e[e.P=80]="P",e[e.Q=81]="Q",e[e.R=82]="R",e[e.S=83]="S",e[e.T=84]="T",e[e.U=85]="U",e[e.V=86]="V",e[e.W=87]="W",e[e.X=88]="X",e[e.Y=89]="Y",e[e.Z=90]="Z"}(t.KeyCode||(t.KeyCode={})),t.Move=new Map([[13,"ENTER"],[27,"ESC"],[32,"SPACE"],[33,"PAGE_UP"],[34,"PAGE_DOWN"],[35,"END"],[36,"HOME"],[37,"LEFT"],[38,"UP"],[39,"RIGHT"],[40,"DOWN"],[9,"TAB"],[188,"LESS"],[190,"GREATER"],[189,"DASH"],[48,"ZERO"],[49,"ONE"],[50,"TWO"],[51,"THREE"],[52,"FOUR"],[53,"FIVE"],[54,"SIX"],[55,"SEVEN"],[56,"EIGHT"],[57,"NINE"],[65,"A"],[66,"B"],[67,"C"],[68,"D"],[69,"E"],[70,"F"],[71,"G"],[72,"H"],[73,"I"],[74,"J"],[75,"K"],[76,"L"],[77,"M"],[78,"N"],[79,"O"],[80,"P"],[81,"Q"],[82,"R"],[83,"S"],[84,"T"],[85,"U"],[86,"V"],[87,"W"],[88,"X"],[89,"Y"],[90,"Z"]]),function(e){e.CLICK="click",e.DBLCLICK="dblclick",e.MOUSEDOWN="mousedown",e.MOUSEUP="mouseup",e.MOUSEOVER="mouseover",e.MOUSEOUT="mouseout",e.MOUSEMOVE="mousemove",e.SELECTSTART="selectstart",e.KEYPRESS="keypress",e.KEYDOWN="keydown",e.KEYUP="keyup",e.TOUCHSTART="touchstart",e.TOUCHMOVE="touchmove",e.TOUCHEND="touchend",e.TOUCHCANCEL="touchcancel"}(t.EventType||(t.EventType={}));t.Event=class{constructor(e,t,n){this.src=e,this.type=t,this.callback=n}add(){this.src.addEventListener(this.type,this.callback)}remove(){this.src.removeEventListener(this.type,this.callback)}}},7129:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localePath=t.makePath=void 0;const r=n(4755);function i(e){return e.match("/$")?e:e+"/"}t.makePath=i,t.localePath=function(e,t="json"){return i(r.default.jsonPath)+e+(t.match(/^\./)?t:"."+t)}},3539:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.KeyProcessor=t.Processor=void 0;const r=n(6988);class i{constructor(e,t){this.name=e,this.process=t.processor,this.postprocess=t.postprocessor||((e,t)=>e),this.processor=this.postprocess?function(e){return this.postprocess(this.process(e),e)}:this.process,this.print=t.print||i.stringify_,this.pprint=t.pprint||this.print}static stringify_(e){return e?e.toString():e}}t.Processor=i,i.LocalState={walker:null,speechGenerator:null,highlighter:null};class o extends i{constructor(e,t){super(e,t),this.key=t.key||o.getKey_}static getKey_(e){return"string"==typeof e?r.KeyCode[e.toUpperCase()]:e}}t.KeyProcessor=o},9615:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.keypress=t.output=t.print=t.process=t.set=void 0;const r=n(4253),i=n(7450),o=n(9009),s=n(4524),a=n(1939),c=n(7317),l=n(144),u=n(907),d=n(8835),h=n(6671),p=n(4886),f=n(4998),m=n(3539),g=n(5024),S=new Map;function b(e){S.set(e.name,e)}function N(e){const t=S.get(e);if(!t)throw new p.SREError("Unknown processor "+e);return t}function E(e,t){const n=N(e);try{return n.processor(t)}catch(e){throw new p.SREError("Processing error for expression "+t)}}function y(e,t){const n=N(e);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(t):n.print(t)}t.set=b,t.process=E,t.print=y,t.output=function(e,t){const n=N(e);try{const e=n.processor(t);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(e):n.print(e)}catch(e){throw new p.SREError("Processing error for expression "+t)}},t.keypress=function(e,t){const n=N(e),r=n instanceof m.KeyProcessor?n.key(t):t,i=n.processor(r);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(i):n.print(i)},b(new m.Processor("semantic",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e);return a.xmlTree(t)},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=p.default.getInstance().speech;if(n===f.Speech.NONE)return e;const i=h.cloneNode(e);let o=l.computeMarkup(i);if(n===f.Speech.SHALLOW)return e.setAttribute("speech",r.finalize(o)),e;const s=g.evalXPath(".//*[@id]",e),a=g.evalXPath(".//*[@id]",i);for(let e,t,n=0;e=s[n],t=a[n];n++)o=l.computeMarkup(t),e.setAttribute("speech",r.finalize(o));return e},pprint:function(e){return h.formatXml(e.toString())}})),b(new m.Processor("speech",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e),n=a.xmlTree(t),i=l.computeSpeech(n);return r.finalize(r.markup(i))},pprint:function(e){const t=e.toString();return r.isXml()?h.formatXml(t):t}})),b(new m.Processor("json",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e);return a.getTree(t).toJson()},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=p.default.getInstance().speech;if(n===f.Speech.NONE)return e;const i=h.parseInput(t),o=a.xmlTree(i),s=l.computeMarkup(o);if(n===f.Speech.SHALLOW)return e.stree.speech=r.finalize(s),e;const c=e=>{const t=g.evalXPath(`.//*[@id=${e.id}]`,o)[0],n=l.computeMarkup(t);e.speech=r.finalize(n),e.children&&e.children.forEach(c)};return c(e.stree),e},print:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e)},pprint:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e,null,2)}})),b(new m.Processor("description",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e),n=a.xmlTree(t);return l.computeSpeech(n)},print:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e)},pprint:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e,null,2)}})),b(new m.Processor("enriched",{processor:function(e){return i.semanticMathmlSync(e)},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=d.getSemanticRoot(e);let r;switch(p.default.getInstance().speech){case f.Speech.NONE:break;case f.Speech.SHALLOW:r=c.generator("Adhoc"),r.getSpeech(n,e);break;case f.Speech.DEEP:r=c.generator("Tree"),r.getSpeech(e,e)}return e},pprint:function(e){return h.formatXml(e.toString())}})),b(new m.Processor("walker",{processor:function(e){const t=c.generator("Node");m.Processor.LocalState.speechGenerator=t,t.setOptions({modality:p.default.getInstance().modality,locale:p.default.getInstance().locale,domain:p.default.getInstance().domain,style:p.default.getInstance().style}),m.Processor.LocalState.highlighter=o.highlighter({color:"black"},{color:"white"},{renderer:"NativeMML"});const n=E("enriched",e),r=y("enriched",n);return m.Processor.LocalState.walker=u.walker(p.default.getInstance().walker,n,t,m.Processor.LocalState.highlighter,r),m.Processor.LocalState.walker},print:function(e){return m.Processor.LocalState.walker.speech()}})),b(new m.KeyProcessor("move",{processor:function(e){if(!m.Processor.LocalState.walker)return null;return!1===m.Processor.LocalState.walker.move(e)?r.error(e):m.Processor.LocalState.walker.speech()}})),b(new m.Processor("number",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("ordinal",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("numericOrdinal",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("vulgar",{processor:function(e){const[t,n]=e.split("/").map((e=>parseInt(e,10)));return isNaN(t)||isNaN(n)?"":E("speech",`${t}${n}`)}}))},9037:function(e,t,n){var r=this&&this.__awaiter||function(e,t,n,r){return new(n||(n=Promise))((function(i,o){function s(e){try{c(r.next(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function a(e){try{c(r.throw(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function c(e){var t;e.done?i(e.value):(t=e.value,t instanceof n?t:new n((function(e){e(t)}))).then(s,a)}c((r=r.apply(e,t||[])).next())}))};Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localePath=t.exit=t.move=t.walk=t.processFile=t.file=t.vulgar=t.numericOrdinal=t.ordinal=t.number=t.toEnriched=t.toDescription=t.toJson=t.toSemantic=t.toSpeech=t.localeLoader=t.engineReady=t.engineSetup=t.setupEngine=t.version=void 0;const i=n(4886),o=n(985),s=n(4998),a=n(7129),c=n(9615),l=n(4755),u=n(4513),d=n(5659);function h(e){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return(0,o.setup)(e)}))}function p(e,t){return c.process(e,t)}function f(e,t,n){switch(i.default.getInstance().mode){case s.Mode.ASYNC:return function(e,t,n){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){const r=yield l.default.fs.promises.readFile(t,{encoding:"utf8"}),o=c.output(e,r);if(n)try{l.default.fs.promises.writeFile(n,o)}catch(e){throw new i.SREError("Can not write to file: "+n)}return o}))}(e,t,n);case s.Mode.SYNC:return function(e,t,n){const r=function(e){let t;try{t=l.default.fs.readFileSync(e,{encoding:"utf8"})}catch(t){throw new i.SREError("Can not open file: "+e)}return t}(t),o=c.output(e,r);if(n)try{l.default.fs.writeFileSync(n,o)}catch(e){throw new i.SREError("Can not write to file: "+n)}return o}(e,t,n);default:throw new i.SREError(`Can process files in ${i.default.getInstance().mode} mode`)}}t.version=u.Variables.VERSION,t.setupEngine=h,t.engineSetup=function(){const e=["mode"].concat(i.default.STRING_FEATURES,i.default.BINARY_FEATURES),t=i.default.getInstance(),n={};return e.forEach((function(e){n[e]=t[e]})),n.json=l.default.jsonPath,n.xpath=l.default.WGXpath,n.rules=t.ruleSets.slice(),n},t.engineReady=function(){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return h({}).then((()=>i.EnginePromise.getall()))}))},t.localeLoader=d.standardLoader,t.toSpeech=function(e){return p("speech",e)},t.toSemantic=function(e){return p("semantic",e)},t.toJson=function(e){return p("json",e)},t.toDescription=function(e){return p("description",e)},t.toEnriched=function(e){return p("enriched",e)},t.number=function(e){return p("number",e)},t.ordinal=function(e){return p("ordinal",e)},t.numericOrdinal=function(e){return p("numericOrdinal",e)},t.vulgar=function(e){return p("vulgar",e)},t.file={},t.file.toSpeech=function(e,t){return f("speech",e,t)},t.file.toSemantic=function(e,t){return f("semantic",e,t)},t.file.toJson=function(e,t){return f("json",e,t)},t.file.toDescription=function(e,t){return f("description",e,t)},t.file.toEnriched=function(e,t){return f("enriched",e,t)},t.processFile=f,t.walk=function(e){return c.output("walker",e)},t.move=function(e){return c.keypress("move",e)},t.exit=function(e){const t=e||0;i.EnginePromise.getall().then((()=>process.exit(t)))},t.localePath=a.localePath,l.default.documentSupported?h({mode:s.Mode.HTTP}).then((()=>h({}))):h({mode:s.Mode.SYNC}).then((()=>h({mode:s.Mode.ASYNC})))},4755:function(__unused_webpack_module,exports,__webpack_require__){var __dirname="/";Object.defineProperty(exports,"__esModule",{value:!0});const variables_1=__webpack_require__(4513);class SystemExternal{static extRequire(library){if("undefined"!=typeof process){const nodeRequire=eval("require");return nodeRequire(library)}return null}}exports.default=SystemExternal,SystemExternal.windowSupported=!("undefined"==typeof window),SystemExternal.documentSupported=SystemExternal.windowSupported&&!(void 0===window.document),SystemExternal.xmldom=SystemExternal.documentSupported?window:SystemExternal.extRequire("xmldom-sre"),SystemExternal.document=SystemExternal.documentSupported?window.document:(new SystemExternal.xmldom.DOMImplementation).createDocument("","",0),SystemExternal.xpath=SystemExternal.documentSupported?document:function(){const e={document:{},XPathResult:{}};return SystemExternal.extRequire("wicked-good-xpath").install(e),e.document.XPathResult=e.XPathResult,e.document}(),SystemExternal.mathmapsIePath="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/sre-mathmaps-ie@"+variables_1.Variables.VERSION+"mathmaps_ie.js",SystemExternal.commander=SystemExternal.documentSupported?null:SystemExternal.extRequire("commander"),SystemExternal.fs=SystemExternal.documentSupported?null:SystemExternal.extRequire("fs"),SystemExternal.url=variables_1.Variables.url,SystemExternal.jsonPath=(SystemExternal.documentSupported?SystemExternal.url:process.env.SRE_JSON_PATH||__webpack_require__.g.SRE_JSON_PATH||__dirname+"/mathmaps")+"/",SystemExternal.WGXpath=variables_1.Variables.WGXpath,SystemExternal.wgxpath=null},4513:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Variables=void 0;class n{static ensureLocale(e,t){return n.LOCALES.get(e)?e:(console.error(`Locale ${e} does not exist! Using ${n.LOCALES.get(t)} instead.`),t)}}t.Variables=n,n.VERSION="4.0.6",n.LOCALES=new Map([["ca","Catalan"],["da","Danish"],["de","German"],["en","English"],["es","Spanish"],["fr","French"],["hi","Hindi"],["it","Italian"],["nb","Bokm\xe5l"],["nn","Nynorsk"],["sv","Swedish"],["nemeth","Nemeth"]]),n.mathjaxVersion="3.2.1",n.url="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/speech-rule-engine@"+n.VERSION+"/lib/mathmaps",n.WGXpath="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/wicked-good-xpath@1.3.0/dist/wgxpath.install.js"},5024:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.updateEvaluator=t.evaluateString=t.evaluateBoolean=t.getLeafNodes=t.evalXPath=t.resolveNameSpace=t.xpath=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4755);function s(){return"undefined"!=typeof XPathResult}t.xpath={currentDocument:null,evaluate:s()?document.evaluate:o.default.xpath.evaluate,result:s()?XPathResult:o.default.xpath.XPathResult,createNSResolver:s()?document.createNSResolver:o.default.xpath.createNSResolver};const a={xhtml:"http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",mathml:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML",mml:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML",svg:"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"};function c(e){return a[e]||null}t.resolveNameSpace=c;class l{constructor(){this.lookupNamespaceURI=c}}function u(e,n,o){return r.default.getInstance().mode!==i.Mode.HTTP||r.default.getInstance().isIE||r.default.getInstance().isEdge?t.xpath.evaluate(e,n,new l,o,null):t.xpath.currentDocument.evaluate(e,n,c,o,null)}function d(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.ORDERED_NODE_ITERATOR_TYPE)}catch(e){return[]}const i=[];for(let e=r.iterateNext();e;e=r.iterateNext())i.push(e);return i}t.evalXPath=d,t.getLeafNodes=function(e){return d(".//*[count(*)=0]",e)},t.evaluateBoolean=function(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.BOOLEAN_TYPE)}catch(e){return!1}return r.booleanValue},t.evaluateString=function(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.STRING_TYPE)}catch(e){return""}return r.stringValue},t.updateEvaluator=function(e){if(r.default.getInstance().mode!==i.Mode.HTTP)return;let n=e;for(;n&&!n.evaluate;)n=n.parentNode;n&&n.evaluate?t.xpath.currentDocument=n:e.ownerDocument&&(t.xpath.currentDocument=e.ownerDocument)}},9341:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractEnrichCase=void 0;t.AbstractEnrichCase=class{constructor(e){this.semantic=e}}},4306:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseBinomial=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!e.mathmlTree&&"line"===e.type&&"binomial"===e.role}getMathml(){if(!this.semantic.childNodes.length)return this.mml;const e=this.semantic.childNodes[0];if(this.mml=(0,o.walkTree)(e),this.mml.hasAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE)){const e=r.createElement("mrow");e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),r.replaceNode(this.mml,e),e.appendChild(this.mml),this.mml=e}return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseBinomial=a},8871:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseDoubleScript=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree||!e.childNodes.length)return!1;const t=r.tagName(e.mathmlTree),n=e.childNodes[0].role;return"MSUBSUP"===t&&"subsup"===n||"MUNDEROVER"===t&&"underover"===n}getMathml(){const e=this.semantic.childNodes[0],t=e.childNodes[0],n=this.semantic.childNodes[1],r=e.childNodes[1],i=o.walkTree(n),a=o.walkTree(t),c=o.walkTree(r);return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.CHILDREN,(0,s.makeIdList)([t,r,n])),[a,c,i].forEach((e=>o.getInnerNode(e).setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,this.mml.getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID)))),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE,e.role),o.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,[this.semantic.id,[e.id,t.id,r.id],n.id]),this.mml}}t.CaseDoubleScript=a},928:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseEmbellished=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9444),o=n(9341),s=n(8871),a=n(4308),c=n(439),l=n(8672),u=n(8171);class d extends o.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.fenced=null,this.fencedMml=null,this.fencedMmlNodes=[],this.ofence=null,this.ofenceMml=null,this.ofenceMap={},this.cfence=null,this.cfenceMml=null,this.cfenceMap={},this.parentCleanup=[]}static test(e){return!(!e.mathmlTree||!e.fencePointer||e.mathmlTree.getAttribute("data-semantic-type"))}static makeEmptyNode_(e){const t=r.createElement("mrow"),n=new i.SemanticNode(e);return n.type="empty",n.mathmlTree=t,n}static fencedMap_(e,t){t[e.id]=e.mathmlTree,e.embellished&&d.fencedMap_(e.childNodes[0],t)}getMathml(){this.getFenced_(),this.fencedMml=l.walkTree(this.fenced),this.getFencesMml_(),"empty"!==this.fenced.type||this.fencedMml.parentNode||(this.fencedMml.setAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),this.cfenceMml.parentNode.insertBefore(this.fencedMml,this.cfenceMml)),this.getFencedMml_();return this.rewrite_()}fencedElement(e){return"fenced"===e.type||"matrix"===e.type||"vector"===e.type}getFenced_(){let e=this.semantic;for(;!this.fencedElement(e);)e=e.childNodes[0];this.fenced=e.childNodes[0],this.ofence=e.contentNodes[0],this.cfence=e.contentNodes[1],d.fencedMap_(this.ofence,this.ofenceMap),d.fencedMap_(this.cfence,this.cfenceMap)}getFencedMml_(){let e=this.ofenceMml.nextSibling;for(e=e===this.fencedMml?e:this.fencedMml;e&&e!==this.cfenceMml;)this.fencedMmlNodes.push(e),e=e.nextSibling}getFencesMml_(){let e=this.semantic;const t=Object.keys(this.ofenceMap),n=Object.keys(this.cfenceMap);for(;!(this.ofenceMml&&this.cfenceMml||e===this.fenced);)-1===t.indexOf(e.fencePointer)||this.ofenceMml||(this.ofenceMml=e.mathmlTree),-1===n.indexOf(e.fencePointer)||this.cfenceMml||(this.cfenceMml=e.mathmlTree),e=e.childNodes[0];this.ofenceMml||(this.ofenceMml=this.ofence.mathmlTree),this.cfenceMml||(this.cfenceMml=this.cfence.mathmlTree),this.ofenceMml&&(this.ofenceMml=l.ascendNewNode(this.ofenceMml)),this.cfenceMml&&(this.cfenceMml=l.ascendNewNode(this.cfenceMml))}rewrite_(){let e=this.semantic,t=null;const n=this.introduceNewLayer_();for((0,u.setAttributes)(n,this.fenced.parent);!this.fencedElement(e);){const i=e.mathmlTree,o=this.specialCase_(e,i);if(o)e=o;else{(0,u.setAttributes)(i,e);const t=[];for(let n,r=1;n=e.childNodes[r];r++)t.push(l.walkTree(n));e=e.childNodes[0]}const s=r.createElement("dummy"),a=i.childNodes[0];r.replaceNode(i,s),r.replaceNode(n,i),r.replaceNode(i.childNodes[0],n),r.replaceNode(s,a),t||(t=i)}return l.walkTree(this.ofence),l.walkTree(this.cfence),this.cleanupParents_(),t||n}specialCase_(e,t){const n=r.tagName(t);let i,o=null;if("MSUBSUP"===n?(o=e.childNodes[0],i=s.CaseDoubleScript):"MMULTISCRIPTS"===n&&("superscript"===e.type||"subscript"===e.type?i=a.CaseMultiscripts:"tensor"===e.type&&(i=c.CaseTensor),o=i&&e.childNodes[0]&&"subsup"===e.childNodes[0].role?e.childNodes[0]:e),!o)return null;const l=o.childNodes[0],u=d.makeEmptyNode_(l.id);return o.childNodes[0]=u,t=new i(e).getMathml(),o.childNodes[0]=l,this.parentCleanup.push(t),o.childNodes[0]}introduceNewLayer_(){const e=this.fullFence(this.ofenceMml),t=this.fullFence(this.cfenceMml);let n=r.createElement("mrow");if(r.replaceNode(this.fencedMml,n),this.fencedMmlNodes.forEach((e=>n.appendChild(e))),n.insertBefore(e,this.fencedMml),n.appendChild(t),!n.parentNode){const e=r.createElement("mrow");for(;n.childNodes.length>0;)e.appendChild(n.childNodes[0]);n.appendChild(e),n=e}return n}fullFence(e){const t=this.fencedMml.parentNode;let n=e;for(;n.parentNode&&n.parentNode!==t;)n=n.parentNode;return n}cleanupParents_(){this.parentCleanup.forEach((function(e){const t=e.childNodes[1].getAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT);e.childNodes[0].setAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT,t)}))}}t.CaseEmbellished=d},9763:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseLimit=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree||!e.childNodes.length)return!1;const t=r.tagName(e.mathmlTree),n=e.type;return("limupper"===n||"limlower"===n)&&("MSUBSUP"===t||"MUNDEROVER"===t)||"limboth"===n&&("MSUB"===t||"MUNDER"===t||"MSUP"===t||"MOVER"===t)}static walkTree_(e){e&&o.walkTree(e)}getMathml(){const e=this.semantic.childNodes;return"limboth"!==this.semantic.type&&this.mml.childNodes.length>=3&&(this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer([this.mml],this.semantic)),(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),e[0].mathmlTree||(e[0].mathmlTree=this.semantic.mathmlTree),e.forEach(a.walkTree_),this.mml}}t.CaseLimit=a},7978:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseLine=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&"line"===e.type}getMathml(){return this.semantic.contentNodes.length&&i.walkTree(this.semantic.contentNodes[0]),this.semantic.childNodes.length&&i.walkTree(this.semantic.childNodes[0]),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseLine=s},2124:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseMultiindex=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static multiscriptIndex(e){return"punctuated"===e.type&&"dummy"===e.contentNodes[0].role?o.collapsePunctuated(e):(o.walkTree(e),e.id)}static createNone_(e){const t=r.createElement("none");return e&&(0,s.setAttributes)(t,e),t.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),t}completeMultiscript(e,t){const n=r.toArray(this.mml.childNodes).slice(1);let i=0;const c=e=>{for(let t,r=0;t=e[r];r++){const e=n[i];if(e&&t===parseInt(o.getInnerNode(e).getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID)))o.getInnerNode(e).setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,this.semantic.id.toString()),i++;else{const n=this.semantic.querySelectorAll((e=>e.id===t));this.mml.insertBefore(a.createNone_(n[0]),e||null)}}};c(e),n[i]&&"MPRESCRIPTS"!==r.tagName(n[i])?this.mml.insertBefore(n[i],r.createElement("mprescripts")):i++,c(t)}}t.CaseMultiindex=a},4308:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseMultiscripts=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7984),o=n(2124),s=n(8672),a=n(8171);class c extends o.CaseMultiindex{static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree)return!1;return"MMULTISCRIPTS"===r.tagName(e.mathmlTree)&&("superscript"===e.type||"subscript"===e.type)}constructor(e){super(e)}getMathml(){let e,t,n;if((0,a.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.semantic.childNodes[0]&&"subsup"===this.semantic.childNodes[0].role){const r=this.semantic.childNodes[0];e=r.childNodes[0],t=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]),n=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(r.childNodes[1]);const c=[this.semantic.id,[r.id,e.id,n],t];s.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,c),this.mml.setAttribute(a.Attribute.TYPE,r.role),this.completeMultiscript(i.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(n,t),[])}else{e=this.semantic.childNodes[0],t=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]);const n=[this.semantic.id,e.id,t];s.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,n)}const r=i.SemanticSkeleton.collapsedLeafs(n||[],t),c=s.walkTree(e);return s.getInnerNode(c).setAttribute(a.Attribute.PARENT,this.semantic.id.toString()),r.unshift(e.id),this.mml.setAttribute(a.Attribute.CHILDREN,r.join(",")),this.mml}}t.CaseMultiscripts=c},5326:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseProof=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&("inference"===e.type||"premises"===e.type)}getMathml(){return this.semantic.childNodes.length?(this.semantic.contentNodes.forEach((function(e){i.walkTree(e),(0,o.setAttributes)(e.mathmlTree,e)})),this.semantic.childNodes.forEach((function(e){i.walkTree(e)})),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.getAttribute("data-semantic-id")===this.mml.getAttribute("data-semantic-parent")&&this.mml.removeAttribute("data-semantic-parent"),this.mml):this.mml}}t.CaseProof=s},6998:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseTable=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.inner=[],this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return"matrix"===e.type||"vector"===e.type||"cases"===e.type}getMathml(){const e=o.cloneContentNode(this.semantic.contentNodes[0]),t=this.semantic.contentNodes[1]?o.cloneContentNode(this.semantic.contentNodes[1]):null;if(this.inner=this.semantic.childNodes.map(o.walkTree),this.mml)if("MFENCED"===r.tagName(this.mml)){const n=this.mml.childNodes;this.mml.insertBefore(e,n[0]||null),t&&this.mml.appendChild(t),this.mml=o.rewriteMfenced(this.mml)}else{const n=[e,this.mml];t&&n.push(t),this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer(n,this.semantic)}else this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer([e].concat(this.inner,[t]),this.semantic);return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseTable=a},439:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseTensor=void 0;const r=n(7984),i=n(2124),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.CaseMultiindex{static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&"tensor"===e.type}constructor(e){super(e)}getMathml(){o.walkTree(this.semantic.childNodes[0]);const e=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]),t=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[2]),n=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[3]),a=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[4]);(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic);const c=[this.semantic.id,this.semantic.childNodes[0].id,e,t,n,a];o.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,c);const l=r.SemanticSkeleton.collapsedLeafs(e,t,n,a);return l.unshift(this.semantic.childNodes[0].id),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.CHILDREN,l.join(",")),this.completeMultiscript(r.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(n,a),r.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(e,t)),this.mml}}t.CaseTensor=a},598:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseText=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return"punctuated"===e.type&&("text"===e.role||e.contentNodes.every((e=>"dummy"===e.role)))}getMathml(){const e=[],t=i.collapsePunctuated(this.semantic,e);return this.mml=i.introduceNewLayer(e,this.semantic),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.removeAttribute(o.Attribute.CONTENT),i.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,t),this.mml}}t.CaseText=s},7450:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.prepareMmlString=t.testTranslation__=t.semanticMathml=t.semanticMathmlSync=t.semanticMathmlNode=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4886),s=n(1939),a=n(8672),c=n(8171);function l(e){const t=i.cloneNode(e),n=s.getTree(t);return a.enrich(t,n)}function u(e){return l(i.parseInput(e))}function d(e){return e.match(/^"),e}n(7813),t.semanticMathmlNode=l,t.semanticMathmlSync=u,t.semanticMathml=function(e,t){o.EnginePromise.getall().then((()=>{const n=i.parseInput(e);t(l(n))}))},t.testTranslation__=function(e){r.Debugger.getInstance().init();const t=u(d(e)).toString();return(0,c.removeAttributePrefix)(t),r.Debugger.getInstance().exit(),t},t.prepareMmlString=d},8171:function(e,t){var n;function r(e){return e.map((function(e){return e.id})).join(",")}function i(e,t){const r=[];"mglyph"===t.role&&r.push("image"),t.attributes.href&&r.push("link"),r.length&&e.setAttribute(n.POSTFIX,r.join(" "))}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.addPrefix=t.removeAttributePrefix=t.setPostfix=t.setAttributes=t.makeIdList=t.EnrichAttributes=t.Attribute=t.Prefix=void 0,t.Prefix="data-semantic-",function(e){e.ADDED="data-semantic-added",e.ALTERNATIVE="data-semantic-alternative",e.CHILDREN="data-semantic-children",e.COLLAPSED="data-semantic-collapsed",e.CONTENT="data-semantic-content",e.EMBELLISHED="data-semantic-embellished",e.FENCEPOINTER="data-semantic-fencepointer",e.FONT="data-semantic-font",e.ID="data-semantic-id",e.ANNOTATION="data-semantic-annotation",e.OPERATOR="data-semantic-operator",e.OWNS="data-semantic-owns",e.PARENT="data-semantic-parent",e.POSTFIX="data-semantic-postfix",e.PREFIX="data-semantic-prefix",e.ROLE="data-semantic-role",e.SPEECH="data-semantic-speech",e.STRUCTURE="data-semantic-structure",e.TYPE="data-semantic-type"}(n=t.Attribute||(t.Attribute={})),t.EnrichAttributes=[n.ADDED,n.ALTERNATIVE,n.CHILDREN,n.COLLAPSED,n.CONTENT,n.EMBELLISHED,n.FENCEPOINTER,n.FONT,n.ID,n.ANNOTATION,n.OPERATOR,n.OWNS,n.PARENT,n.POSTFIX,n.PREFIX,n.ROLE,n.SPEECH,n.STRUCTURE,n.TYPE],t.makeIdList=r,t.setAttributes=function(e,o){e.setAttribute(n.TYPE,o.type);const s=o.allAttributes();for(let n,r=0;n=s[r];r++)e.setAttribute(t.Prefix+n[0].toLowerCase(),n[1]);o.childNodes.length&&e.setAttribute(n.CHILDREN,r(o.childNodes)),o.contentNodes.length&&e.setAttribute(n.CONTENT,r(o.contentNodes)),o.parent&&e.setAttribute(n.PARENT,o.parent.id.toString()),i(e,o)},t.setPostfix=i,t.removeAttributePrefix=function(e){return e.toString().replace(new RegExp(t.Prefix,"g"),"")},t.addPrefix=function(e){return t.Prefix+e}},9775:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.factory=t.getCase=void 0,t.getCase=function(e){for(let n,r=0;n=t.factory[r];r++)if(n.test(e))return n.constr(e);return null},t.factory=[]},7813:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4306),i=n(8871),o=n(928),s=n(9763),a=n(7978),c=n(4308),l=n(5326),u=n(6998),d=n(439),h=n(598);n(9775).factory.push({test:s.CaseLimit.test,constr:e=>new s.CaseLimit(e)},{test:o.CaseEmbellished.test,constr:e=>new o.CaseEmbellished(e)},{test:i.CaseDoubleScript.test,constr:e=>new i.CaseDoubleScript(e)},{test:d.CaseTensor.test,constr:e=>new d.CaseTensor(e)},{test:c.CaseMultiscripts.test,constr:e=>new c.CaseMultiscripts(e)},{test:a.CaseLine.test,constr:e=>new a.CaseLine(e)},{test:r.CaseBinomial.test,constr:e=>new r.CaseBinomial(e)},{test:l.CaseProof.test,constr:e=>new l.CaseProof(e)},{test:u.CaseTable.test,constr:e=>new u.CaseTable(e)},{test:h.CaseText.test,constr:e=>new h.CaseText(e)})},8672:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.printNodeList__=t.collapsePunctuated=t.formattedOutput_=t.formattedOutput=t.getInnerNode=t.setOperatorAttribute_=t.createInvisibleOperator_=t.rewriteMfenced=t.cloneContentNode=t.addCollapsedAttribute=t.parentNode_=t.isIgnorable_=t.unitChild_=t.descendNode_=t.ascendNewNode=t.validLca_=t.pathToRoot_=t.attachedElement_=t.prunePath_=t.mathmlLca_=t.lcaType=t.functionApplication_=t.isDescendant_=t.insertNewChild_=t.mergeChildren_=t.collectChildNodes_=t.collateChildNodes_=t.childrenSubset_=t.moveSemanticAttributes_=t.introduceLayerAboveLca=t.introduceNewLayer=t.walkTree=t.enrich=t.SETTINGS=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4886),s=n(4020),a=n(2721),c=n(7984),l=n(8901),u=n(8171),d=n(9775);function h(e){const t=(0,d.getCase)(e);let n;if(t)return n=t.getMathml(),I(n);if(1===e.mathml.length)return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 0"),n=e.mathml[0],u.setAttributes(n,e),e.childNodes.length&&(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 0.1"),e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){"empty"===e.type&&n.appendChild(h(e))}))),I(n);const i=e.contentNodes.map(F);k(e,i);const o=e.childNodes.map(h),s=c.SemanticSkeleton.combineContentChildren(e,i,o);if(n=e.mathmlTree,null===n)r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1"),n=p(s,e);else{const e=v(s);r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2"),e?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2.1"),n=e.parentNode):(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2.2"),n=U(n))}return n=D(n),N(n,s,e),u.setAttributes(n,e),I(n)}function p(e,t){const n=C(e);let o=n.node;const s=n.type;if(s!==_.VALID||!l.hasEmptyTag(o))if(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1"),o=i.createElement("mrow"),s===_.PRUNED)r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.0"),o=f(o,n.node,e);else if(e[0]){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.1");const t=v(e),n=g(t.parentNode,e);i.replaceNode(t,o),n.forEach((function(e){o.appendChild(e)}))}return t.mathmlTree||(t.mathmlTree=o),o}function f(e,t,n){let o=L(t);if(l.hasMathTag(o)){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.0.0"),m(o,e),i.toArray(o.childNodes).forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)}));const t=e;e=o,o=t}const s=n.indexOf(t);return n[s]=o,i.replaceNode(o,e),e.appendChild(o),n.forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)})),e}function m(e,t){for(const n of u.EnrichAttributes)e.hasAttribute(n)&&(t.setAttribute(n,e.getAttribute(n)),e.removeAttribute(n))}function g(e,t){const n=i.toArray(e.childNodes);let r=1/0,o=-1/0;return t.forEach((function(e){const t=n.indexOf(e);-1!==t&&(r=Math.min(r,t),o=Math.max(o,t))})),n.slice(r,o+1)}function S(e,t,n){const r=[];let o=i.toArray(e.childNodes),s=!1;for(;o.length;){const e=o.shift();if(e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)){r.push(e);continue}const t=b(e);0!==t.length&&(1!==t.length?(s?e.setAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit",!0):s=!0,o=t.concat(o)):r.push(e))}const a=[],c=n.childNodes.map((function(e){return e.mathmlTree}));for(;c.length;){const e=c.pop();if(e){if(-1!==r.indexOf(e))break;-1!==t.indexOf(e)&&a.unshift(e)}}return r.concat(a)}function b(e){const t=[];let n=i.toArray(e.childNodes);for(;n.length;){const e=n.shift();e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&(e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)?t.push(e):n=i.toArray(e.childNodes).concat(n))}return t}function N(e,t,n){const r="implicit"===n.role&&a.flags.combine_juxtaposition?S(e,t,n):i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!r.length)return void t.forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)}));let o=0;for(;t.length;){const n=t[0];r[o]===n||A(r[o],n)?(t.shift(),o++):r[o]&&-1===t.indexOf(r[o])?o++:(y(n,e)||E(e,r[o],n),t.shift())}}function E(e,t,n){if(!t)return void e.insertBefore(n,null);let r=t,i=P(r);for(;i&&i.firstChild===r&&!r.hasAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit")&&i!==e;)r=i,i=P(r);i&&(i.insertBefore(n,r),r.removeAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit"))}function y(e,t){if(!e)return!1;do{if((e=e.parentNode)===t)return!0}while(e);return!1}function A(e,t){const n=s.functionApplication();if(e&&t&&e.textContent&&t.textContent&&e.textContent===n&&t.textContent===n&&"true"===t.getAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED)){for(let n,r=0;n=e.attributes[r];r++)t.hasAttribute(n.nodeName)||t.setAttribute(n.nodeName,n.nodeValue);return i.replaceNode(e,t),!0}return!1}var _;function C(e){const t=v(e);if(!t)return{type:_.INVALID,node:null};const n=v(e.slice().reverse());if(t===n)return{type:_.VALID,node:t};const r=O(t),i=T(r,e),o=O(n,(function(e){return-1!==i.indexOf(e)})),s=o[0],a=i.indexOf(s);return-1===a?{type:_.INVALID,node:null}:{type:i.length!==r.length?_.PRUNED:M(i[a+1],o[1])?_.VALID:_.INVALID,node:s}}function T(e,t){let n=0;for(;e[n]&&-1===t.indexOf(e[n]);)n++;return e.slice(0,n+1)}function v(e){let t=0,n=null;for(;!n&&t!1),r=[e];for(;!n(e)&&!l.hasMathTag(e)&&e.parentNode;)e=P(e),r.unshift(e);return r}function M(e,t){return!(!e||!t||e.previousSibling||t.nextSibling)}function I(e){for(;!l.hasMathTag(e)&&R(e);)e=P(e);return e}function L(e){const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!t)return e;const n=t.filter((function(e){return e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&!l.hasIgnoreTag(e)}));return 1===n.length&&l.hasEmptyTag(n[0])&&!n[0].hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)?L(n[0]):e}function R(e){const t=P(e);return!(!t||!l.hasEmptyTag(t))&&i.toArray(t.childNodes).every((function(t){return t===e||x(t)}))}function x(e){if(e.nodeType!==i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE)return!0;if(!e||l.hasIgnoreTag(e))return!0;const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);return!(!l.hasEmptyTag(e)&&t.length||l.hasDisplayTag(e)||e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)||l.isOrphanedGlyph(e))&&i.toArray(e.childNodes).every(x)}function P(e){return e.parentNode}function F(e){if(e.mathml.length)return h(e);const n=t.SETTINGS.implicit?w(e):i.createElement("mrow");return e.mathml=[n],n}function D(e){if("MFENCED"!==i.tagName(e))return e;const t=i.createElement("mrow");for(let n,r=0;n=e.attributes[r];r++)-1===["open","close","separators"].indexOf(n.name)&&t.setAttribute(n.name,n.value);return i.toArray(e.childNodes).forEach((function(e){t.appendChild(e)})),i.replaceNode(e,t),t}function w(e){const t=i.createElement("mo"),n=i.createTextNode(e.textContent);return t.appendChild(n),u.setAttributes(t,e),t.setAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),t}function k(e,t){const n=e.type+(e.textContent?","+e.textContent:"");t.forEach((function(e){U(e).setAttribute(u.Attribute.OPERATOR,n)}))}function U(e){const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!t)return e;const n=t.filter((function(e){return!x(e)})),r=[];for(let e,t=0;e=n[t];t++)if(l.hasEmptyTag(e)){const t=U(e);t&&t!==e&&r.push(t)}else r.push(e);return 1===r.length?r[0]:e}function B(e,t,n,r){const i=r||!1;j(e,"Original MathML",i),j(n,"Semantic Tree",i),j(t,"Semantically enriched MathML",i)}function j(e,t,n){const r=i.formatXml(e.toString());n?console.info(t+":\n```html\n"+u.removeAttributePrefix(r)+"\n```\n"):console.info(r)}t.SETTINGS={collapsed:!0,implicit:!0},t.enrich=function(e,t){const n=i.cloneNode(e);return h(t.root),o.default.getInstance().structure&&e.setAttribute(u.Attribute.STRUCTURE,c.SemanticSkeleton.fromStructure(e,t).toString()),r.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((function(){return B(n,e,t,!0),[]})),e},t.walkTree=h,t.introduceNewLayer=p,t.introduceLayerAboveLca=f,t.moveSemanticAttributes_=m,t.childrenSubset_=g,t.collateChildNodes_=S,t.collectChildNodes_=b,t.mergeChildren_=N,t.insertNewChild_=E,t.isDescendant_=y,t.functionApplication_=A,function(e){e.VALID="valid",e.INVALID="invalid",e.PRUNED="pruned"}(_=t.lcaType||(t.lcaType={})),t.mathmlLca_=C,t.prunePath_=T,t.attachedElement_=v,t.pathToRoot_=O,t.validLca_=M,t.ascendNewNode=I,t.descendNode_=L,t.unitChild_=R,t.isIgnorable_=x,t.parentNode_=P,t.addCollapsedAttribute=function(e,t){const n=new c.SemanticSkeleton(t);e.setAttribute(u.Attribute.COLLAPSED,n.toString())},t.cloneContentNode=F,t.rewriteMfenced=D,t.createInvisibleOperator_=w,t.setOperatorAttribute_=k,t.getInnerNode=U,t.formattedOutput=B,t.formattedOutput_=j,t.collapsePunctuated=function(e,t){const n=!!t,r=t||[],i=e.parent,o=e.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e.id}));o.unshift("c");const s=[e.id,o];for(let t,o=0;t=e.childNodes[o];o++){const e=h(t);r.push(e);const o=U(e);i&&!n&&o.setAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT,i.id.toString()),s.push(t.id)}return s},t.printNodeList__=function(e,t){console.info(e),i.toArray(t).forEach((function(e){console.info(e.toString())})),console.info("<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<")}},7228:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(5024),i=n(8171);class o{constructor(){this.color=null,this.mactionName="",this.currentHighlights=[]}highlight(e){this.currentHighlights.push(e.map((e=>{const t=this.highlightNode(e);return this.setHighlighted(e),t})))}highlightAll(e){const t=this.getMactionNodes(e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)this.highlight([e])}unhighlight(){const e=this.currentHighlights.pop();e&&e.forEach((e=>{this.isHighlighted(e.node)&&(this.unhighlightNode(e),this.unsetHighlighted(e.node))}))}unhighlightAll(){for(;this.currentHighlights.length>0;)this.unhighlight()}setColor(e){this.color=e}colorString(){return this.color.rgba()}addEvents(e,t){const n=this.getMactionNodes(e);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)for(const n in t)e.addEventListener(n,t[n])}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByClassName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){const t=e.className||e.getAttribute("class");return!!t&&!!t.match(new RegExp(this.mactionName))}isHighlighted(e){return e.hasAttribute(o.ATTR)}setHighlighted(e){e.setAttribute(o.ATTR,"true")}unsetHighlighted(e){e.removeAttribute(o.ATTR)}colorizeAll(e){r.evalXPath(`.//*[@${i.Attribute.ID}]`,e).forEach((e=>this.colorize(e)))}uncolorizeAll(e){r.evalXPath(`.//*[@${i.Attribute.ID}]`,e).forEach((e=>this.uncolorize(e)))}colorize(e){const t=(0,i.addPrefix)("foreground");e.hasAttribute(t)&&(e.setAttribute(t+"-old",e.style.color),e.style.color=e.getAttribute(t))}uncolorize(e){const t=(0,i.addPrefix)("foreground")+"-old";e.hasAttribute(t)&&(e.style.color=e.getAttribute(t))}}t.AbstractHighlighter=o,o.ATTR="sre-highlight"},7567:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ChtmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(9400);class i extends r.CssHighlighter{constructor(){super()}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName.toUpperCase()===this.mactionName.toUpperCase()}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}}t.ChtmlHighlighter=i},1123:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ContrastPicker=t.ColorPicker=void 0;const n={red:{red:255,green:0,blue:0},green:{red:0,green:255,blue:0},blue:{red:0,green:0,blue:255},yellow:{red:255,green:255,blue:0},cyan:{red:0,green:255,blue:255},magenta:{red:255,green:0,blue:255},white:{red:255,green:255,blue:255},black:{red:0,green:0,blue:0}};function r(e,t){const r=e||{color:t};let i=Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,"color")?n[r.color]:r;return i||(i=n[t]),i.alpha=Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,"alpha")?r.alpha:1,function(e){const t=e=>(e=Math.max(e,0),e=Math.min(255,e),Math.round(e));return e.red=t(e.red),e.green=t(e.green),e.blue=t(e.blue),e.alpha=Math.max(e.alpha,0),e.alpha=Math.min(1,e.alpha),e}(i)}class i{constructor(e,t){this.foreground=r(t,i.DEFAULT_FOREGROUND_),this.background=r(e,i.DEFAULT_BACKGROUND_)}static toHex(e){const t=e.toString(16);return 1===t.length?"0"+t:t}rgba(){const e=function(e){return"rgba("+e.red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+","+e.alpha+")"};return{background:e(this.background),foreground:e(this.foreground)}}rgb(){const e=function(e){return"rgb("+e.red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+")"};return{background:e(this.background),alphaback:this.background.alpha.toString(),foreground:e(this.foreground),alphafore:this.foreground.alpha.toString()}}hex(){const e=function(e){return"#"+i.toHex(e.red)+i.toHex(e.green)+i.toHex(e.blue)};return{background:e(this.background),alphaback:this.background.alpha.toString(),foreground:e(this.foreground),alphafore:this.foreground.alpha.toString()}}}t.ColorPicker=i,i.DEFAULT_BACKGROUND_="blue",i.DEFAULT_FOREGROUND_="black";t.ContrastPicker=class{constructor(){this.hue=10,this.sat=100,this.light=50,this.incr=50}generate(){return t=function(e,t,n){t=t>1?t/100:t,n=n>1?n/100:n;const r=(1-Math.abs(2*n-1))*t,i=r*(1-Math.abs(e/60%2-1)),o=n-r/2;let s=0,a=0,c=0;return 0<=e&&e<60?[s,a,c]=[r,i,0]:60<=e&&e<120?[s,a,c]=[i,r,0]:120<=e&&e<180?[s,a,c]=[0,r,i]:180<=e&&e<240?[s,a,c]=[0,i,r]:240<=e&&e<300?[s,a,c]=[i,0,r]:300<=e&&e<360&&([s,a,c]=[r,0,i]),{red:s+o,green:a+o,blue:c+o}}(this.hue,this.sat,this.light),"rgb("+(e={red:Math.round(255*t.red),green:Math.round(255*t.green),blue:Math.round(255*t.blue)}).red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+")";var e,t}increment(){this.hue=(this.hue+this.incr)%360}}},9400:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CssHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(7228);class i extends r.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="mjx-maction"}highlightNode(e){const t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},n=this.colorString();return e.style.backgroundColor=n.background,e.style.color=n.foreground,t}unhighlightNode(e){e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,e.node.style.color=e.foreground}}t.CssHighlighter=i},9009:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.highlighterMapping_=t.addEvents=t.highlighter=void 0;const r=n(7567),i=n(1123),o=n(9400),s=n(7872),a=n(3711),c=n(4662),l=n(3507),u=n(280);t.highlighter=function(e,n,r){const o=new i.ColorPicker(e,n),s="NativeMML"===r.renderer&&"Safari"===r.browser?"MML-CSS":"SVG"===r.renderer&&"v3"===r.browser?"SVG-V3":r.renderer,a=new(t.highlighterMapping_[s]||t.highlighterMapping_.NativeMML);return a.setColor(o),a},t.addEvents=function(e,n,r){const i=t.highlighterMapping_[r.renderer];i&&(new i).addEvents(e,n)},t.highlighterMapping_={SVG:l.SvgHighlighter,"SVG-V3":u.SvgV3Highlighter,NativeMML:c.MmlHighlighter,"HTML-CSS":s.HtmlHighlighter,"MML-CSS":a.MmlCssHighlighter,CommonHTML:o.CssHighlighter,CHTML:r.ChtmlHighlighter}},7872:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.HtmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7228);class o extends i.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){const t={node:e,foreground:e.style.color,position:e.style.position},n=this.color.rgb();e.style.color=n.foreground,e.style.position="relative";const i=e.bbox;if(i&&i.w){const o=.05,s=0,a=r.createElement("span"),c=parseFloat(e.style.paddingLeft||"0");a.style.backgroundColor=n.background,a.style.opacity=n.alphaback.toString(),a.style.display="inline-block",a.style.height=i.h+i.d+2*o+"em",a.style.verticalAlign=-i.d+"em",a.style.marginTop=a.style.marginBottom=-o+"em",a.style.width=i.w+2*s+"em",a.style.marginLeft=c-s+"em",a.style.marginRight=-i.w-s-c+"em",e.parentNode.insertBefore(a,e),t.box=a}return t}unhighlightNode(e){const t=e.node;t.style.color=e.foreground,t.style.position=e.position,e.box&&e.box.parentNode.removeChild(e.box)}}t.HtmlHighlighter=o},3711:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MmlCssHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(9400);class i extends r.CssHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName===this.mactionName}}t.MmlCssHighlighter=i},4662:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(7228);class i extends r.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){let t=e.getAttribute("style");return t+=";background-color: "+this.colorString().background,t+=";color: "+this.colorString().foreground,e.setAttribute("style",t),{node:e}}unhighlightNode(e){let t=e.node.getAttribute("style");t=t.replace(";background-color: "+this.colorString().background,""),t=t.replace(";color: "+this.colorString().foreground,""),e.node.setAttribute("style",t)}colorString(){return this.color.rgba()}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName===this.mactionName}}t.MmlHighlighter=i},3507:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SvgHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7228);class o extends i.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="mjx-svg-maction"}highlightNode(e){let t;if(this.isHighlighted(e))return t={node:e.previousSibling||e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},t;if("svg"===e.tagName){const t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color};return e.style.backgroundColor=this.colorString().background,e.style.color=this.colorString().foreground,t}const n=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","rect");let o;if("use"===e.nodeName){const t=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","g");e.parentNode.insertBefore(t,e),t.appendChild(e),o=t.getBBox(),t.parentNode.replaceChild(e,t)}else o=e.getBBox();n.setAttribute("x",(o.x-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("y",(o.y-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("width",(o.width+80).toString()),n.setAttribute("height",(o.height+80).toString());const s=e.getAttribute("transform");return s&&n.setAttribute("transform",s),n.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().background),n.setAttribute(i.AbstractHighlighter.ATTR,"true"),e.parentNode.insertBefore(n,e),t={node:n,foreground:e.getAttribute("fill")},e.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().foreground),t}setHighlighted(e){"svg"===e.tagName&&super.setHighlighted(e)}unhighlightNode(e){if("background"in e)return e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,void(e.node.style.color=e.foreground);e.foreground?e.node.nextSibling.setAttribute("fill",e.foreground):e.node.nextSibling.removeAttribute("fill"),e.node.parentNode.removeChild(e.node)}isMactionNode(e){let t=e.className||e.getAttribute("class");return t=void 0!==t.baseVal?t.baseVal:t,!!t&&!!t.match(new RegExp(this.mactionName))}}t.SvgHighlighter=o},280:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SvgV3Highlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(5024),o=n(7228),s=n(1123),a=n(3507);class c extends a.SvgHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){let t;if(this.isHighlighted(e))return t={node:e,background:this.colorString().background,foreground:this.colorString().foreground},t;if("svg"===e.tagName||"MJX-CONTAINER"===e.tagName)return t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},e.style.backgroundColor=this.colorString().background,e.style.color=this.colorString().foreground,t;const n=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","rect");n.setAttribute("sre-highlighter-added","true");const i=e.getBBox();n.setAttribute("x",(i.x-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("y",(i.y-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("width",(i.width+80).toString()),n.setAttribute("height",(i.height+80).toString());const a=e.getAttribute("transform");if(a&&n.setAttribute("transform",a),n.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().background),e.setAttribute(o.AbstractHighlighter.ATTR,"true"),e.parentNode.insertBefore(n,e),t={node:e,foreground:e.getAttribute("fill")},"rect"===e.nodeName){const t=new s.ColorPicker({alpha:0,color:"black"});e.setAttribute("fill",t.rgba().foreground)}else e.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().foreground);return t}unhighlightNode(e){const t=e.node.previousSibling;if(t&&t.hasAttribute("sre-highlighter-added"))return e.foreground?e.node.setAttribute("fill",e.foreground):e.node.removeAttribute("fill"),void e.node.parentNode.removeChild(t);e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,e.node.style.color=e.foreground}isMactionNode(e){return e.getAttribute("data-mml-node")===this.mactionName}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(i.evalXPath(`.//*[@data-mml-node="${this.mactionName}"]`,e))}}t.SvgV3Highlighter=c},1473:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.StaticTrieNode=t.AbstractTrieNode=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(9259);class o{constructor(e,t){this.constraint=e,this.test=t,this.children_={},this.kind=i.TrieNodeKind.ROOT}getConstraint(){return this.constraint}getKind(){return this.kind}applyTest(e){return this.test(e)}addChild(e){const t=e.getConstraint(),n=this.children_[t];return this.children_[t]=e,n}getChild(e){return this.children_[e]}getChildren(){const e=[];for(const t in this.children_)e.push(this.children_[t]);return e}findChildren(e){const t=[];for(const n in this.children_){const r=this.children_[n];r.applyTest(e)&&t.push(r)}return t}removeChild(e){delete this.children_[e]}toString(){return this.constraint}}t.AbstractTrieNode=o;t.StaticTrieNode=class extends o{constructor(e,t){super(e,t),this.rule_=null,this.kind=i.TrieNodeKind.STATIC}getRule(){return this.rule_}setRule(e){this.rule_&&r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Replacing rule "+this.rule_+" with "+e),this.rule_=e}toString(){return this.getRule()?this.constraint+"\n==> "+this.getRule().action:this.constraint}}},2803:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Trie=void 0;const r=n(9259),i=n(9146);class o{constructor(){this.root=(0,i.getNode)(r.TrieNodeKind.ROOT,"",null)}static collectRules_(e){const t=[];let n=[e];for(;n.length;){const e=n.shift();if(e.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.QUERY||e.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.BOOLEAN){const n=e.getRule();n&&t.unshift(n)}n=n.concat(e.getChildren())}return t}static printWithDepth_(e,t,n){n+=new Array(t+2).join(t.toString())+": "+e.toString()+"\n";const r=e.getChildren();for(let e,i=0;e=r[i];i++)n=o.printWithDepth_(e,t+1,n);return n}static order_(e){const t=e.getChildren();if(!t.length)return 0;const n=Math.max.apply(null,t.map(o.order_));return Math.max(t.length,n)}addRule(e){let t=this.root;const n=e.context,i=e.dynamicCstr.getValues();for(let e=0,o=i.length;e{t.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.DYNAMIC&&-1===e.indexOf(t.getConstraint())||i.push(t)}))}n=i.slice()}for(;n.length;){const t=n.shift();if(t.getRule){const e=t.getRule();e&&i.push(e)}const r=t.findChildren(e);n=n.concat(r)}return i}hasSubtrie(e){let t=this.root;for(let n=0,r=e.length;n!0)),this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.ROOT}}t.RootTrieNode=u;class d extends a.AbstractTrieNode{constructor(e){super(e,(t=>t===e)),this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.DYNAMIC}}t.DynamicTrieNode=d;const h={"=":(e,t)=>e===t,"!=":(e,t)=>e!==t,"<":(e,t)=>e":(e,t)=>e>t,"<=":(e,t)=>e<=t,">=":(e,t)=>e>=t};function p(e){if(e.match(/^self::\*$/))return e=>!0;if(e.match(/^self::\w+$/)){const t=e.slice(6).toUpperCase();return e=>e.tagName&&r.tagName(e)===t}if(e.match(/^self::\w+:\w+$/)){const t=e.split(":"),n=i.resolveNameSpace(t[2]);if(!n)return null;const r=t[3].toUpperCase();return e=>e.localName&&e.localName.toUpperCase()===r&&e.namespaceURI===n}if(e.match(/^@\w+$/)){const t=e.slice(1);return e=>e.hasAttribute&&e.hasAttribute(t)}if(e.match(/^@\w+="[\w\d ]+"$/)){const t=e.split("="),n=t[0].slice(1),r=t[1].slice(1,-1);return e=>e.hasAttribute&&e.hasAttribute(n)&&e.getAttribute(n)===r}if(e.match(/^@\w+!="[\w\d ]+"$/)){const t=e.split("!="),n=t[0].slice(1),r=t[1].slice(1,-1);return e=>!e.hasAttribute||!e.hasAttribute(n)||e.getAttribute(n)!==r}if(e.match(/^contains\(\s*@grammar\s*,\s*"[\w\d ]+"\s*\)$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1];return e=>!!o.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter(t)}if(e.match(/^not\(\s*contains\(\s*@grammar\s*,\s*"[\w\d ]+"\s*\)\s*\)$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1];return e=>!o.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter(t)}if(e.match(/^name\(\.\.\/\.\.\)="\w+"$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1].toUpperCase();return e=>{var n,i;return(null===(i=null===(n=e.parentNode)||void 0===n?void 0:n.parentNode)||void 0===i?void 0:i.tagName)&&r.tagName(e.parentNode.parentNode)===t}}if(e.match(/^count\(preceding-sibling::\*\)=\d+$/)){const t=e.split("="),n=parseInt(t[1],10);return e=>{var t;return(null===(t=e.parentNode)||void 0===t?void 0:t.childNodes[n])===e}}if(e.match(/^.+\[@category!?=".+"\]$/)){let[,t,n,r]=e.match(/^(.+)\[@category(!?=)"(.+)"\]$/);const o=r.match(/^unit:(.+)$/);let a="";return o&&(r=o[1],a=":unit"),e=>{const o=i.evalXPath(t,e)[0];if(o){const e=s.lookupCategory(o.textContent+a);return"="===n?e===r:e!==r}return!1}}if(e.match(/^string-length\(.+\)\W+\d+/)){const[,t,n,r]=e.match(/^string-length\((.+)\)(\W+)(\d+)/),o=h[n]||h["="],s=parseInt(r,10);return e=>{const n=i.evalXPath(t,e)[0];return!!n&&o(Array.from(n.textContent).length,s)}}return null}t.constraintTest_=p;class f extends c.StaticTrieNode{constructor(e,t){super(e,p(e)),this.context=t,this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.QUERY}applyTest(e){return this.test?this.test(e):this.context.applyQuery(e,this.constraint)===e}}t.QueryTrieNode=f;class m extends c.StaticTrieNode{constructor(e,t){super(e,p(e)),this.context=t,this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.BOOLEAN}applyTest(e){return this.test?this.test(e):this.context.applyConstraint(e,this.constraint)}}t.BooleanTrieNode=m},2371:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.completeLocale=t.getLocale=t.setLocale=t.locales=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4513),o=n(1058),s=n(8597),a=n(9883),c=n(2523),l=n(3938),u=n(9139),d=n(1547),h=n(346),p=n(13),f=n(6238),m=n(2913),g=n(3305),S=n(9770),b=n(4524);function N(){const e=i.Variables.ensureLocale(r.default.getInstance().locale,r.default.getInstance().defaultLocale);return r.default.getInstance().locale=e,t.locales[e]()}t.locales={ca:s.ca,da:a.da,de:c.de,en:l.en,es:u.es,fr:d.fr,hi:h.hi,it:p.it,nb:f.nb,nn:g.nn,sv:S.sv,nemeth:m.nemeth},t.setLocale=function(){const e=N();if(function(e){const t=r.default.getInstance().subiso;-1===e.SUBISO.all.indexOf(t)&&(r.default.getInstance().subiso=e.SUBISO.default);e.SUBISO.current=r.default.getInstance().subiso}(e),e){for(const t of Object.getOwnPropertyNames(e))b.LOCALE[t]=e[t];for(const[t,n]of Object.entries(e.CORRECTIONS))o.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection(t,n)}},t.getLocale=N,t.completeLocale=function(e){const n=t.locales[e.locale];if(!n)return void console.error("Locale "+e.locale+" does not exist!");const r=e.kind.toUpperCase(),i=e.messages;if(!i)return;const o=n();for(const[e,t]of Object.entries(i))o[r][e]=t}},4524:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.createLocale=t.LOCALE=void 0;const r=n(4277);function i(){return{FUNCTIONS:(0,r.FUNCTIONS)(),MESSAGES:(0,r.MESSAGES)(),ALPHABETS:(0,r.ALPHABETS)(),NUMBERS:(0,r.NUMBERS)(),COMBINERS:{},CORRECTIONS:{},SUBISO:(0,r.SUBISO)()}}t.LOCALE=i(),t.createLocale=i},3319:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localeFontCombiner=t.extractString=t.localEnclose=t.localRole=t.localFont=t.combinePostfixIndex=t.nestingToString=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(9385);function o(e,t){return void 0===e?t:"string"==typeof e?e:e[0]}t.nestingToString=function(e){switch(e){case 1:return r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ONCE||"";case 2:return r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.TWICE;default:return e.toString()}},t.combinePostfixIndex=function(e,t){return e===r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX||e===r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.INDEX?e:e+" "+t},t.localFont=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.font[e],e)},t.localRole=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.role[e],e)},t.localEnclose=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.enclose[e],e)},t.extractString=o,t.localeFontCombiner=function(e){return"string"==typeof e?{font:e,combiner:r.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.combiner}:{font:e[0],combiner:r.LOCALE.COMBINERS[e[1]]||i.Combiners[e[1]]||r.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.combiner}}},8597:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ca=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(165),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e="sans serif "+(n?n+" "+e:e),t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.ca=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.sansserif=a,e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=i.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>e+n,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e+" "),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*os$/.test(e)?e+"sos":/.*s$/.test(e)?e+"os":/.*ga$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"gues":/.*\xe7a$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ces":/.*ca$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ques":/.*ja$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ges":/.*qua$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-3)+"q\xfces":/.*a$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"es":/.*(e|i)$/.test(e)?e+"ns":/.*\xed$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ins":e+"s",e.FUNCTIONS.si=(e,t)=>(t.match(/^metre/)&&(e=e.replace(/a$/,"\xe0").replace(/o$/,"\xf2").replace(/i$/,"\xed")),e+t),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e}()),c}},9883:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.da=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(5571),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.da=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=t=>t===e.ALPHABETS.capPrefix.default?RegExp("^"+t+" "):RegExp(" "+t+"$"),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.postfixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e}()),a}},2523:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.de=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(3319),o=n(4524),s=n(757),a=function(e,t,n){return"s"===n&&(t=t.split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"")})).join(" "),n=""),e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?t+" "+e:e},c=function(e,t,n){return e=n&&"s"!==n?n+" "+e:e,t?e+" "+t:e};let l=null;t.de=function(){return l||(l=function(){const e=(0,o.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.COMBINERS.germanPostfix=c,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=t=>t>1?e.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t)+"fach":"",e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=(e,t)=>{const n=t?t+"wurzel":"";return e.replace("Wurzel",n)},e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>{const r=(t?t+" ":"")+(e=n.match(/exponent$/)?e+"r":e);return n.match(/ /)?n.replace(/ /," "+r+" "):r+" "+n},e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=function(e){return e=e.split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"(|s)")})).join(" "),new RegExp("((^"+e+" )|( "+e+"$))")},e.CORRECTIONS.correctOne=e=>e.replace(/^eins$/,"ein"),e.CORRECTIONS.localFontNumber=e=>(0,i.localFont)(e).split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"")})).join(" "),e.CORRECTIONS.lowercase=e=>e.toLowerCase(),e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>{const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("case"),n=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("plural");return"dative"===t?{der:"dem",die:n?"den":"der",das:"dem"}[e]:e},e.CORRECTIONS.masculine=e=>"dative"===r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("case")?e+"n":e,e}()),l}},3938:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.en=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(4524),o=n(3319),s=n(166),a=n(9385);let c=null;t.en=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=o.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*s$/.test(e)?e:e+"s",e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=s.default.numberToWords,e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("noArticle")?"":e,e}()),c}},9139:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.es=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(6154),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e="sans serif "+(n?n+" "+e:e),t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.es=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.sansserif=a,e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=i.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>e+n,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e+" "),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*(a|e|i|o|u)$/.test(e)?e+"s":/.*z$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ces":/.*c$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ques":/.*g$/.test(e)?e+"ues":/.*\u00f3n$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ones":e+"es",e.FUNCTIONS.si=(e,t)=>(t.match(/^metro/)&&(e=e.replace(/a$/,"\xe1").replace(/o$/,"\xf3").replace(/i$/,"\xed")),e+t),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e}()),c}},1547:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.fr=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(4524),o=n(3319),s=n(4394),a=n(9385);let c=null;t.fr=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=o.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=o.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction=(e,t,n)=>n.replace(/ $/g,"")+t+e,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>n+" "+e,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp(" (en |)"+e+"$"),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*s$/.test(e)?e:e+"s",e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("noArticle")?"":e,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a.Combiners.romanceCombiner,e.SUBISO={default:"fr",current:"fr",all:["fr","be","ch"]},e}()),c}},346:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.hi=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(1779),o=n(9385),s=n(3319);let a=null;t.hi=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=i.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=o.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=s.nestingToString,e}()),a}},13:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.it=void 0;const r=n(3319),i=n(4524),o=n(5952),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e.match(/^[a-zA-Z]$/)&&(t=t.replace("cerchiato","cerchiata")),e=n?e+" "+n:e,t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.it=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.italianPostfix=a,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=r.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=r.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction=(e,t,n)=>n.replace(/ $/g,"")+t+e,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>n+" "+e,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp(" (en |)"+e+"$"),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.romanceCombiner,e}()),c}},6238:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nb=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(984),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.nb=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e}()),a}},2913:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nemeth=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3669),o=n(9385),s=function(e){return e.match(RegExp("^"+h.ALPHABETS.languagePrefix.english))?e.slice(1):e},a=function(e,t,n){return e=s(e),t?e+t:e},c=function(e,t,n){return t+s(e)},l=function(e,t,n){return t+(n||"")+(e=s(e))+"\u283b"},u=function(e,t,n){return t+(n||"")+(e=s(e))+"\u283b\u283b"},d=function(e,t,n){return t+(e=s(e))+"\u283e"};let h=null;t.nemeth=function(){return h||(h=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=i.default,e.COMBINERS={postfixCombiner:a,germanCombiner:c,embellishCombiner:l,doubleEmbellishCombiner:u,parensCombiner:d},e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e),e.FUNCTIONS.si=o.identityTransformer,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=(e,t,n)=>t?t+n+e:s(e),e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans={default:i.default.numberToWords},e}()),h}},3305:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nn=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(984),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.nn=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.SUBISO={default:"",current:"",all:["","alt"]},e}()),a}},9770:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.sv=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(6416),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.sv=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=function(e){return new RegExp("((^"+e+" )|( "+e+"$))")},e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.CORRECTIONS.correctOne=e=>e.replace(/^ett$/,"en"),e}()),a}},4277:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SUBISO=t.FUNCTIONS=t.ALPHABETS=t.NUMBERS=t.MESSAGES=void 0;const r=n(9385);t.MESSAGES=function(){return{MS:{},MSroots:{},font:{},embellish:{},role:{},enclose:{},navigate:{},regexp:{},unitTimes:""}},t.NUMBERS=function(){return{zero:"zero",ones:[],tens:[],large:[],special:{},wordOrdinal:r.identityTransformer,numericOrdinal:r.identityTransformer,numberToWords:r.identityTransformer,numberToOrdinal:r.pluralCase,vulgarSep:" ",numSep:" "}},t.ALPHABETS=function(){return{latinSmall:[],latinCap:[],greekSmall:[],greekCap:[],capPrefix:{default:""},smallPrefix:{default:""},digitPrefix:{default:""},languagePrefix:{},digitTrans:{default:r.identityTransformer,mathspeak:r.identityTransformer,clearspeak:r.identityTransformer},letterTrans:{default:r.identityTransformer},combiner:(e,t,n)=>e}},t.FUNCTIONS=function(){return{fracNestDepth:e=>r.vulgarFractionSmall(e,10,100),radicalNestDepth:e=>"",combineRootIndex:function(e,t){return e},combineNestedFraction:r.Combiners.identityCombiner,combineNestedRadical:r.Combiners.identityCombiner,fontRegexp:function(e){return new RegExp("^"+e.split(/ |-/).join("( |-)")+"( |-)")},si:r.siCombiner,plural:r.identityTransformer}},t.SUBISO=function(){return{default:"",current:"",all:[]}}},165:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){const t=e%1e3,n=Math.floor(t/100),r=n?1===n?"cent":a.ones[n]+"-cents":"",i=function(e){const t=e%100;if(t<20)return a.ones[t];const n=Math.floor(t/10),r=a.tens[n],i=a.ones[t%10];return r&&i?r+(2===n?"-i-":"-")+i:r||i}(t%100);return r&&i?r+a.numSep+i:r||i}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%(t>1?1e6:1e3);if(r){let e=a.large[t];if(t)if(1===t)n=(1===r?"":i(r)+a.numSep)+e+(n?a.numSep+n:"");else{const t=o(r);e=1===r?e:e.replace(/\u00f3$/,"ons"),n=t+a.numSep+e+(n?a.numSep+n:"")}else n=i(r)}e=Math.floor(e/(t>1?1e6:1e3)),t++}return n}function s(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("f"===t?"a":"n")}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.numericOrdinal=s,a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(e>1999)return s(e);if(e<=10)return a.special.onesOrdinals[e-1];const n=o(e);return n.match(/mil$/)?n.replace(/mil$/,"mil\xb7l\xe8sima"):n.match(/u$/)?n.replace(/u$/,"vena"):n.match(/a$/)?n.replace(/a$/,"ena"):n+(n.match(/e$/)?"na":"ena")},t.default=a},5571:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?t?"et":"en":e}function i(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,i="",o=a.ones[Math.floor(n/100)];if(i+=o?r(o,!0)+" hundrede":"",n%=100,n)if(i+=i?" og ":"",o=t?a.special.smallOrdinals[n]:a.ones[n],o)i+=o;else{const e=t?a.special.tensOrdinals[Math.floor(n/10)]:a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)];o=a.ones[n%10],i+=o?r(o)+"og"+e:e}return i}function o(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,o="";for(;e>0;){const s=e%1e3;if(s){const e=i(s,t&&!n);if(n){const t=a.large[n],i=s>1?"er":"";o=r(e,n<=1)+" "+t+i+(o?" og ":"")+o}else o=r(e)+o}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return o}function s(e){if(e%100)return o(e,!0);const t=o(e);return t.match(/e$/)?t:t+"e"}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return 1===e?t?"hel":"hele":2===e?t?"halv":"halve":s(e)+(t?"dele":"del")},t.default=a},757:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?t?"eine":"ein":e}function i(e){let t=e%1e3,n="",i=a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)];if(n+=i?r(i)+"hundert":"",t%=100,t)if(n+=n?a.numSep:"",i=a.ones[t],i)n+=i;else{const e=a.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];i=a.ones[t%10],n+=i?r(i)+"und"+e:e}return n}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const s=i(e%1e3);if(t){const e=a.large[t],i=t>1&&o>1?e.match(/e$/)?"n":"en":"";n=r(s,t>1)+e+i+n}else n=r(s,t>1)+n}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/ein$/,"eins")}function s(e){if(1===e)return"erste";if(3===e)return"dritte";if(7===e)return"siebte";if(8===e)return"achte";return o(e)+(e<19?"te":"ste")}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return 1===e?"eintel":2===e?t?"halbe":"halb":s(e)+"l"},t.default=a},166:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";return n+=s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+s.numSep+"hundred":"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]||s.tens[Math.floor(t/10)]+(t%10?s.numSep+s.ones[t%10]:"")),n}function i(e){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){e%1e3&&(n=r(e%1e3)+(t?"-"+s.large[t]+"-":"")+n),e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}function o(e){let t=i(e);return t.match(/one$/)?t=t.slice(0,-3)+"first":t.match(/two$/)?t=t.slice(0,-3)+"second":t.match(/three$/)?t=t.slice(0,-5)+"third":t.match(/five$/)?t=t.slice(0,-4)+"fifth":t.match(/eight$/)?t=t.slice(0,-5)+"eighth":t.match(/nine$/)?t=t.slice(0,-4)+"ninth":t.match(/twelve$/)?t=t.slice(0,-6)+"twelfth":t.match(/ty$/)?t=t.slice(0,-2)+"tieth":t+="th",t}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=e%100,n=e.toString();if(t>10&&t<20)return n+"th";switch(e%10){case 1:return n+"st";case 2:return n+"nd";case 3:return n+"rd";default:return n+"th"}},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(1===e)return t?"oneths":"oneth";if(2===e)return t?"halves":"half";const n=o(e);return t?n+"s":n},t.default=s},6154:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){const t=e%1e3,n=Math.floor(t/100),r=o.special.hundreds[n],i=function(e){const t=e%100;if(t<30)return o.ones[t];const n=o.tens[Math.floor(t/10)],r=o.ones[t%10];return n&&r?n+" y "+r:n||r}(t%100);return 1===n?i?r+"to "+i:r:r&&i?r+" "+i:r||i}const o=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();o.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("f"===t?"a":"o")},o.numberToWords=function(e){if(0===e)return o.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%1e3;if(r){let e=o.large[t];const s=i(r);t?1===r?(e=e.match("/^mil( |$)/")?e:"un "+e,n=e+(n?" "+n:"")):(e=e.replace(/\u00f3n$/,"ones"),n=i(r)+" "+e+(n?" "+n:"")):n=s}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n},o.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(e>1999)return e.toString()+"a";if(e<=12)return o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1];const n=[];if(e>=1e3&&(e-=1e3,n.push("mil\xe9sima")),!e)return n.join(" ");let r=0;return r=Math.floor(e/100),r>0&&(n.push(o.special.hundredsOrdinals[r-1]),e%=100),e<=12?n.push(o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1]):(r=Math.floor(e/10),r>0&&(n.push(o.special.tensOrdinals[r-1]),e%=10),e>0&&n.push(o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1])),n.join(" ")},t.default=o},4394:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4886),i=n(1058),o=n(4277);function s(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";if(n+=u.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?u.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+"-cent":"",t%=100,t){n+=n?"-":"";let e=u.ones[t];if(e)n+=e;else{const r=u.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];r.match(/-dix$/)?(e=u.ones[t%10+10],n+=r.replace(/-dix$/,"")+"-"+e):n+=r+(t%10?"-"+u.ones[t%10]:"")}}const r=n.match(/s-\w+$/);return r?n.replace(/s-\w+$/,r[0].slice(1)):n.replace(/-un$/,"-et-un")}function a(e){if(0===e)return u.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();u.special["tens-"+r.default.getInstance().subiso]&&(u.tens=u.special["tens-"+r.default.getInstance().subiso]);let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%1e3;if(r){let e=u.large[t];const i=s(r);if(e&&e.match(/^mille /)){const r=e.replace(/^mille /,"");n=n.match(RegExp(r))?i+(t?"-mille-":"")+n:n.match(RegExp(r.replace(/s$/,"")))?i+(t?"-mille-":"")+n.replace(r.replace(/s$/,""),r):i+(t?"-"+e+"-":"")+n}else e=1===r&&e?e.replace(/s$/,""):e,n=i+(t?"-"+e+"-":"")+n}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}const c={1:"uni\xe8me",2:"demi",3:"tiers",4:"quart"};function l(e){if(1===e)return"premi\xe8re";let t=a(e);return t.match(/^neuf$/)?t=t.slice(0,-1)+"v":t.match(/cinq$/)?t+="u":t.match(/trois$/)?t+="":(t.match(/e$/)||t.match(/s$/))&&(t=t.slice(0,-1)),t+="i\xe8me",t}const u=(0,o.NUMBERS)();u.wordOrdinal=l,u.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=i.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return 1===e?e.toString()+("m"===t?"er":"re"):e.toString()+"e"},u.numberToWords=a,u.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){const n=c[e]||l(e);return 3===e?n:t?n+"s":n},t.default=u},1779:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,32))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";const r=function(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";return n+=s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+s.numSep+s.special.hundred:"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]),n}(e%1e3);if(!(e=Math.floor(e/1e3)))return r;for(;e>0;){const r=e%100;r&&(n=s.ones[r]+s.numSep+s.large[t]+(n?s.numSep+n:"")),e=Math.floor(e/100),t++}return r?n+s.numSep+r:n}function o(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");if(e<=0)return e.toString();if(e<10)return"f"===t?s.special.ordinalsFeminine[e]:s.special.ordinalsMasculine[e];return i(e)+("f"===t?"\u0935\u0940\u0902":"\u0935\u093e\u0901")}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e>0&&e<10?"f"===t?s.special.simpleSmallOrdinalsFeminine[e]:s.special.simpleSmallOrdinalsMasculine[e]:e.toString().split("").map((function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.special.simpleNumbers[t]})).join("")+("f"===t?"\u0935\u0940\u0902":"\u0935\u093e\u0901")},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return e<=10?s.special.smallDenominators[e]:o(e)+" \u0905\u0902\u0936"},t.default=s},5952:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";if(n+=a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+a.numSep+"cento":"",t%=100,t){n+=n?a.numSep:"";const e=a.ones[t];if(e)n+=e;else{let e=a.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];const r=t%10;1!==r&&8!==r||(e=e.slice(0,-1)),n+=e,n+=r?a.numSep+a.ones[t%10]:""}}return n}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();if(1===e&&r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("fraction"))return"un";let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){e%1e3&&(n=i(e%1e3)+(t?"-"+a.large[t]+"-":"")+n),e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}function s(e){const t="m"===r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender")?"o":"a";let n=a.special.onesOrdinals[e];return n?n.slice(0,-1)+t:(n=o(e),n.slice(0,-1)+"esim"+t)}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("m"===t?"o":"a")},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(2===e)return t?"mezzi":"mezzo";const n=s(e);if(!t)return n;const r=n.match(/o$/)?"i":"e";return n.slice(0,-1)+r},t.default=a},3669:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){return e.toString().split("").map((function(e){return i.ones[parseInt(e,10)]})).join("")}const i=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();i.numberToWords=r,i.numberToOrdinal=r,t.default=i},984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4886);function i(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,r="";const i=Math.floor(n/100),s=a.ones[i];if(r+=s?(1===i?"":s)+"hundre":"",n%=100,n){if(r+=r?"og":"",t){const e=a.special.smallOrdinals[n];if(e)return r+e;if(n%10)return r+a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)]+a.special.smallOrdinals[n%10]}r+=a.ones[n]||a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)]+(n%10?a.ones[n%10]:"")}return t?o(r):r}function o(e){const t=a.special.endOrdinal[0];return"a"===t&&e.match(/en$/)?e.slice(0,-2)+a.special.endOrdinal:e.match(/(d|n)$/)||e.match(/hundre$/)?e+"de":e.match(/i$/)?e+a.special.endOrdinal:"a"===t&&e.match(/e$/)?e.slice(0,-1)+a.special.endOrdinal:(e.match(/e$/),e+"nde")}function s(e){return u(e,!0)}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();function c(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?"ein"===e?"eitt ":t?"et":"ett":e}function l(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,r="",i=a.ones[Math.floor(n/100)];if(r+=i?c(i)+"hundre":"",n%=100,n){if(r+=r?"og":"",t){const e=a.special.smallOrdinals[n];if(e)return r+e}if(i=a.ones[n],i)r+=i;else{const e=a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)];i=a.ones[n%10],r+=i?i+"og"+e:e}}return t?o(r):r}function u(e,t=!1){const n="alt"===r.default.getInstance().subiso?function(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return t?a.special.smallOrdinals[0]:a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,r="";for(;e>0;){const i=e%1e3;if(i){const o=l(e%1e3,!n&&t);!n&&t&&(t=!t),r=(1===n?c(o,!0):o)+(n>1?a.numSep:"")+(n?a.large[n]+(n>1&&i>1?"er":""):"")+(n>1&&r?a.numSep:"")+r}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return t?r+(r.match(/tusen$/)?"de":"te"):r}(e,t):function(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return t?a.special.smallOrdinals[0]:a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,r="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const s=i(e%1e3,!n&&t);!n&&t&&(t=!t),r=s+(n?" "+a.large[n]+(n>1&&o>1?"er":"")+(r?" ":""):"")+r}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return t?r+(r.match(/tusen$/)?"de":"te"):r}(e,t);return n}a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=u,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return s(e)},t.default=a},6416:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";const r=Math.floor(t/100);return n+=s.ones[r]?(1===r?"":s.ones[r]+s.numSep)+"hundra":"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]||s.tens[Math.floor(t/10)]+(t%10?s.numSep+s.ones[t%10]:"")),n}function i(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,i="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const a=s.large[n],c=o>1&&n>1&&!t?"er":"";i=(1===n&&1===o?"":(n>1&&1===o?"en":r(e%1e3))+(n>1?" ":""))+(n?a+c+(n>1?" ":""):"")+i}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return i.replace(/ $/,"")}function o(e){let t=i(e,!0);return t.match(/^noll$/)?t="nollte":t.match(/ett$/)?t=t.replace(/ett$/,"f\xf6rsta"):t.match(/tv\xe5$/)?t=t.replace(/tv\xe5$/,"andra"):t.match(/tre$/)?t=t.replace(/tre$/,"tredje"):t.match(/fyra$/)?t=t.replace(/fyra$/,"fj\xe4rde"):t.match(/fem$/)?t=t.replace(/fem$/,"femte"):t.match(/sex$/)?t=t.replace(/sex$/,"sj\xe4tte"):t.match(/sju$/)?t=t.replace(/sju$/,"sjunde"):t.match(/\xe5tta$/)?t=t.replace(/\xe5tta$/,"\xe5ttonde"):t.match(/nio$/)?t=t.replace(/nio$/,"nionde"):t.match(/tio$/)?t=t.replace(/tio$/,"tionde"):t.match(/elva$/)?t=t.replace(/elva$/,"elfte"):t.match(/tolv$/)?t=t.replace(/tolv$/,"tolfte"):t.match(/tusen$/)?t=t.replace(/tusen$/,"tusonde"):t.match(/jard$/)||t.match(/jon$/)?t+="te":t+="de",t}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=e.toString();return t.match(/11$|12$/)?t+":e":t+(t.match(/1$|2$/)?":a":":e")},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(1===e)return"hel";if(2===e)return t?"halva":"halv";let n=o(e);return n=n.match(/de$/)?n.replace(/de$/,""):n,n+(t?"delar":"del")},t.default=s},9385:function(e,t){function n(e,t=""){if(!e.childNodes||!e.childNodes[0]||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes||e.childNodes[0].childNodes.length<2||"number"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName||"integer"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].getAttribute("role")||"number"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].tagName||"integer"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role"))return{convertible:!1,content:e.textContent};const n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent,r=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent,i=Number(n),o=Number(r);return isNaN(i)||isNaN(o)?{convertible:!1,content:`${r} ${t} ${n}`}:{convertible:!0,enumerator:o,denominator:i}}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.vulgarFractionSmall=t.convertVulgarFraction=t.Combiners=t.siCombiner=t.identityTransformer=t.pluralCase=void 0,t.pluralCase=function(e,t){return e.toString()},t.identityTransformer=function(e){return e.toString()},t.siCombiner=function(e,t){return e+t.toLowerCase()},t.Combiners={},t.Combiners.identityCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e+t+n},t.Combiners.prefixCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?t+" "+e:e},t.Combiners.postfixCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?e+" "+t:e},t.Combiners.romanceCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?e+" "+n:e,t?e+" "+t:e},t.convertVulgarFraction=n,t.vulgarFractionSmall=function(e,t,r){const i=n(e);if(i.convertible){const e=i.enumerator,n=i.denominator;return e>0&&e0&&n{const s=this.parseCstr(t.toString().replace(i,""));this.addRule(new o.SpeechRule(e,s,r,n))}))}getFullPreconditions(e){const t=this.preconditions.get(e);return t||!this.inherits?t:this.inherits.getFullPreconditions(e)}definePrecondition(e,t,n,...r){const i=this.parsePrecondition(n,r),o=this.parseCstr(t);i&&o?(i.rank=this.rank++,this.preconditions.set(e,new c(o,i))):console.error(`Precondition Error: ${n}, (${t})`)}inheritRules(){if(!this.inherits||!this.inherits.getSpeechRules().length)return;const e=new RegExp("^\\w+\\.\\w+\\."+(this.domain?"\\w+\\.":""));this.inherits.getSpeechRules().forEach((t=>{const n=this.parseCstr(t.dynamicCstr.toString().replace(e,""));this.addRule(new o.SpeechRule(t.name,n,t.precondition,t.action))}))}ignoreRules(e,...t){let n=this.findAllRules((t=>t.name===e));if(!t.length)return void n.forEach(this.deleteRule.bind(this));let r=[];for(const e of t){const t=this.parseCstr(e);for(const e of n)t.equal(e.dynamicCstr)?this.deleteRule(e):r.push(e);n=r,r=[]}}parsePrecondition_(e){const t=this.context.customGenerators.lookup(e);return t?t():[e]}}t.BaseRuleStore=a;class c{constructor(e,t){this.base=e,this._conditions=[],this.constraints=[],this.allCstr={},this.constraints.push(e),this.addCondition(e,t)}get conditions(){return this._conditions}addConstraint(e){if(this.constraints.filter((t=>t.equal(e))).length)return;this.constraints.push(e);const t=[];for(const[n,r]of this.conditions)this.base.equal(n)&&t.push([e,r]);this._conditions=this._conditions.concat(t)}addBaseCondition(e){this.addCondition(this.base,e)}addFullCondition(e){this.constraints.forEach((t=>this.addCondition(t,e)))}addCondition(e,t){const n=e.toString()+" "+t.toString();this.allCstr.condStr||(this.allCstr[n]=!0,this._conditions.push([e,t]))}}t.Condition=c},1462:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.BrailleStore=void 0;const r=n(4036),i=n(7478);class o extends i.MathStore{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.modality="braille",this.customTranscriptions={"\u22ca":"\u2808\u2821\u2833"}}evaluateString(e){const t=[],n=Array.from(e);for(let e=0;ee.push(this.getProperty(t).slice()))),e}toString(){const e=[];return this.order.forEach((t=>e.push(t+": "+this.getProperty(t).toString()))),e.join("\n")}}t.DynamicProperties=r;class i extends r{constructor(e,t){const n={};for(const[t,r]of Object.entries(e))n[t]=[r];super(n,t),this.components=e}static createCstr(...e){const t=i.DEFAULT_ORDER,n={};for(let r=0,i=e.length,o=t.length;r{const n=t.indexOf(e);return-1!==n&&t.splice(n,1)}))}getComponents(){return this.components}getValue(e){return this.components[e]}getValues(){return this.order.map((e=>this.getValue(e)))}allProperties(){const e=super.allProperties();for(let t,n,r=0;t=e[r],n=this.order[r];r++){const e=this.getValue(n);-1===t.indexOf(e)&&t.unshift(e)}return e}toString(){return this.getValues().join(".")}equal(e){const t=e.getAxes();if(this.order.length!==t.length)return!1;for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++){const t=this.getValue(n);if(!t||e.getValue(n)!==t)return!1}return!0}}t.DynamicCstr=i,i.DEFAULT_ORDER=[n.LOCALE,n.MODALITY,n.DOMAIN,n.STYLE,n.TOPIC],i.BASE_LOCALE="base",i.DEFAULT_VALUE="default",i.DEFAULT_VALUES={[n.LOCALE]:"en",[n.DOMAIN]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.STYLE]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.TOPIC]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.MODALITY]:"speech"};t.DynamicCstrParser=class{constructor(e){this.order=e}parse(e){const t=e.split("."),n={};if(t.length>this.order.length)throw new Error("Invalid dynamic constraint: "+n);let r=0;for(let e,i=0;e=this.order[i],t.length;i++,r++){const r=t.shift();n[e]=r}return new i(n,this.order.slice(0,r))}};t.DefaultComparator=class{constructor(e,t=new r(e.getProperties(),e.getOrder())){this.reference=e,this.fallback=t,this.order=this.reference.getOrder()}getReference(){return this.reference}setReference(e,t){this.reference=e,this.fallback=t||new r(e.getProperties(),e.getOrder()),this.order=this.reference.getOrder()}match(e){const t=e.getAxes();return t.length===this.reference.getAxes().length&&t.every((t=>{const n=e.getValue(t);return n===this.reference.getValue(t)||-1!==this.fallback.getProperty(t).indexOf(n)}))}compare(e,t){let n=!1;for(let r,i=0;r=this.order[i];i++){const i=e.getValue(r),o=t.getValue(r);if(!n){const e=this.reference.getValue(r);if(e===i&&e!==o)return-1;if(e===o&&e!==i)return 1;if(e===i&&e===o)continue;e!==i&&e!==o&&(n=!0)}const s=this.fallback.getProperty(r),a=s.indexOf(i),c=s.indexOf(o);if(a!h.equal(e.cstr))),c.push(m),this.rules.set(t,c),p.setReference(f)}lookupRule(e,t){let n=this.getRules(t.getValue(i.Axis.LOCALE));return n=n.filter((function(e){return o.testDynamicConstraints_(t,e)})),1===n.length?n[0]:n.length?n.sort(((e,t)=>r.default.getInstance().comparator.compare(e.cstr,t.cstr)))[0]:null}}t.MathSimpleStore=o},7478:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MathStore=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(4524),o=n(4036),s=n(1970),a=n(7039);class c extends s.BaseRuleStore{constructor(){super(),this.annotators=[],this.parseMethods.Alias=this.defineAlias,this.parseMethods.SpecializedRule=this.defineSpecializedRule,this.parseMethods.Specialized=this.defineSpecialized}initialize(){this.initialized||(this.annotations(),this.initialized=!0)}annotations(){for(let e,t=0;e=this.annotators[t];t++)(0,o.activate)(this.domain,e)}defineAlias(e,t,...n){const r=this.parsePrecondition(t,n);if(!r)return void console.error(`Precondition Error: ${t} ${n}`);const i=this.preconditions.get(e);i?i.addFullCondition(r):console.error(`Alias Error: No precondition by the name of ${e}`)}defineRulesAlias(e,t,...n){const r=this.findAllRules((function(t){return t.name===e}));if(0===r.length)throw new a.OutputError("Rule with name "+e+" does not exist.");const i=[];r.forEach((e=>{(e=>{const t=e.dynamicCstr.toString(),n=e.action.toString();for(let e,r=0;e=i[r];r++)if(e.action===n&&e.cstr===t)return!1;return i.push({cstr:t,action:n}),!0})(e)&&this.addAlias_(e,t,n)}))}defineSpecializedRule(e,t,n,r){const i=this.parseCstr(t),o=this.findRule((t=>t.name===e&&i.equal(t.dynamicCstr))),s=this.parseCstr(n);if(!o&&r)throw new a.OutputError("Rule named "+e+" with style "+t+" does not exist.");const c=r?a.Action.fromString(r):o.action,l=new a.SpeechRule(o.name,s,o.precondition,c);this.addRule(l)}defineSpecialized(e,t,n){const r=this.parseCstr(n);if(!r)return void console.error(`Dynamic Constraint Error: ${n}`);const i=this.preconditions.get(e);i?i.addConstraint(r):console.error(`Alias Error: No precondition by the name of ${e}`)}evaluateString(e){const t=[];if(e.match(/^\s+$/))return t;let n=this.matchNumber_(e);if(n&&n.length===e.length)return t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n.number)),t;const o=r.removeEmpty(e.replace(/\s/g," ").split(" "));for(let e,r=0;e=o[r];r++)if(1===e.length)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e));else if(e.match(new RegExp("^["+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.TEXT+"]+$")))t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e));else{let r=e;for(;r;){n=this.matchNumber_(r);const e=r.match(new RegExp("^["+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.TEXT+"]+"));if(n)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n.number)),r=r.substring(n.length);else if(e)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e[0])),r=r.substring(e[0].length);else{const e=Array.from(r),n=e[0];t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n)),r=e.slice(1).join("")}}}return t}parse(e){super.parse(e),this.annotators=e.annotators||[]}addAlias_(e,t,n){const r=this.parsePrecondition(t,n),i=new a.SpeechRule(e.name,e.dynamicCstr,r,e.action);i.name=e.name,this.addRule(i)}matchNumber_(e){const t=e.match(new RegExp("^"+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.NUMBER)),n=e.match(new RegExp("^"+c.regexp.NUMBER));if(!t&&!n)return null;const r=n&&n[0]===e;if(t&&t[0]===e||!r)return t?{number:t[0],length:t[0].length}:null;return{number:n[0].replace(new RegExp(c.regexp.DIGIT_GROUP,"g"),"X").replace(new RegExp(c.regexp.DECIMAL_MARK,"g"),i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.DECIMAL_MARK).replace(/X/g,i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.DIGIT_GROUP.replace(/\\/g,"")),length:n[0].length}}}t.MathStore=c,c.regexp={NUMBER:"((\\d{1,3})(?=(,| ))((,| )\\d{3})*(\\.\\d+)?)|^\\d*\\.\\d+|^\\d+",DECIMAL_MARK:"\\.",DIGIT_GROUP:","}},7039:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.OutputError=t.Precondition=t.Action=t.Component=t.ActionType=t.SpeechRule=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(1058);var o;function s(e){switch(e){case"[n]":return o.NODE;case"[m]":return o.MULTI;case"[t]":return o.TEXT;case"[p]":return o.PERSONALITY;default:throw"Parse error: "+e}}t.SpeechRule=class{constructor(e,t,n,r){this.name=e,this.dynamicCstr=t,this.precondition=n,this.action=r,this.context=null}toString(){return this.name+" | "+this.dynamicCstr.toString()+" | "+this.precondition.toString()+" ==> "+this.action.toString()}},function(e){e.NODE="NODE",e.MULTI="MULTI",e.TEXT="TEXT",e.PERSONALITY="PERSONALITY"}(o=t.ActionType||(t.ActionType={}));class a{constructor({type:e,content:t,attributes:n,grammar:r}){this.type=e,this.content=t,this.attributes=n,this.grammar=r}static grammarFromString(e){return i.Grammar.parseInput(e)}static fromString(e){const t={type:s(e.substring(0,3))};let n=e.slice(3).trim();if(!n)throw new u("Missing content.");switch(t.type){case o.TEXT:if('"'===n[0]){const e=d(n,"\\(")[0].trim();if('"'!==e.slice(-1))throw new u("Invalid string syntax.");t.content=e,n=n.slice(e.length).trim(),-1===n.indexOf("(")&&(n="");break}case o.NODE:case o.MULTI:{const e=n.indexOf(" (");if(-1===e){t.content=n.trim(),n="";break}t.content=n.substring(0,e).trim(),n=n.slice(e).trim()}}if(n){const e=a.attributesFromString(n);e.grammar&&(t.grammar=e.grammar,delete e.grammar),Object.keys(e).length&&(t.attributes=e)}return new a(t)}static attributesFromString(e){if("("!==e[0]||")"!==e.slice(-1))throw new u("Invalid attribute expression: "+e);const t={},n=d(e.slice(1,-1),",");for(let e=0,r=n.length;e0?"("+e.join(", ")+")":""}getAttributes(){const e=[];for(const t in this.attributes){const n=this.attributes[t];"true"===n?e.push(t):e.push(t+":"+n)}return e}}t.Component=a;class c{constructor(e){this.components=e}static fromString(e){const t=d(e,";").filter((function(e){return e.match(/\S/)})).map((function(e){return e.trim()})),n=[];for(let e=0,r=t.length;e0?n[0]:null}applyConstraint(e,t){return!!this.applyQuery(e,t)||r.evaluateBoolean(t,e)}constructString(e,t){if(!t)return"";if('"'===t.charAt(0))return t.slice(1,-1);const n=this.customStrings.lookup(t);return n?n(e):r.evaluateString(t,e)}parse(e){const t=Array.isArray(e)?e:Object.entries(e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++){switch(e[0].slice(0,3)){case"CQF":this.customQueries.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CSF":this.customStrings.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CTF":this.contextFunctions.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CGF":this.customGenerators.add(e[0],e[1]);break;default:console.error("FunctionError: Invalid function name "+e[0])}}}}},6060:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.storeFactory=t.SpeechRuleEngine=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(1984),o=n(6671),s=n(4886),a=n(4998),c=n(5024),l=n(7278),u=n(9805),d=n(1462),h=n(8310),p=n(1058),f=n(7478),m=n(7039),g=n(2803);class S{constructor(){this.trie=null,this.evaluators_={},this.trie=new g.Trie}static getInstance(){return S.instance=S.instance||new S,S.instance}static debugSpeechRule(e,t){const n=e.precondition,r=e.context.applyQuery(t,n.query);i.Debugger.getInstance().output(n.query,r?r.toString():r),n.constraints.forEach((n=>i.Debugger.getInstance().output(n,e.context.applyConstraint(t,n))))}static debugNamedSpeechRule(e,t){const n=S.getInstance().trie.collectRules().filter((t=>t.name==e));for(let r,o=0;r=n[o];o++)i.Debugger.getInstance().output("Rule",e,"DynamicCstr:",r.dynamicCstr.toString(),"number",o),S.debugSpeechRule(r,t)}evaluateNode(e){(0,c.updateEvaluator)(e);const t=(new Date).getTime();let n=[];try{n=this.evaluateNode_(e)}catch(e){console.error("Something went wrong computing speech."),i.Debugger.getInstance().output(e)}const r=(new Date).getTime();return i.Debugger.getInstance().output("Time:",r-t),n}toString(){return this.trie.collectRules().map((e=>e.toString())).join("\n")}runInSetting(e,t){const n=s.default.getInstance(),r={};for(const t in e)r[t]=n[t],n[t]=e[t];n.setDynamicCstr();const i=t();for(const e in r)n[e]=r[e];return n.setDynamicCstr(),i}addStore(e){const t=N(e);"abstract"!==t.kind&&t.getSpeechRules().forEach((e=>this.trie.addRule(e))),this.addEvaluator(t)}processGrammar(e,t,n){const r={};for(const i in n){const o=n[i];r[i]="string"==typeof o?e.constructString(t,o):o}p.Grammar.getInstance().pushState(r)}addEvaluator(e){const t=e.evaluateDefault.bind(e),n=this.evaluators_[e.locale];if(n)return void(n[e.modality]=t);const r={};r[e.modality]=t,this.evaluators_[e.locale]=r}getEvaluator(e,t){const n=this.evaluators_[e]||this.evaluators_[h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.LOCALE]];return n[t]||n[h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY]]}enumerate(e){return this.trie.enumerate(e)}evaluateNode_(e){return e?(this.updateConstraint_(),this.evaluateTree_(e)):[]}evaluateTree_(e){const t=s.default.getInstance();let n;i.Debugger.getInstance().output(t.mode!==a.Mode.HTTP?e.toString():e),p.Grammar.getInstance().setAttribute(e);const o=this.lookupRule(e,t.dynamicCstr);if(!o)return t.strict?[]:(n=this.getEvaluator(t.locale,t.modality)(e),e.attributes&&this.addPersonality_(n,{},!1,e),n);i.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((()=>["Apply Rule:",o.name,o.dynamicCstr.toString(),(t.mode,a.Mode.HTTP,e).toString()]));const l=o.context,u=o.action.components;n=[];for(let t,i=0;t=u[i];i++){let i=[];const o=t.content||"",a=t.attributes||{};let u=!1;t.grammar&&this.processGrammar(l,e,t.grammar);let d=null;if(a.engine){d=s.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr.getComponents();const e=p.Grammar.parseInput(a.engine);s.default.getInstance().setDynamicCstr(e)}switch(t.type){case m.ActionType.NODE:{const t=l.applyQuery(e,o);t&&(i=this.evaluateTree_(t))}break;case m.ActionType.MULTI:{u=!0;const t=l.applySelector(e,o);t.length>0&&(i=this.evaluateNodeList_(l,t,a.sepFunc,l.constructString(e,a.separator),a.ctxtFunc,l.constructString(e,a.context)))}break;case m.ActionType.TEXT:{const t=a.span,n={};if(t){const r=(0,c.evalXPath)(t,e);r.length&&(n.extid=r[0].getAttribute("extid"))}const s=l.constructString(e,o);(s||""===s)&&(i=Array.isArray(s)?s.map((function(e){return r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:e.speech,attributes:e.attributes},{adjust:!0})})):[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:s,attributes:n},{adjust:!0})])}break;case m.ActionType.PERSONALITY:default:i=[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:o})]}i[0]&&!u&&(a.context&&(i[0].context=l.constructString(e,a.context)+(i[0].context||"")),a.annotation&&(i[0].annotation=a.annotation)),this.addLayout(i,a,u),t.grammar&&p.Grammar.getInstance().popState(),n=n.concat(this.addPersonality_(i,a,u,e)),d&&s.default.getInstance().setDynamicCstr(d)}return n}evaluateNodeList_(e,t,n,i,o,s){if(!t.length)return[];const a=i||"",c=s||"",l=e.contextFunctions.lookup(o),u=l?l(t,c):function(){return c},d=e.contextFunctions.lookup(n),h=d?d(t,a):function(){return[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:a},{translate:!0})]};let p=[];for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++){const r=this.evaluateTree_(e);if(r.length>0&&(r[0].context=u()+(r[0].context||""),p=p.concat(r),n=0;t--){const r=n[t].name;!e.attributes[r]&&r.match(/^ext/)&&(e.attributes[r]=n[t].value)}}}addRelativePersonality_(e,t){if(!e.personality)return e.personality=t,e;const n=e.personality;for(const e in t)n[e]&&"number"==typeof n[e]&&"number"==typeof t[e]?n[e]=n[e]+t[e]:n[e]||(n[e]=t[e]);return e}updateConstraint_(){const e=s.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr,t=s.default.getInstance().strict,n=this.trie,r={};let i=e.getValue(h.Axis.LOCALE),o=e.getValue(h.Axis.MODALITY),a=e.getValue(h.Axis.DOMAIN);n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(a=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.DOMAIN],n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(o=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY],n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(i=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.LOCALE]))),r[h.Axis.LOCALE]=[i],r[h.Axis.MODALITY]=["summary"!==o?o:h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY]],r[h.Axis.DOMAIN]=["speech"!==o?h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.DOMAIN]:a];const c=e.getOrder();for(let n,i=0;n=c[i];i++)if(!r[n]){const i=e.getValue(n),o=this.makeSet_(i,e.preference),s=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[n];t||i===s||o.push(s),r[n]=o}e.updateProperties(r)}makeSet_(e,t){return t&&Object.keys(t).length?e.split(":"):[e]}lookupRule(e,t){if(!e||e.nodeType!==o.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&e.nodeType!==o.NodeType.TEXT_NODE)return null;const n=this.lookupRules(e,t);return n.length>0?this.pickMostConstraint_(t,n):null}lookupRules(e,t){return this.trie.lookupRules(e,t.allProperties())}pickMostConstraint_(e,t){const n=s.default.getInstance().comparator;return t.sort((function(e,t){return n.compare(e.dynamicCstr,t.dynamicCstr)||t.precondition.priority-e.precondition.priority||t.precondition.constraints.length-e.precondition.constraints.length||t.precondition.rank-e.precondition.rank})),i.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((()=>t.map((e=>e.name+"("+e.dynamicCstr.toString()+")"))).bind(this)),t[0]}}t.SpeechRuleEngine=S;const b=new Map;function N(e){const t=`${e.locale}.${e.modality}.${e.domain}`;if("actions"===e.kind){const n=b.get(t);return n.parse(e),n}u.init(),e&&!e.functions&&(e.functions=l.getStore(e.locale,e.modality,e.domain));const n="braille"===e.modality?new d.BrailleStore:new f.MathStore;return b.set(t,n),e.inherits&&(n.inherits=b.get(`${e.inherits}.${e.modality}.${e.domain}`)),n.parse(e),n.initialize(),n}t.storeFactory=N,s.default.nodeEvaluator=S.getInstance().evaluateNode.bind(S.getInstance())},3686:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CustomGenerators=t.ContextFunctions=t.CustomStrings=t.CustomQueries=void 0;class n{constructor(e,t){this.prefix=e,this.store=t}add(e,t){this.checkCustomFunctionSyntax_(e)&&(this.store[e]=t)}addStore(e){const t=Object.keys(e.store);for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++)this.add(n,e.store[n])}lookup(e){return this.store[e]}checkCustomFunctionSyntax_(e){const t=new RegExp("^"+this.prefix);return!!e.match(t)||(console.error("FunctionError: Invalid function name. Expected prefix "+this.prefix),!1)}}t.CustomQueries=class extends n{constructor(){super("CQF",{})}};t.CustomStrings=class extends n{constructor(){super("CSF",{})}};t.ContextFunctions=class extends n{constructor(){super("CTF",{})}};t.CustomGenerators=class extends n{constructor(){super("CGF",{})}}},931:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.contentIterator=t.pauseSeparator=t.nodeCounter=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(5024),o=n(4886);t.nodeCounter=function(e,t){const n=e.length;let r=0,i=t;return t||(i=""),function(){return r0?i.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=n.shift(),i=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!e)return i;const s=o.default.evaluateNode(e);return i.concat(s)}}},1939:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getTreeFromString=t.getTree=t.xmlTree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(1784);function o(e){return new i.SemanticTree(e)}t.xmlTree=function(e){return o(e).xml()},t.getTree=o,t.getTreeFromString=function(e){return o(r.parseInput(e))}},4036:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.annotate=t.activate=t.register=t.visitors=t.annotators=void 0;const r=n(241);t.annotators=new Map,t.visitors=new Map,t.register=function(e){const n=e.domain+":"+e.name;e instanceof r.SemanticAnnotator?t.annotators.set(n,e):t.visitors.set(n,e)},t.activate=function(e,n){const r=e+":"+n,i=t.annotators.get(r)||t.visitors.get(r);i&&(i.active=!0)},t.annotate=function(e){for(const n of t.annotators.values())n.active&&n.annotate(e);for(const n of t.visitors.values())n.active&&n.visit(e,Object.assign({},n.def))}},241:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticVisitor=t.SemanticAnnotator=void 0;t.SemanticAnnotator=class{constructor(e,t,n){this.domain=e,this.name=t,this.func=n,this.active=!1}annotate(e){e.childNodes.forEach(this.annotate.bind(this)),e.addAnnotation(this.domain,this.func(e))}};t.SemanticVisitor=class{constructor(e,t,n,r={}){this.domain=e,this.name=t,this.func=n,this.def=r,this.active=!1}visit(e,t){let n=this.func(e,t);e.addAnnotation(this.domain,n[0]);for(let t,r=0;t=e.childNodes[r];r++)n=this.visit(t,n[1]);return n}}},4020:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.lookupSecondary=t.isEmbellishedType=t.isMatchingFence=t.functionApplication=t.invisibleComma=t.invisiblePlus=t.invisibleTimes=t.lookupMeaning=t.lookupRole=t.lookupType=t.equal=t.allLettersRegExp=void 0;const n=String.fromCodePoint(8291),r=["\uff0c","\ufe50",",",n],i=["\xaf","\u2012","\u2013","\u2014","\u2015","\ufe58","-","\u207b","\u208b","\u2212","\u2796","\ufe63","\uff0d","\u2010","\u2011","\u203e","_"],o=["~","\u0303","\u223c","\u02dc","\u223d","\u02f7","\u0334","\u0330"],s={"(":")","[":"]","{":"}","\u2045":"\u2046","\u2329":"\u232a","\u2768":"\u2769","\u276a":"\u276b","\u276c":"\u276d","\u276e":"\u276f","\u2770":"\u2771","\u2772":"\u2773","\u2774":"\u2775","\u27c5":"\u27c6","\u27e6":"\u27e7","\u27e8":"\u27e9","\u27ea":"\u27eb","\u27ec":"\u27ed","\u27ee":"\u27ef","\u2983":"\u2984","\u2985":"\u2986","\u2987":"\u2988","\u2989":"\u298a","\u298b":"\u298c","\u298d":"\u298e","\u298f":"\u2990","\u2991":"\u2992","\u2993":"\u2994","\u2995":"\u2996","\u2997":"\u2998","\u29d8":"\u29d9","\u29da":"\u29db","\u29fc":"\u29fd","\u2e22":"\u2e23","\u2e24":"\u2e25","\u2e26":"\u2e27","\u2e28":"\u2e29","\u3008":"\u3009","\u300a":"\u300b","\u300c":"\u300d","\u300e":"\u300f","\u3010":"\u3011","\u3014":"\u3015","\u3016":"\u3017","\u3018":"\u3019","\u301a":"\u301b","\u301d":"\u301e","\ufd3e":"\ufd3f","\ufe17":"\ufe18","\ufe59":"\ufe5a","\ufe5b":"\ufe5c","\ufe5d":"\ufe5e","\uff08":"\uff09","\uff3b":"\uff3d","\uff5b":"\uff5d","\uff5f":"\uff60","\uff62":"\uff63","\u2308":"\u2309","\u230a":"\u230b","\u230c":"\u230d","\u230e":"\u230f","\u231c":"\u231d","\u231e":"\u231f","\u239b":"\u239e","\u239c":"\u239f","\u239d":"\u23a0","\u23a1":"\u23a4","\u23a2":"\u23a5","\u23a3":"\u23a6","\u23a7":"\u23ab","\u23a8":"\u23ac","\u23a9":"\u23ad","\u23b0":"\u23b1","\u23b8":"\u23b9"},a={"\u23b4":"\u23b5","\u23dc":"\u23dd","\u23de":"\u23df","\u23e0":"\u23e1","\ufe35":"\ufe36","\ufe37":"\ufe38","\ufe39":"\ufe3a","\ufe3b":"\ufe3c","\ufe3d":"\ufe3e","\ufe3f":"\ufe40","\ufe41":"\ufe42","\ufe43":"\ufe44","\ufe47":"\ufe48"},c=Object.keys(s),l=Object.values(s);l.push("\u301f");const u=Object.keys(a),d=Object.values(a),h=["|","\xa6","\u2223","\u23d0","\u23b8","\u23b9","\u2758","\uff5c","\uffe4","\ufe31","\ufe32"],p=["\u2016","\u2225","\u2980","\u2af4"],f=["A","B","C","D","E","F","G","H","I","J","K","L","M","N","O","P","Q","R","S","T","U","V","W","X","Y","Z"],m=["a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","i","j","k","l","m","n","o","p","q","r","s","t","u","v","w","x","y","z","\u0131","\u0237"],g=["\uff21","\uff22","\uff23","\uff24","\uff25","\uff26","\uff27","\uff28","\uff29","\uff2a","\uff2b","\uff2c","\uff2d","\uff2e","\uff2f","\uff30","\uff31","\uff32","\uff33","\uff34","\uff35","\uff36","\uff37","\uff38","\uff39","\uff3a"],S=["\uff41","\uff42","\uff43","\uff44","\uff45","\uff46","\uff47","\uff48","\uff49","\uff4a","\uff4b","\uff4c","\uff4d","\uff4e","\uff4f","\uff50","\uff51","\uff52","\uff53","\uff54","\uff55","\uff56","\uff57","\uff58","\uff59","\uff5a"],b=["\ud835\udc00","\ud835\udc01","\ud835\udc02","\ud835\udc03","\ud835\udc04","\ud835\udc05","\ud835\udc06","\ud835\udc07","\ud835\udc08","\ud835\udc09","\ud835\udc0a","\ud835\udc0b","\ud835\udc0c","\ud835\udc0d","\ud835\udc0e","\ud835\udc0f","\ud835\udc10","\ud835\udc11","\ud835\udc12","\ud835\udc13","\ud835\udc14","\ud835\udc15","\ud835\udc16","\ud835\udc17","\ud835\udc18","\ud835\udc19"],N=["\ud835\udc1a","\ud835\udc1b","\ud835\udc1c","\ud835\udc1d","\ud835\udc1e","\ud835\udc1f","\ud835\udc20","\ud835\udc21","\ud835\udc22","\ud835\udc23","\ud835\udc24","\ud835\udc25","\ud835\udc26","\ud835\udc27","\ud835\udc28","\ud835\udc29","\ud835\udc2a","\ud835\udc2b","\ud835\udc2c","\ud835\udc2d","\ud835\udc2e","\ud835\udc2f","\ud835\udc30","\ud835\udc31","\ud835\udc32","\ud835\udc33"],E=["\ud835\udc34","\ud835\udc35","\ud835\udc36","\ud835\udc37","\ud835\udc38","\ud835\udc39","\ud835\udc3a","\ud835\udc3b","\ud835\udc3c","\ud835\udc3d","\ud835\udc3e","\ud835\udc3f","\ud835\udc40","\ud835\udc41","\ud835\udc42","\ud835\udc43","\ud835\udc44","\ud835\udc45","\ud835\udc46","\ud835\udc47","\ud835\udc48","\ud835\udc49","\ud835\udc4a","\ud835\udc4b","\ud835\udc4c","\ud835\udc4d"],y=["\ud835\udc4e","\ud835\udc4f","\ud835\udc50","\ud835\udc51","\ud835\udc52","\ud835\udc53","\ud835\udc54","\u210e","\ud835\udc56","\ud835\udc57","\ud835\udc58","\ud835\udc59","\ud835\udc5a","\ud835\udc5b","\ud835\udc5c","\ud835\udc5d","\ud835\udc5e","\ud835\udc5f","\ud835\udc60","\ud835\udc61","\ud835\udc62","\ud835\udc63","\ud835\udc64","\ud835\udc65","\ud835\udc66","\ud835\udc67","\ud835\udea4","\ud835\udea5"],A=["\ud835\udc68","\ud835\udc69","\ud835\udc6a","\ud835\udc6b","\ud835\udc6c","\ud835\udc6d","\ud835\udc6e","\ud835\udc6f","\ud835\udc70","\ud835\udc71","\ud835\udc72","\ud835\udc73","\ud835\udc74","\ud835\udc75","\ud835\udc76","\ud835\udc77","\ud835\udc78","\ud835\udc79","\ud835\udc7a","\ud835\udc7b","\ud835\udc7c","\ud835\udc7d","\ud835\udc7e","\ud835\udc7f","\ud835\udc80","\ud835\udc81"],_=["\ud835\udc82","\ud835\udc83","\ud835\udc84","\ud835\udc85","\ud835\udc86","\ud835\udc87","\ud835\udc88","\ud835\udc89","\ud835\udc8a","\ud835\udc8b","\ud835\udc8c","\ud835\udc8d","\ud835\udc8e","\ud835\udc8f","\ud835\udc90","\ud835\udc91","\ud835\udc92","\ud835\udc93","\ud835\udc94","\ud835\udc95","\ud835\udc96","\ud835\udc97","\ud835\udc98","\ud835\udc99","\ud835\udc9a","\ud835\udc9b"],C=["\ud835\udc9c","\u212c","\ud835\udc9e","\ud835\udc9f","\u2130","\u2131","\ud835\udca2","\u210b","\u2110","\ud835\udca5","\ud835\udca6","\u2112","\u2133","\ud835\udca9","\ud835\udcaa","\ud835\udcab","\ud835\udcac","\u211b","\ud835\udcae","\ud835\udcaf","\ud835\udcb0","\ud835\udcb1","\ud835\udcb2","\ud835\udcb3","\ud835\udcb4","\ud835\udcb5","\u2118"],T=["\ud835\udcb6","\ud835\udcb7","\ud835\udcb8","\ud835\udcb9","\u212f","\ud835\udcbb","\u210a","\ud835\udcbd","\ud835\udcbe","\ud835\udcbf","\ud835\udcc0","\ud835\udcc1","\ud835\udcc2","\ud835\udcc3","\u2134","\ud835\udcc5","\ud835\udcc6","\ud835\udcc7","\ud835\udcc8","\ud835\udcc9","\ud835\udcca","\ud835\udccb","\ud835\udccc","\ud835\udccd","\ud835\udcce","\ud835\udccf","\u2113"],v=["\ud835\udcd0","\ud835\udcd1","\ud835\udcd2","\ud835\udcd3","\ud835\udcd4","\ud835\udcd5","\ud835\udcd6","\ud835\udcd7","\ud835\udcd8","\ud835\udcd9","\ud835\udcda","\ud835\udcdb","\ud835\udcdc","\ud835\udcdd","\ud835\udcde","\ud835\udcdf","\ud835\udce0","\ud835\udce1","\ud835\udce2","\ud835\udce3","\ud835\udce4","\ud835\udce5","\ud835\udce6","\ud835\udce7","\ud835\udce8","\ud835\udce9"],O=["\ud835\udcea","\ud835\udceb","\ud835\udcec","\ud835\udced","\ud835\udcee","\ud835\udcef","\ud835\udcf0","\ud835\udcf1","\ud835\udcf2","\ud835\udcf3","\ud835\udcf4","\ud835\udcf5","\ud835\udcf6","\ud835\udcf7","\ud835\udcf8","\ud835\udcf9","\ud835\udcfa","\ud835\udcfb","\ud835\udcfc","\ud835\udcfd","\ud835\udcfe","\ud835\udcff","\ud835\udd00","\ud835\udd01","\ud835\udd02","\ud835\udd03"],M=["\ud835\udd04","\ud835\udd05","\u212d","\ud835\udd07","\ud835\udd08","\ud835\udd09","\ud835\udd0a","\u210c","\u2111","\ud835\udd0d","\ud835\udd0e","\ud835\udd0f","\ud835\udd10","\ud835\udd11","\ud835\udd12","\ud835\udd13","\ud835\udd14","\u211c","\ud835\udd16","\ud835\udd17","\ud835\udd18","\ud835\udd19","\ud835\udd1a","\ud835\udd1b","\ud835\udd1c","\u2128"],I=["\ud835\udd1e","\ud835\udd1f","\ud835\udd20","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd22","\ud835\udd23","\ud835\udd24","\ud835\udd25","\ud835\udd26","\ud835\udd27","\ud835\udd28","\ud835\udd29","\ud835\udd2a","\ud835\udd2b","\ud835\udd2c","\ud835\udd2d","\ud835\udd2e","\ud835\udd2f","\ud835\udd30","\ud835\udd31","\ud835\udd32","\ud835\udd33","\ud835\udd34","\ud835\udd35","\ud835\udd36","\ud835\udd37"],L=["\ud835\udd38","\ud835\udd39","\u2102","\ud835\udd3b","\ud835\udd3c","\ud835\udd3d","\ud835\udd3e","\u210d","\ud835\udd40","\ud835\udd41","\ud835\udd42","\ud835\udd43","\ud835\udd44","\u2115","\ud835\udd46","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\ud835\udd4a","\ud835\udd4b","\ud835\udd4c","\ud835\udd4d","\ud835\udd4e","\ud835\udd4f","\ud835\udd50","\u2124"],R=["\ud835\udd52","\ud835\udd53","\ud835\udd54","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd56","\ud835\udd57","\ud835\udd58","\ud835\udd59","\ud835\udd5a","\ud835\udd5b","\ud835\udd5c","\ud835\udd5d","\ud835\udd5e","\ud835\udd5f","\ud835\udd60","\ud835\udd61","\ud835\udd62","\ud835\udd63","\ud835\udd64","\ud835\udd65","\ud835\udd66","\ud835\udd67","\ud835\udd68","\ud835\udd69","\ud835\udd6a","\ud835\udd6b"],x=["\ud835\udd6c","\ud835\udd6d","\ud835\udd6e","\ud835\udd6f","\ud835\udd70","\ud835\udd71","\ud835\udd72","\ud835\udd73","\ud835\udd74","\ud835\udd75","\ud835\udd76","\ud835\udd77","\ud835\udd78","\ud835\udd79","\ud835\udd7a","\ud835\udd7b","\ud835\udd7c","\ud835\udd7d","\ud835\udd7e","\ud835\udd7f","\ud835\udd80","\ud835\udd81","\ud835\udd82","\ud835\udd83","\ud835\udd84","\ud835\udd85"],P=["\ud835\udd86","\ud835\udd87","\ud835\udd88","\ud835\udd89","\ud835\udd8a","\ud835\udd8b","\ud835\udd8c","\ud835\udd8d","\ud835\udd8e","\ud835\udd8f","\ud835\udd90","\ud835\udd91","\ud835\udd92","\ud835\udd93","\ud835\udd94","\ud835\udd95","\ud835\udd96","\ud835\udd97","\ud835\udd98","\ud835\udd99","\ud835\udd9a","\ud835\udd9b","\ud835\udd9c","\ud835\udd9d","\ud835\udd9e","\ud835\udd9f"],F=["\ud835\udda0","\ud835\udda1","\ud835\udda2","\ud835\udda3","\ud835\udda4","\ud835\udda5","\ud835\udda6","\ud835\udda7","\ud835\udda8","\ud835\udda9","\ud835\uddaa","\ud835\uddab","\ud835\uddac","\ud835\uddad","\ud835\uddae","\ud835\uddaf","\ud835\uddb0","\ud835\uddb1","\ud835\uddb2","\ud835\uddb3","\ud835\uddb4","\ud835\uddb5","\ud835\uddb6","\ud835\uddb7","\ud835\uddb8","\ud835\uddb9"],D=["\ud835\uddba","\ud835\uddbb","\ud835\uddbc","\ud835\uddbd","\ud835\uddbe","\ud835\uddbf","\ud835\uddc0","\ud835\uddc1","\ud835\uddc2","\ud835\uddc3","\ud835\uddc4","\ud835\uddc5","\ud835\uddc6","\ud835\uddc7","\ud835\uddc8","\ud835\uddc9","\ud835\uddca","\ud835\uddcb","\ud835\uddcc","\ud835\uddcd","\ud835\uddce","\ud835\uddcf","\ud835\uddd0","\ud835\uddd1","\ud835\uddd2","\ud835\uddd3"],w=["\ud835\uddd4","\ud835\uddd5","\ud835\uddd6","\ud835\uddd7","\ud835\uddd8","\ud835\uddd9","\ud835\uddda","\ud835\udddb","\ud835\udddc","\ud835\udddd","\ud835\uddde","\ud835\udddf","\ud835\udde0","\ud835\udde1","\ud835\udde2","\ud835\udde3","\ud835\udde4","\ud835\udde5","\ud835\udde6","\ud835\udde7","\ud835\udde8","\ud835\udde9","\ud835\uddea","\ud835\uddeb","\ud835\uddec","\ud835\udded"],k=["\ud835\uddee","\ud835\uddef","\ud835\uddf0","\ud835\uddf1","\ud835\uddf2","\ud835\uddf3","\ud835\uddf4","\ud835\uddf5","\ud835\uddf6","\ud835\uddf7","\ud835\uddf8","\ud835\uddf9","\ud835\uddfa","\ud835\uddfb","\ud835\uddfc","\ud835\uddfd","\ud835\uddfe","\ud835\uddff","\ud835\ude00","\ud835\ude01","\ud835\ude02","\ud835\ude03","\ud835\ude04","\ud835\ude05","\ud835\ude06","\ud835\ude07"],U=["\ud835\ude08","\ud835\ude09","\ud835\ude0a","\ud835\ude0b","\ud835\ude0c","\ud835\ude0d","\ud835\ude0e","\ud835\ude0f","\ud835\ude10","\ud835\ude11","\ud835\ude12","\ud835\ude13","\ud835\ude14","\ud835\ude15","\ud835\ude16","\ud835\ude17","\ud835\ude18","\ud835\ude19","\ud835\ude1a","\ud835\ude1b","\ud835\ude1c","\ud835\ude1d","\ud835\ude1e","\ud835\ude1f","\ud835\ude20","\ud835\ude21"],B=["\ud835\ude22","\ud835\ude23","\ud835\ude24","\ud835\ude25","\ud835\ude26","\ud835\ude27","\ud835\ude28","\ud835\ude29","\ud835\ude2a","\ud835\ude2b","\ud835\ude2c","\ud835\ude2d","\ud835\ude2e","\ud835\ude2f","\ud835\ude30","\ud835\ude31","\ud835\ude32","\ud835\ude33","\ud835\ude34","\ud835\ude35","\ud835\ude36","\ud835\ude37","\ud835\ude38","\ud835\ude39","\ud835\ude3a","\ud835\ude3b"],j=["\ud835\ude3c","\ud835\ude3d","\ud835\ude3e","\ud835\ude3f","\ud835\ude40","\ud835\ude41","\ud835\ude42","\ud835\ude43","\ud835\ude44","\ud835\ude45","\ud835\ude46","\ud835\ude47","\ud835\ude48","\ud835\ude49","\ud835\ude4a","\ud835\ude4b","\ud835\ude4c","\ud835\ude4d","\ud835\ude4e","\ud835\ude4f","\ud835\ude50","\ud835\ude51","\ud835\ude52","\ud835\ude53","\ud835\ude54","\ud835\ude55"],G=["\ud835\ude56","\ud835\ude57","\ud835\ude58","\ud835\ude59","\ud835\ude5a","\ud835\ude5b","\ud835\ude5c","\ud835\ude5d","\ud835\ude5e","\ud835\ude5f","\ud835\ude60","\ud835\ude61","\ud835\ude62","\ud835\ude63","\ud835\ude64","\ud835\ude65","\ud835\ude66","\ud835\ude67","\ud835\ude68","\ud835\ude69","\ud835\ude6a","\ud835\ude6b","\ud835\ude6c","\ud835\ude6d","\ud835\ude6e","\ud835\ude6f"],V=["\ud835\ude70","\ud835\ude71","\ud835\ude72","\ud835\ude73","\ud835\ude74","\ud835\ude75","\ud835\ude76","\ud835\ude77","\ud835\ude78","\ud835\ude79","\ud835\ude7a","\ud835\ude7b","\ud835\ude7c","\ud835\ude7d","\ud835\ude7e","\ud835\ude7f","\ud835\ude80","\ud835\ude81","\ud835\ude82","\ud835\ude83","\ud835\ude84","\ud835\ude85","\ud835\ude86","\ud835\ude87","\ud835\ude88","\ud835\ude89"],$=["\ud835\ude8a","\ud835\ude8b","\ud835\ude8c","\ud835\ude8d","\ud835\ude8e","\ud835\ude8f","\ud835\ude90","\ud835\ude91","\ud835\ude92","\ud835\ude93","\ud835\ude94","\ud835\ude95","\ud835\ude96","\ud835\ude97","\ud835\ude98","\ud835\ude99","\ud835\ude9a","\ud835\ude9b","\ud835\ude9c","\ud835\ude9d","\ud835\ude9e","\ud835\ude9f","\ud835\udea0","\ud835\udea1","\ud835\udea2","\ud835\udea3"],H=["\u2145","\u2146","\u2147","\u2148","\u2149"],W=["\u0391","\u0392","\u0393","\u0394","\u0395","\u0396","\u0397","\u0398","\u0399","\u039a","\u039b","\u039c","\u039d","\u039e","\u039f","\u03a0","\u03a1","\u03a3","\u03a4","\u03a5","\u03a6","\u03a7","\u03a8","\u03a9"],X=["\u03b1","\u03b2","\u03b3","\u03b4","\u03b5","\u03b6","\u03b7","\u03b8","\u03b9","\u03ba","\u03bb","\u03bc","\u03bd","\u03be","\u03bf","\u03c0","\u03c1","\u03c2","\u03c3","\u03c4","\u03c5","\u03c6","\u03c7","\u03c8","\u03c9"],q=["\ud835\udea8","\ud835\udea9","\ud835\udeaa","\ud835\udeab","\ud835\udeac","\ud835\udead","\ud835\udeae","\ud835\udeaf","\ud835\udeb0","\ud835\udeb1","\ud835\udeb2","\ud835\udeb3","\ud835\udeb4","\ud835\udeb5","\ud835\udeb6","\ud835\udeb7","\ud835\udeb8","\ud835\udeba","\ud835\udebb","\ud835\udebc","\ud835\udebd","\ud835\udebe","\ud835\udebf","\ud835\udec0"],Y=["\ud835\udec2","\ud835\udec3","\ud835\udec4","\ud835\udec5","\ud835\udec6","\ud835\udec7","\ud835\udec8","\ud835\udec9","\ud835\udeca","\ud835\udecb","\ud835\udecc","\ud835\udecd","\ud835\udece","\ud835\udecf","\ud835\uded0","\ud835\uded1","\ud835\uded2","\ud835\uded3","\ud835\uded4","\ud835\uded5","\ud835\uded6","\ud835\uded7","\ud835\uded8","\ud835\uded9","\ud835\udeda"],K=["\ud835\udee2","\ud835\udee3","\ud835\udee4","\ud835\udee5","\ud835\udee6","\ud835\udee7","\ud835\udee8","\ud835\udee9","\ud835\udeea","\ud835\udeeb","\ud835\udeec","\ud835\udeed","\ud835\udeee","\ud835\udeef","\ud835\udef0","\ud835\udef1","\ud835\udef2","\ud835\udef4","\ud835\udef5","\ud835\udef6","\ud835\udef7","\ud835\udef8","\ud835\udef9","\ud835\udefa"],z=["\ud835\udefc","\ud835\udefd","\ud835\udefe","\ud835\udeff","\ud835\udf00","\ud835\udf01","\ud835\udf02","\ud835\udf03","\ud835\udf04","\ud835\udf05","\ud835\udf06","\ud835\udf07","\ud835\udf08","\ud835\udf09","\ud835\udf0a","\ud835\udf0b","\ud835\udf0c","\ud835\udf0d","\ud835\udf0e","\ud835\udf0f","\ud835\udf10","\ud835\udf11","\ud835\udf12","\ud835\udf13","\ud835\udf14"],J=["\ud835\udf1c","\ud835\udf1d","\ud835\udf1e","\ud835\udf1f","\ud835\udf20","\ud835\udf21","\ud835\udf22","\ud835\udf23","\ud835\udf24","\ud835\udf25","\ud835\udf26","\ud835\udf27","\ud835\udf28","\ud835\udf29","\ud835\udf2a","\ud835\udf2b","\ud835\udf2c","\ud835\udf2e","\ud835\udf2f","\ud835\udf30","\ud835\udf31","\ud835\udf32","\ud835\udf33","\ud835\udf34"],Q=["\ud835\udf36","\ud835\udf37","\ud835\udf38","\ud835\udf39","\ud835\udf3a","\ud835\udf3b","\ud835\udf3c","\ud835\udf3d","\ud835\udf3e","\ud835\udf3f","\ud835\udf40","\ud835\udf41","\ud835\udf42","\ud835\udf43","\ud835\udf44","\ud835\udf45","\ud835\udf46","\ud835\udf47","\ud835\udf48","\ud835\udf49","\ud835\udf4a","\ud835\udf4b","\ud835\udf4c","\ud835\udf4d","\ud835\udf4e"],Z=["\ud835\udf56","\ud835\udf57","\ud835\udf58","\ud835\udf59","\ud835\udf5a","\ud835\udf5b","\ud835\udf5c","\ud835\udf5d","\ud835\udf5e","\ud835\udf5f","\ud835\udf60","\ud835\udf61","\ud835\udf62","\ud835\udf63","\ud835\udf64","\ud835\udf65","\ud835\udf66","\ud835\udf68","\ud835\udf69","\ud835\udf6a","\ud835\udf6b","\ud835\udf6c","\ud835\udf6d","\ud835\udf6e"],ee=["\ud835\udf70","\ud835\udf71","\ud835\udf72","\ud835\udf73","\ud835\udf74","\ud835\udf75","\ud835\udf76","\ud835\udf77","\ud835\udf78","\ud835\udf79","\ud835\udf7a","\ud835\udf7b","\ud835\udf7c","\ud835\udf7d","\ud835\udf7e","\ud835\udf7f","\ud835\udf80","\ud835\udf81","\ud835\udf82","\ud835\udf83","\ud835\udf84","\ud835\udf85","\ud835\udf86","\ud835\udf87","\ud835\udf88"],te=["\ud835\udf90","\ud835\udf91","\ud835\udf92","\ud835\udf93","\ud835\udf94","\ud835\udf95","\ud835\udf96","\ud835\udf97","\ud835\udf98","\ud835\udf99","\ud835\udf9a","\ud835\udf9b","\ud835\udf9c","\ud835\udf9d","\ud835\udf9e","\ud835\udf9f","\ud835\udfa0","\ud835\udfa2","\ud835\udfa3","\ud835\udfa4","\ud835\udfa5","\ud835\udfa6","\ud835\udfa7","\ud835\udfa8"],ne=["\ud835\udfaa","\ud835\udfab","\ud835\udfac","\ud835\udfad","\ud835\udfae","\ud835\udfaf","\ud835\udfb0","\ud835\udfb1","\ud835\udfb2","\ud835\udfb3","\ud835\udfb4","\ud835\udfb5","\ud835\udfb6","\ud835\udfb7","\ud835\udfb8","\ud835\udfb9","\ud835\udfba","\ud835\udfbb","\ud835\udfbc","\ud835\udfbd","\ud835\udfbe","\ud835\udfbf","\ud835\udfc0","\ud835\udfc1","\ud835\udfc2"],re=["\u213c","\u213d","\u213e","\u213f"],ie=["\u03d0","\u03d1","\u03d5","\u03d6","\u03d7","\u03f0","\u03f1","\u03f5","\u03f6","\u03f4"],oe=["\ud835\udedc","\ud835\udedd","\ud835\udede","\ud835\udedf","\ud835\udee0","\ud835\udee1"],se=["\ud835\udf16","\ud835\udf17","\ud835\udf18","\ud835\udf19","\ud835\udf1a","\ud835\udf1b"],ae=["\ud835\udf8a","\ud835\udf8b","\ud835\udf8c","\ud835\udf8d","\ud835\udf8e","\ud835\udf8f"],ce=["\u2135","\u2136","\u2137","\u2138"],le=f.concat(m,g,S,b,N,E,A,_,y,C,T,v,O,M,I,L,R,x,P,F,D,w,k,U,B,j,G,V,$,H,W,X,q,Y,K,z,J,Q,Z,ee,re,ie,te,ne,oe,se,ae,ce);t.allLettersRegExp=new RegExp(le.join("|"));const ue=["+","\xb1","\u2213","\u2214","\u2227","\u2228","\u2229","\u222a","\u228c","\u228d","\u228e","\u2293","\u2294","\u229d","\u229e","\u22a4","\u22a5","\u22ba","\u22bb","\u22bc","\u22c4","\u22ce","\u22cf","\u22d2","\u22d3","\u2a5e","\u2295","\u22d4"],de=String.fromCodePoint(8292);ue.push(de);const he=["\u2020","\u2021","\u2210","\u2217","\u2218","\u2219","\u2240","\u229a","\u229b","\u22a0","\u22a1","\u22c5","\u22c6","\u22c7","\u22c8","\u22c9","\u22ca","\u22cb","\u22cc","\u25cb","\xb7","*","\u2297","\u2299"],pe=String.fromCodePoint(8290);he.push(pe);const fe=String.fromCodePoint(8289),me=["\xbc","\xbd","\xbe","\u2150","\u2151","\u2152","\u2153","\u2154","\u2155","\u2156","\u2157","\u2158","\u2159","\u215a","\u215b","\u215c","\u215d","\u215e","\u215f","\u2189"],ge=["\xb2","\xb3","\xb9","\u2070","\u2074","\u2075","\u2076","\u2077","\u2078","\u2079"].concat(["\u2080","\u2081","\u2082","\u2083","\u2084","\u2085","\u2086","\u2087","\u2088","\u2089"],["\u2460","\u2461","\u2462","\u2463","\u2464","\u2465","\u2466","\u2467","\u2468","\u2469","\u246a","\u246b","\u246c","\u246d","\u246e","\u246f","\u2470","\u2471","\u2472","\u2473","\u24ea","\u24eb","\u24ec","\u24ed","\u24ee","\u24ef","\u24f0","\u24f1","\u24f2","\u24f3","\u24f4","\u24f5","\u24f6","\u24f7","\u24f8","\u24f9","\u24fa","\u24fb","\u24fc","\u24fd","\u24fe","\u24ff","\u2776","\u2777","\u2778","\u2779","\u277a","\u277b","\u277c","\u277d","\u277e","\u277f","\u2780","\u2781","\u2782","\u2783","\u2784","\u2785","\u2786","\u2787","\u2788","\u2789","\u278a","\u278b","\u278c","\u278d","\u278e","\u278f","\u2790","\u2791","\u2792","\u2793","\u3248","\u3249","\u324a","\u324b","\u324c","\u324d","\u324e","\u324f","\u3251","\u3252","\u3253","\u3254","\u3255","\u3256","\u3257","\u3258","\u3259","\u325a","\u325b","\u325c","\u325d","\u325e","\u325f","\u32b1","\u32b2","\u32b3","\u32b4","\u32b5","\u32b6","\u32b7","\u32b8","\u32b9","\u32ba","\u32bb","\u32bc","\u32bd","\u32be","\u32bf"],["\u2474","\u2475","\u2476","\u2477","\u2478","\u2479","\u247a","\u247b","\u247c","\u247d","\u247e","\u247f","\u2480","\u2481","\u2482","\u2483","\u2484","\u2485","\u2486","\u2487"],["\u2488","\u2489","\u248a","\u248b","\u248c","\u248d","\u248e","\u248f","\u2490","\u2491","\u2492","\u2493","\u2494","\u2495","\u2496","\u2497","\u2498","\u2499","\u249a","\u249b","\ud83c\udd00","\ud83c\udd01","\ud83c\udd02","\ud83c\udd03","\ud83c\udd04","\ud83c\udd05","\ud83c\udd06","\ud83c\udd07","\ud83c\udd08","\ud83c\udd09","\ud83c\udd0a"]),Se=["cos","cot","csc","sec","sin","tan","arccos","arccot","arccsc","arcsec","arcsin","arctan","arc cos","arc cot","arc csc","arc sec","arc sin","arc tan"].concat(["cosh","coth","csch","sech","sinh","tanh","arcosh","arcoth","arcsch","arsech","arsinh","artanh","arccosh","arccoth","arccsch","arcsech","arcsinh","arctanh"],["deg","det","dim","hom","ker","Tr","tr"],["log","ln","lg","exp","expt","gcd","gcd","arg","im","re","Pr"]),be=[{set:["!",'"',"#","%","&",";","?","@","\\","\xa1","\xa7","\xb6","\xbf","\u2017","\u2020","\u2021","\u2022","\u2023","\u2024","\u2025","\u2027","\u2030","\u2031","\u2038","\u203b","\u203c","\u203d","\u203e","\u2041","\u2042","\u2043","\u2047","\u2048","\u2049","\u204b","\u204c","\u204d","\u204e","\u204f","\u2050","\u2051","\u2053","\u2055","\u2056","\u2058","\u2059","\u205a","\u205b","\u205c","\u205d","\u205e","\ufe10","\ufe14","\ufe15","\ufe16","\ufe30","\ufe45","\ufe46","\ufe49","\ufe4a","\ufe4b","\ufe4c","\ufe54","\ufe56","\ufe57","\ufe5f","\ufe60","\ufe61","\ufe68","\ufe6a","\ufe6b","\uff01","\uff02","\uff03","\uff05","\uff06","\uff07","\uff0a","\uff0f","\uff1b","\uff1f","\uff20","\uff3c"],type:"punctuation",role:"unknown"},{set:["\ufe13",":","\uff1a","\ufe55"],type:"punctuation",role:"colon"},{set:r,type:"punctuation",role:"comma"},{set:["\u2026","\u22ee","\u22ef","\u22f0","\u22f1","\ufe19"],type:"punctuation",role:"ellipsis"},{set:[".","\ufe52","\uff0e"],type:"punctuation",role:"fullstop"},{set:i,type:"operator",role:"dash"},{set:o,type:"operator",role:"tilde"},{set:["'","\u2032","\u2033","\u2034","\u2035","\u2036","\u2037","\u2057","\u02b9","\u02ba"],type:"punctuation",role:"prime"},{set:["\xb0"],type:"punctuation",role:"degree"},{set:c,type:"fence",role:"open"},{set:l,type:"fence",role:"close"},{set:u,type:"fence",role:"top"},{set:d,type:"fence",role:"bottom"},{set:h,type:"fence",role:"neutral"},{set:p,type:"fence",role:"metric"},{set:m,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:f,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:S,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:g,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:N,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold"},{set:b,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold"},{set:y,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"italic"},{set:E,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"italic"},{set:_,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:A,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:T,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"script"},{set:C,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"script"},{set:O,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-script"},{set:v,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-script"},{set:I,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"fraktur"},{set:M,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"fraktur"},{set:R,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:L,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:P,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-fraktur"},{set:x,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-fraktur"},{set:D,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif"},{set:F,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif"},{set:k,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:w,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:B,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-italic"},{set:U,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-italic"},{set:G,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:j,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:$,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"monospace"},{set:V,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"monospace"},{set:H,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck-italic"},{set:X,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:W,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:Y,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:q,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:z,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:K,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:Q,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:J,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:ee,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:Z,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:te,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:ne,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:re,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:ie,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:oe,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:se,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:ae,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:ce,type:"identifier",role:"otherletter",font:"normal"},{set:["0","1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"normal"},{set:["\uff10","\uff11","\uff12","\uff13","\uff14","\uff15","\uff16","\uff17","\uff18","\uff19"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"normal"},{set:["\ud835\udfce","\ud835\udfcf","\ud835\udfd0","\ud835\udfd1","\ud835\udfd2","\ud835\udfd3","\ud835\udfd4","\ud835\udfd5","\ud835\udfd6","\ud835\udfd7"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"bold"},{set:["\ud835\udfd8","\ud835\udfd9","\ud835\udfda","\ud835\udfdb","\ud835\udfdc","\ud835\udfdd","\ud835\udfde","\ud835\udfdf","\ud835\udfe0","\ud835\udfe1"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"double-struck"},{set:["\ud835\udfe2","\ud835\udfe3","\ud835\udfe4","\ud835\udfe5","\ud835\udfe6","\ud835\udfe7","\ud835\udfe8","\ud835\udfe9","\ud835\udfea","\ud835\udfeb"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"sans-serif"},{set:["\ud835\udfec","\ud835\udfed","\ud835\udfee","\ud835\udfef","\ud835\udff0","\ud835\udff1","\ud835\udff2","\ud835\udff3","\ud835\udff4","\ud835\udff5"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:["\ud835\udff6","\ud835\udff7","\ud835\udff8","\ud835\udff9","\ud835\udffa","\ud835\udffb","\ud835\udffc","\ud835\udffd","\ud835\udffe","\ud835\udfff"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"monospace"},{set:me,type:"number",role:"float"},{set:ge,type:"number",role:"othernumber"},{set:ue,type:"operator",role:"addition"},{set:he,type:"operator",role:"multiplication"},{set:["\xaf","-","\u2052","\u207b","\u208b","\u2212","\u2216","\u2238","\u2242","\u2296","\u229f","\u2796","\u2a29","\u2a2a","\u2a2b","\u2a2c","\u2a3a","\u2a41","\ufe63","\uff0d","\u2010","\u2011"],type:"operator",role:"subtraction"},{set:["/","\xf7","\u2044","\u2215","\u2298","\u27cc","\u29bc","\u2a38"],type:"operator",role:"division"},{set:["\u2200","\u2203","\u2206","\u2207","\u2202","\u2201","\u2204"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator"},{set:["\ud835\udec1","\ud835\udedb","\ud835\udfca","\ud835\udfcb"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"bold"},{set:["\ud835\udefb","\ud835\udf15"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"italic"},{set:["\ud835\udf6f","\ud835\udf89"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:["=","~","\u207c","\u208c","\u223c","\u223d","\u2243","\u2245","\u2248","\u224a","\u224b","\u224c","\u224d","\u224e","\u2251","\u2252","\u2253","\u2254","\u2255","\u2256","\u2257","\u2258","\u2259","\u225a","\u225b","\u225c","\u225d","\u225e","\u225f","\u2261","\u2263","\u29e4","\u2a66","\u2a6e","\u2a6f","\u2a70","\u2a71","\u2a72","\u2a73","\u2a74","\u2a75","\u2a76","\u2a77","\u2a78","\u22d5","\u2a6d","\u2a6a","\u2a6b","\u2a6c","\ufe66","\uff1d","\u2a6c","\u229c","\u2237"],type:"relation",role:"equality"},{set:["<",">","\u2241","\u2242","\u2244","\u2246","\u2247","\u2249","\u224f","\u2250","\u2260","\u2262","\u2264","\u2265","\u2266","\u2267","\u2268","\u2269","\u226a","\u226b","\u226c","\u226d","\u226e","\u226f","\u2270","\u2271","\u2272","\u2273","\u2274","\u2275","\u2276","\u2277","\u2278","\u2279","\u227a","\u227b","\u227c","\u227d","\u227e","\u227f","\u2280","\u2281","\u22d6","\u22d7","\u22d8","\u22d9","\u22da","\u22db","\u22dc","\u22dd","\u22de","\u22df","\u22e0","\u22e1","\u22e6","\u22e7","\u22e8","\u22e9","\u2a79","\u2a7a","\u2a7b","\u2a7c","\u2a7d","\u2a7e","\u2a7f","\u2a80","\u2a81","\u2a82","\u2a83","\u2a84","\u2a85","\u2a86","\u2a87","\u2a88","\u2a89","\u2a8a","\u2a8b","\u2a8c","\u2a8d","\u2a8e","\u2a8f","\u2a90","\u2a91","\u2a92","\u2a93","\u2a94","\u2a95","\u2a96","\u2a97","\u2a98","\u2a99","\u2a9a","\u2a9b","\u2a9c","\u2a9d","\u2a9e","\u2a9f","\u2aa0","\u2aa1","\u2aa2","\u2aa3","\u2aa4","\u2aa5","\u2aa6","\u2aa7","\u2aa8","\u2aa9","\u2aaa","\u2aab","\u2aac","\u2aad","\u2aae","\u2aaf","\u2ab0","\u2ab1","\u2ab2","\u2ab3","\u2ab4","\u2ab5","\u2ab6","\u2ab7","\u2ab8","\u2ab9","\u2aba","\u2abb","\u2abc","\u2af7","\u2af8","\u2af9","\u2afa","\u29c0","\u29c1","\ufe64","\ufe65","\uff1c","\uff1e"],type:"relation",role:"inequality"},{set:["\u22e2","\u22e3","\u22e4","\u22e5","\u2282","\u2283","\u2284","\u2285","\u2286","\u2287","\u2288","\u2289","\u228a","\u228b","\u228f","\u2290","\u2291","\u2292","\u2abd","\u2abe","\u2abf","\u2ac0","\u2ac1","\u2ac2","\u2ac3","\u2ac4","\u2ac5","\u2ac6","\u2ac7","\u2ac8","\u2ac9","\u2aca","\u2acb","\u2acc","\u2acd","\u2ace","\u2acf","\u2ad0","\u2ad1","\u2ad2","\u2ad3","\u2ad4","\u2ad5","\u2ad6","\u2ad7","\u2ad8","\u22d0","\u22d1","\u22ea","\u22eb","\u22ec","\u22ed","\u22b2","\u22b3","\u22b4","\u22b5"],type:"relation",role:"set"},{set:["\u22a2","\u22a3","\u22a6","\u22a7","\u22a8","\u22a9","\u22aa","\u22ab","\u22ac","\u22ad","\u22ae","\u22af","\u2ade","\u2adf","\u2ae0","\u2ae1","\u2ae2","\u2ae3","\u2ae4","\u2ae5","\u2ae6","\u2ae7","\u2ae8","\u2ae9","\u2aea","\u2aeb","\u2aec","\u2aed"],type:"relation",role:"unknown"},{set:["\u2190","\u2191","\u2192","\u2193","\u2194","\u2195","\u2196","\u2197","\u2198","\u2199","\u219a","\u219b","\u219c","\u219d","\u219e","\u219f","\u21a0","\u21a1","\u21a2","\u21a3","\u21a4","\u21a5","\u21a6","\u21a7","\u21a8","\u21a9","\u21aa","\u21ab","\u21ac","\u21ad","\u21ae","\u21af","\u21b0","\u21b1","\u21b2","\u21b3","\u21b4","\u21b5","\u21b6","\u21b7","\u21b8","\u21b9","\u21ba","\u21bb","\u21c4","\u21c5","\u21c6","\u21c7","\u21c8","\u21c9","\u21ca","\u21cd","\u21ce","\u21cf","\u21d0","\u21d1","\u21d2","\u21d3","\u21d4","\u21d5","\u21d6","\u21d7","\u21d8","\u21d9","\u21da","\u21db","\u21dc","\u21dd","\u21de","\u21df","\u21e0","\u21e1","\u21e2","\u21e3","\u21e4","\u21e5","\u21e6","\u21e7","\u21e8","\u21e9","\u21ea","\u21eb","\u21ec","\u21ed","\u21ee","\u21ef","\u21f0","\u21f1","\u21f2","\u21f3","\u21f4","\u21f5","\u21f6","\u21f7","\u21f8","\u21f9","\u21fa","\u21fb","\u21fc","\u21fd","\u21fe","\u21ff","\u2301","\u2303","\u2304","\u2324","\u238b","\u2794","\u2798","\u2799","\u279a","\u279b","\u279c","\u279d","\u279e","\u279f","\u27a0","\u27a1","\u27a2","\u27a3","\u27a4","\u27a5","\u27a6","\u27a7","\u27a8","\u27a9","\u27aa","\u27ab","\u27ac","\u27ad","\u27ae","\u27af","\u27b1","\u27b2","\u27b3","\u27b4","\u27b5","\u27b6","\u27b7","\u27b8","\u27b9","\u27ba","\u27bb","\u27bc","\u27bd","\u27be","\u27f0","\u27f1","\u27f2","\u27f3","\u27f4","\u27f5","\u27f6","\u27f7","\u27f8","\u27f9","\u27fa","\u27fb","\u27fc","\u27fd","\u27fe","\u27ff","\u2900","\u2901","\u2902","\u2903","\u2904","\u2905","\u2906","\u2907","\u2908","\u2909","\u290a","\u290b","\u290c","\u290d","\u290e","\u290f","\u2910","\u2911","\u2912","\u2913","\u2914","\u2915","\u2916","\u2917","\u2918","\u2919","\u291a","\u291b","\u291c","\u291d","\u291e","\u291f","\u2920","\u2921","\u2922","\u2923","\u2924","\u2925","\u2926","\u2927","\u2928","\u2929","\u292a","\u292d","\u292e","\u292f","\u2930","\u2931","\u2932","\u2933","\u2934","\u2935","\u2936","\u2937","\u2938","\u2939","\u293a","\u293b","\u293c","\u293d","\u293e","\u293f","\u2940","\u2941","\u2942","\u2943","\u2944","\u2945","\u2946","\u2947","\u2948","\u2949","\u2970","\u2971","\u2972","\u2973","\u2974","\u2975","\u2976","\u2977","\u2978","\u2979","\u297a","\u297b","\u29b3","\u29b4","\u29bd","\u29ea","\u29ec","\u29ed","\u2a17","\u2b00","\u2b01","\u2b02","\u2b03","\u2b04","\u2b05","\u2b06","\u2b07","\u2b08","\u2b09","\u2b0a","\u2b0b","\u2b0c","\u2b0d","\u2b0e","\u2b0f","\u2b10","\u2b11","\u2b30","\u2b31","\u2b32","\u2b33","\u2b34","\u2b35","\u2b36","\u2b37","\u2b38","\u2b39","\u2b3a","\u2b3b","\u2b3c","\u2b3d","\u2b3e","\u2b3f","\u2b40","\u2b41","\u2b42","\u2b43","\u2b44","\u2b45","\u2b46","\u2b47","\u2b48","\u2b49","\u2b4a","\u2b4b","\u2b4c","\uffe9","\uffea","\uffeb","\uffec","\u21bc","\u21bd","\u21be","\u21bf","\u21c0","\u21c1","\u21c2","\u21c3","\u21cb","\u21cc","\u294a","\u294b","\u294c","\u294d","\u294e","\u294f","\u2950","\u2951","\u2952","\u2953","\u2954","\u2955","\u2956","\u2957","\u2958","\u2959","\u295a","\u295b","\u295c","\u295d","\u295e","\u295f","\u2960","\u2961","\u2962","\u2963","\u2964","\u2965","\u2966","\u2967","\u2968","\u2969","\u296a","\u296b","\u296c","\u296d","\u296e","\u296f","\u297c","\u297d","\u297e","\u297f"],type:"relation",role:"arrow"},{set:["\u2208","\u220a","\u22f2","\u22f3","\u22f4","\u22f5","\u22f6","\u22f7","\u22f8","\u22f9","\u22ff"],type:"operator",role:"element"},{set:["\u2209"],type:"operator",role:"nonelement"},{set:["\u220b","\u220d","\u22fa","\u22fb","\u22fc","\u22fd","\u22fe"],type:"operator",role:"reelement"},{set:["\u220c"],type:"operator",role:"renonelement"},{set:["\u2140","\u220f","\u2210","\u2211","\u22c0","\u22c1","\u22c2","\u22c3","\u2a00","\u2a01","\u2a02","\u2a03","\u2a04","\u2a05","\u2a06","\u2a07","\u2a08","\u2a09","\u2a0a","\u2a0b","\u2afc","\u2aff"],type:"largeop",role:"sum"},{set:["\u222b","\u222c","\u222d","\u222e","\u222f","\u2230","\u2231","\u2232","\u2233","\u2a0c","\u2a0d","\u2a0e","\u2a0f","\u2a10","\u2a11","\u2a12","\u2a13","\u2a14","\u2a15","\u2a16","\u2a17","\u2a18","\u2a19","\u2a1a","\u2a1b","\u2a1c"],type:"largeop",role:"integral"},{set:["\u221f","\u2220","\u2221","\u2222","\u22be","\u22bf","\u25b3","\u25b7","\u25bd","\u25c1"],type:"operator",role:"geometry"},{set:["inf","lim","liminf","limsup","max","min","sup","injlim","projlim","inj lim","proj lim"],type:"function",role:"limit function"},{set:Se,type:"function",role:"prefix function"},{set:["mod","rem"],type:"operator",role:"prefix function"}],Ne=function(){const e={};for(let t,n=0;t=be[n];n++)t.set.forEach((function(n){e[n]={role:t.role||"unknown",type:t.type||"unknown",font:t.font||"unknown"}}));return e}();t.equal=function(e,t){return e.type===t.type&&e.role===t.role&&e.font===t.font},t.lookupType=function(e){var t;return(null===(t=Ne[e])||void 0===t?void 0:t.type)||"unknown"},t.lookupRole=function(e){var t;return(null===(t=Ne[e])||void 0===t?void 0:t.role)||"unknown"},t.lookupMeaning=function(e){return Ne[e]||{role:"unknown",type:"unknown",font:"unknown"}},t.invisibleTimes=function(){return pe},t.invisiblePlus=function(){return de},t.invisibleComma=function(){return n},t.functionApplication=function(){return fe},t.isMatchingFence=function(e,t){return-1!==h.indexOf(e)||-1!==p.indexOf(e)?e===t:s[e]===t||a[e]===t},t.isEmbellishedType=function(e){return"operator"===e||"relation"===e||"fence"===e||"punctuation"===e};const Ee=new Map;function ye(e,t){return`${e} ${t}`}function Ae(e,t,n=""){for(const r of t)Ee.set(ye(e,r),n||e)}Ae("d",["d","\u2146","\uff44","\ud835\udc1d","\ud835\udc51","\ud835\udcb9","\ud835\udced","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd89","\ud835\uddbd","\ud835\uddf1","\ud835\ude25","\ud835\ude8d"]),Ae("bar",i),Ae("tilde",o),t.lookupSecondary=function(e,t){return Ee.get(ye(e,t))}},7405:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMeaningCollator=t.SemanticNodeCollator=t.SemanticDefault=void 0;const r=n(4020),i=n(178);class o{constructor(){this.map={}}static key(e,t){return t?e+":"+t:e}add(e,t){this.map[o.key(e,t.font)]=t}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e.meaning())}retrieve(e,t){return this.map[o.key(e,t)]}retrieveNode(e){return this.retrieve(e.textContent,e.font)}size(){return Object.keys(this.map).length}}t.SemanticDefault=o;class s{constructor(){this.map={}}add(e,t){const n=this.map[e];n?n.push(t):this.map[e]=[t]}retrieve(e,t){return this.map[o.key(e,t)]}retrieveNode(e){return this.retrieve(e.textContent,e.font)}copy(){const e=this.copyCollator();for(const t in this.map)e.map[t]=this.map[t];return e}minimize(){for(const e in this.map)1===this.map[e].length&&delete this.map[e]}minimalCollator(){const e=this.copy();for(const t in e.map)1===e.map[t].length&&delete e.map[t];return e}isMultiValued(){for(const e in this.map)if(this.map[e].length>1)return!0;return!1}isEmpty(){return!Object.keys(this.map).length}}class a extends s{copyCollator(){return new a}add(e,t){const n=o.key(e,t.font);super.add(n,t)}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e)}toString(){const e=[];for(const t in this.map){const n=Array(t.length+3).join(" "),r=this.map[t],i=[];for(let e,t=0;e=r[t];t++)i.push(e.toString());e.push(t+": "+i.join("\n"+n))}return e.join("\n")}collateMeaning(){const e=new c;for(const t in this.map)e.map[t]=this.map[t].map((function(e){return e.meaning()}));return e}}t.SemanticNodeCollator=a;class c extends s{copyCollator(){return new c}add(e,t){const n=this.retrieve(e,t.font);if(!n||!n.find((function(e){return r.equal(e,t)}))){const n=o.key(e,t.font);super.add(n,t)}}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e.meaning())}toString(){const e=[];for(const t in this.map){const n=Array(t.length+3).join(" "),r=this.map[t],i=[];for(let e,t=0;e=r[t];t++)i.push("{type: "+e.type+", role: "+e.role+", font: "+e.font+"}");e.push(t+": "+i.join("\n"+n))}return e.join("\n")}reduce(){for(const e in this.map)1!==this.map[e].length&&(this.map[e]=(0,i.reduce)(this.map[e]))}default(){const e=new o;for(const t in this.map)1===this.map[t].length&&(e.map[t]=this.map[t][0]);return e}newDefault(){const e=this.default();this.reduce();const t=this.default();return e.size()!==t.size()?t:null}}t.SemanticMeaningCollator=c},5958:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMultiHeuristic=t.SemanticTreeHeuristic=t.SemanticAbstractHeuristic=void 0;class n{constructor(e,t,n=(e=>!1)){this.name=e,this.apply=t,this.applicable=n}}t.SemanticAbstractHeuristic=n;t.SemanticTreeHeuristic=class extends n{};t.SemanticMultiHeuristic=class extends n{}},2721:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.lookup=t.run=t.add=t.blacklist=t.flags=t.updateFactory=t.factory=void 0,t.factory=null,t.updateFactory=function(e){t.factory=e};const n=new Map;function r(e){return n.get(e)}t.flags={combine_juxtaposition:!0,convert_juxtaposition:!0,multioperator:!0},t.blacklist={},t.add=function(e){const r=e.name;n.set(r,e),t.flags[r]||(t.flags[r]=!1)},t.run=function(e,n,i){const o=r(e);return o&&!t.blacklist[e]&&(t.flags[e]||o.applicable(n))?o.apply(n):i?i(n):n},t.lookup=r},7103:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1984),i=n(4886),o=n(4020),s=n(2721),a=n(5958),c=n(6161),l=n(7793),u=n(8901);function d(e,t,n){let r=null;if(!e.length)return r;const i=n[n.length-1],o=i&&i.length,s=t&&t.length,a=l.default.getInstance();if(o&&s){if("infixop"===t[0].type&&"implicit"===t[0].role)return r=e.pop(),i.push(a.postfixNode_(i.pop(),e)),r;r=e.shift();const n=a.prefixNode_(t.shift(),e);return t.unshift(n),r}return o?(i.push(a.postfixNode_(i.pop(),e)),r):(s&&t.unshift(a.prefixNode_(t.shift(),e)),r)}function h(e,t,n){if(!t.length)return e;const i=e.pop(),o=t.shift(),a=n.shift();if(c.isImplicitOp(o)){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 2");const s=(i?[i,o]:[o]).concat(a);return h(e.concat(s),t,n)}if(!i)return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 3"),h([o].concat(a),t,n);const l=a.shift();if(!l){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 9");const a=s.factory.makeBranchNode("infixop",[i,t.shift()],[o],o.textContent);return a.role="implicit",s.run("combine_juxtaposition",a),t.unshift(a),h(e,t,n)}if(c.isOperator(i)||c.isOperator(l))return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 4"),h(e.concat([i,o,l]).concat(a),t,n);let u=null;return c.isImplicitOp(i)&&c.isImplicitOp(l)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 5"),i.contentNodes.push(o),i.contentNodes=i.contentNodes.concat(l.contentNodes),i.childNodes.push(l),i.childNodes=i.childNodes.concat(l.childNodes),l.childNodes.forEach((e=>e.parent=i)),o.parent=i,i.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),i.addMathmlNodes(l.mathml),u=i):c.isImplicitOp(i)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 6"),i.contentNodes.push(o),i.childNodes.push(l),l.parent=i,o.parent=i,i.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),i.addMathmlNodes(l.mathml),u=i):c.isImplicitOp(l)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 7"),l.contentNodes.unshift(o),l.childNodes.unshift(i),i.parent=l,o.parent=l,l.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),l.addMathmlNodes(i.mathml),u=l):(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 8"),u=s.factory.makeBranchNode("infixop",[i,l],[o],o.textContent),u.role="implicit"),e.push(u),h(e.concat(a),t,n)}s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("combine_juxtaposition",(function(e){for(let t,n=e.childNodes.length-1;t=e.childNodes[n];n--)c.isImplicitOp(t)&&!t.nobreaking&&(e.childNodes.splice(n,1,...t.childNodes),e.contentNodes.splice(n,0,...t.contentNodes),t.childNodes.concat(t.contentNodes).forEach((function(t){t.parent=e})),e.addMathmlNodes(t.mathml));return e}))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("propagateSimpleFunction",(e=>("infixop"!==e.type&&"fraction"!==e.type||!e.childNodes.every(c.isSimpleFunction)||(e.role="composed function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("simpleNamedFunction",(e=>("unit"!==e.role&&-1!==["f","g","h","F","G","H"].indexOf(e.textContent)&&(e.role="simple function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("propagateComposedFunction",(e=>("fenced"===e.type&&"composed function"===e.childNodes[0].role&&(e.role="composed function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("multioperator",(e=>{if("unknown"!==e.role||e.textContent.length<=1)return;const t=[...e.textContent].map(o.lookupMeaning).reduce((function(e,t){return e&&t.role&&"unknown"!==t.role&&t.role!==e?"unknown"===e?t.role:null:e}),"unknown");t&&(e.role=t)}))),s.add(new a.SemanticMultiHeuristic("convert_juxtaposition",(e=>{let t=u.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===o.invisibleTimes()&&"operator"===e.type}));t=t.rel.length?function(e){const t=[],n=[];let r=e.comp.shift(),i=null,o=[];for(;e.comp.length;)if(o=[],r.length)i&&t.push(i),n.push(r),i=e.rel.shift(),r=e.comp.shift();else{for(i&&o.push(i);!r.length&&e.comp.length;)r=e.comp.shift(),o.push(e.rel.shift());i=d(o,r,n)}o.length||r.length?(t.push(i),n.push(r)):(o.push(i),d(o,r,n));return{rel:t,comp:n}}(t):t,e=t.comp[0];for(let n,r,i=1;n=t.comp[i],r=t.rel[i-1];i++)e.push(r),e=e.concat(n);return t=u.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===o.invisibleTimes()&&("operator"===e.type||"infixop"===e.type)})),t.rel.length?h(t.comp.shift(),t.rel,t.comp):e}))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("simple2prefix",(e=>(e.textContent.length>1&&!e.textContent[0].match(/[A-Z]/)&&(e.role="prefix function"),e)),(e=>"braille"===i.default.getInstance().modality&&"identifier"===e.type))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("detect_cycle",(e=>{e.type="matrix",e.role="cycle";const t=e.childNodes[0];return t.type="row",t.role="cycle",t.textContent="",t.contentNodes=[],e}),(e=>"fenced"===e.type&&"infixop"===e.childNodes[0].type&&"implicit"===e.childNodes[0].role&&e.childNodes[0].childNodes.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type}))&&e.childNodes[0].contentNodes.every((function(e){return"space"===e.role})))))},8122:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMathml=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(6098),o=n(6161),s=n(7793),a=n(8901);class c extends i.SemanticAbstractParser{constructor(){super("MathML"),this.parseMap_={SEMANTICS:this.semantics_.bind(this),MATH:this.rows_.bind(this),MROW:this.rows_.bind(this),MPADDED:this.rows_.bind(this),MSTYLE:this.rows_.bind(this),MFRAC:this.fraction_.bind(this),MSUB:this.limits_.bind(this),MSUP:this.limits_.bind(this),MSUBSUP:this.limits_.bind(this),MOVER:this.limits_.bind(this),MUNDER:this.limits_.bind(this),MUNDEROVER:this.limits_.bind(this),MROOT:this.root_.bind(this),MSQRT:this.sqrt_.bind(this),MTABLE:this.table_.bind(this),MLABELEDTR:this.tableLabeledRow_.bind(this),MTR:this.tableRow_.bind(this),MTD:this.tableCell_.bind(this),MS:this.text_.bind(this),MTEXT:this.text_.bind(this),MSPACE:this.space_.bind(this),"ANNOTATION-XML":this.text_.bind(this),MI:this.identifier_.bind(this),MN:this.number_.bind(this),MO:this.operator_.bind(this),MFENCED:this.fenced_.bind(this),MENCLOSE:this.enclosed_.bind(this),MMULTISCRIPTS:this.multiscripts_.bind(this),ANNOTATION:this.empty_.bind(this),NONE:this.empty_.bind(this),MACTION:this.action_.bind(this)};const e={type:"identifier",role:"numbersetletter",font:"double-struck"};["C","H","N","P","Q","R","Z","\u2102","\u210d","\u2115","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\u2124"].forEach((t=>this.getFactory().defaultMap.add(t,e)).bind(this))}static getAttribute_(e,t,n){if(!e.hasAttribute(t))return n;const r=e.getAttribute(t);return r.match(/^\s*$/)?null:r}parse(e){s.default.getInstance().setNodeFactory(this.getFactory());const t=r.toArray(e.childNodes),n=r.tagName(e),i=this.parseMap_[n],o=(i||this.dummy_.bind(this))(e,t);return a.addAttributes(o,e),-1!==["MATH","MROW","MPADDED","MSTYLE","SEMANTICS"].indexOf(n)||(o.mathml.unshift(e),o.mathmlTree=e),o}semantics_(e,t){return t.length?this.parse(t[0]):this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode()}rows_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("semantics");if(n&&n.match("bspr_"))return s.default.proof(e,n,this.parseList.bind(this));let r;return 1===(t=a.purgeNodes(t)).length?(r=this.parse(t[0]),"empty"!==r.type||r.mathmlTree||(r.mathmlTree=e)):r=s.default.getInstance().row(this.parseList(t)),r.mathml.unshift(e),r}fraction_(e,t){if(!t.length)return this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode();const n=this.parse(t[0]),r=t[1]?this.parse(t[1]):this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode();return s.default.getInstance().fractionLikeNode(n,r,e.getAttribute("linethickness"),"true"===e.getAttribute("bevelled"))}limits_(e,t){return s.default.getInstance().limitNode(r.tagName(e),this.parseList(t))}root_(e,t){return t[1]?this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("root",[this.parse(t[1]),this.parse(t[0])],[]):this.sqrt_(e,t)}sqrt_(e,t){const n=this.parseList(a.purgeNodes(t));return this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("sqrt",[s.default.getInstance().row(n)],[])}table_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("semantics");if(n&&n.match("bspr_"))return s.default.proof(e,n,this.parseList.bind(this));const r=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("table",this.parseList(t),[]);return r.mathmlTree=e,s.default.tableToMultiline(r),r}tableRow_(e,t){const n=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("row",this.parseList(t),[]);return n.role="table",n}tableLabeledRow_(e,t){if(!t.length)return this.tableRow_(e,t);const n=this.parse(t[0]);n.role="label";const r=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("row",this.parseList(t.slice(1)),[n]);return r.role="table",r}tableCell_(e,t){const n=this.parseList(a.purgeNodes(t));let r;r=n.length?1===n.length&&o.isType(n[0],"empty")?n:[s.default.getInstance().row(n)]:[];const i=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("cell",r,[]);return i.role="table",i}space_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("width"),i=n&&n.match(/[a-z]*$/);if(!i)return this.empty_(e,t);const o=i[0],a=parseFloat(n.slice(0,i.index)),c={cm:.4,pc:.5,em:.5,ex:1,in:.15,pt:5,mm:5}[o];if(!c||isNaN(a)||a1?this.parse(t[1]):this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e)}dummy_(e,t){const n=this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e);return n.role=e.tagName,n.textContent=e.textContent,n}leaf_(e,t){if(1===t.length&&t[0].nodeType!==r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){const n=this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e);return n.role=t[0].tagName,a.addAttributes(n,t[0]),n}return this.getFactory().makeLeafNode(e.textContent,s.default.getInstance().font(e.getAttribute("mathvariant")))}}t.SemanticMathml=c},9444:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticNode=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(4020),o=n(8901);class s{constructor(e){this.id=e,this.mathml=[],this.parent=null,this.type="unknown",this.role="unknown",this.font="unknown",this.embellished=null,this.fencePointer="",this.childNodes=[],this.textContent="",this.mathmlTree=null,this.contentNodes=[],this.annotation={},this.attributes={},this.nobreaking=!1}static fromXml(e){const t=parseInt(e.getAttribute("id"),10),n=new s(t);return n.type=e.tagName,s.setAttribute(n,e,"role"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"font"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"embellished"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"fencepointer","fencePointer"),e.getAttribute("annotation")&&n.parseAnnotation(e.getAttribute("annotation")),o.addAttributes(n,e),s.processChildren(n,e),n}static setAttribute(e,t,n,r){r=r||n;const i=t.getAttribute(n);i&&(e[r]=i)}static processChildren(e,t){for(const n of r.toArray(t.childNodes)){if(n.nodeType===r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){e.textContent=n.textContent;continue}const t=r.toArray(n.childNodes).map(s.fromXml);t.forEach((t=>t.parent=e)),"CONTENT"===r.tagName(n)?e.contentNodes=t:e.childNodes=t}}querySelectorAll(e){let t=[];for(let n,r=0;n=this.childNodes[r];r++)t=t.concat(n.querySelectorAll(e));for(let n,r=0;n=this.contentNodes[r];r++)t=t.concat(n.querySelectorAll(e));return e(this)&&t.unshift(this),t}xml(e,t){const n=function(n,r){const i=r.map((function(n){return n.xml(e,t)})),o=e.createElementNS("",n);for(let e,t=0;e=i[t];t++)o.appendChild(e);return o},r=e.createElementNS("",this.type);return t||this.xmlAttributes(r),r.textContent=this.textContent,this.contentNodes.length>0&&r.appendChild(n("content",this.contentNodes)),this.childNodes.length>0&&r.appendChild(n("children",this.childNodes)),r}toString(e=!1){const t=r.parseInput("");return r.serializeXml(this.xml(t,e))}allAttributes(){const e=[];return e.push(["role",this.role]),"unknown"!==this.font&&e.push(["font",this.font]),Object.keys(this.annotation).length&&e.push(["annotation",this.xmlAnnotation()]),this.embellished&&e.push(["embellished",this.embellished]),this.fencePointer&&e.push(["fencepointer",this.fencePointer]),e.push(["id",this.id.toString()]),e}xmlAnnotation(){const e=[];for(const t in this.annotation)this.annotation[t].forEach((function(n){e.push(t+":"+n)}));return e.join(";")}toJson(){const e={};e.type=this.type;const t=this.allAttributes();for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++)e[n[0]]=n[1].toString();return this.textContent&&(e.$t=this.textContent),this.childNodes.length&&(e.children=this.childNodes.map((function(e){return e.toJson()}))),this.contentNodes.length&&(e.content=this.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e.toJson()}))),e}updateContent(e,t){const n=t?e.replace(/^[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]*/,"").replace(/[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]*$/,""):e.trim();if(e=e&&!n?e:n,this.textContent===e)return;const r=(0,i.lookupMeaning)(e);this.textContent=e,this.role=r.role,this.type=r.type,this.font=r.font}addMathmlNodes(e){for(let t,n=0;t=e[n];n++)-1===this.mathml.indexOf(t)&&this.mathml.push(t)}appendChild(e){this.childNodes.push(e),this.addMathmlNodes(e.mathml),e.parent=this}replaceChild(e,t){const n=this.childNodes.indexOf(e);if(-1===n)return;e.parent=null,t.parent=this,this.childNodes[n]=t;const r=e.mathml.filter((function(e){return-1===t.mathml.indexOf(e)})),i=t.mathml.filter((function(t){return-1===e.mathml.indexOf(t)}));this.removeMathmlNodes(r),this.addMathmlNodes(i)}appendContentNode(e){e&&(this.contentNodes.push(e),this.addMathmlNodes(e.mathml),e.parent=this)}removeContentNode(e){if(e){const t=this.contentNodes.indexOf(e);-1!==t&&this.contentNodes.slice(t,1)}}equals(e){if(!e)return!1;if(this.type!==e.type||this.role!==e.role||this.textContent!==e.textContent||this.childNodes.length!==e.childNodes.length||this.contentNodes.length!==e.contentNodes.length)return!1;for(let t,n,r=0;t=this.childNodes[r],n=e.childNodes[r];r++)if(!t.equals(n))return!1;for(let t,n,r=0;t=this.contentNodes[r],n=e.contentNodes[r];r++)if(!t.equals(n))return!1;return!0}displayTree(){console.info(this.displayTree_(0))}addAnnotation(e,t){t&&this.addAnnotation_(e,t)}getAnnotation(e){const t=this.annotation[e];return t||[]}hasAnnotation(e,t){const n=this.annotation[e];return!!n&&-1!==n.indexOf(t)}parseAnnotation(e){const t=e.split(";");for(let e=0,n=t.length;e1)return!1;const n=t[0];if("infixop"===n.type){if("implicit"!==n.role)return!1;if(n.childNodes.some((e=>o(e,"infixop"))))return!1}return!0},t.isPrefixFunctionBoundary=function(e){return l(e)&&!a(e,"division")||o(e,"appl")||c(e)},t.isBigOpBoundary=function(e){return l(e)||c(e)},t.isIntegralDxBoundary=function(e,t){return!!t&&o(t,"identifier")&&r.lookupSecondary("d",e.textContent)},t.isIntegralDxBoundarySingle=function(e){if(o(e,"identifier")){const t=e.textContent[0];return t&&e.textContent[1]&&r.lookupSecondary("d",t)}return!1},t.isGeneralFunctionBoundary=c,t.isEmbellished=function(e){return e.embellished?e.embellished:r.isEmbellishedType(e.type)?e.type:null},t.isOperator=l,t.isRelation=u,t.isPunctuation=d,t.isFence=h,t.isElligibleEmbellishedFence=function(e){return!(!e||!h(e))&&(!e.embellished||p(e))},t.isTableOrMultiline=f,t.tableIsMatrixOrVector=function(e){return!!e&&m(e)&&f(e.childNodes[0])},t.isFencedElement=m,t.tableIsCases=function(e,t){return t.length>0&&a(t[t.length-1],"openfence")},t.tableIsMultiline=function(e){return e.childNodes.every((function(e){return e.childNodes.length<=1}))},t.lineIsLabelled=function(e){return o(e,"line")&&e.contentNodes.length&&a(e.contentNodes[0],"label")},t.isBinomial=function(e){return 2===e.childNodes.length},t.isLimitBase=function e(t){return o(t,"largeop")||o(t,"limboth")||o(t,"limlower")||o(t,"limupper")||o(t,"function")&&a(t,"limit function")||(o(t,"overscore")||o(t,"underscore"))&&e(t.childNodes[0])},t.isSimpleFunctionHead=function(e){return"identifier"===e.type||"latinletter"===e.role||"greekletter"===e.role||"otherletter"===e.role},t.singlePunctAtPosition=function(e,t,n){return 1===t.length&&("punctuation"===e[n].type||"punctuation"===e[n].embellished)&&e[n]===t[0]},t.isSimpleFunction=function(e){return o(e,"identifier")&&a(e,"simple function")},t.isLeftBrace=g,t.isRightBrace=S,t.isSetNode=function(e){return g(e.contentNodes[0])&&S(e.contentNodes[1])},t.illegalSingleton_=["punctuation","punctuated","relseq","multirel","table","multiline","cases","inference"],t.scriptedElement_=["limupper","limlower","limboth","subscript","superscript","underscore","overscore","tensor"],t.isSingletonSetContent=function e(n){const r=n.type;return-1===t.illegalSingleton_.indexOf(r)&&("infixop"!==r||"implicit"===n.role)&&("fenced"===r?"leftright"!==n.role||e(n.childNodes[0]):-1===t.scriptedElement_.indexOf(r)||e(n.childNodes[0]))},t.isNumber=b,t.isUnitCounter=function(e){return b(e)||"vulgar"===e.role||"mixed"===e.role},t.isPureUnit=function(e){const t=e.childNodes;return"unit"===e.role&&(!t.length||"unit"===t[0].role)},t.isImplicit=function(e){return"implicit"===e.role||"unit"===e.role&&!!e.contentNodes.length&&e.contentNodes[0].textContent===r.invisibleTimes()},t.isImplicitOp=function(e){return"infixop"===e.type&&"implicit"===e.role},t.isNeutralFence=N,t.compareNeutralFences=function(e,t){return N(e)&&N(t)&&(0,i.getEmbellishedInner)(e).textContent===(0,i.getEmbellishedInner)(t).textContent},t.elligibleLeftNeutral=function(e){return!!N(e)&&(!e.embellished||"superscript"!==e.type&&"subscript"!==e.type&&("tensor"!==e.type||"empty"===e.childNodes[3].type&&"empty"===e.childNodes[4].type))},t.elligibleRightNeutral=function(e){return!!N(e)&&(!e.embellished||("tensor"!==e.type||"empty"===e.childNodes[1].type&&"empty"===e.childNodes[2].type))},t.isMembership=function(e){return["element","nonelement","reelement","renonelement"].includes(e.role)}},7793:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(6671),i=n(4020),o=n(2721),s=n(4790),a=n(6161),c=n(8901);class l{constructor(){this.funcAppls={},this.factory_=new s.SemanticNodeFactory,o.updateFactory(this.factory_)}static getInstance(){return l.instance=l.instance||new l,l.instance}static tableToMultiline(e){if(a.tableIsMultiline(e)){e.type="multiline";for(let t,n=0;t=e.childNodes[n];n++)l.rowToLine_(t,"multiline");1===e.childNodes.length&&!a.lineIsLabelled(e.childNodes[0])&&a.isFencedElement(e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0])&&l.tableToMatrixOrVector_(l.rewriteFencedLine_(e)),l.binomialForm_(e),l.classifyMultiline(e)}else l.classifyTable(e)}static number(e){"unknown"!==e.type&&"identifier"!==e.type||(e.type="number"),l.numberRole_(e),l.exprFont_(e)}static classifyMultiline(e){let t=0;const n=e.childNodes.length;let r;for(;t=n)return;const i=r.childNodes[0].role;"unknown"!==i&&e.childNodes.every((function(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];return!t||t.role===i&&(a.isType(t,"relation")||a.isType(t,"relseq"))}))&&(e.role=i)}static classifyTable(e){const t=l.computeColumns_(e);l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"equality")||l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"inequality",["equality"])||l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"arrow")||l.detectCaleyTable(e)}static detectCaleyTable(e){if(!e.mathmlTree)return!1;const t=e.mathmlTree,n=t.getAttribute("columnlines"),r=t.getAttribute("rowlines");return!(!n||!r)&&(!(!l.cayleySpacing(n)||!l.cayleySpacing(r))&&(e.role="cayley",!0))}static cayleySpacing(e){const t=e.split(" ");return("solid"===t[0]||"dashed"===t[0])&&t.slice(1).every((e=>"none"===e))}static proof(e,t,n){const r=l.separateSemantics(t);return l.getInstance().proof(e,r,n)}static findSemantics(e,t,n){const r=null==n?null:n,i=l.getSemantics(e);return!!i&&(!!i[t]&&(null==r||i[t]===r))}static getSemantics(e){const t=e.getAttribute("semantics");return t?l.separateSemantics(t):null}static removePrefix(e){const[,...t]=e.split("_");return t.join("_")}static separateSemantics(e){const t={};return e.split(";").forEach((function(e){const[n,r]=e.split(":");t[l.removePrefix(n)]=r})),t}static matchSpaces_(e,t){for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++){const t=e[r].mathmlTree,i=e[r+1].mathmlTree;if(!t||!i)continue;const o=t.nextSibling;if(!o||o===i)continue;const s=l.getSpacer_(o);s&&(n.mathml.push(s),n.mathmlTree=s,n.role="space")}}static getSpacer_(e){if("MSPACE"===r.tagName(e))return e;for(;c.hasEmptyTag(e)&&1===e.childNodes.length;)if(e=e.childNodes[0],"MSPACE"===r.tagName(e))return e;return null}static fenceToPunct_(e){const t=l.FENCE_TO_PUNCT_[e.role];if(t){for(;e.embellished;)e.embellished="punctuation",a.isRole(e,"subsup")||a.isRole(e,"underover")||(e.role=t),e=e.childNodes[0];e.type="punctuation",e.role=t}}static classifyFunction_(e,t){if("appl"===e.type||"bigop"===e.type||"integral"===e.type)return"";if(t[0]&&t[0].textContent===i.functionApplication()){l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id]=t.shift();let n="simple function";return o.run("simple2prefix",e),"prefix function"!==e.role&&"limit function"!==e.role||(n=e.role),l.propagateFunctionRole_(e,n),"prefix"}const n=l.CLASSIFY_FUNCTION_[e.role];return n||(a.isSimpleFunctionHead(e)?"simple":"")}static propagateFunctionRole_(e,t){if(e){if("infixop"===e.type)return;a.isRole(e,"subsup")||a.isRole(e,"underover")||(e.role=t),l.propagateFunctionRole_(e.childNodes[0],t)}}static getFunctionOp_(e,t){if(t(e))return e;for(let n,r=0;n=e.childNodes[r];r++){const e=l.getFunctionOp_(n,t);if(e)return e}return null}static tableToMatrixOrVector_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];a.isType(t,"multiline")?l.tableToVector_(e):l.tableToMatrix_(e),e.contentNodes.forEach(t.appendContentNode.bind(t));for(let e,n=0;e=t.childNodes[n];n++)l.assignRoleToRow_(e,l.getComponentRoles_(t));return t.parent=null,t}static tableToVector_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];t.type="vector",1!==t.childNodes.length?l.binomialForm_(t):l.tableToSquare_(e)}static binomialForm_(e){a.isBinomial(e)&&(e.role="binomial",e.childNodes[0].role="binomial",e.childNodes[1].role="binomial")}static tableToMatrix_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];t.type="matrix",t.childNodes&&t.childNodes.length>0&&t.childNodes[0].childNodes&&t.childNodes.length===t.childNodes[0].childNodes.length?l.tableToSquare_(e):t.childNodes&&1===t.childNodes.length&&(t.role="rowvector")}static tableToSquare_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];a.isNeutralFence(e)?t.role="determinant":t.role="squarematrix"}static getComponentRoles_(e){const t=e.role;return t&&"unknown"!==t?t:e.type.toLowerCase()||"unknown"}static tableToCases_(e,t){for(let t,n=0;t=e.childNodes[n];n++)l.assignRoleToRow_(t,"cases");return e.type="cases",e.appendContentNode(t),a.tableIsMultiline(e)&&l.binomialForm_(e),e}static rewriteFencedLine_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0],n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],r=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes[0];return n.parent=e.parent,e.parent=n,r.parent=t,n.childNodes=[e],t.childNodes=[r],n}static rowToLine_(e,t){const n=t||"unknown";a.isType(e,"row")&&(e.type="line",e.role=n,1===e.childNodes.length&&a.isType(e.childNodes[0],"cell")&&(e.childNodes=e.childNodes[0].childNodes,e.childNodes.forEach((function(t){t.parent=e}))))}static assignRoleToRow_(e,t){a.isType(e,"line")?e.role=t:a.isType(e,"row")&&(e.role=t,e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){a.isType(e,"cell")&&(e.role=t)})))}static nextSeparatorFunction_(e){let t;if(e){if(e.match(/^\s+$/))return null;t=e.replace(/\s/g,"").split("").filter((function(e){return e}))}else t=[","];return function(){return t.length>1?t.shift():t[0]}}static numberRole_(e){if("unknown"!==e.role)return;const t=[...e.textContent].filter((e=>e.match(/[^\s]/))),n=t.map(i.lookupMeaning);if(n.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type&&"integer"===e.role||"punctuation"===e.type&&"comma"===e.role})))return e.role="integer",void("0"===t[0]&&e.addAnnotation("general","basenumber"));n.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type&&"integer"===e.role||"punctuation"===e.type}))?e.role="float":e.role="othernumber"}static exprFont_(e){if("unknown"!==e.font)return;const t=[...e.textContent].map(i.lookupMeaning).reduce((function(e,t){return e&&t.font&&"unknown"!==t.font&&t.font!==e?"unknown"===e?t.font:null:e}),"unknown");t&&(e.font=t)}static purgeFences_(e){const t=e.rel,n=e.comp,r=[],i=[];for(;t.length>0;){const e=t.shift();let o=n.shift();a.isElligibleEmbellishedFence(e)?(r.push(e),i.push(o)):(l.fenceToPunct_(e),o.push(e),o=o.concat(n.shift()),n.unshift(o))}return i.push(n.shift()),{rel:r,comp:i}}static rewriteFencedNode_(e){const t=e.contentNodes[0],n=e.contentNodes[1];let r=l.rewriteFence_(e,t);return e.contentNodes[0]=r.fence,r=l.rewriteFence_(r.node,n),e.contentNodes[1]=r.fence,e.contentNodes[0].parent=e,e.contentNodes[1].parent=e,r.node.parent=null,r.node}static rewriteFence_(e,t){if(!t.embellished)return{node:e,fence:t};const n=t.childNodes[0],r=l.rewriteFence_(e,n);return a.isType(t,"superscript")||a.isType(t,"subscript")||a.isType(t,"tensor")?(a.isRole(t,"subsup")||(t.role=e.role),n!==r.node&&(t.replaceChild(n,r.node),n.parent=e),l.propagateFencePointer_(t,n),{node:t,fence:r.fence}):(t.replaceChild(n,r.fence),t.mathmlTree&&-1===t.mathml.indexOf(t.mathmlTree)&&t.mathml.push(t.mathmlTree),{node:r.node,fence:t})}static propagateFencePointer_(e,t){e.fencePointer=t.fencePointer||t.id.toString(),e.embellished=null}static classifyByColumns_(e,t,n,r){return!!(3===t.length&&l.testColumns_(t,1,(e=>l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))||2===t.length&&(l.testColumns_(t,1,(e=>l.isEndRelation_(e,n)||l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))||l.testColumns_(t,0,(e=>l.isEndRelation_(e,n,!0)||l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))))&&(e.role=n,!0)}static isEndRelation_(e,t,n){const r=n?e.childNodes.length-1:0;return a.isType(e,"relseq")&&a.isRole(e,t)&&a.isType(e.childNodes[r],"empty")}static isPureRelation_(e,t){return a.isType(e,"relation")&&a.isRole(e,t)}static computeColumns_(e){const t=[];for(let n,r=0;n=e.childNodes[r];r++)for(let e,r=0;e=n.childNodes[r];r++){t[r]?t[r].push(e):t[r]=[e]}return t}static testColumns_(e,t,n){const r=e[t];return!!r&&(r.some((function(e){return e.childNodes.length&&n(e.childNodes[0])}))&&r.every((function(e){return!e.childNodes.length||n(e.childNodes[0])})))}setNodeFactory(e){l.getInstance().factory_=e,o.updateFactory(l.getInstance().factory_)}getNodeFactory(){return l.getInstance().factory_}identifierNode(e,t,n){if("MathML-Unit"===n)e.type="identifier",e.role="unit";else if(!t&&1===e.textContent.length&&("integer"===e.role||"latinletter"===e.role||"greekletter"===e.role)&&"normal"===e.font)return e.font="italic",o.run("simpleNamedFunction",e);return"unknown"===e.type&&(e.type="identifier"),l.exprFont_(e),o.run("simpleNamedFunction",e)}implicitNode(e){if(e=l.getInstance().getMixedNumbers_(e),1===(e=l.getInstance().combineUnits_(e)).length)return e[0];const t=l.getInstance().implicitNode_(e);return o.run("combine_juxtaposition",t)}text(e,t){return l.exprFont_(e),e.type="text","MS"===t?(e.role="string",e):"MSPACE"===t||e.textContent.match(/^\s*$/)?(e.role="space",e):e}row(e){return 0===(e=e.filter((function(e){return!a.isType(e,"empty")}))).length?l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode():(e=l.getInstance().getFencesInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().tablesInRow(e),e=l.getInstance().getPunctuationInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().getTextInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e),l.getInstance().relationsInRow_(e))}limitNode(e,t){if(!t.length)return l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();let n,r=t[0],i="unknown";if(!t[1])return r;if(a.isLimitBase(r)){n=l.MML_TO_LIMIT_[e];const o=n.length;if(i=n.type,t=t.slice(0,n.length+1),1===o&&a.isAccent(t[1])||2===o&&a.isAccent(t[1])&&a.isAccent(t[2]))return n=l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_[e],l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,t,n.type,n.length,n.accent);if(2===o){if(a.isAccent(t[1]))return r=l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,[r,t[1]],{MSUBSUP:"subscript",MUNDEROVER:"underscore"}[e],1,!0),t[2]?l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,[r,t[2]],null,"limupper"):r;if(t[2]&&a.isAccent(t[2]))return r=l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,[r,t[2]],{MSUBSUP:"superscript",MUNDEROVER:"overscore"}[e],1,!0),l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,[r,t[1]],null,"limlower");t[o]||(i="limlower")}return l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,t,null,i)}return n=l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_[e],l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,t,n.type,n.length,n.accent)}tablesInRow(e){let t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.tableIsMatrixOrVector),n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++)n=n.concat(t.comp.shift()),n.push(l.tableToMatrixOrVector_(e));n=n.concat(t.comp.shift()),t=c.partitionNodes(n,a.isTableOrMultiline),n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const r=t.comp.shift();a.tableIsCases(e,r)&&l.tableToCases_(e,r.pop()),n=n.concat(r),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp.shift())}mfenced(e,t,n,r){if(n&&r.length>0){const e=l.nextSeparatorFunction_(n),t=[r.shift()];r.forEach((n=>{t.push(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e())),t.push(n)})),r=t}return e&&t?l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e),l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(t),r):(e&&r.unshift(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e)),t&&r.push(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(t)),l.getInstance().row(r))}fractionLikeNode(e,t,n,r){let i;if(!r&&c.isZeroLength(n)){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("line",[e],[]),r=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("line",[t],[]);return i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("multiline",[n,r],[]),l.binomialForm_(i),l.classifyMultiline(i),i}return i=l.getInstance().fractionNode_(e,t),r&&i.addAnnotation("general","bevelled"),i}tensor(e,t,n,r,i){const o=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("tensor",[e,l.getInstance().scriptNode_(t,"leftsub"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(n,"leftsuper"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(r,"rightsub"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(i,"rightsuper")],[]);return o.role=e.role,o.embellished=a.isEmbellished(e),o}pseudoTensor(e,t,n){const r=e=>!a.isType(e,"empty"),i=t.filter(r).length,o=n.filter(r).length;if(!i&&!o)return e;const s=i?o?"MSUBSUP":"MSUB":"MSUP",c=[e];return i&&c.push(l.getInstance().scriptNode_(t,"rightsub",!0)),o&&c.push(l.getInstance().scriptNode_(n,"rightsuper",!0)),l.getInstance().limitNode(s,c)}font(e){const t=l.MATHJAX_FONTS[e];return t||e}proof(e,t,n){if(t.inference||t.axiom||console.log("Noise"),t.axiom){const t=l.getInstance().cleanInference(e.childNodes),r=t.length?l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",n(t),[]):l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();return r.role="axiom",r.mathmlTree=e,r}const r=l.getInstance().inference(e,t,n);return t.proof&&(r.role="proof",r.childNodes[0].role="final"),r}inference(e,t,n){if(t.inferenceRule){const t=l.getInstance().getFormulas(e,[],n);return l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",[t.conclusion,t.premises],[])}const i=t.labelledRule,o=r.toArray(e.childNodes),s=[];"left"!==i&&"both"!==i||s.push(l.getInstance().getLabel(e,o,n,"left")),"right"!==i&&"both"!==i||s.push(l.getInstance().getLabel(e,o,n,"right"));const a=l.getInstance().getFormulas(e,o,n),c=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",[a.conclusion,a.premises],s);return c.mathmlTree=e,c}getLabel(e,t,n,i){const o=l.getInstance().findNestedRow(t,"prooflabel",i),s=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("rulelabel",n(r.toArray(o.childNodes)),[]);return s.role=i,s.mathmlTree=o,s}getFormulas(e,t,n){const i=t.length?l.getInstance().findNestedRow(t,"inferenceRule"):e,o="up"===l.getSemantics(i).inferenceRule,s=o?i.childNodes[1]:i.childNodes[0],a=o?i.childNodes[0]:i.childNodes[1],c=s.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],u=r.toArray(c.childNodes[0].childNodes),d=[];let h=1;for(const e of u)h%2&&d.push(e.childNodes[0]),h++;const p=n(d),f=n(r.toArray(a.childNodes[0].childNodes))[0],m=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("premises",p,[]);m.mathmlTree=c;const g=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("conclusion",[f],[]);return g.mathmlTree=a.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],{conclusion:g,premises:m}}findNestedRow(e,t,n){return l.getInstance().findNestedRow_(e,t,0,n)}cleanInference(e){return r.toArray(e).filter((function(e){return"MSPACE"!==r.tagName(e)}))}operatorNode(e){return"unknown"===e.type&&(e.type="operator"),o.run("multioperator",e)}implicitNode_(e){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeMultipleContentNodes(e.length-1,i.invisibleTimes());l.matchSpaces_(e,t);const n=l.getInstance().infixNode_(e,t[0]);return n.role="implicit",t.forEach((function(e){e.parent=n})),n.contentNodes=t,n}infixNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("infixop",e,[t],c.getEmbellishedInner(t).textContent);return n.role=t.role,o.run("propagateSimpleFunction",n)}explicitMixed_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===i.invisiblePlus()}));if(!t.rel.length)return e;let n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const i=t.comp[r],o=t.comp[r+1],s=i.length-1;if(i[s]&&o[0]&&a.isType(i[s],"number")&&!a.isRole(i[s],"mixed")&&a.isType(o[0],"fraction")){const e=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("number",[i[s],o[0]],[]);e.role="mixed",n=n.concat(i.slice(0,s)),n.push(e),o.shift()}else n=n.concat(i),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp[t.comp.length-1])}concatNode_(e,t,n){if(0===t.length)return e;const r=t.map((function(e){return c.getEmbellishedInner(e).textContent})).join(" "),i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(n,[e],t,r);return t.length>1&&(i.role="multiop"),i}prefixNode_(e,t){const n=c.partitionNodes(t,(e=>a.isRole(e,"subtraction")));let r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(e,n.comp.pop(),"prefixop");for(1===r.contentNodes.length&&"addition"===r.contentNodes[0].role&&"+"===r.contentNodes[0].textContent&&(r.role="positive");n.rel.length>0;)r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(r,[n.rel.pop()],"prefixop"),r.role="negative",r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(r,n.comp.pop(),"prefixop");return r}postfixNode_(e,t){return t.length?l.getInstance().concatNode_(e,t,"postfixop"):e}combineUnits_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return!a.isRole(e,"unit")}));if(e.length===t.rel.length)return t.rel;const n=[];let r,i;do{const e=t.comp.shift();r=t.rel.shift();let o=null;i=n.pop(),i&&(e.length&&a.isUnitCounter(i)?e.unshift(i):n.push(i)),1===e.length&&(o=e.pop()),e.length>1&&(o=l.getInstance().implicitNode_(e),o.role="unit"),o&&n.push(o),r&&n.push(r)}while(r);return n}getMixedNumbers_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return a.isType(e,"fraction")&&a.isRole(e,"vulgar")}));if(!t.rel.length)return e;let n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const i=t.comp[r],o=i.length-1;if(i[o]&&a.isType(i[o],"number")&&(a.isRole(i[o],"integer")||a.isRole(i[o],"float"))){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("number",[i[o],e],[]);t.role="mixed",n=n.concat(i.slice(0,o)),n.push(t)}else n=n.concat(i),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp[t.comp.length-1])}getTextInRow_(e){if(e.length<=1)return e;const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"text")));if(0===t.rel.length)return e;const n=[];let r=t.comp[0];r.length>0&&n.push(l.getInstance().row(r));for(let e,i=0;e=t.rel[i];i++)n.push(e),r=t.comp[i+1],r.length>0&&n.push(l.getInstance().row(r));return[l.getInstance().dummyNode_(n)]}relationsInRow_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.isRelation),n=t.rel[0];if(!n)return l.getInstance().operationsInRow_(e);if(1===e.length)return e[0];const r=t.comp.map(l.getInstance().operationsInRow_);let i;return t.rel.some((function(e){return!e.equals(n)}))?(i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("multirel",r,t.rel),t.rel.every((function(e){return e.role===n.role}))&&(i.role=n.role),i):(i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("relseq",r,t.rel,c.getEmbellishedInner(n).textContent),i.role=n.role,i)}operationsInRow_(e){if(0===e.length)return l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();if(1===(e=l.getInstance().explicitMixed_(e)).length)return e[0];const t=[];for(;e.length>0&&a.isOperator(e[0]);)t.push(e.shift());if(0===e.length)return l.getInstance().prefixNode_(t.pop(),t);if(1===e.length)return l.getInstance().prefixNode_(e[0],t);e=o.run("convert_juxtaposition",e);const n=c.sliceNodes(e,a.isOperator),r=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(l.getInstance().implicitNode(n.head),t);return n.div?l.getInstance().operationsTree_(n.tail,r,n.div):r}operationsTree_(e,t,n,r){const i=r||[];if(0===e.length){if(i.unshift(n),"infixop"===t.type){const e=l.getInstance().postfixNode_(t.childNodes.pop(),i);return t.appendChild(e),t}return l.getInstance().postfixNode_(t,i)}const o=c.sliceNodes(e,a.isOperator);if(0===o.head.length)return i.push(o.div),l.getInstance().operationsTree_(o.tail,t,n,i);const s=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(l.getInstance().implicitNode(o.head),i),u=l.getInstance().appendOperand_(t,n,s);return o.div?l.getInstance().operationsTree_(o.tail,u,o.div,[]):u}appendOperand_(e,t,n){if("infixop"!==e.type)return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t);const r=l.getInstance().appendDivisionOp_(e,t,n);return r||(l.getInstance().appendExistingOperator_(e,t,n)?e:"multiplication"===t.role?l.getInstance().appendMultiplicativeOp_(e,t,n):l.getInstance().appendAdditiveOp_(e,t,n))}appendDivisionOp_(e,t,n){return"division"===t.role?a.isImplicit(e)?l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t):l.getInstance().appendLastOperand_(e,t,n):"division"===e.role?l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t):null}appendLastOperand_(e,t,n){let r=e,i=e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];for(;i&&"infixop"===i.type&&!a.isImplicit(i);)r=i,i=r.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];const o=l.getInstance().infixNode_([r.childNodes.pop(),n],t);return r.appendChild(o),e}appendMultiplicativeOp_(e,t,n){if(a.isImplicit(e))return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t);let r=e,i=e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];for(;i&&"infixop"===i.type&&!a.isImplicit(i);)r=i,i=r.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];const o=l.getInstance().infixNode_([r.childNodes.pop(),n],t);return r.appendChild(o),e}appendAdditiveOp_(e,t,n){return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t)}appendExistingOperator_(e,t,n){return!(!e||"infixop"!==e.type||a.isImplicit(e))&&(e.contentNodes[0].equals(t)?(e.appendContentNode(t),e.appendChild(n),!0):l.getInstance().appendExistingOperator_(e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1],t,n))}getFencesInRow_(e){let t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.isFence);t=l.purgeFences_(t);const n=t.comp.shift();return l.getInstance().fences_(t.rel,t.comp,[],[n])}fences_(e,t,n,r){if(0===e.length&&0===n.length)return r[0];const i=e=>a.isRole(e,"open");if(0===e.length){const e=r.shift();for(;n.length>0;){if(i(n[0])){const t=n.shift();l.fenceToPunct_(t),e.push(t)}else{const t=c.sliceNodes(n,i),o=t.head.length-1,s=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(t.head,r.slice(0,o));r=r.slice(o),e.push(...s),t.div&&t.tail.unshift(t.div),n=t.tail}e.push(...r.shift())}return e}const o=n[n.length-1],s=e[0].role;if("open"===s||a.isNeutralFence(e[0])&&(!o||!a.compareNeutralFences(e[0],o))){n.push(e.shift());const i=t.shift();return i&&r.push(i),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&"close"===s&&"open"===o.role){const i=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(n.pop(),e.shift(),r.pop());return r.push(r.pop().concat([i],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&a.compareNeutralFences(e[0],o)){if(!a.elligibleLeftNeutral(o)||!a.elligibleRightNeutral(e[0])){n.push(e.shift());const i=t.shift();return i&&r.push(i),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}const i=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(n.pop(),e.shift(),r.pop());return r.push(r.pop().concat([i],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&"close"===s&&a.isNeutralFence(o)&&n.some(i)){const o=c.sliceNodes(n,i,!0),s=r.pop(),a=r.length-o.tail.length+1,u=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(o.tail,r.slice(a));r=r.slice(0,a);const d=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(o.div,e.shift(),r.pop().concat(u,s));return r.push(r.pop().concat([d],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,o.head,r)}const u=e.shift();return l.fenceToPunct_(u),r.push(r.pop().concat([u],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}neutralFences_(e,t){if(0===e.length)return e;if(1===e.length)return l.fenceToPunct_(e[0]),e;const n=e.shift();if(!a.elligibleLeftNeutral(n)){l.fenceToPunct_(n);const r=t.shift();return r.unshift(n),r.concat(l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t))}const r=c.sliceNodes(e,(function(e){return a.compareNeutralFences(e,n)}));if(!r.div){l.fenceToPunct_(n);const r=t.shift();return r.unshift(n),r.concat(l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t))}if(!a.elligibleRightNeutral(r.div))return l.fenceToPunct_(r.div),e.unshift(n),l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t);const i=l.getInstance().combineFencedContent_(n,r.div,r.head,t);if(r.tail.length>0){const e=i.shift(),t=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(r.tail,i);return e.concat(t)}return i[0]}combineFencedContent_(e,t,n,r){if(0===n.length){const n=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,r.shift());return r.length>0?r[0].unshift(n):r=[[n]],r}const i=r.shift(),o=n.length-1,s=r.slice(0,o),a=(r=r.slice(o)).shift(),c=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(n,s);i.push(...c),i.push(...a);const u=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,i);return r.length>0?r[0].unshift(u):r=[[u]],r}horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,n){const r=l.getInstance().row(n);let i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("fenced",[r],[e,t]);return"open"===e.role?(l.getInstance().classifyHorizontalFence_(i),i=o.run("propagateComposedFunction",i)):i.role=e.role,i=o.run("detect_cycle",i),l.rewriteFencedNode_(i)}classifyHorizontalFence_(e){e.role="leftright";const t=e.childNodes;if(!a.isSetNode(e)||t.length>1)return;if(0===t.length||"empty"===t[0].type)return void(e.role="set empty");const n=t[0].type;if(1===t.length&&a.isSingletonSetContent(t[0]))return void(e.role="set singleton");const r=t[0].role;if("punctuated"===n&&"sequence"===r){if("comma"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role)return 1!==t[0].contentNodes.length||"vbar"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role&&"colon"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role?void 0:(e.role="set extended",void l.getInstance().setExtension_(e));e.role="set collection"}}setExtension_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0];t&&"infixop"===t.type&&1===t.contentNodes.length&&a.isMembership(t.contentNodes[0])&&(t.addAnnotation("set","intensional"),t.contentNodes[0].addAnnotation("set","intensional"))}getPunctuationInRow_(e){if(e.length<=1)return e;const t=e=>{const t=e.type;return"punctuation"===t||"text"===t||"operator"===t||"relation"===t},n=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(n){if(!a.isPunctuation(n))return!1;if(a.isPunctuation(n)&&!a.isRole(n,"ellipsis"))return!0;const r=e.indexOf(n);if(0===r)return!e[1]||!t(e[1]);const i=e[r-1];if(r===e.length-1)return!t(i);const o=e[r+1];return!t(i)||!t(o)}));if(0===n.rel.length)return e;const r=[];let i=n.comp.shift();i.length>0&&r.push(l.getInstance().row(i));let o=0;for(;n.comp.length>0;)r.push(n.rel[o++]),i=n.comp.shift(),i.length>0&&r.push(l.getInstance().row(i));return[l.getInstance().punctuatedNode_(r,n.rel)]}punctuatedNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("punctuated",e,t);if(t.length===e.length){const e=t[0].role;if("unknown"!==e&&t.every((function(t){return t.role===e})))return n.role=e,n}return a.singlePunctAtPosition(e,t,0)?n.role="startpunct":a.singlePunctAtPosition(e,t,e.length-1)?n.role="endpunct":t.every((e=>a.isRole(e,"dummy")))?n.role="text":t.every((e=>a.isRole(e,"space")))?n.role="space":n.role="sequence",n}dummyNode_(e){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeMultipleContentNodes(e.length-1,i.invisibleComma());return t.forEach((function(e){e.role="dummy"})),l.getInstance().punctuatedNode_(e,t)}accentRole_(e,t){if(!a.isAccent(e))return!1;const n=e.textContent,r=i.lookupSecondary("bar",n)||i.lookupSecondary("tilde",n)||e.role;return e.role="underscore"===t?"underaccent":"overaccent",e.addAnnotation("accent",r),!0}accentNode_(e,t,n,r,i){const o=(t=t.slice(0,r+1))[1],s=t[2];let a;if(!i&&s&&(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("subscript",[e,o],[]),a.role="subsup",t=[a,s],n="superscript"),i){const r=l.getInstance().accentRole_(o,n);if(s){l.getInstance().accentRole_(s,"overscore")&&!r?(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("overscore",[e,s],[]),t=[a,o],n="underscore"):(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("underscore",[e,o],[]),t=[a,s],n="overscore"),a.role="underover"}}return l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(e,t,a,n)}makeLimitNode_(e,t,n,r){if("limupper"===r&&"limlower"===e.type)return e.childNodes.push(t[1]),t[1].parent=e,e.type="limboth",e;if("limlower"===r&&"limupper"===e.type)return e.childNodes.splice(1,-1,t[1]),t[1].parent=e,e.type="limboth",e;const i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(r,t,[]),o=a.isEmbellished(e);return n&&(n.embellished=o),i.embellished=o,i.role=e.role,i}getFunctionsInRow_(e,t){const n=t||[];if(0===e.length)return n;const r=e.shift(),i=l.classifyFunction_(r,e);if(!i)return n.push(r),l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e,n);const o=l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e,[]),s=l.getInstance().getFunctionArgs_(r,o,i);return n.concat(s)}getFunctionArgs_(e,t,n){let r,i,o;switch(n){case"integral":{const n=l.getInstance().getIntegralArgs_(t);if(!n.intvar&&!n.integrand.length)return n.rest.unshift(e),n.rest;const r=l.getInstance().row(n.integrand);return o=l.getInstance().integralNode_(e,r,n.intvar),n.rest.unshift(o),n.rest}case"prefix":if(t[0]&&"fenced"===t[0].type){const n=t.shift();return a.isNeutralFence(n)||(n.role="leftright"),o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,n),t.unshift(o),t}if(r=c.sliceNodes(t,a.isPrefixFunctionBoundary),r.head.length)i=l.getInstance().row(r.head),r.div&&r.tail.unshift(r.div);else{if(!r.div||!a.isType(r.div,"appl"))return t.unshift(e),t;i=r.div}return o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,i),r.tail.unshift(o),r.tail;case"bigop":return r=c.sliceNodes(t,a.isBigOpBoundary),r.head.length?(i=l.getInstance().row(r.head),o=l.getInstance().bigOpNode_(e,i),r.div&&r.tail.unshift(r.div),r.tail.unshift(o),r.tail):(t.unshift(e),t);default:{if(0===t.length)return[e];const n=t[0];return"fenced"===n.type&&!a.isNeutralFence(n)&&a.isSimpleFunctionScope(n)?(n.role="leftright",l.propagateFunctionRole_(e,"simple function"),o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,t.shift()),t.unshift(o),t):(t.unshift(e),t)}}}getIntegralArgs_(e,t=[]){if(0===e.length)return{integrand:t,intvar:null,rest:e};const n=e[0];if(a.isGeneralFunctionBoundary(n))return{integrand:t,intvar:null,rest:e};if(a.isIntegralDxBoundarySingle(n))return n.role="integral",{integrand:t,intvar:n,rest:e.slice(1)};if(e[1]&&a.isIntegralDxBoundary(n,e[1])){const r=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(e[1],[n]);return r.role="integral",{integrand:t,intvar:r,rest:e.slice(2)}}return t.push(e.shift()),l.getInstance().getIntegralArgs_(e,t)}functionNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(i.functionApplication()),r=l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id];r&&(n.mathmlTree=r.mathmlTree,n.mathml=r.mathml,n.annotation=r.annotation,n.attributes=r.attributes,delete l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id]),n.type="punctuation",n.role="application";const o=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(function(e){return a.isType(e,"function")||a.isType(e,"identifier")&&a.isRole(e,"simple function")}));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("appl",[e,t],o,[n])}bigOpNode_(e,t){const n=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"largeop")));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("bigop",[e,t],n,[])}integralNode_(e,t,n){t=t||l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode(),n=n||l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();const r=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"largeop")));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("integral",[e,t,n],r,[])}functionalNode_(e,t,n,r){const i=t[0];let o;n&&(o=n.parent,r.push(n));const s=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(e,t,r);return s.role=i.role,o&&(n.parent=o),s}fractionNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("fraction",[e,t],[]);return n.role=n.childNodes.every((function(e){return a.isType(e,"number")&&a.isRole(e,"integer")}))?"vulgar":n.childNodes.every(a.isPureUnit)?"unit":"division",o.run("propagateSimpleFunction",n)}scriptNode_(e,t,n){let r;switch(e.length){case 0:r=l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();break;case 1:if(r=e[0],n)return r;break;default:r=l.getInstance().dummyNode_(e)}return r.role=t,r}findNestedRow_(e,t,n,i){if(n>3)return null;for(let o,s=0;o=e[s];s++){const e=r.tagName(o);if("MSPACE"!==e){if("MROW"===e)return l.getInstance().findNestedRow_(r.toArray(o.childNodes),t,n+1,i);if(l.findSemantics(o,t,i))return o}}return null}}t.default=l,l.FENCE_TO_PUNCT_={metric:"metric",neutral:"vbar",open:"openfence",close:"closefence"},l.MML_TO_LIMIT_={MSUB:{type:"limlower",length:1},MUNDER:{type:"limlower",length:1},MSUP:{type:"limupper",length:1},MOVER:{type:"limupper",length:1},MSUBSUP:{type:"limboth",length:2},MUNDEROVER:{type:"limboth",length:2}},l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_={MSUB:{type:"subscript",length:1,accent:!1},MSUP:{type:"superscript",length:1,accent:!1},MSUBSUP:{type:"subscript",length:2,accent:!1},MUNDER:{type:"underscore",length:1,accent:!0},MOVER:{type:"overscore",length:1,accent:!0},MUNDEROVER:{type:"underscore",length:2,accent:!0}},l.CLASSIFY_FUNCTION_={integral:"integral",sum:"bigop","prefix function":"prefix","limit function":"prefix","simple function":"prefix","composed function":"prefix"},l.MATHJAX_FONTS={"-tex-caligraphic":"caligraphic","-tex-caligraphic-bold":"caligraphic-bold","-tex-calligraphic":"caligraphic","-tex-calligraphic-bold":"caligraphic-bold","-tex-oldstyle":"oldstyle","-tex-oldstyle-bold":"oldstyle-bold","-tex-mathit":"italic"}},7984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticSkeleton=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(5024),o=n(8171);class s{constructor(e){this.parents=null,this.levelsMap=null,e=0===e?e:e||[],this.array=e}static fromTree(e){return s.fromNode(e.root)}static fromNode(e){return new s(s.fromNode_(e))}static fromString(e){return new s(s.fromString_(e))}static simpleCollapseStructure(e){return"number"==typeof e}static contentCollapseStructure(e){return!!e&&!s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)&&"c"===e[0]}static interleaveIds(e,t){return r.interleaveLists(s.collapsedLeafs(e),s.collapsedLeafs(t))}static collapsedLeafs(...e){return e.reduce(((e,t)=>{return e.concat((n=t,s.simpleCollapseStructure(n)?[n]:s.contentCollapseStructure(n[1])?n.slice(2):n.slice(1)));var n}),[])}static fromStructure(e,t){return new s(s.tree_(e,t.root))}static combineContentChildren(e,t,n){switch(e.type){case"relseq":case"infixop":case"multirel":return r.interleaveLists(n,t);case"prefixop":return t.concat(n);case"postfixop":return n.concat(t);case"fenced":return n.unshift(t[0]),n.push(t[1]),n;case"appl":return[n[0],t[0],n[1]];case"root":return[n[1],n[0]];case"row":case"line":return t.length&&n.unshift(t[0]),n;default:return n}}static makeSexp_(e){return s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?e.toString():s.contentCollapseStructure(e)?"(c "+e.slice(1).map(s.makeSexp_).join(" ")+")":"("+e.map(s.makeSexp_).join(" ")+")"}static fromString_(e){let t=e.replace(/\(/g,"[");return t=t.replace(/\)/g,"]"),t=t.replace(/ /g,","),t=t.replace(/c/g,'"c"'),JSON.parse(t)}static fromNode_(e){if(!e)return[];const t=e.contentNodes;let n;t.length&&(n=t.map(s.fromNode_),n.unshift("c"));const r=e.childNodes;if(!r.length)return t.length?[e.id,n]:e.id;const i=r.map(s.fromNode_);return t.length&&i.unshift(n),i.unshift(e.id),i}static tree_(e,t){if(!t)return[];if(!t.childNodes.length)return t.id;const n=t.id,r=[n],a=i.evalXPath(`.//self::*[@${o.Attribute.ID}=${n}]`,e)[0],c=s.combineContentChildren(t,t.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e})),t.childNodes.map((function(e){return e})));a&&s.addOwns_(a,c);for(let t,n=0;t=c[n];n++)r.push(s.tree_(e,t));return r}static addOwns_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute(o.Attribute.COLLAPSED),r=n?s.realLeafs_(s.fromString(n).array):t.map((e=>e.id));e.setAttribute(o.Attribute.OWNS,r.join(" "))}static realLeafs_(e){if(s.simpleCollapseStructure(e))return[e];if(s.contentCollapseStructure(e))return[];let t=[];for(let n=1;ns.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?e:s.contentCollapseStructure(e)?e[1]:e[0]))}subtreeNodes(e){if(!this.isRoot(e))return[];const t=(e,n)=>{s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?n.push(e):(s.contentCollapseStructure(e)&&(e=e.slice(1)),e.forEach((e=>t(e,n))))},n=this.levelsMap[e],r=[];return t(n.slice(1),r),r}}t.SemanticSkeleton=s},1784:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticTree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(4036),o=n(241),s=n(8122),a=n(9444),c=n(6161);n(7103);class l{constructor(e){this.mathml=e,this.parser=new s.SemanticMathml,this.root=this.parser.parse(e),this.collator=this.parser.getFactory().leafMap.collateMeaning();const t=this.collator.newDefault();t&&(this.parser=new s.SemanticMathml,this.parser.getFactory().defaultMap=t,this.root=this.parser.parse(e)),u.visit(this.root,{}),(0,i.annotate)(this.root)}static empty(){const e=r.parseInput(""),t=new l(e);return t.mathml=e,t}static fromNode(e,t){const n=l.empty();return n.root=e,t&&(n.mathml=t),n}static fromRoot(e,t){let n=e;for(;n.parent;)n=n.parent;const r=l.fromNode(n);return t&&(r.mathml=t),r}static fromXml(e){const t=l.empty();return e.childNodes[0]&&(t.root=a.SemanticNode.fromXml(e.childNodes[0])),t}xml(e){const t=r.parseInput(""),n=this.root.xml(t.ownerDocument,e);return t.appendChild(n),t}toString(e){return r.serializeXml(this.xml(e))}formatXml(e){const t=this.toString(e);return r.formatXml(t)}displayTree(){this.root.displayTree()}replaceNode(e,t){const n=e.parent;n?n.replaceChild(e,t):this.root=t}toJson(){const e={};return e.stree=this.root.toJson(),e}}t.SemanticTree=l;const u=new o.SemanticVisitor("general","unit",((e,t)=>{if("infixop"===e.type&&("multiplication"===e.role||"implicit"===e.role)){const t=e.childNodes;t.length&&(c.isPureUnit(t[0])||c.isUnitCounter(t[0]))&&e.childNodes.slice(1).every(c.isPureUnit)&&(e.role="unit")}return!1}))},8901:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.partitionNodes=t.sliceNodes=t.getEmbellishedInner=t.addAttributes=t.isZeroLength=t.purgeNodes=t.isOrphanedGlyph=t.hasDisplayTag=t.hasEmptyTag=t.hasIgnoreTag=t.hasLeafTag=t.hasMathTag=t.directSpeechKeys=t.DISPLAYTAGS=t.EMPTYTAGS=t.IGNORETAGS=t.LEAFTAGS=void 0;const r=n(6671);function i(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.LEAFTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))}function o(e,t,n){n&&e.reverse();const r=[];for(let i,o=0;i=e[o];o++){if(t(i))return n?{head:e.slice(o+1).reverse(),div:i,tail:r.reverse()}:{head:r,div:i,tail:e.slice(o+1)};r.push(i)}return n?{head:[],div:null,tail:r.reverse()}:{head:r,div:null,tail:[]}}t.LEAFTAGS=["MO","MI","MN","MTEXT","MS","MSPACE"],t.IGNORETAGS=["MERROR","MPHANTOM","MALIGNGROUP","MALIGNMARK","MPRESCRIPTS","ANNOTATION","ANNOTATION-XML"],t.EMPTYTAGS=["MATH","MROW","MPADDED","MACTION","NONE","MSTYLE","SEMANTICS"],t.DISPLAYTAGS=["MROOT","MSQRT"],t.directSpeechKeys=["aria-label","exact-speech","alt"],t.hasMathTag=function(e){return!!e&&"MATH"===r.tagName(e)},t.hasLeafTag=i,t.hasIgnoreTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.IGNORETAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.hasEmptyTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.EMPTYTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.hasDisplayTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.DISPLAYTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.isOrphanedGlyph=function(e){return!!e&&"MGLYPH"===r.tagName(e)&&!i(e.parentNode)},t.purgeNodes=function(e){const n=[];for(let i,o=0;i=e[o];o++){if(i.nodeType!==r.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE)continue;const e=r.tagName(i);-1===t.IGNORETAGS.indexOf(e)&&(-1!==t.EMPTYTAGS.indexOf(e)&&0===i.childNodes.length||n.push(i))}return n},t.isZeroLength=function(e){if(!e)return!1;if(-1!==["negativeveryverythinmathspace","negativeverythinmathspace","negativethinmathspace","negativemediummathspace","negativethickmathspace","negativeverythickmathspace","negativeveryverythickmathspace"].indexOf(e))return!0;const t=e.match(/[0-9.]+/);return!!t&&0===parseFloat(t[0])},t.addAttributes=function(e,n){if(n.hasAttributes()){const r=n.attributes;for(let n=r.length-1;n>=0;n--){const i=r[n].name;i.match(/^ext/)&&(e.attributes[i]=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0),-1!==t.directSpeechKeys.indexOf(i)&&(e.attributes["ext-speech"]=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0),i.match(/texclass$/)&&(e.attributes.texclass=r[n].value),"href"===i&&(e.attributes.href=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0)}}},t.getEmbellishedInner=function e(t){return t&&t.embellished&&t.childNodes.length>0?e(t.childNodes[0]):t},t.sliceNodes=o,t.partitionNodes=function(e,t){let n=e;const r=[],i=[];let s=null;do{s=o(n,t),i.push(s.head),r.push(s.div),n=s.tail}while(s.div);return r.pop(),{rel:r,comp:i}}},9135:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(985),i=n(8171),o=n(1848),s=n(144);t.AbstractSpeechGenerator=class{constructor(){this.modality=i.addPrefix("speech"),this.rebuilt_=null,this.options_={}}getRebuilt(){return this.rebuilt_}setRebuilt(e){this.rebuilt_=e}setOptions(e){this.options_=e||{},this.modality=i.addPrefix(this.options_.modality||"speech")}getOptions(){return this.options_}start(){}end(){}generateSpeech(e,t){return this.rebuilt_||(this.rebuilt_=new o.RebuildStree(t)),(0,r.setup)(this.options_),s.computeMarkup(this.getRebuilt().xml)}}},3153:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AdhocSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135);class i extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){const n=this.generateSpeech(e,t);return e.setAttribute(this.modality,n),n}}t.AdhocSpeechGenerator=i},6281:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ColorGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8171),i=n(1123),o=n(1848),s=n(8835),a=n(9135);class c extends a.AbstractSpeechGenerator{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.modality=(0,r.addPrefix)("foreground"),this.contrast=new i.ContrastPicker}static visitStree_(e,t,n){if(e.childNodes.length){if(e.contentNodes.length&&("punctuated"===e.type&&e.contentNodes.forEach((e=>n[e.id]=!0)),"implicit"!==e.role&&t.push(e.contentNodes.map((e=>e.id)))),e.childNodes.length){if("implicit"===e.role){const r=[];let i=[];for(const t of e.childNodes){const e=[];c.visitStree_(t,e,n),e.length<=2&&r.push(e.shift()),i=i.concat(e)}return t.push(r),void i.forEach((e=>t.push(e)))}e.childNodes.forEach((e=>c.visitStree_(e,t,n)))}}else n[e.id]||t.push(e.id)}getSpeech(e,t){return s.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}generateSpeech(e,t){return this.getRebuilt()||this.setRebuilt(new o.RebuildStree(e)),this.colorLeaves_(e),s.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}colorLeaves_(e){const t=[];c.visitStree_(this.getRebuilt().streeRoot,t,{});for(const n of t){const t=this.contrast.generate();let r=!1;r=Array.isArray(n)?n.map((n=>this.colorLeave_(e,n,t))).reduce(((e,t)=>e||t),!1):this.colorLeave_(e,n.toString(),t),r&&this.contrast.increment()}}colorLeave_(e,t,n){const r=s.getBySemanticId(e,t);return!!r&&(r.setAttribute(this.modality,n),!0)}}t.ColorGenerator=c},1565:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DirectSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8835),i=n(9135);class o extends i.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return r.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}}t.DirectSpeechGenerator=o},7721:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DummySpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135);class i extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return""}}t.DummySpeechGenerator=i},1558:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.NodeSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8835),i=n(7486);class o extends i.TreeSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return super.getSpeech(e,t),r.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}}t.NodeSpeechGenerator=o},7317:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.generatorMapping_=t.generator=void 0;const r=n(3153),i=n(6281),o=n(1565),s=n(7721),a=n(1558),c=n(5778),l=n(7486);t.generator=function(e){return(t.generatorMapping_[e]||t.generatorMapping_.Direct)()},t.generatorMapping_={Adhoc:()=>new r.AdhocSpeechGenerator,Color:()=>new i.ColorGenerator,Direct:()=>new o.DirectSpeechGenerator,Dummy:()=>new s.DummySpeechGenerator,Node:()=>new a.NodeSpeechGenerator,Summary:()=>new c.SummarySpeechGenerator,Tree:()=>new l.TreeSpeechGenerator}},144:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.computeSummary_=t.retrieveSummary=t.connectAllMactions=t.connectMactions=t.nodeAtPosition_=t.computePrefix_=t.retrievePrefix=t.addPrefix=t.addModality=t.addSpeech=t.recomputeMarkup=t.computeMarkup=t.recomputeSpeech=t.computeSpeech=void 0;const r=n(4253),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(8171),a=n(6060),c=n(1784),l=n(8835);function u(e){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(e)}function d(e){return u(c.SemanticTree.fromNode(e).xml())}function h(e){const t=d(e);return r.markup(t)}function p(e){const t=f(e);return r.markup(t)}function f(e){const t=c.SemanticTree.fromRoot(e),n=o.evalXPath('.//*[@id="'+e.id+'"]',t.xml());let r=n[0];return n.length>1&&(r=m(e,n)||r),r?a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().runInSetting({modality:"prefix",domain:"default",style:"default",strict:!0,speech:!0},(function(){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(r)})):[]}function m(e,t){const n=t[0];if(!e.parent)return n;const r=[];for(;e;)r.push(e.id),e=e.parent;const i=function(e,t){for(;t.length&&t.shift().toString()===e.getAttribute("id")&&e.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode;)e=e.parentNode.parentNode;return!t.length};for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if(i(e,r.slice()))return e;return n}function g(e){return e?a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().runInSetting({modality:"summary",strict:!1,speech:!0},(function(){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(e)})):[]}t.computeSpeech=u,t.recomputeSpeech=d,t.computeMarkup=function(e){const t=u(e);return r.markup(t)},t.recomputeMarkup=h,t.addSpeech=function(e,t,n){const o=i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",t.id.toString())[0],a=o?r.markup(u(o)):h(t);e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.SPEECH,a)},t.addModality=function(e,t,n){const r=h(t);e.setAttribute(n,r)},t.addPrefix=function(e,t){const n=p(t);n&&e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.PREFIX,n)},t.retrievePrefix=p,t.computePrefix_=f,t.nodeAtPosition_=m,t.connectMactions=function(e,t,n){const r=i.querySelectorAll(t,"maction");for(let t,o=0;t=r[o];o++){const r=t.getAttribute("id"),o=i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(e,"id",r)[0];if(!o)continue;const a=t.childNodes[1],c=a.getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID);let u=l.getBySemanticId(e,c);if(u&&"dummy"!==u.getAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE))continue;if(u=o.childNodes[0],u.getAttribute("sre-highlighter-added"))continue;const d=a.getAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT);d&&u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,d),u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE,"dummy"),u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ID,c);i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",c)[0].setAttribute("alternative",c)}},t.connectAllMactions=function(e,t){const n=i.querySelectorAll(e,"maction");for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++){const n=e.childNodes[1].getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID);i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(t,"id",n)[0].setAttribute("alternative",n)}},t.retrieveSummary=function(e){const t=g(e);return r.markup(t)},t.computeSummary_=g},5778:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SummarySpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135),i=n(144);class o extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return i.connectAllMactions(t,this.getRebuilt().xml),this.generateSpeech(e,t)}}t.SummarySpeechGenerator=o},7486:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.TreeSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8171),i=n(8835),o=n(9135),s=n(144);class a extends o.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){const n=this.generateSpeech(e,t),o=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict;for(const n in o){const a=o[n],c=i.getBySemanticId(t,n),l=i.getBySemanticId(e,n);c&&l&&(this.modality&&this.modality!==r.Attribute.SPEECH?s.addModality(l,a,this.modality):s.addSpeech(l,a,this.getRebuilt().xml),this.modality===r.Attribute.SPEECH&&s.addPrefix(l,a))}return n}}t.TreeSpeechGenerator=a},650:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.INTERVALS=t.makeLetter=t.numberRules=t.alphabetRules=t.getFont=t.makeInterval=t.generate=t.makeDomains_=t.Domains_=t.Base=t.Embellish=t.Font=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(2371),o=n(4524),s=n(3319),a=n(4161);var c,l,u;function d(){const e=o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS,n=(e,t)=>{const n={};return Object.keys(e).forEach((e=>n[e]=!0)),Object.keys(t).forEach((e=>n[e]=!0)),Object.keys(n)};t.Domains_.small=n(e.smallPrefix,e.letterTrans),t.Domains_.capital=n(e.capPrefix,e.letterTrans),t.Domains_.digit=n(e.digitPrefix,e.digitTrans)}function h(e){const t=e.toString(16).toUpperCase();return t.length>3?t:("000"+t).slice(-4)}function p([e,t],n){const r=parseInt(e,16),i=parseInt(t,16),o=[];for(let e=r;e<=i;e++){let t=h(e);!1!==n[t]&&(t=n[t]||t,o.push(t))}return o}function f(e){const t="normal"===e||"fullwidth"===e?"":o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.font[e]||o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.embellish[e]||"";return(0,s.localeFontCombiner)(t)}function m(e,n,r,i,s,a){const c=f(i);for(let i,l,u,d=0;i=e[d],l=n[d],u=r[d];d++){const e=a?o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.capPrefix:o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.smallPrefix,n=a?t.Domains_.capital:t.Domains_.small;S(c.combiner,i,l,u,c.font,e,s,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.letterTrans,n)}}function g(e,n,r,i,s){const a=f(r);for(let r,c,l=0;r=e[l],c=n[l];l++){const e=o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.digitPrefix,n=l+s;S(a.combiner,r,c,n,a.font,e,i,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.digitTrans,t.Domains_.digit)}}function S(e,t,n,r,i,o,s,c,l){for(let u,d=0;u=l[d];d++){const l=u in c?c[u]:c.default,d=u in o?o[u]:o.default;a.defineRule(t.toString(),u,"default",s,n,e(l(r),i,d))}}!function(e){e.BOLD="bold",e.BOLDFRAKTUR="bold-fraktur",e.BOLDITALIC="bold-italic",e.BOLDSCRIPT="bold-script",e.DOUBLESTRUCK="double-struck",e.FULLWIDTH="fullwidth",e.FRAKTUR="fraktur",e.ITALIC="italic",e.MONOSPACE="monospace",e.NORMAL="normal",e.SCRIPT="script",e.SANSSERIF="sans-serif",e.SANSSERIFITALIC="sans-serif-italic",e.SANSSERIFBOLD="sans-serif-bold",e.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC="sans-serif-bold-italic"}(c=t.Font||(t.Font={})),function(e){e.SUPER="super",e.SUB="sub",e.CIRCLED="circled",e.PARENTHESIZED="parenthesized",e.PERIOD="period",e.NEGATIVECIRCLED="negative-circled",e.DOUBLECIRCLED="double-circled",e.CIRCLEDSANSSERIF="circled-sans-serif",e.NEGATIVECIRCLEDSANSSERIF="negative-circled-sans-serif",e.COMMA="comma",e.SQUARED="squared",e.NEGATIVESQUARED="negative-squared"}(l=t.Embellish||(t.Embellish={})),function(e){e.LATINCAP="latinCap",e.LATINSMALL="latinSmall",e.GREEKCAP="greekCap",e.GREEKSMALL="greekSmall",e.DIGIT="digit"}(u=t.Base||(t.Base={})),t.Domains_={small:["default"],capital:["default"],digit:["default"]},t.makeDomains_=d,t.generate=function(e){const n=r.default.getInstance().locale;r.default.getInstance().locale=e,i.setLocale(),a.addSymbolRules({locale:e}),d();const s=t.INTERVALS;for(let e,t=0;e=s[t];t++){const t=p(e.interval,e.subst),n=t.map((function(e){return String.fromCodePoint(parseInt(e,16))}));if("offset"in e)g(t,n,e.font,e.category,e.offset||0);else{m(t,n,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS[e.base],e.font,e.category,!!e.capital)}}r.default.getInstance().locale=n,i.setLocale()},t.makeInterval=p,t.getFont=f,t.alphabetRules=m,t.numberRules=g,t.makeLetter=S,t.INTERVALS=[{interval:["1D400","1D419"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D41A","1D433"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D56C","1D585"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDFRAKTUR},{interval:["1D586","1D59F"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDFRAKTUR},{interval:["1D468","1D481"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D482","1D49B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D4D0","1D4E9"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDSCRIPT},{interval:["1D4EA","1D503"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDSCRIPT},{interval:["1D538","1D551"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D53A":"2102","1D53F":"210D","1D545":"2115","1D547":"2119","1D548":"211A","1D549":"211D","1D551":"2124"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D552","1D56B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D504","1D51D"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D506":"212D","1D50B":"210C","1D50C":"2111","1D515":"211C","1D51D":"2128"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.FRAKTUR},{interval:["1D51E","1D537"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.FRAKTUR},{interval:["FF21","FF3A"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["FF41","FF5A"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["1D434","1D44D"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D44E","1D467"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{"1D455":"210E"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D670","1D689"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["1D68A","1D6A3"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["0041","005A"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["0061","007A"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["1D49C","1D4B5"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D49D":"212C","1D4A0":"2130","1D4A1":"2131","1D4A3":"210B","1D4A4":"2110","1D4A7":"2112","1D4A8":"2133","1D4AD":"211B"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SCRIPT},{interval:["1D4B6","1D4CF"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{"1D4BA":"212F","1D4BC":"210A","1D4C4":"2134"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SCRIPT},{interval:["1D5A0","1D5B9"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D5BA","1D5D3"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D608","1D621"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFITALIC},{interval:["1D622","1D63B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFITALIC},{interval:["1D5D4","1D5ED"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D5EE","1D607"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D63C","1D655"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D656","1D66F"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["0391","03A9"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{"03A2":"03F4"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["03B0","03D0"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{"03B0":"2207","03CA":"2202","03CB":"03F5","03CC":"03D1","03CD":"03F0","03CE":"03D5","03CF":"03F1","03D0":"03D6"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["1D6A8","1D6C0"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D6C1","1D6E1"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D6E2","1D6FA"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D6FB","1D71B"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D71C","1D734"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D735","1D755"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D756","1D76E"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D76F","1D78F"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D790","1D7A8"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D7A9","1D7C9"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["0030","0039"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["2070","2079"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2071:"00B9",2072:"00B2",2073:"00B3"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.SUPER},{interval:["2080","2089"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.SUB},{interval:["245F","2473"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{"245F":"24EA"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["3251","325F"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:21,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["32B1","32BF"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:36,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["2474","2487"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:1,category:"No",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["2487","249B"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2487:"1F100"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.PERIOD},{interval:["2775","277F"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2775:"24FF"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED},{interval:["24EB","24F4"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:11,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED},{interval:["24F5","24FE"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:1,category:"No",font:l.DOUBLECIRCLED},{interval:["277F","2789"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{"277F":"1F10B"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLEDSANSSERIF},{interval:["2789","2793"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2789:"1F10C"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLEDSANSSERIF},{interval:["FF10","FF19"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["1D7CE","1D7D7"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D7D8","1D7E1"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D7E2","1D7EB"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D7EC","1D7F5"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D7F6","1D7FF"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["1F101","1F10A"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.COMMA},{interval:["24B6","24CF"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["24D0","24E9"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"So",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["1F110","1F129"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["249C","24B5"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"So",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["1F130","1F149"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.SQUARED},{interval:["1F170","1F189"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.NEGATIVESQUARED},{interval:["1F150","1F169"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED}]},3955:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Parser=t.Comparator=t.ClearspeakPreferences=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(8310),s=n(8310),a=n(4161),c=n(6060);class l extends o.DynamicCstr{constructor(e,t){super(e),this.preference=t}static comparator(){return new d(r.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr,s.DynamicProperties.createProp([o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.LOCALE]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.MODALITY]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.DOMAIN]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.STYLE]]))}static fromPreference(e){const t=e.split(":"),n={},r=u.getProperties(),i=Object.keys(r);for(let e,o=0;e=t[o];o++){const t=e.split("_");if(-1===i.indexOf(t[0]))continue;const o=t[1];o&&o!==l.AUTO&&-1!==r[t[0]].indexOf(o)&&(n[t[0]]=t[1])}return n}static toPreference(e){const t=Object.keys(e),n=[];for(let r=0;rs?-1:o0&&t<20&&n>0&&n<11}function _(e){return i.default.getInstance().style===e}function C(e){if(!e.hasAttribute("annotation"))return!1;const t=e.getAttribute("annotation");return!!/clearspeak:simple$|clearspeak:simple;/.exec(t)}function T(e){if(C(e))return!0;if("subscript"!==e.tagName)return!1;const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes,n=t[1];return"identifier"===t[0].tagName&&(v(n)||"infixop"===n.tagName&&n.hasAttribute("role")&&"implicit"===n.getAttribute("role")&&O(n))}function v(e){return"number"===e.tagName&&e.hasAttribute("role")&&"integer"===e.getAttribute("role")}function O(e){return o.evalXPath("children/*",e).every((e=>v(e)||"identifier"===e.tagName))}function M(e){return"text"===e.type||"punctuated"===e.type&&"text"===e.role&&E(e.childNodes[0])&&I(e.childNodes.slice(1))||"identifier"===e.type&&"unit"===e.role||"infixop"===e.type&&("implicit"===e.role||"unit"===e.role)}function I(e){for(let t=0;t10?s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t):s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(t)},t.NESTING_DEPTH=null,t.nestingDepth=function(e){let n=0;const r=e.textContent,i="open"===e.getAttribute("role")?0:1;let o=e.parentNode;for(;o;)"fenced"===o.tagName&&o.childNodes[0].childNodes[i].textContent===r&&n++,o=o.parentNode;return t.NESTING_DEPTH=n>1?s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(n):"",t.NESTING_DEPTH},t.matchingFences=function(e){const t=e.previousSibling;let n,r;return t?(n=t,r=e):(n=e,r=e.nextSibling),r&&(0,h.isMatchingFence)(n.textContent,r.textContent)?[e]:[]},t.insertNesting=L,c.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection("insertNesting",L),t.fencedArguments=function(e){const t=r.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes),n=o.evalXPath("../../children/*",e),i=t.indexOf(e);return x(n[i])||x(n[i+1])?[e]:[]},t.simpleArguments=function(e){const t=r.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes),n=o.evalXPath("../../children/*",e),i=t.indexOf(e);return R(n[i])&&n[i+1]&&(R(n[i+1])||"root"===n[i+1].tagName||"sqrt"===n[i+1].tagName||"superscript"===n[i+1].tagName&&n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0]&&("number"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName||"identifier"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName)&&("2"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent||"3"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent))?[e]:[]},t.simpleFactor_=R,t.fencedFactor_=x,t.layoutFactor_=P,t.wordOrdinal=function(e){return s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(parseInt(e.textContent,10))}},5659:function(e,t,n){var r=this&&this.__awaiter||function(e,t,n,r){return new(n||(n=Promise))((function(i,o){function s(e){try{c(r.next(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function a(e){try{c(r.throw(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function c(e){var t;e.done?i(e.value):(t=e.value,t instanceof n?t:new n((function(e){e(t)}))).then(s,a)}c((r=r.apply(e,t||[])).next())}))};Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.loadAjax=t.loadFileSync=t.loadFile=t.parseMaps=t.retrieveFiles=t.standardLoader=t.loadLocale=t.store=void 0;const i=n(9501),o=n(4886),s=n(4998),a=n(7129),c=n(4755),l=n(8310),u=n(4161),d=n(6060),h=n(2371),p=n(650);t.store=u;const f={functions:u.addFunctionRules,symbols:u.addSymbolRules,units:u.addUnitRules,si:u.setSiPrefixes};let m=!1;function g(e=o.default.getInstance().locale){o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]||(o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!1,!1],function(e){if(o.default.getInstance().isIE&&o.default.getInstance().mode===s.Mode.HTTP)return void y(e);b(e)}(e))}function S(){switch(o.default.getInstance().mode){case s.Mode.ASYNC:return A;case s.Mode.HTTP:return C;case s.Mode.SYNC:default:return _}}function b(e){const t=o.default.getInstance().customLoader?o.default.getInstance().customLoader:S(),n=new Promise((n=>{t(e).then((t=>{N(t),o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!0,!0],n(e)}),(t=>{o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!0,!1],console.error(`Unable to load locale: ${e}`),o.default.getInstance().locale=o.default.getInstance().defaultLocale,n(e)}))}));o.EnginePromise.promises[e]=n}function N(e){E(JSON.parse(e))}function E(e,t){let n=!0;for(let r,i=0;r=Object.keys(e)[i];i++){const i=r.split("/");t&&t!==i[0]||("rules"===i[1]?d.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().addStore(e[r]):"messages"===i[1]?(0,h.completeLocale)(e[r]):(n&&(p.generate(i[0]),n=!1),e[r].forEach(f[i[1]])))}}function y(e,t){let n=t||1;i.mapsForIE?E(i.mapsForIE,e):n<=5&&setTimeout((()=>y(e,n++)).bind(this),300)}function A(e){const t=a.localePath(e);return new Promise(((e,n)=>{c.default.fs.readFile(t,"utf8",((t,r)=>{if(t)return n(t);e(r)}))}))}function _(e){const t=a.localePath(e);return new Promise(((e,n)=>{let r="{}";try{r=c.default.fs.readFileSync(t,"utf8")}catch(e){return n(e)}e(r)}))}function C(e){const t=a.localePath(e),n=new XMLHttpRequest;return new Promise(((e,r)=>{n.onreadystatechange=function(){if(4===n.readyState){const t=n.status;0===t||t>=200&&t<400?e(n.responseText):r(t)}},n.open("GET",t,!0),n.send()}))}t.loadLocale=function(e=o.default.getInstance().locale){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return m||(g(l.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE),m=!0),o.EnginePromise.promises[l.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE].then((()=>r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){const t=o.default.getInstance().defaultLocale;return t?(g(t),o.EnginePromise.promises[t].then((()=>r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return g(e),o.EnginePromise.promises[e]}))))):(g(e),o.EnginePromise.promises[e])}))))}))},t.standardLoader=S,t.retrieveFiles=b,t.parseMaps=N,t.loadFile=A,t.loadFileSync=_,t.loadAjax=C},3784:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.leftSubscriptBrief=t.leftSuperscriptBrief=t.leftSubscriptVerbose=t.leftSuperscriptVerbose=t.baselineBrief=t.baselineVerbose=void 0;const r=n(3269);t.baselineVerbose=function(e){return r.baselineVerbose(e).replace(/-$/,"")},t.baselineBrief=function(e){return r.baselineBrief(e).replace(/-$/,"")},t.leftSuperscriptVerbose=function(e){return r.superscriptVerbose(e).replace(/^exposant/,"exposant gauche")},t.leftSubscriptVerbose=function(e){return r.subscriptVerbose(e).replace(/^indice/,"indice gauche")},t.leftSuperscriptBrief=function(e){return r.superscriptBrief(e).replace(/^sup/,"sup gauche")},t.leftSubscriptBrief=function(e){return r.subscriptBrief(e).replace(/^sub/,"sub gauche")}},4972:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MathspeakRules=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(931),o=n(3784),s=n(3269),a=n(2110),c=n(7278),l=n(9771);t.MathspeakRules=function(){c.addStore(r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak","",{CQFspaceoutNumber:s.spaceoutNumber,CQFspaceoutIdentifier:s.spaceoutIdentifier,CSFspaceoutText:s.spaceoutText,CSFopenFracVerbose:s.openingFractionVerbose,CSFcloseFracVerbose:s.closingFractionVerbose,CSFoverFracVerbose:s.overFractionVerbose,CSFopenFracBrief:s.openingFractionBrief,CSFcloseFracBrief:s.closingFractionBrief,CSFopenFracSbrief:s.openingFractionSbrief,CSFcloseFracSbrief:s.closingFractionSbrief,CSFoverFracSbrief:s.overFractionSbrief,CSFvulgarFraction:a.vulgarFraction,CQFvulgarFractionSmall:s.isSmallVulgarFraction,CSFopenRadicalVerbose:s.openingRadicalVerbose,CSFcloseRadicalVerbose:s.closingRadicalVerbose,CSFindexRadicalVerbose:s.indexRadicalVerbose,CSFopenRadicalBrief:s.openingRadicalBrief,CSFcloseRadicalBrief:s.closingRadicalBrief,CSFindexRadicalBrief:s.indexRadicalBrief,CSFopenRadicalSbrief:s.openingRadicalSbrief,CSFindexRadicalSbrief:s.indexRadicalSbrief,CQFisSmallRoot:s.smallRoot,CSFsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFbaselineVerbose:s.baselineVerbose,CSFbaselineBrief:s.baselineBrief,CSFleftsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFleftsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFrightsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFrightsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFleftsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFleftsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFrightsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFrightsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFunderscript:s.nestedUnderscript,CSFoverscript:s.nestedOverscript,CSFendscripts:s.endscripts,CTFordinalCounter:a.ordinalCounter,CTFwordCounter:a.wordCounter,CTFcontentIterator:i.contentIterator,CQFdetIsSimple:s.determinantIsSimple,CSFRemoveParens:s.removeParens,CQFresetNesting:s.resetNestingDepth,CGFbaselineConstraint:s.generateBaselineConstraint,CGFtensorRules:s.generateTensorRules}),c.addStore("es.speech.mathspeak",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CTFunitMultipliers:l.unitMultipliers,CQFoneLeft:l.oneLeft}),c.addStore("fr.speech.mathspeak",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CSFbaselineVerbose:o.baselineVerbose,CSFbaselineBrief:o.baselineBrief,CSFleftsuperscriptVerbose:o.leftSuperscriptVerbose,CSFleftsubscriptVerbose:o.leftSubscriptVerbose,CSFleftsuperscriptBrief:o.leftSuperscriptBrief,CSFleftsubscriptBrief:o.leftSubscriptBrief})}},3269:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.smallRoot=t.generateTensorRules=t.removeParens=t.generateBaselineConstraint=t.determinantIsSimple=t.nestedOverscript=t.endscripts=t.overscoreNestingDepth=t.nestedUnderscript=t.underscoreNestingDepth=t.indexRadicalSbrief=t.openingRadicalSbrief=t.indexRadicalBrief=t.closingRadicalBrief=t.openingRadicalBrief=t.indexRadicalVerbose=t.closingRadicalVerbose=t.openingRadicalVerbose=t.getRootIndex=t.nestedRadical=t.radicalNestingDepth=t.baselineBrief=t.baselineVerbose=t.superscriptBrief=t.superscriptVerbose=t.subscriptBrief=t.subscriptVerbose=t.nestedSubSuper=t.isSmallVulgarFraction=t.overFractionSbrief=t.closingFractionSbrief=t.openingFractionSbrief=t.closingFractionBrief=t.openingFractionBrief=t.overFractionVerbose=t.closingFractionVerbose=t.openingFractionVerbose=t.nestedFraction=t.fractionNestingDepth=t.computeNestingDepth_=t.containsAttr=t.getNestingDepth=t.resetNestingDepth=t.nestingBarriers=t.spaceoutIdentifier=t.spaceoutNumber=t.spaceoutNodes=t.spaceoutText=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(4524),a=n(7793);let c={};function l(e,t){const n=Array.from(e.textContent),r=[],i=a.default.getInstance(),o=e.ownerDocument;for(let e,s=0;e=n[s];s++){const n=i.getNodeFactory().makeLeafNode(e,"unknown"),s=i.identifierNode(n,"unknown","");t(s),r.push(s.xml(o))}return r}function u(e,n,o,s,a,l){s=s||t.nestingBarriers,a=a||{},l=l||function(e){return!1};const u=i.serializeXml(n);if(c[e]||(c[e]={}),c[e][u])return c[e][u];if(l(n)||o.indexOf(n.tagName)<0)return 0;const d=h(n,o,r.setdifference(s,o),a,l,0);return c[e][u]=d,d}function d(e,t){if(!e.attributes)return!1;const n=i.toArray(e.attributes);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)if(t[e.nodeName]===e.nodeValue)return!0;return!1}function h(e,t,n,r,o,s){if(o(e)||n.indexOf(e.tagName)>-1||d(e,r))return s;if(t.indexOf(e.tagName)>-1&&s++,!e.childNodes||0===e.childNodes.length)return s;const a=i.toArray(e.childNodes);return Math.max.apply(null,a.map((function(e){return h(e,t,n,r,o,s)})))}function p(e){return u("fraction",e,["fraction"],t.nestingBarriers,{},s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth)}function f(e,t,n){const r=p(e),i=Array(r).fill(t);return n&&i.push(n),i.join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_FRAC)}function m(e,t,n){for(;e.parentNode;){const r=e.parentNode,i=r.parentNode;if(!i)break;const o=e.getAttribute&&e.getAttribute("role");("subscript"===i.tagName&&e===r.childNodes[1]||"tensor"===i.tagName&&o&&("leftsub"===o||"rightsub"===o))&&(t=n.sub+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_SUBSUPER+t),("superscript"===i.tagName&&e===r.childNodes[1]||"tensor"===i.tagName&&o&&("leftsuper"===o||"rightsuper"===o))&&(t=n.sup+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_SUBSUPER+t),e=i}return t.trim()}function g(e){return u("radical",e,["sqrt","root"],t.nestingBarriers,{})}function S(e,t,n){const r=g(e),i=b(e);return n=i?s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex(n,i):n,1===r?n:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical(t,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(r-1),n)}function b(e){const t="sqrt"===e.tagName?"2":o.evalXPath("children/*[1]",e)[0].textContent.trim();return s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MSroots[t]||""}function N(e){return u("underscore",e,["underscore"],t.nestingBarriers,{},(function(e){return e.tagName&&"underscore"===e.tagName&&"underaccent"===e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role")}))}function E(e){return u("overscore",e,["overscore"],t.nestingBarriers,{},(function(e){return e.tagName&&"overscore"===e.tagName&&"overaccent"===e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role")}))}t.spaceoutText=function(e){return Array.from(e.textContent).join(" ")},t.spaceoutNodes=l,t.spaceoutNumber=function(e){return l(e,(function(e){e.textContent.match(/\W/)||(e.type="number")}))},t.spaceoutIdentifier=function(e){return l(e,(function(e){e.font="unknown",e.type="identifier"}))},t.nestingBarriers=["cases","cell","integral","line","matrix","multiline","overscore","root","row","sqrt","subscript","superscript","table","underscore","vector"],t.resetNestingDepth=function(e){return c={},[e]},t.getNestingDepth=u,t.containsAttr=d,t.computeNestingDepth_=h,t.fractionNestingDepth=p,t.nestedFraction=f,t.openingFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.START,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_V)},t.closingFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.END,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_V)},t.overFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER)},t.openingFractionBrief=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.START,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_B)},t.closingFractionBrief=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.END,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_B)},t.openingFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_S:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_S)},t.closingFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDFRAC:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDFRAC)},t.overFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER)},t.isSmallVulgarFraction=function(e){return s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth(e)?[e]:[]},t.nestedSubSuper=m,t.subscriptVerbose=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUBSCRIPT,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.subscriptBrief=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.superscriptVerbose=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPERSCRIPT,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.superscriptBrief=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.baselineVerbose=function(e){const t=m(e,"",{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB});return t?t.replace(new RegExp(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB+"$"),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUBSCRIPT).replace(new RegExp(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER+"$"),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPERSCRIPT):s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.BASELINE},t.baselineBrief=function(e){return m(e,"",{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})||s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.BASE},t.radicalNestingDepth=g,t.nestedRadical=S,t.getRootIndex=b,t.openingRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.openingRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.openingRadicalSbrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOT)},t.indexRadicalSbrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.INDEX)},t.underscoreNestingDepth=N,t.nestedUnderscript=function(e){const t=N(e);return Array(t).join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.UNDER)+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.UNDERSCRIPT},t.overscoreNestingDepth=E,t.endscripts=function(e){return s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDSCRIPTS},t.nestedOverscript=function(e){const t=E(e);return Array(t).join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.OVER)+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.OVERSCRIPT},t.determinantIsSimple=function(e){if("matrix"!==e.tagName||"determinant"!==e.getAttribute("role"))return[];const t=o.evalXPath("children/row/children/cell/children/*",e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if("number"!==e.tagName){if("identifier"===e.tagName){const t=e.getAttribute("role");if("latinletter"===t||"greekletter"===t||"otherletter"===t)continue}return[]}return[e]},t.generateBaselineConstraint=function(){const e=e=>e.map((e=>"ancestor::"+e)),t=e=>"not("+e+")",n=t(e(["subscript","superscript","tensor"]).join(" or ")),r=e(["relseq","multrel"]),i=e(["fraction","punctuation","fenced","sqrt","root"]);let o=[];for(let e,t=0;e=i[t];t++)o=o.concat(r.map((function(t){return e+"/"+t})));return[["ancestor::*/following-sibling::*",n,t(o.join(" | "))].join(" and ")]},t.removeParens=function(e){if(!e.childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes.length)return"";const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent;return t.match(/^\(.+\)$/)?t.slice(1,-1):t};const y=new Map([[3,"CSFleftsuperscript"],[4,"CSFleftsubscript"],[2,"CSFbaseline"],[1,"CSFrightsubscript"],[0,"CSFrightsuperscript"]]),A=new Map([[4,2],[3,3],[2,1],[1,4],[0,5]]);function _(e){const t=[];let n="",r="",i=parseInt(e,2);for(let e=0;e<5;e++){const o="children/*["+A.get(e)+"]";if(1&i){const t=y.get(e%5);n="[t] "+t+"Verbose; [n] "+o+";"+n,r="[t] "+t+"Brief; [n] "+o+";"+r}else t.unshift("name("+o+')="empty"');i>>=1}return[t,n,r]}t.generateTensorRules=function(e,t=!0){const n=["11111","11110","11101","11100","10111","10110","10101","10100","01111","01110","01101","01100"];for(let r,i=0;r=n[i];i++){let n="tensor"+r,[i,o,s]=_(r);e.defineRule(n,"default",o,"self::tensor",...i),t&&(e.defineRule(n,"brief",s,"self::tensor",...i),e.defineRule(n,"sbrief",s,"self::tensor",...i));const a=y.get(2);o+="; [t]"+a+"Verbose",s+="; [t]"+a+"Brief",n+="-baseline";const c="((.//*[not(*)])[last()]/@id)!=(((.//ancestor::fraction|ancestor::root|ancestor::sqrt|ancestor::cell|ancestor::line|ancestor::stree)[1]//*[not(*)])[last()]/@id)";e.defineRule(n,"default",o,"self::tensor",c,...i),t&&(e.defineRule(n,"brief",s,"self::tensor",c,...i),e.defineRule(n,"sbrief",s,"self::tensor",c,...i))}},t.smallRoot=function(e){let t=Object.keys(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MSroots).length;if(!t)return[];if(t++,!e.childNodes||0===e.childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes)return[];const n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent;if(!/^\d+$/.test(n))return[];const r=parseInt(n,10);return r>1&&r<=t?[e]:[]}},9570:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.implicitIterator=t.relationIterator=t.propagateNumber=t.checkParent_=t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_=t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_=t.enlargeFence=t.indexRadical=t.closingRadical=t.openingRadical=t.radicalNestingDepth=t.nestedRadical=t.overBevelledFraction=t.overFraction=t.closingFraction=t.openingFraction=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(1058),a=n(4886),c=n(4036),l=n(241),u=n(4524),d=n(3269);function h(e,t){const n=p(e);return 1===n?t:new Array(n).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED)+t}function p(e,t){const n=t||0;return e.parentNode?p(e.parentNode,"root"===e.tagName||"sqrt"===e.tagName?n+1:n):n}function f(e){const t="\u2820";if(1===e.length)return t+e;const n=e.split("");return n.every((function(e){return"\u2833"===e}))?t+n.join(t):e.slice(0,-1)+t+e.slice(-1)}function m(e,n){const r=e.parent;if(!r)return!1;const i=r.type;return-1!==t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_.indexOf(i)||"prefixop"===i&&"negative"===r.role&&!n.script||"prefixop"===i&&"geometry"===r.role||!("punctuated"!==i||n.enclosed&&"text"!==r.role)}function g(e,n){return e.childNodes.length?(-1!==t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_.indexOf(e.type)&&(n.script=!0),"fenced"===e.type?(n.number=!1,n.enclosed=!0,["",n]):(m(e,n)&&(n.number=!0,n.enclosed=!1),["",n])):(m(e,n)&&(n.number=!0,n.script=!1,n.enclosed=!1),[n.number?"number":"",{number:!1,enclosed:n.enclosed,script:n.script}])}t.openingFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_START},t.closingFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_END},t.overFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_OVER},t.overBevelledFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+"\u2838"+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_OVER},t.nestedRadical=h,t.radicalNestingDepth=p,t.openingRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.enlargeFence=f,s.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection("enlargeFence",f),t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_=["multirel","relseq","appl","row","line"],t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_=["subscript","superscript","overscore","underscore"],t.checkParent_=m,t.propagateNumber=g,(0,c.register)(new l.SemanticVisitor("nemeth","number",g,{number:!0})),t.relationIterator=function(e,t){const n=e.slice(0);let s,c=!0;return s=e.length>0?o.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=s.shift(),o=n.shift(),l=n[0],h=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!e)return h;const p=o?d.nestedSubSuper(o,"",{sup:u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB}):"",f=o&&"EMPTY"!==i.tagName(o)||c&&e.parentNode.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode.previousSibling?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"+p},{})]:[],m=l&&"EMPTY"!==i.tagName(l)||!s.length&&e.parentNode.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode.nextSibling?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"},{})]:[],g=a.default.evaluateNode(e);return c=!1,h.concat(f,g,m)}},t.implicitIterator=function(e,t){const n=e.slice(0);let s;return s=e.length>0?o.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=n.shift(),o=n[0],a=s.shift(),c=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!a)return c;const l=e&&"NUMBER"===i.tagName(e),u=o&&"NUMBER"===i.tagName(o);return c.concat(l&&u&&"space"===a.getAttribute("role")?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"},{})]:[])}}},2110:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ordinalPosition=t.vulgarFraction=t.wordCounter=t.ordinalCounter=void 0;const r=n(1930),i=n(6671),o=n(4524),s=n(9385);t.ordinalCounter=function(e,t){let n=0;return function(){return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(++n)+" "+t}},t.wordCounter=function(e,t){let n=0;return function(){return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToOrdinal(++n,!1)+" "+t}},t.vulgarFraction=function(e){const t=(0,s.convertVulgarFraction)(e,o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER);return t.convertible&&t.enumerator&&t.denominator?[new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t.enumerator),{extid:e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].getAttribute("extid"),separator:""}),new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.vulgarSep,{separator:""}),new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToOrdinal(t.denominator,1!==t.enumerator),{extid:e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("extid")})]:[new r.Span(t.content||"",{extid:e.getAttribute("extid")})]},t.ordinalPosition=function(e){const t=i.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes);return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t.indexOf(e)+1).toString()}},3724:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.BrailleRules=t.OtherRules=t.PrefixRules=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(931),o=n(3269),s=n(9570),a=n(2110),c=n(7278);t.PrefixRules=function(){c.addStore("en.prefix.default","",{CSFordinalPosition:a.ordinalPosition})},t.OtherRules=function(){c.addStore("en.speech.chromevox","",{CTFnodeCounter:i.nodeCounter,CTFcontentIterator:i.contentIterator}),c.addStore("en.speech.emacspeak","en.speech.chromevox",{CQFvulgarFractionSmall:o.isSmallVulgarFraction,CSFvulgarFraction:a.vulgarFraction})},t.BrailleRules=function(){c.addStore("nemeth.braille.default",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CSFopenFraction:s.openingFraction,CSFcloseFraction:s.closingFraction,CSFoverFraction:s.overFraction,CSFoverBevFraction:s.overBevelledFraction,CSFopenRadical:s.openingRadical,CSFcloseRadical:s.closingRadical,CSFindexRadical:s.indexRadical,CSFsubscript:o.subscriptVerbose,CSFsuperscript:o.superscriptVerbose,CSFbaseline:o.baselineVerbose,CGFtensorRules:e=>o.generateTensorRules(e,!1),CTFrelationIterator:s.relationIterator,CTFimplicitIterator:s.implicitIterator})}},9805:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.init=t.INIT_=void 0;const r=n(127),i=n(4972),o=n(3724);t.INIT_=!1,t.init=function(){t.INIT_||((0,i.MathspeakRules)(),(0,r.ClearspeakRules)(),(0,o.PrefixRules)(),(0,o.OtherRules)(),(0,o.BrailleRules)(),t.INIT_=!0)}},7278:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getStore=t.addStore=t.funcStore=void 0;const r=n(8310);t.funcStore=new Map,t.addStore=function(e,n,r){const i={};if(n){const e=t.funcStore.get(n)||{};Object.assign(i,e)}t.funcStore.set(e,Object.assign(i,r))},t.getStore=function(e,n,i){return t.funcStore.get([e,n,i].join("."))||t.funcStore.get([r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE],n,i].join("."))||t.funcStore.get([r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE,n,i].join("."))||{}}},9771:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.oneLeft=t.leftMostUnit=t.rightMostUnit=t.unitMultipliers=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(5024),o=n(4524);t.unitMultipliers=function(e,t){const n=e;let i=0;return function(){const e=r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:a(n[i])&&c(n[i+1])?o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.unitTimes:""},{});return i++,[e]}};const s=["superscript","subscript","overscore","underscore"];function a(e){for(;e;){if("unit"===e.getAttribute("role"))return!0;const t=e.tagName,n=i.evalXPath("children/*",e);e=-1!==s.indexOf(t)?n[0]:n[n.length-1]}return!1}function c(e){for(;e;){if("unit"===e.getAttribute("role"))return!0;e=i.evalXPath("children/*",e)[0]}return!1}t.rightMostUnit=a,t.leftMostUnit=c,t.oneLeft=function(e){for(;e;){if("number"===e.tagName&&"1"===e.textContent)return[e];if("infixop"!==e.tagName||"multiplication"!==e.getAttribute("role")&&"implicit"!==e.getAttribute("role"))return[];e=i.evalXPath("children/*",e)[0]}return[]}},4660:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractWalker=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(4253),o=n(6671),s=n(4998),a=n(985),c=n(6988),l=n(8171),u=n(4524),d=n(1058),h=n(7984),p=n(7317),f=n(144),m=n(3955),g=n(5658),S=n(1848),b=n(8119),N=n(8835),E=n(5024);class y{constructor(e,t,n,r){this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.modifier=!1,this.keyMapping=new Map([[c.KeyCode.UP,this.up.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.DOWN,this.down.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.RIGHT,this.right.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.LEFT,this.left.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.TAB,this.repeat.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.DASH,this.expand.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.SPACE,this.depth.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.HOME,this.home.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.X,this.summary.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.Z,this.detail.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.V,this.virtualize.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.P,this.previous.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.U,this.undo.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.LESS,this.previousRules.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.GREATER,this.nextRules.bind(this)]]),this.cursors=[],this.xml_=null,this.rebuilt_=null,this.focus_=null,this.active_=!1,this.node.id?this.id=this.node.id:this.node.hasAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR)?this.id=this.node.getAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR):(this.node.setAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR,y.ID_COUNTER.toString()),this.id=y.ID_COUNTER++),this.rootNode=N.getSemanticRoot(e),this.rootId=this.rootNode.getAttribute(l.Attribute.ID),this.xmlString_=r,this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.ENTER}getXml(){return this.xml_||(this.xml_=o.parseInput(this.xmlString_)),this.xml_}getRebuilt(){return this.rebuilt_||this.rebuildStree(),this.rebuilt_}isActive(){return this.active_}activate(){this.isActive()||(this.generator.start(),this.toggleActive_())}deactivate(){this.isActive()&&(b.WalkerState.setState(this.id,this.primaryId()),this.generator.end(),this.toggleActive_())}getFocus(e=!1){return this.focus_||(this.focus_=this.singletonFocus(this.rootId)),e&&this.updateFocus(),this.focus_}setFocus(e){this.focus_=e}getDepth(){return this.levels.depth()-1}isSpeech(){return this.generator.modality===l.Attribute.SPEECH}focusDomNodes(){return this.getFocus().getDomNodes()}focusSemanticNodes(){return this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes()}speech(){const e=this.focusDomNodes();if(!e.length)return"";const t=this.specialMove();if(null!==t)return t;switch(this.moved){case b.WalkerMoves.DEPTH:return this.depth_();case b.WalkerMoves.SUMMARY:return this.summary_();case b.WalkerMoves.DETAIL:return this.detail_();default:{const t=[],n=this.focusSemanticNodes();for(let r=0,i=e.length;r0}restoreState(){if(!this.highlighter)return;const e=b.WalkerState.getState(this.id);if(!e)return;let t=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict[e];const n=[];for(;t;)n.push(t.id),t=t.parent;for(n.pop();n.length>0;){this.down();const e=n.pop(),t=this.findFocusOnLevel(e);if(!t)break;this.setFocus(t)}this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.ENTER}updateFocus(){this.setFocus(g.Focus.factory(this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes().map((e=>e.id.toString())),this.getRebuilt(),this.node))}rebuildStree(){this.rebuilt_=new S.RebuildStree(this.getXml()),this.rootId=this.rebuilt_.stree.root.id.toString(),this.generator.setRebuilt(this.rebuilt_),this.skeleton=h.SemanticSkeleton.fromTree(this.rebuilt_.stree),this.skeleton.populate(),this.focus_=this.singletonFocus(this.rootId),this.levels=this.initLevels(),f.connectMactions(this.node,this.getXml(),this.rebuilt_.xml)}previousLevel(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary();return e?N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.PARENT):this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().parent.id.toString()}nextLevel(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary();let t,n;if(e){t=N.splitAttribute(N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.CHILDREN)),n=N.splitAttribute(N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.CONTENT));const r=N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.TYPE),i=N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.ROLE);return this.combineContentChildren(r,i,n,t)}const r=e=>e.id.toString(),i=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict[this.primaryId()];return t=i.childNodes.map(r),n=i.contentNodes.map(r),0===t.length?[]:this.combineContentChildren(i.type,i.role,n,t)}singletonFocus(e){this.getRebuilt();const t=this.retrieveVisuals(e);return this.focusFromId(e,t)}retrieveVisuals(e){if(!this.skeleton)return[e];const t=parseInt(e,10),n=this.skeleton.subtreeNodes(t);if(!n.length)return[e];n.unshift(t);const r={},i=[];E.updateEvaluator(this.getXml());for(const e of n)r[e]||(i.push(e.toString()),r[e]=!0,this.subtreeIds(e,r));return i}subtreeIds(e,t){const n=E.evalXPath(`//*[@data-semantic-id="${e}"]`,this.getXml());E.evalXPath("*//@data-semantic-id",n[0]).forEach((e=>t[parseInt(e.textContent,10)]=!0))}focusFromId(e,t){return g.Focus.factory(e,t,this.getRebuilt(),this.node)}summary(){return this.moved=this.isSpeech()?b.WalkerMoves.SUMMARY:b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone()}detail(){return this.moved=this.isSpeech()?b.WalkerMoves.DETAIL:b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone()}specialMove(){return null}virtualize(e){return this.cursors.push({focus:this.getFocus(),levels:this.levels,undo:e||!this.cursors.length}),this.levels=this.levels.clone(),this.getFocus().clone()}previous(){const e=this.cursors.pop();return e?(this.levels=e.levels,e.focus):this.getFocus()}undo(){let e;do{e=this.cursors.pop()}while(e&&!e.undo);return e?(this.levels=e.levels,e.focus):this.getFocus()}update(e){this.generator.setOptions(e),(0,a.setup)(e).then((()=>p.generator("Tree").getSpeech(this.node,this.getXml())))}nextRules(){const e=this.generator.getOptions();return"speech"!==e.modality?this.getFocus():(s.DOMAIN_TO_STYLES[e.domain]=e.style,e.domain="mathspeak"===e.domain?"clearspeak":"mathspeak",e.style=s.DOMAIN_TO_STYLES[e.domain],this.update(e),this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone())}nextStyle(e,t){if("mathspeak"===e){const e=["default","brief","sbrief"],n=e.indexOf(t);return-1===n?t:n>=e.length-1?e[0]:e[n+1]}if("clearspeak"===e){const e=m.ClearspeakPreferences.getLocalePreferences().en;if(!e)return"default";const n=m.ClearspeakPreferences.relevantPreferences(this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary()),r=m.ClearspeakPreferences.findPreference(t,n),i=e[n].map((function(e){return e.split("_")[1]})),o=i.indexOf(r);if(-1===o)return t;const s=o>=i.length-1?i[0]:i[o+1];return m.ClearspeakPreferences.addPreference(t,n,s)}return t}previousRules(){const e=this.generator.getOptions();return"speech"!==e.modality?this.getFocus():(e.style=this.nextStyle(e.domain,e.style),this.update(e),this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone())}refocus(){let e,t=this.getFocus();for(;!t.getNodes().length;){e=this.levels.peek();const n=this.up();if(!n)break;this.setFocus(n),t=this.getFocus(!0)}this.levels.push(e),this.setFocus(t)}toggleActive_(){this.active_=!this.active_}mergePrefix_(e,t=[]){const n=this.isSpeech()?this.prefix_():"";n&&e.unshift(n);const r=this.isSpeech()?this.postfix_():"";return r&&e.push(r),i.finalize(i.merge(t.concat(e)))}prefix_(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomNodes(),t=this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes();return e[0]?N.getAttribute(e[0],l.Attribute.PREFIX):f.retrievePrefix(t[0])}postfix_(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomNodes();return e[0]?N.getAttribute(e[0],l.Attribute.POSTFIX):""}depth_(){const e=d.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("depth");d.Grammar.getInstance().setParameter("depth",!0);const t=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary(),n=this.expandable(t)?u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.EXPANDABLE:this.collapsible(t)?u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.COLLAPSIBLE:"",o=u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.LEVEL+" "+this.getDepth(),s=this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes(),a=f.retrievePrefix(s[0]),c=[new r.AuditoryDescription({text:o,personality:{}}),new r.AuditoryDescription({text:a,personality:{}}),new r.AuditoryDescription({text:n,personality:{}})];return d.Grammar.getInstance().setParameter("depth",e),i.finalize(i.markup(c))}actionable_(e){const t=null==e?void 0:e.parentNode;return t&&this.highlighter.isMactionNode(t)?t:null}summary_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),t=this.getRebuilt().xml.getAttribute("id")===e?this.getRebuilt().xml:o.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",e)[0],n=f.retrieveSummary(t);return this.mergePrefix_([n])}detail_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),t=this.getRebuilt().xml.getAttribute("id")===e?this.getRebuilt().xml:o.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",e)[0],n=t.getAttribute("alternative");t.removeAttribute("alternative");const r=f.computeMarkup(t),i=this.mergePrefix_([r]);return t.setAttribute("alternative",n),i}}t.AbstractWalker=y,y.ID_COUNTER=0,y.SRE_ID_ATTR="sre-explorer-id"},4296:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DummyWalker=void 0;const r=n(4660);class i extends r.AbstractWalker{up(){return null}down(){return null}left(){return null}right(){return null}repeat(){return null}depth(){return null}home(){return null}getDepth(){return 0}initLevels(){return null}combineContentChildren(e,t,n,r){return[]}findFocusOnLevel(e){return null}}t.DummyWalker=i},5658:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Focus=void 0;const r=n(8835);class i{constructor(e,t){this.nodes=e,this.primary=t,this.domNodes=[],this.domPrimary_=null,this.allNodes=[]}static factory(e,t,n,o){const s=e=>r.getBySemanticId(o,e),a=n.nodeDict,c=s(e),l=t.map(s),u=t.map((function(e){return a[e]})),d=new i(u,a[e]);return d.domNodes=l,d.domPrimary_=c,d.allNodes=i.generateAllVisibleNodes_(t,l,a,o),d}static generateAllVisibleNodes_(e,t,n,o){const s=e=>r.getBySemanticId(o,e);let a=[];for(let r=0,c=e.length;r=t.length?null:t[e]}depth(){return this.level_.length}clone(){const e=new n;return e.level_=this.level_.slice(0),e}toString(){let e="";for(let t,n=0;t=this.level_[n];n++)e+="\n"+t.map((function(e){return e.toString()}));return e}}t.Levels=n},1848:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.RebuildStree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(8171),o=n(4020),s=n(4790),a=n(7793),c=n(7984),l=n(1784),u=n(8901),d=n(8835);class h{constructor(e){this.mathml=e,this.factory=new s.SemanticNodeFactory,this.nodeDict={},this.mmlRoot=d.getSemanticRoot(e),this.streeRoot=this.assembleTree(this.mmlRoot),this.stree=l.SemanticTree.fromNode(this.streeRoot,this.mathml),this.xml=this.stree.xml(),a.default.getInstance().setNodeFactory(this.factory)}static addAttributes(e,t,n){n&&1===t.childNodes.length&&t.childNodes[0].nodeType!==r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE&&u.addAttributes(e,t.childNodes[0]),u.addAttributes(e,t)}static textContent(e,t,n){if(!n&&t.textContent)return void(e.textContent=t.textContent);const r=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(t,i.Attribute.OPERATOR));r.length>1&&(e.textContent=r[1])}static isPunctuated(e){return!c.SemanticSkeleton.simpleCollapseStructure(e)&&e[1]&&c.SemanticSkeleton.contentCollapseStructure(e[1])}getTree(){return this.stree}assembleTree(e){const t=this.makeNode(e),n=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.CHILDREN)),r=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.CONTENT));if(h.addAttributes(t,e,!(n.length||r.length)),0===r.length&&0===n.length)return h.textContent(t,e),t;if(r.length>0){const e=d.getBySemanticId(this.mathml,r[0]);e&&h.textContent(t,e,!0)}t.contentNodes=r.map((e=>this.setParent(e,t))),t.childNodes=n.map((e=>this.setParent(e,t)));const o=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.COLLAPSED);return o?this.postProcess(t,o):t}makeNode(e){const t=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.TYPE),n=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ROLE),r=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.FONT),o=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ANNOTATION)||"",s=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ID),a=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.EMBELLISHED),c=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.FENCEPOINTER),l=this.createNode(parseInt(s,10));return l.type=t,l.role=n,l.font=r||"unknown",l.parseAnnotation(o),c&&(l.fencePointer=c),a&&(l.embellished=a),l}makePunctuation(e){const t=this.createNode(e);return t.updateContent((0,o.invisibleComma)()),t.role="dummy",t}makePunctuated(e,t,n){const r=this.createNode(t[0]);r.type="punctuated",r.embellished=e.embellished,r.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,r.role=n;const i=t.splice(1,1)[0].slice(1);r.contentNodes=i.map(this.makePunctuation.bind(this)),this.collapsedChildren_(t)}makeEmpty(e,t,n){const r=this.createNode(t);r.type="empty",r.embellished=e.embellished,r.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,r.role=n}makeIndex(e,t,n){if(h.isPunctuated(t))return this.makePunctuated(e,t,n),void(t=t[0]);c.SemanticSkeleton.simpleCollapseStructure(t)&&!this.nodeDict[t.toString()]&&this.makeEmpty(e,t,n)}postProcess(e,t){const n=c.SemanticSkeleton.fromString(t).array;if("subsup"===e.type){const t=this.createNode(n[1][0]);return t.type="subscript",t.role="subsup",e.type="superscript",t.embellished=e.embellished,t.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,this.makeIndex(e,n[1][2],"rightsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e}if("subscript"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsub"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("superscript"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("tensor"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"leftsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[3],"leftsuper"),this.makeIndex(e,n[4],"rightsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[5],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("punctuated"===e.type){if(h.isPunctuated(n)){const t=n.splice(1,1)[0].slice(1);e.contentNodes=t.map(this.makePunctuation.bind(this))}return e}if("underover"===e.type){const t=this.createNode(n[1][0]);return"overaccent"===e.childNodes[1].role?(t.type="overscore",e.type="underscore"):(t.type="underscore",e.type="overscore"),t.role="underover",t.embellished=e.embellished,t.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,this.collapsedChildren_(n),e}return e}createNode(e){const t=this.factory.makeNode(e);return this.nodeDict[e.toString()]=t,t}collapsedChildren_(e){const t=e=>{const n=this.nodeDict[e[0]];n.childNodes=[];for(let r=1,i=e.length;rt.getSemanticPrimary().id===e))}}t.SemanticWalker=o},3531:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SyntaxWalker=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(4660),o=n(1497);class s extends i.AbstractWalker{constructor(e,t,n,r){super(e,t,n,r),this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.levels=null,this.restoreState()}initLevels(){const e=new o.Levels;return e.push([this.primaryId()]),e}up(){super.up();const e=this.previousLevel();return e?(this.levels.pop(),this.singletonFocus(e)):null}down(){super.down();const e=this.nextLevel();if(0===e.length)return null;const t=this.singletonFocus(e[0]);return t&&this.levels.push(e),t}combineContentChildren(e,t,n,i){switch(e){case"relseq":case"infixop":case"multirel":return(0,r.interleaveLists)(i,n);case"prefixop":return n.concat(i);case"postfixop":return i.concat(n);case"matrix":case"vector":case"fenced":return i.unshift(n[0]),i.push(n[1]),i;case"cases":return i.unshift(n[0]),i;case"punctuated":return"text"===t?(0,r.interleaveLists)(i,n):i;case"appl":return[i[0],n[0],i[1]];case"root":return[i[1],i[0]];default:return i}}left(){super.left();const e=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId());if(null===e)return null;const t=this.levels.get(e-1);return t?this.singletonFocus(t):null}right(){super.right();const e=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId());if(null===e)return null;const t=this.levels.get(e+1);return t?this.singletonFocus(t):null}findFocusOnLevel(e){return this.singletonFocus(e.toString())}focusDomNodes(){return[this.getFocus().getDomPrimary()]}focusSemanticNodes(){return[this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary()]}}t.SyntaxWalker=s},4051:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.TableWalker=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(6988),o=n(3531),s=n(8119);class a extends o.SyntaxWalker{constructor(e,t,n,r){super(e,t,n,r),this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.firstJump=null,this.key_=null,this.row_=0,this.currentTable_=null,this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.ZERO,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.ONE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.TWO,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.THREE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.FOUR,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.FIVE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.SIX,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.SEVEN,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.EIGHT,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.NINE,this.jumpCell.bind(this))}move(e){this.key_=e;const t=super.move(e);return this.modifier=!1,t}up(){return this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.UP,this.eligibleCell_()?this.verticalMove_(!1):super.up()}down(){return this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.DOWN,this.eligibleCell_()?this.verticalMove_(!0):super.down()}jumpCell(){if(!this.isInTable_()||null===this.key_)return this.getFocus();if(this.moved===s.WalkerMoves.ROW){this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.CELL;const e=this.key_-i.KeyCode.ZERO;return this.isLegalJump_(this.row_,e)?this.jumpCell_(this.row_,e):this.getFocus()}const e=this.key_-i.KeyCode.ZERO;return e>this.currentTable_.childNodes.length?this.getFocus():(this.row_=e,this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.ROW,this.getFocus().clone())}undo(){const e=super.undo();return e===this.firstJump&&(this.firstJump=null),e}eligibleCell_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary();return this.modifier&&"cell"===e.type&&-1!==a.ELIGIBLE_CELL_ROLES.indexOf(e.role)}verticalMove_(e){const t=this.previousLevel();if(!t)return null;const n=this.getFocus(),r=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId()),i=this.levels.pop(),o=this.levels.indexOf(t),s=this.levels.get(e?o+1:o-1);if(!s)return this.levels.push(i),null;this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(s));const a=this.nextLevel();return a[r]?(this.levels.push(a),this.singletonFocus(a[r])):(this.setFocus(n),this.levels.push(i),null)}jumpCell_(e,t){this.firstJump?this.virtualize(!1):(this.firstJump=this.getFocus(),this.virtualize(!0));const n=this.currentTable_.id.toString();let r;do{r=this.levels.pop()}while(-1===r.indexOf(n));this.levels.push(r),this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(n)),this.levels.push(this.nextLevel());const i=this.currentTable_.childNodes[e-1];return this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(i.id.toString())),this.levels.push(this.nextLevel()),this.singletonFocus(i.childNodes[t-1].id.toString())}isLegalJump_(e,t){const n=r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",this.currentTable_.id.toString())[0];if(!n||n.hasAttribute("alternative"))return!1;const i=this.currentTable_.childNodes[e-1];if(!i)return!1;const o=r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",i.id.toString())[0];return!(!o||o.hasAttribute("alternative"))&&!(!i||!i.childNodes[t-1])}isInTable_(){let e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary();for(;e;){if(-1!==a.ELIGIBLE_TABLE_TYPES.indexOf(e.type))return this.currentTable_=e,!0;e=e.parent}return!1}}t.TableWalker=a,a.ELIGIBLE_CELL_ROLES=["determinant","rowvector","binomial","squarematrix","multiline","matrix","vector","cases","table"],a.ELIGIBLE_TABLE_TYPES=["multiline","matrix","vector","cases","table"]},8119:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.WalkerState=t.WalkerMoves=void 0,function(e){e.UP="up",e.DOWN="down",e.LEFT="left",e.RIGHT="right",e.REPEAT="repeat",e.DEPTH="depth",e.ENTER="enter",e.EXPAND="expand",e.HOME="home",e.SUMMARY="summary",e.DETAIL="detail",e.ROW="row",e.CELL="cell"}(t.WalkerMoves||(t.WalkerMoves={}));class n{static resetState(e){delete n.STATE[e]}static setState(e,t){n.STATE[e]=t}static getState(e){return n.STATE[e]}}t.WalkerState=n,n.STATE={}},907:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.walkerMapping_=t.walker=void 0;const r=n(4296),i=n(1937),o=n(3531),s=n(4051);t.walker=function(e,n,r,i,o){return(t.walkerMapping_[e.toLowerCase()]||t.walkerMapping_.dummy)(n,r,i,o)},t.walkerMapping_={dummy:(e,t,n,i)=>new r.DummyWalker(e,t,n,i),semantic:(e,t,n,r)=>new i.SemanticWalker(e,t,n,r),syntax:(e,t,n,r)=>new o.SyntaxWalker(e,t,n,r),table:(e,t,n,r)=>new s.TableWalker(e,t,n,r)}},8835:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getBySemanticId=t.getSemanticRoot=t.getAttribute=t.splitAttribute=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(8171);t.splitAttribute=function(e){return e?e.split(/,/):[]},t.getAttribute=function(e,t){return e.getAttribute(t)},t.getSemanticRoot=function(e){if(e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.TYPE)&&!e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.PARENT))return e;const t=r.querySelectorAllByAttr(e,i.Attribute.TYPE);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if(!e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.PARENT))return e;return e},t.getBySemanticId=function(e,t){return e.getAttribute(i.Attribute.ID)===t?e:r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(e,i.Attribute.ID,t)[0]}}},__webpack_module_cache__={};function __webpack_require__(e){var t=__webpack_module_cache__[e];if(void 0!==t)return t.exports;var n=__webpack_module_cache__[e]={exports:{}};return __webpack_modules__[e].call(n.exports,n,n.exports,__webpack_require__),n.exports}__webpack_require__.n=function(e){var t=e&&e.__esModule?function(){return e.default}:function(){return e};return __webpack_require__.d(t,{a:t}),t},__webpack_require__.d=function(e,t){for(var n in t)__webpack_require__.o(t,n)&&!__webpack_require__.o(e,n)&&Object.defineProperty(e,n,{enumerable:!0,get:t[n]})},__webpack_require__.g=function(){if("object"==typeof globalThis)return globalThis;try{return this||new Function("return this")()}catch(e){if("object"==typeof window)return window}}(),__webpack_require__.o=function(e,t){return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,t)};var __webpack_exports__={};!function(){var e=__webpack_require__(8723),t=__webpack_require__(7306),n=__webpack_require__(8905),r=__webpack_require__.n(n);MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("a11y/sre",t.q,"a11y"),(0,e.r8)({_:{a11y:{sre:n}}});var i=__webpack_require__(1993);if(MathJax.startup){var o=i.GL.resolvePath("[sre]",!1);if("undefined"!=typeof window)window.SREfeature={json:o};else{try{o=MathJax.config.loader.require.resolve(o+"/base.json").replace(/\/base\.json$/,"")}catch(e){}__webpack_require__.g.SREfeature={json:o}}}MathJax.startup&&(("undefined"!=typeof window?window:__webpack_require__.g).SREfeature.custom=function(e){return r().preloadLocales(e)})}()})();��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692426889.043128
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/adaptors/liteDOM.js�����������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000054437�00000000000�021615� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,n,r,o,i,a,l,u,s={244:function(t,e,n){var r,o=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,n=1,r=arguments.length;n0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteElement=void 0;var a=function(t,e,a){var l,u;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===a&&(a=[]),this.kind=t,this.attributes=n({},e),this.children=o([],r(a),!1);try{for(var s=i(this.children),c=s.next();!c.done;c=s.next())c.value.parent=this}catch(t){l={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(u=s.return)&&u.call(s)}finally{if(l)throw l.error}}this.styles=null};e.LiteElement=a},6:function(t,e){var n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var n="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!n)return t;var r,o,i=n.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},r=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},l=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,n=e&&t[e],r=0;if(n)return n.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&r>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteParser=e.PATTERNS=void 0;var u,s=i(n(29)),c=n(946),p=n(735);!function(t){t.TAGNAME="[a-z][^\\s\\n>]*",t.ATTNAME="[a-z][^\\s\\n>=]*",t.VALUE="(?:'[^']*'|\"[^\"]*\"|[^\\s\\n]+)",t.VALUESPLIT="(?:'([^']*)'|\"([^\"]*)\"|([^\\s\\n]+))",t.SPACE="(?:\\s|\\n)+",t.OPTIONALSPACE="(?:\\s|\\n)*",t.ATTRIBUTE=t.ATTNAME+"(?:"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"="+t.OPTIONALSPACE+t.VALUE+")?",t.ATTRIBUTESPLIT="("+t.ATTNAME+")(?:"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"="+t.OPTIONALSPACE+t.VALUESPLIT+")?",t.TAG="(<(?:"+t.TAGNAME+"(?:"+t.SPACE+t.ATTRIBUTE+")*"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"/?|/"+t.TAGNAME+"|!--[^]*?--|![^]*?)(?:>|$))",t.tag=new RegExp(t.TAG,"i"),t.attr=new RegExp(t.ATTRIBUTE,"i"),t.attrsplit=new RegExp(t.ATTRIBUTESPLIT,"i")}(u=e.PATTERNS||(e.PATTERNS={}));var f=function(){function t(){}return t.prototype.parseFromString=function(t,e,n){void 0===e&&(e="text/html"),void 0===n&&(n=null);for(var r=n.createDocument(),o=n.body(r),i=t.replace(/<\?.*?\?>/g,"").split(u.tag);i.length;){var a=i.shift(),l=i.shift();a&&this.addText(n,o,a),l&&">"===l.charAt(l.length-1)&&("!"===l.charAt(1)?this.addComment(n,o,l):o="/"===l.charAt(1)?this.closeTag(n,o,l):this.openTag(n,o,l,i))}return this.checkDocument(n,r),r},t.prototype.addText=function(t,e,n){return n=s.translate(n),t.append(e,t.text(n))},t.prototype.addComment=function(t,e,n){return t.append(e,new p.LiteComment(n))},t.prototype.closeTag=function(t,e,n){for(var r=n.slice(2,n.length-1).toLowerCase();t.parent(e)&&t.kind(e)!==r;)e=t.parent(e);return t.parent(e)},t.prototype.openTag=function(t,e,n,r){var o=this.constructor.PCDATA,i=this.constructor.SELF_CLOSING,a=n.match(/<(.*?)[\s\n>\/]/)[1].toLowerCase(),l=t.node(a),s=n.replace(/^<.*?[\s\n>]/,"").split(u.attrsplit);return(s.pop().match(/>$/)||s.length<5)&&(this.addAttributes(t,l,s),t.append(e,l),i[a]||n.match(/\/>$/)||(o[a]?this.handlePCDATA(t,l,a,r):e=l)),e},t.prototype.addAttributes=function(t,e,n){for(var r=this.constructor.CDATA_ATTR;n.length;){var o=a(n.splice(0,5),5),i=o[1],l=o[2],u=o[3],c=o[4],p=l||u||c||"";r[i]||(p=s.translate(p)),t.setAttribute(e,i,p)}},t.prototype.handlePCDATA=function(t,e,n,r){for(var o=[],i="",a="";r.length&&a!==i;)o.push(a),o.push(r.shift()),a=r.shift();t.append(e,t.text(o.join("")))},t.prototype.checkDocument=function(t,e){var n,r,o,i,a=this.getOnlyChild(t,t.body(e));if(a){try{for(var u=l(t.childNodes(t.body(e))),s=u.next();!s.done;s=u.next()){if((h=s.value)===a)break;h instanceof p.LiteComment&&h.value.match(/^":">":">".concat(u,""))},t.prototype.serializeInner=function(t,e,n){var r=this;return void 0===n&&(n=!1),this.constructor.PCDATA.hasOwnProperty(e.kind)?t.childNodes(e).map((function(e){return t.value(e)})).join(""):t.childNodes(e).map((function(e){var o=t.kind(e);return"#text"===o?r.protectHTML(t.value(e)):"#comment"===o?e.value:r.serialize(t,e,n)})).join("")},t.prototype.protectAttribute=function(t){return"string"!=typeof t&&(t=String(t)),t.replace(/"/g,""")},t.prototype.protectHTML=function(t){return t.replace(/&/g,"&").replace(//g,">")},t.SELF_CLOSING={area:!0,base:!0,br:!0,col:!0,command:!0,embed:!0,hr:!0,img:!0,input:!0,keygen:!0,link:!0,menuitem:!0,meta:!0,param:!0,source:!0,track:!0,wbr:!0},t.PCDATA={option:!0,textarea:!0,fieldset:!0,title:!0,style:!0,script:!0},t.CDATA_ATTR={style:!0,datafld:!0,datasrc:!0,href:!0,src:!0,longdesc:!0,usemap:!0,cite:!0,datetime:!0,action:!0,axis:!0,profile:!0,content:!0,scheme:!0},t}();e.LiteParser=f},735:function(t,e){var n,r=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteComment=e.LiteText=void 0;var o=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=""),this.value=t}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"#text"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t}();e.LiteText=o;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return r(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"#comment"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e}(o);e.LiteComment=i},492:function(t,e,n){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteWindow=void 0;var r=n(946),o=n(877),i=n(6),a=n(246),l=function(){this.DOMParser=a.LiteParser,this.NodeList=i.LiteList,this.HTMLCollection=i.LiteList,this.HTMLElement=r.LiteElement,this.DocumentFragment=i.LiteList,this.Document=o.LiteDocument,this.document=new o.LiteDocument};e.LiteWindow=l},250:function(t,e,n){var r,o=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,n=1,r=arguments.length;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},l=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var n="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!n)return t;var r,o,i=n.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},u=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o=0&&t.parent.children.splice(e,1),t.parent=null,t},e.prototype.replace=function(t,e){var n=this.childIndex(e);return n>=0&&(e.parent.children[n]=t,t.parent=e.parent,e.parent=null),e},e.prototype.clone=function(t){var e=this,n=new f.LiteElement(t.kind);return n.attributes=i({},t.attributes),n.children=t.children.map((function(t){if("#text"===t.kind)return new h.LiteText(t.value);if("#comment"===t.kind)return new h.LiteComment(t.value);var r=e.clone(t);return r.parent=n,r})),n},e.prototype.split=function(t,e){var n=new h.LiteText(t.value.slice(e));return t.value=t.value.slice(0,e),t.parent.children.splice(this.childIndex(t)+1,0,n),n.parent=t.parent,n},e.prototype.next=function(t){var e=t.parent;if(!e)return null;var n=this.childIndex(t)+1;return n>=0&&n=0?e.children[n]:null},e.prototype.firstChild=function(t){return t.children[0]},e.prototype.lastChild=function(t){return t.children[t.children.length-1]},e.prototype.childNodes=function(t){return u([],l(t.children),!1)},e.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return t.children[e]},e.prototype.kind=function(t){return t.kind},e.prototype.value=function(t){return"#text"===t.kind?t.value:"#comment"===t.kind?t.value.replace(/^$/,"$2"):""},e.prototype.textContent=function(t){var e=this;return t.children.reduce((function(t,n){return t+("#text"===n.kind?n.value:"#comment"===n.kind?"":e.textContent(n))}),"")},e.prototype.innerHTML=function(t){return this.parser.serializeInner(this,t)},e.prototype.outerHTML=function(t){return this.parser.serialize(this,t)},e.prototype.serializeXML=function(t){return this.parser.serialize(this,t,!0)},e.prototype.setAttribute=function(t,e,n,r){void 0===r&&(r=null),"string"!=typeof n&&(n=String(n)),r&&(e=r.replace(/.*\//,"")+":"+e.replace(/^.*:/,"")),t.attributes[e]=n,"style"===e&&(t.styles=null)},e.prototype.getAttribute=function(t,e){return t.attributes[e]},e.prototype.removeAttribute=function(t,e){delete t.attributes[e]},e.prototype.hasAttribute=function(t,e){return t.attributes.hasOwnProperty(e)},e.prototype.allAttributes=function(t){var e,n,r=t.attributes,o=[];try{for(var i=a(Object.keys(r)),l=i.next();!l.done;l=i.next()){var u=l.value;o.push({name:u,value:r[u]})}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return o},e.prototype.addClass=function(t,e){var n=(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /);n.find((function(t){return t===e}))||(n.push(e),t.attributes.class=n.join(" "))},e.prototype.removeClass=function(t,e){var n=(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /),r=n.findIndex((function(t){return t===e}));r>=0&&(n.splice(r,1),t.attributes.class=n.join(" "))},e.prototype.hasClass=function(t,e){return!!(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /).find((function(t){return t===e}))},e.prototype.setStyle=function(t,e,n){t.styles||(t.styles=new v.Styles(this.getAttribute(t,"style"))),t.styles.set(e,n),t.attributes.style=t.styles.cssText},e.prototype.getStyle=function(t,e){if(!t.styles){var n=this.getAttribute(t,"style");if(!n)return"";t.styles=new v.Styles(n)}return t.styles.get(e)},e.prototype.allStyles=function(t){return this.getAttribute(t,"style")},e.prototype.insertRules=function(t,e){t.children=[this.text(e.join("\n\n")+"\n\n"+this.textContent(t))]},e.prototype.fontSize=function(t){return 0},e.prototype.fontFamily=function(t){return""},e.prototype.nodeSize=function(t,e,n){return void 0===e&&(e=1),void 0===n&&(n=null),[0,0]},e.prototype.nodeBBox=function(t){return{left:0,right:0,top:0,bottom:0}},e}(s.AbstractDOMAdaptor);e.LiteBase=b;var m=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}((0,c.NodeMixin)(b));e.LiteAdaptor=m,e.liteAdaptor=function(t){return void 0===t&&(t=null),new m(null,t)}},306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},723:function(t,e){MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},857:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=MathJax._.core.DOMAdaptor.AbstractDOMAdaptor},29:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.options=MathJax._.util.Entities.options,e.entities=MathJax._.util.Entities.entities,e.add=MathJax._.util.Entities.add,e.remove=MathJax._.util.Entities.remove,e.translate=MathJax._.util.Entities.translate,e.numeric=MathJax._.util.Entities.numeric},77:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup},878:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Styles=MathJax._.util.Styles.Styles}},c={};function p(t){var e=c[t];if(void 0!==e)return e.exports;var n=c[t]={exports:{}};return s[t].call(n.exports,n,n.exports,p),n.exports}t=p(723),e=p(306),n=p(250),r=p(877),o=p(946),i=p(6),a=p(246),l=p(735),u=p(492),MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("adaptors/liteDOM",e.q,"adaptors"),(0,t.r8)({_:{adaptors:{liteAdaptor:n,lite:{Document:r,Element:o,List:i,Parser:a,Text:l,Window:u}}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.registerConstructor("liteAdaptor",n.liteAdaptor),MathJax.startup.useAdaptor("liteAdaptor",!0))}();���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0439646
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/core.js�����������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000652641�00000000000�017434� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,r,n,o,i,a,s,l,u,c,p,f,h,d,y,O,M,E,v,m,b,g,L,N,R,T,S,A,C,_,x,I,w,P,j,D,B,k,X,H,W,F,q,J,z,G,V,U,K,$,Y,Z,Q,tt,et,rt,nt,ot,it,at,st,lt,ut,ct,pt,ft,ht,dt,yt,Ot,Mt,Et,vt,mt,bt,gt,Lt,Nt={444:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLAdaptor=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(e){var r=t.call(this,e.document)||this;return r.window=e,r.parser=new e.DOMParser,r}return o(e,t),e.prototype.parse=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e="text/html"),this.parser.parseFromString(t,e)},e.prototype.create=function(t,e){return e?this.document.createElementNS(e,t):this.document.createElement(t)},e.prototype.text=function(t){return this.document.createTextNode(t)},e.prototype.head=function(t){return t.head||t},e.prototype.body=function(t){return t.body||t},e.prototype.root=function(t){return t.documentElement||t},e.prototype.doctype=function(t){return t.doctype?""):""},e.prototype.tags=function(t,e,r){void 0===r&&(r=null);var n=r?t.getElementsByTagNameNS(r,e):t.getElementsByTagName(e);return Array.from(n)},e.prototype.getElements=function(t,e){var r,n,o=[];try{for(var a=i(t),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;"string"==typeof l?o=o.concat(Array.from(this.document.querySelectorAll(l))):Array.isArray(l)||l instanceof this.window.NodeList||l instanceof this.window.HTMLCollection?o=o.concat(Array.from(l)):o.push(l)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return o},e.prototype.contains=function(t,e){return t.contains(e)},e.prototype.parent=function(t){return t.parentNode},e.prototype.append=function(t,e){return t.appendChild(e)},e.prototype.insert=function(t,e){return this.parent(e).insertBefore(t,e)},e.prototype.remove=function(t){return this.parent(t).removeChild(t)},e.prototype.replace=function(t,e){return this.parent(e).replaceChild(t,e)},e.prototype.clone=function(t){return t.cloneNode(!0)},e.prototype.split=function(t,e){return t.splitText(e)},e.prototype.next=function(t){return t.nextSibling},e.prototype.previous=function(t){return t.previousSibling},e.prototype.firstChild=function(t){return t.firstChild},e.prototype.lastChild=function(t){return t.lastChild},e.prototype.childNodes=function(t){return Array.from(t.childNodes)},e.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return t.childNodes[e]},e.prototype.kind=function(t){var e=t.nodeType;return 1===e||3===e||8===e?t.nodeName.toLowerCase():""},e.prototype.value=function(t){return t.nodeValue||""},e.prototype.textContent=function(t){return t.textContent},e.prototype.innerHTML=function(t){return t.innerHTML},e.prototype.outerHTML=function(t){return t.outerHTML},e.prototype.serializeXML=function(t){return(new this.window.XMLSerializer).serializeToString(t)},e.prototype.setAttribute=function(t,e,r,n){return void 0===n&&(n=null),n?(e=n.replace(/.*\//,"")+":"+e.replace(/^.*:/,""),t.setAttributeNS(n,e,r)):t.setAttribute(e,r)},e.prototype.getAttribute=function(t,e){return t.getAttribute(e)},e.prototype.removeAttribute=function(t,e){return t.removeAttribute(e)},e.prototype.hasAttribute=function(t,e){return t.hasAttribute(e)},e.prototype.allAttributes=function(t){return Array.from(t.attributes).map((function(t){return{name:t.name,value:t.value}}))},e.prototype.addClass=function(t,e){t.classList?t.classList.add(e):t.className=(t.className+" "+e).trim()},e.prototype.removeClass=function(t,e){t.classList?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.split(/ /).filter((function(t){return t!==e})).join(" ")},e.prototype.hasClass=function(t,e){return t.classList?t.classList.contains(e):t.className.split(/ /).indexOf(e)>=0},e.prototype.setStyle=function(t,e,r){t.style[e]=r},e.prototype.getStyle=function(t,e){return t.style[e]},e.prototype.allStyles=function(t){return t.style.cssText},e.prototype.insertRules=function(t,e){var r,n;try{for(var o=i(e.reverse()),a=o.next();!a.done;a=o.next()){var s=a.value;try{t.sheet.insertRule(s,0)}catch(t){console.warn("MathJax: can't insert css rule '".concat(s,"': ").concat(t.message))}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.fontSize=function(t){var e=this.window.getComputedStyle(t);return parseFloat(e.fontSize)},e.prototype.fontFamily=function(t){return this.window.getComputedStyle(t).fontFamily||""},e.prototype.nodeSize=function(t,e,r){if(void 0===e&&(e=1),void 0===r&&(r=!1),r&&t.getBBox){var n=t.getBBox();return[n.width/e,n.height/e]}return[t.offsetWidth/e,t.offsetHeight/e]},e.prototype.nodeBBox=function(t){var e=t.getBoundingClientRect();return{left:e.left,right:e.right,top:e.top,bottom:e.bottom}},e}(r(5009).AbstractDOMAdaptor);e.HTMLAdaptor=a},6191:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.browserAdaptor=void 0;var n=r(444);e.browserAdaptor=function(){return new n.HTMLAdaptor(window)}},9515:function(t,e,r){var n=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathJax=e.combineWithMathJax=e.combineDefaults=e.combineConfig=e.isObject=void 0;var o=r(3282);function i(t){return"object"==typeof t&&null!==t}function a(t,e){var r,o;try{for(var s=n(Object.keys(e)),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;"__esModule"!==u&&(!i(t[u])||!i(e[u])||e[u]instanceof Promise?null!==e[u]&&void 0!==e[u]&&(t[u]=e[u]):a(t[u],e[u]))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(o=s.return)&&o.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return t}e.isObject=i,e.combineConfig=a,e.combineDefaults=function t(e,r,o){var a,s;e[r]||(e[r]={}),e=e[r];try{for(var l=n(Object.keys(o)),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;i(e[c])&&i(o[c])?t(e,c,o[c]):null==e[c]&&null!=o[c]&&(e[c]=o[c])}}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(s=l.return)&&s.call(l)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return e},e.combineWithMathJax=function(t){return a(e.MathJax,t)},void 0===r.g.MathJax&&(r.g.MathJax={}),r.g.MathJax.version||(r.g.MathJax={version:o.VERSION,_:{},config:r.g.MathJax}),e.MathJax=r.g.MathJax},3282:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.VERSION=void 0,e.VERSION="3.2.2"},5009:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=void 0;var n=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.document=t}return t.prototype.node=function(t,e,n,o){var i,a;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===n&&(n=[]);var s=this.create(t,o);this.setAttributes(s,e);try{for(var l=r(n),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;this.append(s,c)}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(a=l.return)&&a.call(l)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}return s},t.prototype.setAttributes=function(t,e){var n,o,i,a,s,l;if(e.style&&"string"!=typeof e.style)try{for(var u=r(Object.keys(e.style)),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;this.setStyle(t,p.replace(/-([a-z])/g,(function(t,e){return e.toUpperCase()})),e.style[p])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(o=u.return)&&o.call(u)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}if(e.properties)try{for(var f=r(Object.keys(e.properties)),h=f.next();!h.done;h=f.next()){t[p=h.value]=e.properties[p]}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(a=f.return)&&a.call(f)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}try{for(var d=r(Object.keys(e)),y=d.next();!y.done;y=d.next()){"style"===(p=y.value)&&"string"!=typeof e.style||"properties"===p||this.setAttribute(t,p,e[p])}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{y&&!y.done&&(l=d.return)&&l.call(d)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},t.prototype.replace=function(t,e){return this.insert(t,e),this.remove(e),e},t.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return this.childNodes(t)[e]},t.prototype.allClasses=function(t){var e=this.getAttribute(t,"class");return e?e.replace(/ +/g," ").replace(/^ /,"").replace(/ $/,"").split(/ /):[]},t}();e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=n},3494:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractFindMath=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=function(){function t(t){var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t)}return t.OPTIONS={},t}();e.AbstractFindMath=o},3670:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractHandler=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(r(5722).AbstractMathDocument),a=function(){function t(t,e){void 0===e&&(e=5),this.documentClass=i,this.adaptor=t,this.priority=e}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){return!1},t.prototype.create=function(t,e){return new this.documentClass(t,this.adaptor,e)},t.NAME="generic",t}();e.AbstractHandler=a},805:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HandlerList=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.register=function(t){return this.add(t,t.priority)},e.prototype.unregister=function(t){this.remove(t)},e.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=i(this),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var a=o.value.item;if(a.handlesDocument(t))return a}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}throw new Error("Can't find handler for document")},e.prototype.document=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),this.handlesDocument(t).create(t,e)},e}(r(8666).PrioritizedList);e.HandlerList=a},9206:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractInputJax=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=r(7525),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={}),this.adaptor=null,this.mmlFactory=null;var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.preFilters=new o.FunctionList,this.postFilters=new o.FunctionList}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setAdaptor=function(t){this.adaptor=t},t.prototype.setMmlFactory=function(t){this.mmlFactory=t},t.prototype.initialize=function(){},t.prototype.reset=function(){for(var t=[],e=0;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=e&&s.item.renderDoc(t))return}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.renderMath=function(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===r&&(r=f.STATE.UNPROCESSED);try{for(var a=i(this.items),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(l.priority>=r&&l.item.renderMath(t,e))return}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},e.prototype.renderConvert=function(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===r&&(r=f.STATE.LAST);try{for(var a=i(this.items),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(l.priority>r)return;if(l.item.convert&&l.item.renderMath(t,e))return}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},e.prototype.findID=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=i(this.items),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var a=o.value;if(a.item.id===t)return a.item}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return null},e}(r(8666).PrioritizedList);e.RenderList=y,e.resetOptions={all:!1,processed:!1,inputJax:null,outputJax:null},e.resetAllOptions={all:!0,processed:!0,inputJax:[],outputJax:[]};var O=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.compile=function(t){return null},e}(u.AbstractInputJax),M=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.typeset=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),null},e.prototype.escaped=function(t,e){return null},e}(c.AbstractOutputJax),E=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(p.AbstractMathList),v=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(f.AbstractMathItem),m=function(){function t(e,r,n){var o=this,i=this.constructor;this.document=e,this.options=(0,l.userOptions)((0,l.defaultOptions)({},i.OPTIONS),n),this.math=new(this.options.MathList||E),this.renderActions=y.create(this.options.renderActions),this.processed=new t.ProcessBits,this.outputJax=this.options.OutputJax||new M;var a=this.options.InputJax||[new O];Array.isArray(a)||(a=[a]),this.inputJax=a,this.adaptor=r,this.outputJax.setAdaptor(r),this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.setAdaptor(r)})),this.mmlFactory=this.options.MmlFactory||new h.MmlFactory,this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.setMmlFactory(o.mmlFactory)})),this.outputJax.initialize(),this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.initialize()}))}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return this.constructor.KIND},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.addRenderAction=function(t){for(var e=[],r=1;r=r&&this.state(r-1),t.renderActions.renderMath(this,t,r)},t.prototype.convert=function(t,r){void 0===r&&(r=e.STATE.LAST),t.renderActions.renderConvert(this,t,r)},t.prototype.compile=function(t){this.state()=e.STATE.INSERTED&&this.removeFromDocument(r),t=e.STATE.TYPESET&&(this.outputData={}),t=e.STATE.COMPILED&&(this.inputData={}),this._state=t),this._state},t.prototype.reset=function(t){void 0===t&&(t=!1),this.state(e.STATE.UNPROCESSED,t)},t}();e.AbstractMathItem=r,e.STATE={UNPROCESSED:0,FINDMATH:10,COMPILED:20,CONVERT:100,METRICS:110,RERENDER:125,TYPESET:150,INSERTED:200,LAST:1e4},e.newState=function(t,r){if(t in e.STATE)throw Error("State "+t+" already exists");e.STATE[t]=r}},9e3:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractMathList=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.isBefore=function(t,e){return t.start.i=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Attributes=e.INHERIT=void 0,e.INHERIT="_inherit_";var n=function(){function t(t,e){this.global=e,this.defaults=Object.create(e),this.inherited=Object.create(this.defaults),this.attributes=Object.create(this.inherited),Object.assign(this.defaults,t)}return t.prototype.set=function(t,e){this.attributes[t]=e},t.prototype.setList=function(t){Object.assign(this.attributes,t)},t.prototype.get=function(t){var r=this.attributes[t];return r===e.INHERIT&&(r=this.global[t]),r},t.prototype.getExplicit=function(t){if(this.attributes.hasOwnProperty(t))return this.attributes[t]},t.prototype.getList=function(){for(var t,e,n=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathMLVisitor=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.document=null,e}return o(e,t),e.prototype.visitTree=function(t,e){this.document=e;var r=e.createElement("top");return this.visitNode(t,r),this.document=null,r.firstChild},e.prototype.visitTextNode=function(t,e){e.appendChild(this.document.createTextNode(t.getText()))},e.prototype.visitXMLNode=function(t,e){e.appendChild(t.getXML().cloneNode(!0))},e.prototype.visitInferredMrowNode=function(t,e){var r,n;try{for(var o=i(t.childNodes),a=o.next();!a.done;a=o.next()){var s=a.value;this.visitNode(s,e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var r,n,o=this.document.createElement(t.kind);this.addAttributes(t,o);try{for(var a=i(t.childNodes),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;this.visitNode(l,o)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}e.appendChild(o)},e.prototype.addAttributes=function(t,e){var r,n,o=t.attributes,a=o.getExplicitNames();try{for(var s=i(a),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;e.setAttribute(u,o.getExplicit(u).toString())}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=s.return)&&n.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e}(r(6325).MmlVisitor);e.MathMLVisitor=a},3909:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlFactory=void 0;var i=r(7860),a=r(6336),s=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"MML",{get:function(){return this.node},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.defaultNodes=a.MML,e}(i.AbstractNodeFactory);e.MmlFactory=s},9007:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.XMLNode=e.TextNode=e.AbstractMmlEmptyNode=e.AbstractMmlBaseNode=e.AbstractMmlLayoutNode=e.AbstractMmlTokenNode=e.AbstractMmlNode=e.indentAttributes=e.TEXCLASSNAMES=e.TEXCLASS=void 0;var l=r(91),u=r(4596);e.TEXCLASS={ORD:0,OP:1,BIN:2,REL:3,OPEN:4,CLOSE:5,PUNCT:6,INNER:7,VCENTER:8,NONE:-1},e.TEXCLASSNAMES=["ORD","OP","BIN","REL","OPEN","CLOSE","PUNCT","INNER","VCENTER"];var c=["","thinmathspace","mediummathspace","thickmathspace"],p=[[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[-1,-1,0,3,0,0,0,1],[2,2,0,0,2,0,0,2],[3,3,0,0,3,0,0,3],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],[1,-1,2,3,1,0,1,1]];e.indentAttributes=["indentalign","indentalignfirst","indentshift","indentshiftfirst"];var f=function(t){function r(e,r,n){void 0===r&&(r={}),void 0===n&&(n=[]);var o=t.call(this,e)||this;return o.prevClass=null,o.prevLevel=null,o.texclass=null,o.arity<0&&(o.childNodes=[e.create("inferredMrow")],o.childNodes[0].parent=o),o.setChildren(n),o.attributes=new l.Attributes(e.getNodeClass(o.kind).defaults,e.getNodeClass("math").defaults),o.attributes.setList(r),o}return o(r,t),r.prototype.copy=function(t){var e,r,n,o;void 0===t&&(t=!1);var s=this.factory.create(this.kind);if(s.properties=i({},this.properties),this.attributes){var l=this.attributes.getAllAttributes();try{for(var u=a(Object.keys(l)),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;("id"!==p||t)&&s.attributes.set(p,l[p])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(r=u.return)&&r.call(u)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}if(this.childNodes&&this.childNodes.length){var f=this.childNodes;1===f.length&&f[0].isInferred&&(f=f[0].childNodes);try{for(var h=a(f),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;y?s.appendChild(y.copy()):s.childNodes.push(null)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(o=h.return)&&o.call(h)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}return s},Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){return this.texclass},set:function(t){this.texclass=t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 1/0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"Parent",{get:function(){for(var t=this.parent;t&&t.notParent;)t=t.Parent;return t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.setChildren=function(e){return this.arity<0?this.childNodes[0].setChildren(e):t.prototype.setChildren.call(this,e)},r.prototype.appendChild=function(e){var r,n,o=this;if(this.arity<0)return this.childNodes[0].appendChild(e),e;if(e.isInferred){if(this.arity===1/0)return e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){return t.prototype.appendChild.call(o,e)})),e;var i=e;(e=this.factory.create("mrow")).setChildren(i.childNodes),e.attributes=i.attributes;try{for(var s=a(i.getPropertyNames()),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;e.setProperty(u,i.getProperty(u))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=s.return)&&n.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}}return t.prototype.appendChild.call(this,e)},r.prototype.replaceChild=function(e,r){return this.arity<0?(this.childNodes[0].replaceChild(e,r),e):t.prototype.replaceChild.call(this,e,r)},r.prototype.core=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreIndex=function(){return 0},r.prototype.childPosition=function(){for(var t,e,r=this,n=r.parent;n&&n.notParent;)r=n,n=n.parent;if(n){var o=0;try{for(var i=a(n.childNodes),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){if(s.value===r)return o;o++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(e=i.return)&&e.call(i)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}}return null},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return this.getPrevClass(t),null!=this.texClass?this:t},r.prototype.updateTeXclass=function(t){t&&(this.prevClass=t.prevClass,this.prevLevel=t.prevLevel,t.prevClass=t.prevLevel=null,this.texClass=t.texClass)},r.prototype.getPrevClass=function(t){t&&(this.prevClass=t.texClass,this.prevLevel=t.attributes.get("scriptlevel"))},r.prototype.texSpacing=function(){var t=null!=this.prevClass?this.prevClass:e.TEXCLASS.NONE,r=this.texClass||e.TEXCLASS.ORD;if(t===e.TEXCLASS.NONE||r===e.TEXCLASS.NONE)return"";t===e.TEXCLASS.VCENTER&&(t=e.TEXCLASS.ORD),r===e.TEXCLASS.VCENTER&&(r=e.TEXCLASS.ORD);var n=p[t][r];return(this.prevLevel>0||this.attributes.get("scriptlevel")>0)&&n>=0?"":c[Math.abs(n)]},r.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&this.coreMO().hasSpacingAttributes()},r.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,n,o){var i,l;void 0===t&&(t={}),void 0===e&&(e=!1),void 0===n&&(n=0),void 0===o&&(o=!1);var u=this.attributes.getAllDefaults();try{for(var c=a(Object.keys(t)),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){var f=p.value;if(u.hasOwnProperty(f)||r.alwaysInherit.hasOwnProperty(f)){var h=s(t[f],2),d=h[0],y=h[1];((r.noInherit[d]||{})[this.kind]||{})[f]||this.attributes.setInherited(f,y)}}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(l=c.return)&&l.call(c)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}void 0===this.attributes.getExplicit("displaystyle")&&this.attributes.setInherited("displaystyle",e),void 0===this.attributes.getExplicit("scriptlevel")&&this.attributes.setInherited("scriptlevel",n),o&&this.setProperty("texprimestyle",o);var O=this.arity;if(O>=0&&O!==1/0&&(1===O&&0===this.childNodes.length||1!==O&&this.childNodes.length!==O))if(O=0&&e!==1/0&&(1===e&&0===this.childNodes.length||1!==e&&this.childNodes.length!==e)&&this.mError('Wrong number of children for "'+this.kind+'" node',t,!0),this.verifyChildren(t)}},r.prototype.verifyAttributes=function(t){var e,r;if(t.checkAttributes){var n=this.attributes,o=[];try{for(var i=a(n.getExplicitNames()),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var l=s.value;"data-"===l.substr(0,5)||void 0!==n.getDefault(l)||l.match(/^(?:class|style|id|(?:xlink:)?href)$/)||o.push(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}o.length&&this.mError("Unknown attributes for "+this.kind+" node: "+o.join(", "),t)}},r.prototype.verifyChildren=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.verifyTree(t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},r.prototype.mError=function(t,e,r){if(void 0===r&&(r=!1),this.parent&&this.parent.isKind("merror"))return null;var n=this.factory.create("merror");if(n.attributes.set("data-mjx-message",t),e.fullErrors||r){var o=this.factory.create("mtext"),i=this.factory.create("text");i.setText(e.fullErrors?t:this.kind),o.appendChild(i),n.appendChild(o),this.parent.replaceChild(n,this)}else this.parent.replaceChild(n,this),n.appendChild(this);return n},r.defaults={mathbackground:l.INHERIT,mathcolor:l.INHERIT,mathsize:l.INHERIT,dir:l.INHERIT},r.noInherit={mstyle:{mpadded:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,lspace:!0,voffset:!0},mtable:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,align:!0}},maligngroup:{mrow:{groupalign:!0},mtable:{groupalign:!0}}},r.alwaysInherit={scriptminsize:!0,scriptsizemultiplier:!0},r.verifyDefaults={checkArity:!0,checkAttributes:!1,fullErrors:!1,fixMmultiscripts:!0,fixMtables:!0},r}(u.AbstractNode);e.AbstractMmlNode=f;var h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getText=function(){var t,e,r="";try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i instanceof M&&(r+=i.getText())}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(e=n.return)&&e.call(n)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i;try{for(var s=a(this.childNodes),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;u instanceof f&&u.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,n)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}},e.prototype.walkTree=function(t,e){var r,n;t(this,e);try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;s instanceof f&&s.walkTree(t,e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return e},e.defaults=i(i({},f.defaults),{mathvariant:"normal",mathsize:l.INHERIT}),e}(f);e.AbstractMmlTokenNode=h;var d=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isSpacelike},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isEmbellished},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return-1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.core=function(){return this.childNodes[0]},e.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.childNodes[0].coreMO()},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return t=this.childNodes[0].setTeXclass(t),this.updateTeXclass(this.childNodes[0]),t},e.defaults=f.defaults,e}(f);e.AbstractMmlLayoutNode=d;var y=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isEmbellished},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.core=function(){return this.childNodes[0]},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.childNodes[0].coreMO()},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var r,n;this.getPrevClass(t),this.texClass=e.TEXCLASS.ORD;var o=this.childNodes[0];o?this.isEmbellished||o.isKind("mi")?(t=o.setTeXclass(t),this.updateTeXclass(this.core())):(o.setTeXclass(null),t=this):t=this;try{for(var i=a(this.childNodes.slice(1)),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var l=s.value;l&&l.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return t},r.defaults=f.defaults,r}(f);e.AbstractMmlBaseNode=y;var O=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"Parent",{get:function(){return this.parent},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){return e.TEXCLASS.NONE},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"prevClass",{get:function(){return e.TEXCLASS.NONE},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"prevLevel",{get:function(){return 0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return!1},Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"attributes",{get:function(){return null},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.core=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreIndex=function(){return 0},r.prototype.childPosition=function(){return 0},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return t},r.prototype.texSpacing=function(){return""},r.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){},r.prototype.inheritAttributesFrom=function(t){},r.prototype.verifyTree=function(t){},r.prototype.mError=function(t,e,r){return void 0===r&&(r=!1),null},r}(u.AbstractEmptyNode);e.AbstractMmlEmptyNode=O;var M=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.text="",e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"text"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getText=function(){return this.text},e.prototype.setText=function(t){return this.text=t,this},e.prototype.copy=function(){return this.factory.create(this.kind).setText(this.getText())},e.prototype.toString=function(){return this.text},e}(O);e.TextNode=M;var E=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.xml=null,e.adaptor=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"XML"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getXML=function(){return this.xml},e.prototype.setXML=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),this.xml=t,this.adaptor=e,this},e.prototype.getSerializedXML=function(){return this.adaptor.serializeXML(this.xml)},e.prototype.copy=function(){return this.factory.create(this.kind).setXML(this.adaptor.clone(this.xml))},e.prototype.toString=function(){return"XML data"},e}(O);e.XMLNode=E},3948:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;rthis.childNodes.length&&(t=1),this.attributes.set("selection",t)},e.defaults=i(i({},a.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),{actiontype:"toggle",selection:1}),e}(a.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMaction=s},142:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMfenced=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.texclass=s.TEXCLASS.INNER,e.separators=[],e.open=null,e.close=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mfenced"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){this.getPrevClass(t),this.open&&(t=this.open.setTeXclass(t)),this.childNodes[0]&&(t=this.childNodes[0].setTeXclass(t));for(var e=1,r=this.childNodes.length;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMfrac=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mfrac"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 2},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r;this.getPrevClass(t);try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){(!e||r>0)&&r++,this.childNodes[0].setInheritedAttributes(t,!1,r,n),this.childNodes[1].setInheritedAttributes(t,!1,r,!0)},e.defaults=i(i({},s.AbstractMmlBaseNode.defaults),{linethickness:"medium",numalign:"center",denomalign:"center",bevelled:!1}),e}(s.AbstractMmlBaseNode);e.MmlMfrac=l},3985:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r1&&r.match(e.operatorName)&&"normal"===this.attributes.get("mathvariant")&&void 0===this.getProperty("autoOP")&&void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=a.TEXCLASS.OP,this.setProperty("autoOP",!0)),this},e.defaults=i({},a.AbstractMmlTokenNode.defaults),e.operatorName=/^[a-z][a-z0-9]*$/i,e.singleCharacter=/^[\uD800-\uDBFF]?.[\u0300-\u036F\u1AB0-\u1ABE\u1DC0-\u1DFF\u20D0-\u20EF]*$/,e}(a.AbstractMmlTokenNode);e.MmlMi=s},6405:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMo=void 0;var l=r(9007),u=r(4082),c=r(505),p=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e._texClass=null,e.lspace=5/18,e.rspace=5/18,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){if(null===this._texClass){var t=this.getText(),e=a(this.handleExplicitForm(this.getForms()),3),r=e[0],n=e[1],o=e[2],i=this.constructor.OPTABLE,s=i[r][t]||i[n][t]||i[o][t];return s?s[2]:l.TEXCLASS.REL}return this._texClass},set:function(t){this._texClass=t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mo"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return"newline"===this.attributes.get("linebreak")},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.coreParent=function(){for(var t=this,e=this,r=this.factory.getNodeClass("math");e&&e.isEmbellished&&e.coreMO()===this&&!(e instanceof r);)t=e,e=e.parent;return t},e.prototype.coreText=function(t){if(!t)return"";if(t.isEmbellished)return t.coreMO().getText();for(;((t.isKind("mrow")||t.isKind("TeXAtom")&&t.texClass!==l.TEXCLASS.VCENTER||t.isKind("mstyle")||t.isKind("mphantom"))&&1===t.childNodes.length||t.isKind("munderover"))&&t.childNodes[0];)t=t.childNodes[0];return t.isToken?t.getText():""},e.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return this.attributes.isSet("lspace")||this.attributes.isSet("rspace")},Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isAccent",{get:function(){var t=!1,e=this.coreParent().parent;if(e){var r=e.isKind("mover")?e.childNodes[e.over].coreMO()?"accent":"":e.isKind("munder")?e.childNodes[e.under].coreMO()?"accentunder":"":e.isKind("munderover")?this===e.childNodes[e.over].coreMO()?"accent":this===e.childNodes[e.under].coreMO()?"accentunder":"":"";if(r)t=void 0!==e.attributes.getExplicit(r)?t:this.attributes.get("accent")}return t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e=this.attributes.getList("form","fence"),r=e.form,n=e.fence;return void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.attributes.isSet("lspace")||this.attributes.isSet("rspace"))?null:(n&&this.texClass===l.TEXCLASS.REL&&("prefix"===r&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.OPEN),"postfix"===r&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.CLOSE)),this.adjustTeXclass(t))},e.prototype.adjustTeXclass=function(t){var e=this.texClass,r=this.prevClass;if(e===l.TEXCLASS.NONE)return t;if(t?(!t.getProperty("autoOP")||e!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.REL||(r=t.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD),r=this.prevClass=t.texClass||l.TEXCLASS.ORD,this.prevLevel=this.attributes.getInherited("scriptlevel")):r=this.prevClass=l.TEXCLASS.NONE,e!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN||r!==l.TEXCLASS.NONE&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.OP&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.REL&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.OPEN&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.PUNCT)if(r!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN||e!==l.TEXCLASS.REL&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.CLOSE&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.PUNCT){if(e===l.TEXCLASS.BIN){for(var n=this,o=this.parent;o&&o.parent&&o.isEmbellished&&(1===o.childNodes.length||!o.isKind("mrow")&&o.core()===n);)n=o,o=o.parent;o.childNodes[o.childNodes.length-1]===n&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD)}}else t.texClass=this.prevClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD;else this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD;return this},e.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(e,r,n,o){void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===r&&(r=!1),void 0===n&&(n=0),void 0===o&&(o=!1),t.prototype.setInheritedAttributes.call(this,e,r,n,o);var i=this.getText();this.checkOperatorTable(i),this.checkPseudoScripts(i),this.checkPrimes(i),this.checkMathAccent(i)},e.prototype.checkOperatorTable=function(t){var e,r,n=a(this.handleExplicitForm(this.getForms()),3),o=n[0],i=n[1],l=n[2];this.attributes.setInherited("form",o);var c=this.constructor.OPTABLE,p=c[o][t]||c[i][t]||c[l][t];if(p){void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=p[2]);try{for(var f=s(Object.keys(p[3]||{})),h=f.next();!h.done;h=f.next()){var d=h.value;this.attributes.setInherited(d,p[3][d])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(r=f.return)&&r.call(f)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.lspace=(p[0]+1)/18,this.rspace=(p[1]+1)/18}else{var y=(0,u.getRange)(t);if(y){void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=y[2]);var O=this.constructor.MMLSPACING[y[2]];this.lspace=(O[0]+1)/18,this.rspace=(O[1]+1)/18}}},e.prototype.getForms=function(){for(var t=this,e=this.parent,r=this.Parent;r&&r.isEmbellished;)t=e,e=r.parent,r=r.Parent;if(e&&e.isKind("mrow")&&1!==e.nonSpaceLength()){if(e.firstNonSpace()===t)return["prefix","infix","postfix"];if(e.lastNonSpace()===t)return["postfix","infix","prefix"]}return["infix","prefix","postfix"]},e.prototype.handleExplicitForm=function(t){if(this.attributes.isSet("form")){var e=this.attributes.get("form");t=[e].concat(t.filter((function(t){return t!==e})))}return t},e.prototype.checkPseudoScripts=function(t){var e=this.constructor.pseudoScripts;if(t.match(e)){var r=this.coreParent().Parent,n=!r||!(r.isKind("msubsup")&&!r.isKind("msub"));this.setProperty("pseudoscript",n),n&&(this.attributes.setInherited("lspace",0),this.attributes.setInherited("rspace",0))}},e.prototype.checkPrimes=function(t){var e=this.constructor.primes;if(t.match(e)){var r=this.constructor.remapPrimes,n=(0,c.unicodeString)((0,c.unicodeChars)(t).map((function(t){return r[t]})));this.setProperty("primes",n)}},e.prototype.checkMathAccent=function(t){var e=this.Parent;if(void 0===this.getProperty("mathaccent")&&e&&e.isKind("munderover")){var r=e.childNodes[0];if(!r.isEmbellished||r.coreMO()!==this){var n=this.constructor.mathaccents;t.match(n)&&this.setProperty("mathaccent",!0)}}},e.defaults=i(i({},l.AbstractMmlTokenNode.defaults),{form:"infix",fence:!1,separator:!1,lspace:"thickmathspace",rspace:"thickmathspace",stretchy:!1,symmetric:!1,maxsize:"infinity",minsize:"0em",largeop:!1,movablelimits:!1,accent:!1,linebreak:"auto",lineleading:"1ex",linebreakstyle:"before",indentalign:"auto",indentshift:"0",indenttarget:"",indentalignfirst:"indentalign",indentshiftfirst:"indentshift",indentalignlast:"indentalign",indentshiftlast:"indentshift"}),e.MMLSPACING=u.MMLSPACING,e.OPTABLE=u.OPTABLE,e.pseudoScripts=new RegExp(["^[\"'*`","\xaa","\xb0","\xb2-\xb4","\xb9","\xba","\u2018-\u201f","\u2032-\u2037\u2057","\u2070\u2071","\u2074-\u207f","\u2080-\u208e","]+$"].join("")),e.primes=new RegExp(["^[\"'`","\u2018-\u201f","]+$"].join("")),e.remapPrimes={34:8243,39:8242,96:8245,8216:8245,8217:8242,8218:8242,8219:8245,8220:8246,8221:8243,8222:8243,8223:8246},e.mathaccents=new RegExp(["^[","\xb4\u0301\u02ca","`\u0300\u02cb","\xa8\u0308","~\u0303\u02dc","\xaf\u0304\u02c9","\u02d8\u0306","\u02c7\u030c","^\u0302\u02c6","\u2192\u20d7","\u02d9\u0307","\u02da\u030a","\u20db","\u20dc","]$"].join("")),e}(l.AbstractMmlTokenNode);e.MmlMo=p},7238:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlInferredMrow=e.MmlMrow=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e._core=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mrow"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){var t,e;try{for(var r=a(this.childNodes),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){if(!n.value.isSpacelike)return!1}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(e=r.return)&&e.call(r)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){var t,e,r=!1,n=0;try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;if(s)if(s.isEmbellished){if(r)return!1;r=!0,this._core=n}else if(!s.isSpacelike)return!1;n++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(e=o.return)&&e.call(o)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.core=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&null!=this._core?this.childNodes[this._core]:this},e.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&null!=this._core?this.childNodes[this._core].coreMO():this},e.prototype.nonSpaceLength=function(){var t,e,r=0;try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i&&!i.isSpacelike&&r++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(e=n.return)&&e.call(n)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},e.prototype.firstNonSpace=function(){var t,e;try{for(var r=a(this.childNodes),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){var o=n.value;if(o&&!o.isSpacelike)return o}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(e=r.return)&&e.call(r)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return null},e.prototype.lastNonSpace=function(){for(var t=this.childNodes.length;--t>=0;){var e=this.childNodes[t];if(e&&!e.isSpacelike)return e}return null},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r,n,o;if(null!=this.getProperty("open")||null!=this.getProperty("close")){this.getPrevClass(t),t=null;try{for(var i=a(this.childNodes),l=i.next();!l.done;l=i.next()){t=l.value.setTeXclass(t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}null==this.texClass&&(this.texClass=s.TEXCLASS.INNER)}else{try{for(var u=a(this.childNodes),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){t=c.value.setTeXclass(t)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(o=u.return)&&o.call(u)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}this.childNodes[0]&&this.updateTeXclass(this.childNodes[0])}return t},e.defaults=i({},s.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),e}(s.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMrow=l;var u=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"inferredMrow"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.toString=function(){return"["+this.childNodes.join(",")+"]"},e.defaults=l.defaults,e}(l);e.MmlInferredMrow=u},7265:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMtable=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=r(505),u=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.properties={useHeight:!0},e.texclass=s.TEXCLASS.ORD,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mtable"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(e,r,n,o){var i,l;try{for(var u=a(s.indentAttributes),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;e[p]&&this.attributes.setInherited(p,e[p][1]),void 0!==this.attributes.getExplicit(p)&&delete this.attributes.getAllAttributes()[p]}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(l=u.return)&&l.call(u)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}t.prototype.setInheritedAttributes.call(this,e,r,n,o)},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,s,u;try{for(var c=a(this.childNodes),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){(O=p.value).isKind("mtr")||this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtr"),O).appendChild(O)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(i=c.return)&&i.call(c)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}r=this.getProperty("scriptlevel")||r,e=!(!this.attributes.getExplicit("displaystyle")&&!this.attributes.getDefault("displaystyle")),t=this.addInheritedAttributes(t,{columnalign:this.attributes.get("columnalign"),rowalign:"center"});var f=this.attributes.getExplicit("data-cramped"),h=(0,l.split)(this.attributes.get("rowalign"));try{for(var d=a(this.childNodes),y=d.next();!y.done;y=d.next()){var O=y.value;t.rowalign[1]=h.shift()||t.rowalign[1],O.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,!!f)}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{y&&!y.done&&(u=d.return)&&u.call(d)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},e.prototype.verifyChildren=function(e){for(var r=null,n=this.factory,o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMlabeledtr=e.MmlMtr=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=r(91),u=r(505),c=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mtr"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,s,l;try{for(var c=a(this.childNodes),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){(y=p.value).isKind("mtd")||this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtd"),y).appendChild(y)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(i=c.return)&&i.call(c)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}var f=(0,u.split)(this.attributes.get("columnalign"));1===this.arity&&f.unshift(this.parent.attributes.get("side")),t=this.addInheritedAttributes(t,{rowalign:this.attributes.get("rowalign"),columnalign:"center"});try{for(var h=a(this.childNodes),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;t.columnalign[1]=f.shift()||t.columnalign[1],y.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,n)}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(l=h.return)&&l.call(h)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},e.prototype.verifyChildren=function(e){var r,n;if(!this.parent||this.parent.isKind("mtable")){try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;if(!s.isKind("mtd"))this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtd"),s).appendChild(s),e.fixMtables||s.mError("Children of "+this.kind+" must be mtd",e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}t.prototype.verifyChildren.call(this,e)}else this.mError(this.kind+" can only be a child of an mtable",e,!0)},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r;this.getPrevClass(t);try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this},e.defaults=i(i({},s.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),{rowalign:l.INHERIT,columnalign:l.INHERIT,groupalign:l.INHERIT}),e}(s.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMtr=c;var p=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mlabeledtr"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e}(c);e.MmlMlabeledtr=p},5184:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.OPTABLE=e.MMLSPACING=e.getRange=e.RANGES=e.MO=e.OPDEF=void 0;var o=r(9007);function i(t,e,r,n){return void 0===r&&(r=o.TEXCLASS.BIN),void 0===n&&(n=null),[t,e,r,n]}e.OPDEF=i,e.MO={ORD:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD11:i(1,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD21:i(2,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD02:i(0,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD55:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),NONE:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.NONE),OP:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0,symmetric:!0}),OPFIXED:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0}),INTEGRAL:i(0,1,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,symmetric:!0}),INTEGRAL2:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,symmetric:!0}),BIN3:i(3,3,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN4:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN01:i(0,1,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN5:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),TALLBIN:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{stretchy:!0}),BINOP:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0}),REL:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL),REL1:i(1,1,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{stretchy:!0}),REL4:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.REL),RELSTRETCH:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{stretchy:!0}),RELACCENT:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{accent:!0}),WIDEREL:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{accent:!0,stretchy:!0}),OPEN:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}),CLOSE:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}),INNER:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.INNER),PUNCT:i(0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT),ACCENT:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{accent:!0}),WIDEACCENT:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{accent:!0,stretchy:!0})},e.RANGES=[[32,127,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[160,191,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[192,591,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[688,879,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[880,6688,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[6832,6911,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[6912,7615,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[7616,7679,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[7680,8191,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[8192,8303,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[8304,8351,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[8448,8527,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[8528,8591,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[8592,8703,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[8704,8959,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,"mo"],[8960,9215,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[9312,9471,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[9472,10223,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[10224,10239,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[10240,10495,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mtext"],[10496,10623,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[10624,10751,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[10752,11007,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,"mo"],[11008,11055,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11056,11087,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[11088,11263,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11264,11744,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[11776,11903,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11904,12255,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[12272,12351,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[12352,42143,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[42192,43055,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[43056,43071,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[43072,55295,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[63744,64255,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[64256,65023,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[65024,65135,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[65136,65791,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[65792,65935,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[65936,74751,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[74752,74879,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[74880,113823,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[113824,119391,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[119648,119679,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[119808,120781,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[120782,120831,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[122624,129023,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[129024,129279,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[129280,129535,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[131072,195103,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normnal"]],e.getRange=function(t){var r,o,i=t.codePointAt(0);try{for(var a=n(e.RANGES),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(i<=l[1]){if(i>=l[0])return l;break}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return null},e.MMLSPACING=[[0,0],[1,2],[3,3],[4,4],[0,0],[0,0],[0,3]],e.OPTABLE={prefix:{"(":e.MO.OPEN,"+":e.MO.BIN01,"-":e.MO.BIN01,"[":e.MO.OPEN,"{":e.MO.OPEN,"|":e.MO.OPEN,"||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xac":e.MO.ORD21,"\xb1":e.MO.BIN01,"\u2016":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2018":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0}],"\u201c":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0}],"\u2145":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2146":i(2,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),"\u2200":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2202":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2203":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2204":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2207":e.MO.ORD21,"\u220f":e.MO.OP,"\u2210":e.MO.OP,"\u2211":e.MO.OP,"\u2212":e.MO.BIN01,"\u2213":e.MO.BIN01,"\u221a":[1,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u221b":e.MO.ORD11,"\u221c":e.MO.ORD11,"\u2220":e.MO.ORD,"\u2221":e.MO.ORD,"\u2222":e.MO.ORD,"\u222b":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222c":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222d":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222e":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222f":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2230":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2231":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2232":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2233":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u22c0":e.MO.OP,"\u22c1":e.MO.OP,"\u22c2":e.MO.OP,"\u22c3":e.MO.OP,"\u2308":e.MO.OPEN,"\u230a":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2329":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2772":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27e6":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27e8":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ea":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ec":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ee":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2980":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2983":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2985":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2987":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2989":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298b":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298d":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298f":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2991":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2993":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2995":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2997":e.MO.OPEN,"\u29fc":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2a00":e.MO.OP,"\u2a01":e.MO.OP,"\u2a02":e.MO.OP,"\u2a03":e.MO.OP,"\u2a04":e.MO.OP,"\u2a05":e.MO.OP,"\u2a06":e.MO.OP,"\u2a07":e.MO.OP,"\u2a08":e.MO.OP,"\u2a09":e.MO.OP,"\u2a0a":e.MO.OP,"\u2a0b":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0c":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2a0d":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0e":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0f":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a10":e.MO.OP,"\u2a11":e.MO.OP,"\u2a12":e.MO.OP,"\u2a13":e.MO.OP,"\u2a14":e.MO.OP,"\u2a15":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a16":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a17":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a18":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a19":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1a":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1b":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1c":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2afc":e.MO.OP,"\u2aff":e.MO.OP},postfix:{"!!":i(1,0),"!":[1,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,null],'"':e.MO.ACCENT,"&":e.MO.ORD,")":e.MO.CLOSE,"++":i(0,0),"--":i(0,0),"..":i(0,0),"...":e.MO.ORD,"'":e.MO.ACCENT,"]":e.MO.CLOSE,"^":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,_:e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"`":e.MO.ACCENT,"|":e.MO.CLOSE,"}":e.MO.CLOSE,"~":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xa8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xaa":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xaf":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\xb0":e.MO.ORD,"\xb2":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb3":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb4":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb9":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xba":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02c6":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02c7":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02c9":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02ca":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02cb":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02cd":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02d8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02d9":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02da":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02dc":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02dd":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02f7":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0302":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0311":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u03f6":e.MO.REL,"\u2016":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2019":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0}],"\u201a":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201b":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201d":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0}],"\u201e":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201f":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2032":e.MO.ORD,"\u2033":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2034":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2035":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2036":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2037":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u203e":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u2057":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u20db":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u20dc":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2309":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u230b":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u232a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u23b4":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23b5":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23dc":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23dd":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23de":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23df":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23e0":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23e1":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u25a0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25a1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25aa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ab":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ad":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ae":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25af":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25be":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c0":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c1":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25ce":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25d6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25d7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25e6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u266d":e.MO.ORD02,"\u266e":e.MO.ORD02,"\u266f":e.MO.ORD02,"\u2773":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27e7":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27e9":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27eb":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27ed":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27ef":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2980":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2984":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2986":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2988":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298c":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298e":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2990":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2992":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2994":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2996":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2998":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u29fd":e.MO.CLOSE},infix:{"!=":e.MO.BIN4,"#":e.MO.ORD,$:e.MO.ORD,"%":[3,3,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,null],"&&":e.MO.BIN4,"":e.MO.ORD,"*":e.MO.BIN3,"**":i(1,1),"*=":e.MO.BIN4,"+":e.MO.BIN4,"+=":e.MO.BIN4,",":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"-":e.MO.BIN4,"-=":e.MO.BIN4,"->":e.MO.BIN5,".":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{separator:!0}],"/":e.MO.ORD11,"//":i(1,1),"/=":e.MO.BIN4,":":[1,2,o.TEXCLASS.REL,null],":=":e.MO.BIN4,";":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"<":e.MO.REL,"<=":e.MO.BIN5,"<>":i(1,1),"=":e.MO.REL,"==":e.MO.BIN4,">":e.MO.REL,">=":e.MO.BIN5,"?":[1,1,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,null],"@":e.MO.ORD11,"\\":e.MO.ORD,"^":e.MO.ORD11,_:e.MO.ORD11,"|":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"||":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xb1":e.MO.BIN4,"\xb7":e.MO.BIN4,"\xd7":e.MO.BIN4,"\xf7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u02b9":e.MO.ORD,"\u0300":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0301":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0303":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0304":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0306":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0307":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0308":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u030c":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0332":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0338":e.MO.REL4,"\u2015":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2017":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2020":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2021":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2022":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2026":e.MO.INNER,"\u2043":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2044":e.MO.TALLBIN,"\u2061":e.MO.NONE,"\u2062":e.MO.NONE,"\u2063":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.NONE,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"\u2064":e.MO.NONE,"\u20d7":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2111":e.MO.ORD,"\u2113":e.MO.ORD,"\u2118":e.MO.ORD,"\u211c":e.MO.ORD,"\u2190":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2191":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2192":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2193":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2194":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2195":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2196":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2197":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2198":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2199":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u219a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u219b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u219c":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219d":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a3":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21aa":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ab":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ac":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ad":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ae":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21af":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b0":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b2":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b4":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b6":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21b7":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21b8":e.MO.REL,"\u21b9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ba":e.MO.REL,"\u21bb":e.MO.REL,"\u21bc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21bd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21be":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21bf":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c1":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c2":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c7":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ca":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21cb":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21cc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21cd":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21ce":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21cf":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21d0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d6":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d9":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21da":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21db":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21dc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21dd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21de":e.MO.REL,"\u21df":e.MO.REL,"\u21e0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e5":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e8":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e9":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ea":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21eb":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ec":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ed":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ee":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ef":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21f1":e.MO.REL,"\u21f2":e.MO.REL,"\u21f3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f4":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21f7":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f8":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f9":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fa":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fb":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fc":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21fe":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ff":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2201":i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),"\u2205":e.MO.ORD,"\u2206":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2208":e.MO.REL,"\u2209":e.MO.REL,"\u220a":e.MO.REL,"\u220b":e.MO.REL,"\u220c":e.MO.REL,"\u220d":e.MO.REL,"\u220e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2212":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2213":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2214":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2215":e.MO.TALLBIN,"\u2216":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2217":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2218":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2219":e.MO.BIN4,"\u221d":e.MO.REL,"\u221e":e.MO.ORD,"\u221f":e.MO.REL,"\u2223":e.MO.REL,"\u2224":e.MO.REL,"\u2225":e.MO.REL,"\u2226":e.MO.REL,"\u2227":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2228":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2229":e.MO.BIN4,"\u222a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2234":e.MO.REL,"\u2235":e.MO.REL,"\u2236":e.MO.REL,"\u2237":e.MO.REL,"\u2238":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2239":e.MO.REL,"\u223a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u223b":e.MO.REL,"\u223c":e.MO.REL,"\u223d":e.MO.REL,"\u223d\u0331":e.MO.BIN3,"\u223e":e.MO.REL,"\u223f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2240":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2241":e.MO.REL,"\u2242":e.MO.REL,"\u2242\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2243":e.MO.REL,"\u2244":e.MO.REL,"\u2245":e.MO.REL,"\u2246":e.MO.REL,"\u2247":e.MO.REL,"\u2248":e.MO.REL,"\u2249":e.MO.REL,"\u224a":e.MO.REL,"\u224b":e.MO.REL,"\u224c":e.MO.REL,"\u224d":e.MO.REL,"\u224e":e.MO.REL,"\u224e\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u224f":e.MO.REL,"\u224f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2250":e.MO.REL,"\u2251":e.MO.REL,"\u2252":e.MO.REL,"\u2253":e.MO.REL,"\u2254":e.MO.REL,"\u2255":e.MO.REL,"\u2256":e.MO.REL,"\u2257":e.MO.REL,"\u2258":e.MO.REL,"\u2259":e.MO.REL,"\u225a":e.MO.REL,"\u225b":e.MO.REL,"\u225c":e.MO.REL,"\u225d":e.MO.REL,"\u225e":e.MO.REL,"\u225f":e.MO.REL,"\u2260":e.MO.REL,"\u2261":e.MO.REL,"\u2262":e.MO.REL,"\u2263":e.MO.REL,"\u2264":e.MO.REL,"\u2265":e.MO.REL,"\u2266":e.MO.REL,"\u2266\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2267":e.MO.REL,"\u2268":e.MO.REL,"\u2269":e.MO.REL,"\u226a":e.MO.REL,"\u226a\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u226b":e.MO.REL,"\u226b\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u226c":e.MO.REL,"\u226d":e.MO.REL,"\u226e":e.MO.REL,"\u226f":e.MO.REL,"\u2270":e.MO.REL,"\u2271":e.MO.REL,"\u2272":e.MO.REL,"\u2273":e.MO.REL,"\u2274":e.MO.REL,"\u2275":e.MO.REL,"\u2276":e.MO.REL,"\u2277":e.MO.REL,"\u2278":e.MO.REL,"\u2279":e.MO.REL,"\u227a":e.MO.REL,"\u227b":e.MO.REL,"\u227c":e.MO.REL,"\u227d":e.MO.REL,"\u227e":e.MO.REL,"\u227f":e.MO.REL,"\u227f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2280":e.MO.REL,"\u2281":e.MO.REL,"\u2282":e.MO.REL,"\u2282\u20d2":e.MO.REL,"\u2283":e.MO.REL,"\u2283\u20d2":e.MO.REL,"\u2284":e.MO.REL,"\u2285":e.MO.REL,"\u2286":e.MO.REL,"\u2287":e.MO.REL,"\u2288":e.MO.REL,"\u2289":e.MO.REL,"\u228a":e.MO.REL,"\u228b":e.MO.REL,"\u228c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228f":e.MO.REL,"\u228f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2290":e.MO.REL,"\u2290\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2291":e.MO.REL,"\u2292":e.MO.REL,"\u2293":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2294":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2295":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2296":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2297":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2298":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2299":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a0":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a1":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a2":e.MO.REL,"\u22a3":e.MO.REL,"\u22a4":e.MO.ORD55,"\u22a5":e.MO.REL,"\u22a6":e.MO.REL,"\u22a7":e.MO.REL,"\u22a8":e.MO.REL,"\u22a9":e.MO.REL,"\u22aa":e.MO.REL,"\u22ab":e.MO.REL,"\u22ac":e.MO.REL,"\u22ad":e.MO.REL,"\u22ae":e.MO.REL,"\u22af":e.MO.REL,"\u22b0":e.MO.REL,"\u22b1":e.MO.REL,"\u22b2":e.MO.REL,"\u22b3":e.MO.REL,"\u22b4":e.MO.REL,"\u22b5":e.MO.REL,"\u22b6":e.MO.REL,"\u22b7":e.MO.REL,"\u22b8":e.MO.REL,"\u22b9":e.MO.REL,"\u22ba":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22be":e.MO.BIN3,"\u22bf":e.MO.BIN3,"\u22c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c8":e.MO.REL,"\u22c9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22ca":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cd":e.MO.REL,"\u22ce":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d0":e.MO.REL,"\u22d1":e.MO.REL,"\u22d2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d4":e.MO.REL,"\u22d5":e.MO.REL,"\u22d6":e.MO.REL,"\u22d7":e.MO.REL,"\u22d8":e.MO.REL,"\u22d9":e.MO.REL,"\u22da":e.MO.REL,"\u22db":e.MO.REL,"\u22dc":e.MO.REL,"\u22dd":e.MO.REL,"\u22de":e.MO.REL,"\u22df":e.MO.REL,"\u22e0":e.MO.REL,"\u22e1":e.MO.REL,"\u22e2":e.MO.REL,"\u22e3":e.MO.REL,"\u22e4":e.MO.REL,"\u22e5":e.MO.REL,"\u22e6":e.MO.REL,"\u22e7":e.MO.REL,"\u22e8":e.MO.REL,"\u22e9":e.MO.REL,"\u22ea":e.MO.REL,"\u22eb":e.MO.REL,"\u22ec":e.MO.REL,"\u22ed":e.MO.REL,"\u22ee":e.MO.ORD55,"\u22ef":e.MO.INNER,"\u22f0":e.MO.REL,"\u22f1":[5,5,o.TEXCLASS.INNER,null],"\u22f2":e.MO.REL,"\u22f3":e.MO.REL,"\u22f4":e.MO.REL,"\u22f5":e.MO.REL,"\u22f6":e.MO.REL,"\u22f7":e.MO.REL,"\u22f8":e.MO.REL,"\u22f9":e.MO.REL,"\u22fa":e.MO.REL,"\u22fb":e.MO.REL,"\u22fc":e.MO.REL,"\u22fd":e.MO.REL,"\u22fe":e.MO.REL,"\u22ff":e.MO.REL,"\u2305":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2306":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2322":e.MO.REL4,"\u2323":e.MO.REL4,"\u2329":e.MO.OPEN,"\u232a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u23aa":e.MO.ORD,"\u23af":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u23b0":e.MO.OPEN,"\u23b1":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2500":e.MO.ORD,"\u25b3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25ef":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2660":e.MO.ORD,"\u2661":e.MO.ORD,"\u2662":e.MO.ORD,"\u2663":e.MO.ORD,"\u2758":e.MO.REL,"\u27f0":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u27f1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u27f5":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f7":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f8":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fa":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fb":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fe":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27ff":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2900":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2901":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2902":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2903":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2904":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2905":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2906":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2907":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2908":e.MO.REL,"\u2909":e.MO.REL,"\u290a":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u290b":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u290c":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290d":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2910":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2911":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2912":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2913":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2914":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2915":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2916":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2917":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2918":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2919":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291e":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291f":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2920":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2921":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2922":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2923":e.MO.REL,"\u2924":e.MO.REL,"\u2925":e.MO.REL,"\u2926":e.MO.REL,"\u2927":e.MO.REL,"\u2928":e.MO.REL,"\u2929":e.MO.REL,"\u292a":e.MO.REL,"\u292b":e.MO.REL,"\u292c":e.MO.REL,"\u292d":e.MO.REL,"\u292e":e.MO.REL,"\u292f":e.MO.REL,"\u2930":e.MO.REL,"\u2931":e.MO.REL,"\u2932":e.MO.REL,"\u2933":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2934":e.MO.REL,"\u2935":e.MO.REL,"\u2936":e.MO.REL,"\u2937":e.MO.REL,"\u2938":e.MO.REL,"\u2939":e.MO.REL,"\u293a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293e":e.MO.REL,"\u293f":e.MO.REL,"\u2940":e.MO.REL,"\u2941":e.MO.REL,"\u2942":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2943":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2944":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2945":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2946":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2947":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2948":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2949":e.MO.REL,"\u294a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u294b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u294c":e.MO.REL,"\u294d":e.MO.REL,"\u294e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u294f":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2950":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2951":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2952":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2953":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2954":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2955":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2956":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2957":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2958":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2959":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295a":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295b":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295c":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295d":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2960":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2961":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2962":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2963":e.MO.REL,"\u2964":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2965":e.MO.REL,"\u2966":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2967":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2968":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2969":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296e":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u296f":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2970":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2971":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2972":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2973":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2974":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2975":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2976":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2977":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2978":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2979":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297e":e.MO.REL,"\u297f":e.MO.REL,"\u2981":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2982":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2999":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299a":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299b":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299c":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299d":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a4":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a5":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a6":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a7":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29aa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ab":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ac":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ad":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ae":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29af":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b4":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b5":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29ba":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29be":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c0":e.MO.REL,"\u29c1":e.MO.REL,"\u29c2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29c3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ca":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cc":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cd":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ce":e.MO.REL,"\u29cf":e.MO.REL,"\u29cf\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u29d0":e.MO.REL,"\u29d0\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u29d1":e.MO.REL,"\u29d2":e.MO.REL,"\u29d3":e.MO.REL,"\u29d4":e.MO.REL,"\u29d5":e.MO.REL,"\u29d6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29d7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29d8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29d9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29db":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29dc":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29dd":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29de":e.MO.REL,"\u29df":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e1":e.MO.REL,"\u29e2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29e3":e.MO.REL,"\u29e4":e.MO.REL,"\u29e5":e.MO.REL,"\u29e6":e.MO.REL,"\u29e7":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ea":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29eb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ec":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ed":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ee":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ef":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f4":e.MO.REL,"\u29f5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fe":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29ff":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a1d":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a1e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a1f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a20":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a21":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a22":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a23":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a24":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a25":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a26":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a27":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a28":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a29":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a30":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a31":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a32":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a33":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a34":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a35":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a36":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a37":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a38":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a39":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a40":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a41":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a42":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a43":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a44":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a45":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a46":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a47":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a48":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a49":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a50":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a51":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a52":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a53":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a54":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a55":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a56":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a57":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a58":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a59":e.MO.REL,"\u2a5a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a60":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a61":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a62":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a63":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a64":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a65":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a66":e.MO.REL,"\u2a67":e.MO.REL,"\u2a68":e.MO.REL,"\u2a69":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a70":e.MO.REL,"\u2a71":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a72":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a73":e.MO.REL,"\u2a74":e.MO.REL,"\u2a75":e.MO.REL,"\u2a76":e.MO.REL,"\u2a77":e.MO.REL,"\u2a78":e.MO.REL,"\u2a79":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7d\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7e\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a80":e.MO.REL,"\u2a81":e.MO.REL,"\u2a82":e.MO.REL,"\u2a83":e.MO.REL,"\u2a84":e.MO.REL,"\u2a85":e.MO.REL,"\u2a86":e.MO.REL,"\u2a87":e.MO.REL,"\u2a88":e.MO.REL,"\u2a89":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a90":e.MO.REL,"\u2a91":e.MO.REL,"\u2a92":e.MO.REL,"\u2a93":e.MO.REL,"\u2a94":e.MO.REL,"\u2a95":e.MO.REL,"\u2a96":e.MO.REL,"\u2a97":e.MO.REL,"\u2a98":e.MO.REL,"\u2a99":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9f":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa0":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa1":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa1\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa2":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa2\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa3":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa4":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa5":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa6":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa7":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa8":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaa":e.MO.REL,"\u2aab":e.MO.REL,"\u2aac":e.MO.REL,"\u2aad":e.MO.REL,"\u2aae":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaf":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaf\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab0\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aba":e.MO.REL,"\u2abb":e.MO.REL,"\u2abc":e.MO.REL,"\u2abd":e.MO.REL,"\u2abe":e.MO.REL,"\u2abf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aca":e.MO.REL,"\u2acb":e.MO.REL,"\u2acc":e.MO.REL,"\u2acd":e.MO.REL,"\u2ace":e.MO.REL,"\u2acf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad9":e.MO.REL,"\u2ada":e.MO.REL,"\u2adb":e.MO.REL,"\u2add":e.MO.REL,"\u2add\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ade":e.MO.REL,"\u2adf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aea":e.MO.REL,"\u2aeb":e.MO.REL,"\u2aec":e.MO.REL,"\u2aed":e.MO.REL,"\u2aee":e.MO.REL,"\u2aef":e.MO.REL,"\u2af0":e.MO.REL,"\u2af1":e.MO.REL,"\u2af2":e.MO.REL,"\u2af3":e.MO.REL,"\u2af4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af7":e.MO.REL,"\u2af8":e.MO.REL,"\u2af9":e.MO.REL,"\u2afa":e.MO.REL,"\u2afb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2afd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2afe":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2b45":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2b46":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u3008":e.MO.OPEN,"\u3009":e.MO.CLOSE,"\ufe37":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\ufe38":e.MO.WIDEACCENT}},e.OPTABLE.infix["^"]=e.MO.WIDEREL,e.OPTABLE.infix._=e.MO.WIDEREL,e.OPTABLE.infix["\u2adc"]=e.MO.REL},9259:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.SerializedMmlVisitor=e.toEntity=e.DATAMJX=void 0;var s=r(6325),l=r(9007),u=r(450);e.DATAMJX="data-mjx-";e.toEntity=function(t){return"&#x"+t.codePointAt(0).toString(16).toUpperCase()+";"};var c=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),r.prototype.visitTree=function(t){return this.visitNode(t,"")},r.prototype.visitTextNode=function(t,e){return this.quoteHTML(t.getText())},r.prototype.visitXMLNode=function(t,e){return e+t.getSerializedXML()},r.prototype.visitInferredMrowNode=function(t,e){var r,n,o=[];try{for(var a=i(t.childNodes),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;o.push(this.visitNode(l,e))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return o.join("\n")},r.prototype.visitTeXAtomNode=function(t,e){var r=this.childNodeMml(t,e+" ","\n");return e+""+(r.match(/\S/)?"\n"+r+e:"")+""},r.prototype.visitAnnotationNode=function(t,e){return e+""+this.childNodeMml(t,"","")+""},r.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var r=t.kind,n=a(t.isToken||0===t.childNodes.length?["",""]:["\n",e],2),o=n[0],i=n[1],s=this.childNodeMml(t,e+" ",o);return e+"<"+r+this.getAttributes(t)+">"+(s.match(/\S/)?o+s+i:"")+""},r.prototype.childNodeMml=function(t,e,r){var n,o,a="";try{for(var s=i(t.childNodes),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;a+=this.visitNode(u,e)+r}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(o=s.return)&&o.call(s)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},r.prototype.getAttributes=function(t){var e,r,n=[],o=this.constructor.defaultAttributes[t.kind]||{},a=Object.assign({},o,this.getDataAttributes(t),t.attributes.getAllAttributes()),s=this.constructor.variants;a.hasOwnProperty("mathvariant")&&s.hasOwnProperty(a.mathvariant)&&(a.mathvariant=s[a.mathvariant]);try{for(var l=i(Object.keys(a)),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value,p=String(a[c]);void 0!==p&&n.push(c+'="'+this.quoteHTML(p)+'"')}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(r=l.return)&&r.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return n.length?" "+n.join(" "):""},r.prototype.getDataAttributes=function(t){var e={},r=t.attributes.getExplicit("mathvariant"),n=this.constructor.variants;r&&n.hasOwnProperty(r)&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"variant",r),t.getProperty("variantForm")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"alternate","1"),t.getProperty("pseudoscript")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"pseudoscript","true"),!1===t.getProperty("autoOP")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"auto-op","false");var o=t.getProperty("scriptalign");o&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"script-align",o);var i=t.getProperty("texClass");if(void 0!==i){var a=!0;if(i===l.TEXCLASS.OP&&t.isKind("mi")){var s=t.getText();a=!(s.length>1&&s.match(u.MmlMi.operatorName))}a&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"texclass",i<0?"NONE":l.TEXCLASSNAMES[i])}return t.getProperty("scriptlevel")&&!1===t.getProperty("useHeight")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"smallmatrix","true"),e},r.prototype.setDataAttribute=function(t,r,n){t[e.DATAMJX+r]=n},r.prototype.quoteHTML=function(t){return t.replace(/&/g,"&").replace(//g,">").replace(/\"/g,""").replace(/[\uD800-\uDBFF]./g,e.toEntity).replace(/[\u0080-\uD7FF\uE000-\uFFFF]/g,e.toEntity)},r.variants={"-tex-calligraphic":"script","-tex-bold-calligraphic":"bold-script","-tex-oldstyle":"normal","-tex-bold-oldstyle":"bold","-tex-mathit":"italic"},r.defaultAttributes={math:{xmlns:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"}},r}(s.MmlVisitor);e.SerializedMmlVisitor=c},2975:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractOutputJax=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=r(7525),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={}),this.adaptor=null;var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.postFilters=new o.FunctionList}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setAdaptor=function(t){this.adaptor=t},t.prototype.initialize=function(){},t.prototype.reset=function(){for(var t=[],e=0;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractEmptyNode=e.AbstractNode=void 0;var a=function(){function t(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===r&&(r=[]),this.factory=t,this.parent=null,this.properties={},this.childNodes=[];try{for(var a=i(Object.keys(e)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;this.setProperty(l,e[l])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}r.length&&this.setChildren(r)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"unknown"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setProperty=function(t,e){this.properties[t]=e},t.prototype.getProperty=function(t){return this.properties[t]},t.prototype.getPropertyNames=function(){return Object.keys(this.properties)},t.prototype.getAllProperties=function(){return this.properties},t.prototype.removeProperty=function(){for(var t,e,r=[],n=0;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},o=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},i=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLDocument=void 0;var l=r(5722),u=r(7233),c=r(3363),p=r(3335),f=r(5138),h=r(4474),d=function(t){function e(e,r,n){var o=this,i=a((0,u.separateOptions)(n,f.HTMLDomStrings.OPTIONS),2),s=i[0],l=i[1];return(o=t.call(this,e,r,s)||this).domStrings=o.options.DomStrings||new f.HTMLDomStrings(l),o.domStrings.adaptor=r,o.styles=[],o}return o(e,t),e.prototype.findPosition=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,l=this.adaptor;try{for(var u=s(n[t]),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value,f=a(p,2),h=f[0],d=f[1];if(e<=d&&"#text"===l.kind(h))return{node:h,n:Math.max(e,0),delim:r};e-=d}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(i=u.return)&&i.call(u)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return{node:null,n:0,delim:r}},e.prototype.mathItem=function(t,e,r){var n=t.math,o=this.findPosition(t.n,t.start.n,t.open,r),i=this.findPosition(t.n,t.end.n,t.close,r);return new this.options.MathItem(n,e,t.display,o,i)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){var e,r,n,o,i,l,c,p,f;if(!this.processed.isSet("findMath")){this.adaptor.document=this.document,t=(0,u.userOptions)({elements:this.options.elements||[this.adaptor.body(this.document)]},t);try{for(var h=s(this.adaptor.getElements(t.elements,this.document)),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value,O=a([null,null],2),M=O[0],E=O[1];try{for(var v=(n=void 0,s(this.inputJax)),m=v.next();!m.done;m=v.next()){var b=m.value,g=new this.options.MathList;if(b.processStrings){null===M&&(M=(i=a(this.domStrings.find(y),2))[0],E=i[1]);try{for(var L=(l=void 0,s(b.findMath(M))),N=L.next();!N.done;N=L.next()){var R=N.value;g.push(this.mathItem(R,b,E))}}catch(t){l={error:t}}finally{try{N&&!N.done&&(c=L.return)&&c.call(L)}finally{if(l)throw l.error}}}else try{for(var T=(p=void 0,s(b.findMath(y))),S=T.next();!S.done;S=T.next()){R=S.value;var A=new this.options.MathItem(R.math,b,R.display,R.start,R.end);g.push(A)}}catch(t){p={error:t}}finally{try{S&&!S.done&&(f=T.return)&&f.call(T)}finally{if(p)throw p.error}}this.math.merge(g)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{m&&!m.done&&(o=v.return)&&o.call(v)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(r=h.return)&&r.call(h)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.processed.set("findMath")}return this},e.prototype.updateDocument=function(){return this.processed.isSet("updateDocument")||(this.addPageElements(),this.addStyleSheet(),t.prototype.updateDocument.call(this),this.processed.set("updateDocument")),this},e.prototype.addPageElements=function(){var t=this.adaptor.body(this.document),e=this.documentPageElements();e&&this.adaptor.append(t,e)},e.prototype.addStyleSheet=function(){var t=this.documentStyleSheet(),e=this.adaptor;if(t&&!e.parent(t)){var r=e.head(this.document),n=this.findSheet(r,e.getAttribute(t,"id"));n?e.replace(t,n):e.append(r,t)}},e.prototype.findSheet=function(t,e){var r,n;if(e)try{for(var o=s(this.adaptor.tags(t,"style")),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;if(this.adaptor.getAttribute(a,"id")===e)return a}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return null},e.prototype.removeFromDocument=function(t){var e,r;if(void 0===t&&(t=!1),this.processed.isSet("updateDocument"))try{for(var n=s(this.math),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i.state()>=h.STATE.INSERTED&&i.state(h.STATE.TYPESET,t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this.processed.clear("updateDocument"),this},e.prototype.documentStyleSheet=function(){return this.outputJax.styleSheet(this)},e.prototype.documentPageElements=function(){return this.outputJax.pageElements(this)},e.prototype.addStyles=function(t){this.styles.push(t)},e.prototype.getStyles=function(){return this.styles},e.KIND="HTML",e.OPTIONS=i(i({},l.AbstractMathDocument.OPTIONS),{renderActions:(0,u.expandable)(i(i({},l.AbstractMathDocument.OPTIONS.renderActions),{styles:[h.STATE.INSERTED+1,"","updateStyleSheet",!1]})),MathList:p.HTMLMathList,MathItem:c.HTMLMathItem,DomStrings:null}),e}(l.AbstractMathDocument);e.HTMLDocument=d},5138:function(t,e,r){var n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLDomStrings=void 0;var o=r(7233),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null);var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,o.userOptions)((0,o.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.init(),this.getPatterns()}return t.prototype.init=function(){this.strings=[],this.string="",this.snodes=[],this.nodes=[],this.stack=[]},t.prototype.getPatterns=function(){var t=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.skipHtmlTags),e=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.ignoreHtmlClass),r=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.processHtmlClass);this.skipHtmlTags=new RegExp("^(?:"+t.join("|")+")$","i"),this.ignoreHtmlClass=new RegExp("(?:^| )(?:"+e.join("|")+")(?: |$)"),this.processHtmlClass=new RegExp("(?:^| )(?:"+r+")(?: |$)")},t.prototype.pushString=function(){this.string.match(/\S/)&&(this.strings.push(this.string),this.nodes.push(this.snodes)),this.string="",this.snodes=[]},t.prototype.extendString=function(t,e){this.snodes.push([t,e.length]),this.string+=e},t.prototype.handleText=function(t,e){return e||this.extendString(t,this.adaptor.value(t)),this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.handleTag=function(t,e){if(!e){var r=this.options.includeHtmlTags[this.adaptor.kind(t)];this.extendString(t,r)}return this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.handleContainer=function(t,e){this.pushString();var r=this.adaptor.getAttribute(t,"class")||"",n=this.adaptor.kind(t)||"",o=this.processHtmlClass.exec(r),i=t;return!this.adaptor.firstChild(t)||this.adaptor.getAttribute(t,"data-MJX")||!o&&this.skipHtmlTags.exec(n)?i=this.adaptor.next(t):(this.adaptor.next(t)&&this.stack.push([this.adaptor.next(t),e]),i=this.adaptor.firstChild(t),e=(e||this.ignoreHtmlClass.exec(r))&&!o),[i,e]},t.prototype.handleOther=function(t,e){return this.pushString(),this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.find=function(t){var e,r;this.init();for(var o=this.adaptor.next(t),i=!1,a=this.options.includeHtmlTags;t&&t!==o;){var s=this.adaptor.kind(t);"#text"===s?t=this.handleText(t,i):a.hasOwnProperty(s)?t=this.handleTag(t,i):s?(t=(e=n(this.handleContainer(t,i),2))[0],i=e[1]):t=this.handleOther(t,i),!t&&this.stack.length&&(this.pushString(),t=(r=n(this.stack.pop(),2))[0],i=r[1])}this.pushString();var l=[this.strings,this.nodes];return this.init(),l},t.OPTIONS={skipHtmlTags:["script","noscript","style","textarea","pre","code","annotation","annotation-xml"],includeHtmlTags:{br:"\n",wbr:"","#comment":""},ignoreHtmlClass:"mathjax_ignore",processHtmlClass:"mathjax_process"},t}();e.HTMLDomStrings=i},3726:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLHandler=void 0;var i=r(3670),a=r(3683),s=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.documentClass=a.HTMLDocument,e}return o(e,t),e.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){var e=this.adaptor;if("string"==typeof t)try{t=e.parse(t,"text/html")}catch(t){}return t instanceof e.window.Document||t instanceof e.window.HTMLElement||t instanceof e.window.DocumentFragment},e.prototype.create=function(e,r){var n=this.adaptor;if("string"==typeof e)e=n.parse(e,"text/html");else if(e instanceof n.window.HTMLElement||e instanceof n.window.DocumentFragment){var o=e;e=n.parse("","text/html"),n.append(n.body(e),o)}return t.prototype.create.call(this,e,r)},e}(i.AbstractHandler);e.HTMLHandler=s},3363:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLMathItem=void 0;var i=r(4474),a=function(t){function e(e,r,n,o,i){return void 0===n&&(n=!0),void 0===o&&(o={node:null,n:0,delim:""}),void 0===i&&(i={node:null,n:0,delim:""}),t.call(this,e,r,n,o,i)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"adaptor",{get:function(){return this.inputJax.adaptor},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.updateDocument=function(t){if(this.state()=i.STATE.TYPESET){var e=this.adaptor,r=this.start.node,n=e.text("");if(t){var o=this.start.delim+this.math+this.end.delim;if(this.inputJax.processStrings)n=e.text(o);else{var a=e.parse(o,"text/html");n=e.firstChild(e.body(a))}}e.parent(r)&&e.replace(n,r),this.start.node=this.end.node=n,this.start.n=this.end.n=0}},e}(i.AbstractMathItem);e.HTMLMathItem=a},3335:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLMathList=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(r(9e3).AbstractMathList);e.HTMLMathList=i},5713:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.mathjax=void 0;var n=r(3282),o=r(805),i=r(4542);e.mathjax={version:n.VERSION,handlers:new o.HandlerList,document:function(t,r){return e.mathjax.handlers.document(t,r)},handleRetriesFor:i.handleRetriesFor,retryAfter:i.retryAfter,asyncLoad:null}},9923:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.asyncLoad=void 0;var n=r(5713);e.asyncLoad=function(t){return n.mathjax.asyncLoad?new Promise((function(e,r){var o=n.mathjax.asyncLoad(t);o instanceof Promise?o.then((function(t){return e(t)})).catch((function(t){return r(t)})):e(o)})):Promise.reject("Can't load '".concat(t,"': No asyncLoad method specified"))}},6469:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.BBox=void 0;var n=r(6010),o=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={w:0,h:-n.BIGDIMEN,d:-n.BIGDIMEN}),this.w=t.w||0,this.h="h"in t?t.h:-n.BIGDIMEN,this.d="d"in t?t.d:-n.BIGDIMEN,this.L=this.R=this.ic=this.sk=this.dx=0,this.scale=this.rscale=1,this.pwidth=""}return t.zero=function(){return new t({h:0,d:0,w:0})},t.empty=function(){return new t},t.prototype.empty=function(){return this.w=0,this.h=this.d=-n.BIGDIMEN,this},t.prototype.clean=function(){this.w===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.w=0),this.h===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.h=0),this.d===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.d=0)},t.prototype.rescale=function(t){this.w*=t,this.h*=t,this.d*=t},t.prototype.combine=function(t,e,r){void 0===e&&(e=0),void 0===r&&(r=0);var n=t.rscale,o=e+n*(t.w+t.L+t.R),i=r+n*t.h,a=n*t.d-r;o>this.w&&(this.w=o),i>this.h&&(this.h=i),a>this.d&&(this.d=a)},t.prototype.append=function(t){var e=t.rscale;this.w+=e*(t.w+t.L+t.R),e*t.h>this.h&&(this.h=e*t.h),e*t.d>this.d&&(this.d=e*t.d)},t.prototype.updateFrom=function(t){this.h=t.h,this.d=t.d,this.w=t.w,t.pwidth&&(this.pwidth=t.pwidth)},t.fullWidth="100%",t.StyleAdjust=[["borderTopWidth","h"],["borderRightWidth","w"],["borderBottomWidth","d"],["borderLeftWidth","w",0],["paddingTop","h"],["paddingRight","w"],["paddingBottom","d"],["paddingLeft","w",0]],t}();e.BBox=o},6751:function(t,e){var r,n=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),o=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},i=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o",gtdot:"\u22d7",harrw:"\u21ad",hbar:"\u210f",hellip:"\u2026",hookleftarrow:"\u21a9",hookrightarrow:"\u21aa",imath:"\u0131",infin:"\u221e",intcal:"\u22ba",iota:"\u03b9",jmath:"\u0237",kappa:"\u03ba",kappav:"\u03f0",lEg:"\u2a8b",lambda:"\u03bb",lap:"\u2a85",larrlp:"\u21ab",larrtl:"\u21a2",lbrace:"{",lbrack:"[",le:"\u2264",leftleftarrows:"\u21c7",leftthreetimes:"\u22cb",lessdot:"\u22d6",lmoust:"\u23b0",lnE:"\u2268",lnap:"\u2a89",lne:"\u2a87",lnsim:"\u22e6",longmapsto:"\u27fc",looparrowright:"\u21ac",lowast:"\u2217",loz:"\u25ca",lt:"<",ltimes:"\u22c9",ltri:"\u25c3",macr:"\xaf",malt:"\u2720",mho:"\u2127",mu:"\u03bc",multimap:"\u22b8",nLeftarrow:"\u21cd",nLeftrightarrow:"\u21ce",nRightarrow:"\u21cf",nVDash:"\u22af",nVdash:"\u22ae",natur:"\u266e",nearr:"\u2197",nharr:"\u21ae",nlarr:"\u219a",not:"\xac",nrarr:"\u219b",nu:"\u03bd",nvDash:"\u22ad",nvdash:"\u22ac",nwarr:"\u2196",omega:"\u03c9",omicron:"\u03bf",or:"\u2228",osol:"\u2298",period:".",phi:"\u03c6",phiv:"\u03d5",pi:"\u03c0",piv:"\u03d6",prap:"\u2ab7",precnapprox:"\u2ab9",precneqq:"\u2ab5",precnsim:"\u22e8",prime:"\u2032",psi:"\u03c8",quot:'"',rarrtl:"\u21a3",rbrace:"}",rbrack:"]",rho:"\u03c1",rhov:"\u03f1",rightrightarrows:"\u21c9",rightthreetimes:"\u22cc",ring:"\u02da",rmoust:"\u23b1",rtimes:"\u22ca",rtri:"\u25b9",scap:"\u2ab8",scnE:"\u2ab6",scnap:"\u2aba",scnsim:"\u22e9",sdot:"\u22c5",searr:"\u2198",sect:"\xa7",sharp:"\u266f",sigma:"\u03c3",sigmav:"\u03c2",simne:"\u2246",smile:"\u2323",spades:"\u2660",sub:"\u2282",subE:"\u2ac5",subnE:"\u2acb",subne:"\u228a",supE:"\u2ac6",supnE:"\u2acc",supne:"\u228b",swarr:"\u2199",tau:"\u03c4",theta:"\u03b8",thetav:"\u03d1",tilde:"\u02dc",times:"\xd7",triangle:"\u25b5",triangleq:"\u225c",upsi:"\u03c5",upuparrows:"\u21c8",veebar:"\u22bb",vellip:"\u22ee",weierp:"\u2118",xi:"\u03be",yen:"\xa5",zeta:"\u03b6",zigrarr:"\u21dd",nbsp:"\xa0",rsquo:"\u2019",lsquo:"\u2018"};var i={};function a(t,r){if("#"===r.charAt(0))return s(r.slice(1));if(e.entities[r])return e.entities[r];if(e.options.loadMissingEntities){var a=r.match(/^[a-zA-Z](fr|scr|opf)$/)?RegExp.$1:r.charAt(0).toLowerCase();i[a]||(i[a]=!0,(0,n.retryAfter)((0,o.asyncLoad)("./util/entities/"+a+".js")))}return t}function s(t){var e="x"===t.charAt(0)?parseInt(t.slice(1),16):parseInt(t);return String.fromCodePoint(e)}e.add=function(t,r){Object.assign(e.entities,t),i[r]=!0},e.remove=function(t){delete e.entities[t]},e.translate=function(t){return t.replace(/&([a-z][a-z0-9]*|#(?:[0-9]+|x[0-9a-f]+));/gi,a)},e.numeric=s},7525:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0&&o[o.length-1])||6!==i[0]&&2!==i[0])){a=0;continue}if(3===i[0]&&(!o||i[1]>o[0]&&i[1]0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LinkedList=e.ListItem=e.END=void 0,e.END=Symbol();var a=function(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.next=null,this.prev=null,this.data=t};e.ListItem=a;var s=function(){function t(){for(var t=[],r=0;r1;){var u=o.shift(),c=o.shift();u.merge(c,e),o.push(u)}return o.length&&(this.list=o[0].list),this},t.prototype.merge=function(t,r){var o,i,a,s,l;void 0===r&&(r=null),null===r&&(r=this.isBefore.bind(this));for(var u=this.list.next,c=t.list.next;u.data!==e.END&&c.data!==e.END;)r(c.data,u.data)?(o=n([u,c],2),c.prev.next=o[0],u.prev.next=o[1],i=n([u.prev,c.prev],2),c.prev=i[0],u.prev=i[1],a=n([t.list,this.list],2),this.list.prev.next=a[0],t.list.prev.next=a[1],s=n([t.list.prev,this.list.prev],2),this.list.prev=s[0],t.list.prev=s[1],u=(l=n([c.next,u],2))[0],c=l[1]):u=u.next;return c.data!==e.END&&(this.list.prev.next=t.list.next,t.list.next.prev=this.list.prev,t.list.prev.next=this.list,this.list.prev=t.list.prev,t.list.next=t.list.prev=t.list),this},t}();e.LinkedList=s},7233:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;oe.length}}}},t.prototype.add=function(e,r){void 0===r&&(r=t.DEFAULTPRIORITY);var n=this.items.length;do{n--}while(n>=0&&r=0&&this.items[e].item!==t);e>=0&&this.items.splice(e,1)},t.DEFAULTPRIORITY=5,t}();e.PrioritizedList=r},4542:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.retryAfter=e.handleRetriesFor=void 0,e.handleRetriesFor=function(t){return new Promise((function e(r,n){try{r(t())}catch(t){t.retry&&t.retry instanceof Promise?t.retry.then((function(){return e(r,n)})).catch((function(t){return n(t)})):t.restart&&t.restart.isCallback?MathJax.Callback.After((function(){return e(r,n)}),t.restart):n(t)}}))},e.retryAfter=function(t){var e=new Error("MathJax retry");throw e.retry=t,e}},4139:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.CssStyles=void 0;var n=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.styles={},this.addStyles(t)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"cssText",{get:function(){return this.getStyleString()},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.addStyles=function(t){var e,n;if(t)try{for(var o=r(Object.keys(t)),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;this.styles[a]||(this.styles[a]={}),Object.assign(this.styles[a],t[a])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},t.prototype.removeStyles=function(){for(var t,e,n=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o1;)e.shift(),r.push(e.shift());return r}function l(t){var e,n,o=s(this.styles[t]);0===o.length&&o.push(""),1===o.length&&o.push(o[0]),2===o.length&&o.push(o[0]),3===o.length&&o.push(o[1]);try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var l=a.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,l),o.shift())}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}function u(t){var e,n,o=v.connect[t].children,i=[];try{for(var a=r(o),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value,u=this.styles[t+"-"+l];if(!u)return void delete this.styles[t];i.push(u)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}i[3]===i[1]&&(i.pop(),i[2]===i[0]&&(i.pop(),i[1]===i[0]&&i.pop())),this.styles[t]=i.join(" ")}function c(t){var e,n;try{for(var o=r(v.connect[t].children),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,a),this.styles[t])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}function p(t){var e,i,a=o([],n(v.connect[t].children),!1),s=this.styles[this.childName(t,a.shift())];try{for(var l=r(a),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;if(this.styles[this.childName(t,c)]!==s)return void delete this.styles[t]}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.styles[t]=s}var f=/^(?:[\d.]+(?:[a-z]+)|thin|medium|thick|inherit|initial|unset)$/,h=/^(?:none|hidden|dotted|dashed|solid|double|groove|ridge|inset|outset|inherit|initial|unset)$/;function d(t){var e,n,o,i,a={width:"",style:"",color:""};try{for(var l=r(s(this.styles[t])),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;c.match(f)&&""===a.width?a.width=c:c.match(h)&&""===a.style?a.style=c:a.color=c}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(n=l.return)&&n.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}try{for(var p=r(v.connect[t].children),d=p.next();!d.done;d=p.next()){var y=d.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,y),a[y])}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(i=p.return)&&i.call(p)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}}function y(t){var e,n,o=[];try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.styles[this.childName(t,s)];l&&o.push(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}o.length?this.styles[t]=o.join(" "):delete this.styles[t]}var O={style:/^(?:normal|italic|oblique|inherit|initial|unset)$/,variant:new RegExp("^(?:"+["normal|none","inherit|initial|unset","common-ligatures|no-common-ligatures","discretionary-ligatures|no-discretionary-ligatures","historical-ligatures|no-historical-ligatures","contextual|no-contextual","(?:stylistic|character-variant|swash|ornaments|annotation)\\([^)]*\\)","small-caps|all-small-caps|petite-caps|all-petite-caps|unicase|titling-caps","lining-nums|oldstyle-nums|proportional-nums|tabular-nums","diagonal-fractions|stacked-fractions","ordinal|slashed-zero","jis78|jis83|jis90|jis04|simplified|traditional","full-width|proportional-width","ruby"].join("|")+")$"),weight:/^(?:normal|bold|bolder|lighter|[1-9]00|inherit|initial|unset)$/,stretch:new RegExp("^(?:"+["normal","(?:(?:ultra|extra|semi)-)?condensed","(?:(?:semi|extra|ulta)-)?expanded","inherit|initial|unset"].join("|")+")$"),size:new RegExp("^(?:"+["xx-small|x-small|small|medium|large|x-large|xx-large|larger|smaller","[d.]+%|[d.]+[a-z]+","inherit|initial|unset"].join("|")+")(?:/(?:normal|[d.+](?:%|[a-z]+)?))?$")};function M(t){var e,o,i,a,l=s(this.styles[t]),u={style:"",variant:[],weight:"",stretch:"",size:"",family:"","line-height":""};try{for(var c=r(l),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){var f=p.value;u.family=f;try{for(var h=(i=void 0,r(Object.keys(O))),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;if((Array.isArray(u[y])||""===u[y])&&f.match(O[y]))if("size"===y){var M=n(f.split(/\//),2),E=M[0],m=M[1];u[y]=E,m&&(u["line-height"]=m)}else""===u.size&&(Array.isArray(u[y])?u[y].push(f):u[y]=f)}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(a=h.return)&&a.call(h)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(o=c.return)&&o.call(c)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}!function(t,e){var n,o;try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.childName(t,s);if(Array.isArray(e[s])){var u=e[s];u.length&&(this.styles[l]=u.join(" "))}else""!==e[s]&&(this.styles[l]=e[s])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}(t,u),delete this.styles[t]}function E(t){}var v=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=""),this.parse(t)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"cssText",{get:function(){var t,e,n=[];try{for(var o=r(Object.keys(this.styles)),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value,s=this.parentName(a);this.styles[s]||n.push(a+": "+this.styles[a]+";")}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(e=o.return)&&e.call(o)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return n.join(" ")},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.set=function(e,r){for(e=this.normalizeName(e),this.setStyle(e,r),t.connect[e]&&!t.connect[e].combine&&(this.combineChildren(e),delete this.styles[e]);e.match(/-/)&&(e=this.parentName(e),t.connect[e]);)t.connect[e].combine.call(this,e)},t.prototype.get=function(t){return t=this.normalizeName(t),this.styles.hasOwnProperty(t)?this.styles[t]:""},t.prototype.setStyle=function(e,r){this.styles[e]=r,t.connect[e]&&t.connect[e].children&&t.connect[e].split.call(this,e),""===r&&delete this.styles[e]},t.prototype.combineChildren=function(e){var n,o,i=this.parentName(e);try{for(var a=r(t.connect[e].children),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value,u=this.childName(i,l);t.connect[u].combine.call(this,u)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},t.prototype.parentName=function(t){var e=t.replace(/-[^-]*$/,"");return t===e?"":e},t.prototype.childName=function(e,r){return r.match(/-/)?r:(t.connect[e]&&!t.connect[e].combine&&(r+=e.replace(/.*-/,"-"),e=this.parentName(e)),e+"-"+r)},t.prototype.normalizeName=function(t){return t.replace(/[A-Z]/g,(function(t){return"-"+t.toLowerCase()}))},t.prototype.parse=function(t){void 0===t&&(t="");var e=this.constructor.pattern;this.styles={};for(var r=t.replace(e.comment,"").split(e.style);r.length>1;){var o=n(r.splice(0,3),3),i=o[0],a=o[1],s=o[2];if(i.match(/[^\s\n]/))return;this.set(a,s)}},t.pattern={style:/([-a-z]+)[\s\n]*:[\s\n]*((?:'[^']*'|"[^"]*"|\n|.)*?)[\s\n]*(?:;|$)/g,comment:/\/\*[^]*?\*\//g},t.connect={padding:{children:i,split:l,combine:u},border:{children:i,split:c,combine:p},"border-top":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-right":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-bottom":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-left":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-width":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},"border-style":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},"border-color":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},font:{children:["style","variant","weight","stretch","line-height","size","family"],split:M,combine:E}},t}();e.Styles=v},6010:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.px=e.emRounded=e.em=e.percent=e.length2em=e.MATHSPACE=e.RELUNITS=e.UNITS=e.BIGDIMEN=void 0,e.BIGDIMEN=1e6,e.UNITS={px:1,in:96,cm:96/2.54,mm:96/25.4},e.RELUNITS={em:1,ex:.431,pt:.1,pc:1.2,mu:1/18},e.MATHSPACE={veryverythinmathspace:1/18,verythinmathspace:2/18,thinmathspace:3/18,mediummathspace:4/18,thickmathspace:5/18,verythickmathspace:6/18,veryverythickmathspace:7/18,negativeveryverythinmathspace:-1/18,negativeverythinmathspace:-2/18,negativethinmathspace:-3/18,negativemediummathspace:-4/18,negativethickmathspace:-5/18,negativeverythickmathspace:-6/18,negativeveryverythickmathspace:-7/18,thin:.04,medium:.06,thick:.1,normal:1,big:2,small:1/Math.sqrt(2),infinity:e.BIGDIMEN},e.length2em=function(t,r,n,o){if(void 0===r&&(r=0),void 0===n&&(n=1),void 0===o&&(o=16),"string"!=typeof t&&(t=String(t)),""===t||null==t)return r;if(e.MATHSPACE[t])return e.MATHSPACE[t];var i=t.match(/^\s*([-+]?(?:\.\d+|\d+(?:\.\d*)?))?(pt|em|ex|mu|px|pc|in|mm|cm|%)?/);if(!i)return r;var a=parseFloat(i[1]||"1"),s=i[2];return e.UNITS.hasOwnProperty(s)?a*e.UNITS[s]/o/n:e.RELUNITS.hasOwnProperty(s)?a*e.RELUNITS[s]:"%"===s?a/100*r:a*r},e.percent=function(t){return(100*t).toFixed(1).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"%"},e.em=function(t){return Math.abs(t)<.001?"0":t.toFixed(3).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"em"},e.emRounded=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=16),t=(Math.round(t*e)+.05)/e,Math.abs(t)<.001?"0em":t.toFixed(3).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"em"},e.px=function(t,r,n){return void 0===r&&(r=-e.BIGDIMEN),void 0===n&&(n=16),t*=n,r&&t0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},n=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=s.next()).done;)r.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return r};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AsciiMath=void 0;var o=i(309),l=i(406),u=i(77),h=i(577),p=function(t){function e(i){var n=this,a=r((0,u.separateOptions)(i,h.FindAsciiMath.OPTIONS,e.OPTIONS),3),s=a[1],o=a[2];return(n=t.call(this,o)||this).findAsciiMath=n.options.FindAsciiMath||new h.FindAsciiMath(s),n}return a(e,t),e.prototype.compile=function(t,e){return l.LegacyAsciiMath.Compile(t.math,t.display)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){return this.findAsciiMath.findMath(t)},e.NAME="AsciiMath",e.OPTIONS=s(s({},o.AbstractInputJax.OPTIONS),{FindAsciiMath:null}),e}(o.AbstractInputJax);e.AsciiMath=p},577:function(t,e,i){"use strict";var n,a=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var i in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,i)&&(t[i]=e[i])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function i(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(i.prototype=e.prototype,new i)}),s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var i="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!i)return t;var n,a,s=i.call(t),r=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=s.next()).done;)r.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return r};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.FindAsciiMath=void 0;var r=i(649),o=i(720),l=i(769),u=function(t){function e(e){var i=t.call(this,e)||this;return i.getPatterns(),i}return a(e,t),e.prototype.getPatterns=function(){var t=this,e=this.options,i=[];this.end={},e.delimiters.forEach((function(e){return t.addPattern(i,e,!1)})),this.start=new RegExp(i.join("|"),"g"),this.hasPatterns=i.length>0},e.prototype.addPattern=function(t,e,i){var n=s(e,2),a=n[0],r=n[1];t.push((0,o.quotePattern)(a)),this.end[a]=[r,i,new RegExp((0,o.quotePattern)(r),"g")]},e.prototype.findEnd=function(t,e,i,n){var a=s(n,3),r=a[1],o=a[2],u=o.lastIndex=i.index+i[0].length,h=o.exec(t);return h?(0,l.protoItem)(i[0],t.substr(u,h.index-u),h[0],e,i.index,h.index+h[0].length,r):null},e.prototype.findMathInString=function(t,e,i){var n,a;for(this.start.lastIndex=0;n=this.start.exec(i);)(a=this.findEnd(i,e,n,this.end[n[0]]))&&(t.push(a),this.start.lastIndex=a.end.n)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){var e=[];if(this.hasPatterns)for(var i=0,n=t.length;i1&&(t=2===arguments.length&&"function"!=typeof arguments[0]&&arguments[0]instanceof Object&&"number"==typeof arguments[1]?[].slice.call(t,e):[].slice.call(arguments,0)),t instanceof Array&&1===t.length&&(t=t[0]),"function"==typeof t)return t.execute===i.prototype.execute?t:i({hook:t});if(t instanceof Array){if("string"==typeof t[0]&&t[1]instanceof Object&&"function"==typeof t[1][t[0]])return i({hook:t[1][t[0]],object:t[1],data:t.slice(2)});if("function"==typeof t[0])return i({hook:t[0],data:t.slice(1)});if("function"==typeof t[1])return i({hook:t[1],object:t[0],data:t.slice(2)})}else{if("string"==typeof t)return s&&s(),i({hook:a,data:[t]});if(t instanceof Object)return i(t);if(void 0===t)return i({})}throw Error("Can't make callback from given data")},o=function(t,e){(t=r(t)).called||(p(t,e),e.pending++)},l=function(){var t=this.signal;delete this.signal,this.execute=this.oldExecute,delete this.oldExecute;var e=this.execute.apply(this,arguments);if(n(e)&&!e.called)p(e,t);else for(var i=0,a=t.length;i0&&e=0;t--)this.hooks.splice(t,1);this.remove=[]}}),f=e.Object.Subclass({Init:function(){this.pending=this.running=0,this.queue=[],this.Push.apply(this,arguments)},Push:function(){for(var t,e=0,i=arguments.length;e=this.timeout?(t(this.STATUS.ERROR),1):0},file:function(t,i){i<0?e.Ajax.loadTimeout(t):e.Ajax.loadComplete(t)},execute:function(){this.hook.call(this.object,this,this.data[0],this.data[1])},checkSafari2:function(t,e,i){t.time(i)||(c.styleSheets.length>e&&c.styleSheets[e].cssRules&&c.styleSheets[e].cssRules.length?i(t.STATUS.OK):setTimeout(t,t.delay))},checkLength:function(t,i,n){if(!t.time(n)){var a=0,s=i.sheet||i.styleSheet;try{(s.cssRules||s.rules||[]).length>0&&(a=1)}catch(t){(t.message.match(/protected variable|restricted URI/)||t.message.match(/Security error/))&&(a=1)}a?setTimeout(e.Callback([n,t.STATUS.OK]),0):setTimeout(t,t.delay)}}},loadComplete:function(t){t=this.fileURL(t);var i=this.loading[t];return i&&!i.preloaded?(e.Message.Clear(i.message),i.timeout&&clearTimeout(i.timeout),i.script&&(0===a.length&&setTimeout(s,0),a.push(i.script)),this.loaded[t]=i.status,delete this.loading[t],this.addHook(t,i.callback)):(i&&delete this.loading[t],this.loaded[t]=this.STATUS.OK,i={status:this.STATUS.OK}),this.loadHooks[t]?this.loadHooks[t].Execute(i.status):null},loadTimeout:function(t){this.loading[t].timeout&&clearTimeout(this.loading[t].timeout),this.loading[t].status=this.STATUS.ERROR,this.loadError(t),this.loadComplete(t)},loadError:function(t){e.Message.Set(["LoadFailed","File failed to load: %1",t],null,2e3),e.Hub.signal.Post(["file load error",t])},Styles:function(t,i){var n=this.StyleString(t);if(""===n)(i=e.Callback(i))();else{var a=c.createElement("style");a.type="text/css",this.head=(this.head,null),this.head.appendChild(a),a.styleSheet&&void 0!==a.styleSheet.cssText?a.styleSheet.cssText=n:a.appendChild(c.createTextNode(n)),i=this.timer.create.call(this,i,a)}return i},StyleString:function(t){if("string"==typeof t)return t;var e,i,n="";for(e in t)if(t.hasOwnProperty(e))if("string"==typeof t[e])n+=e+" {"+t[e]+"}\n";else if(t[e]instanceof Array)for(var a=0;a="0"&&r<="9")s[n]=e[s[n]-1],"number"==typeof s[n]&&(s[n]=this.number(s[n]));else if("{"===r)if((r=s[n].substr(1))>="0"&&r<="9")s[n]=e[s[n].substr(1,s[n].length-2)-1],"number"==typeof s[n]&&(s[n]=this.number(s[n]));else{var o=s[n].match(/^\{([a-z]+):%(\d+)\|(.*)\}$/);if(o)if("plural"===o[1]){var l=e[o[2]-1];if(void 0===l)s[n]="???";else{l=this.plural(l)-1;var u=o[3].replace(/(^|[^%])(%%)*%\|/g,"$1$2%\uefef").split(/\|/);l>=0&&l=3?i.push([s[0],s[1],this.processSnippet(t,s[2])]):i.push(e[n])}else i.push(e[n]);return i},markdownPattern:/(%.)|(\*{1,3})((?:%.|.)+?)\2|(`+)((?:%.|.)+?)\4|\[((?:%.|.)+?)\]\(([^\s\)]+)\)/,processMarkdown:function(t,e,i){for(var n,a=[],s=t.split(this.markdownPattern),r=s[0],o=1,l=s.length;o0||this.Get("scriptlevel")>0)&&n>=0?"":this.TEXSPACELENGTH[Math.abs(n)]},TEXSPACELENGTH:["",t.LENGTH.THINMATHSPACE,t.LENGTH.MEDIUMMATHSPACE,t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE],TEXSPACE:[[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[-1,-1,0,3,0,0,0,1],[2,2,0,0,2,0,0,2],[3,3,0,0,3,0,0,3],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],[1,-1,2,3,1,0,1,1]],autoDefault:function(t){return""},isSpacelike:function(){return!1},isEmbellished:function(){return!1},Core:function(){return this},CoreMO:function(){return this},childIndex:function(t){if(null!=t)for(var e=0,i=this.data.length;e=55296&&i.charCodeAt(0)<56320?t.VARIANT.ITALIC:t.VARIANT.NORMAL}return""},setTeXclass:function(e){this.getPrevClass(e);var i=this.data.join("");return i.length>1&&i.match(/^[a-z][a-z0-9]*$/i)&&this.texClass===t.TEXCLASS.ORD&&(this.texClass=t.TEXCLASS.OP,this.autoOP=!0),this}}),t.mn=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mn",isToken:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,defaults:{mathvariant:t.INHERIT,mathsize:t.INHERIT,mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT}}),t.mo=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mo",isToken:!0,defaults:{mathvariant:t.INHERIT,mathsize:t.INHERIT,mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT,form:t.AUTO,fence:t.AUTO,separator:t.AUTO,lspace:t.AUTO,rspace:t.AUTO,stretchy:t.AUTO,symmetric:t.AUTO,maxsize:t.AUTO,minsize:t.AUTO,largeop:t.AUTO,movablelimits:t.AUTO,accent:t.AUTO,linebreak:t.LINEBREAK.AUTO,lineleading:t.INHERIT,linebreakstyle:t.AUTO,linebreakmultchar:t.INHERIT,indentalign:t.INHERIT,indentshift:t.INHERIT,indenttarget:t.INHERIT,indentalignfirst:t.INHERIT,indentshiftfirst:t.INHERIT,indentalignlast:t.INHERIT,indentshiftlast:t.INHERIT,texClass:t.AUTO},defaultDef:{form:t.FORM.INFIX,fence:!1,separator:!1,lspace:t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE,rspace:t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE,stretchy:!1,symmetric:!1,maxsize:t.SIZE.INFINITY,minsize:"0em",largeop:!1,movablelimits:!1,accent:!1,linebreak:t.LINEBREAK.AUTO,lineleading:"1ex",linebreakstyle:"before",indentalign:t.INDENTALIGN.AUTO,indentshift:"0",indenttarget:"",indentalignfirst:t.INDENTALIGN.INDENTALIGN,indentshiftfirst:t.INDENTSHIFT.INDENTSHIFT,indentalignlast:t.INDENTALIGN.INDENTALIGN,indentshiftlast:t.INDENTSHIFT.INDENTSHIFT,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.REL},SPACE_ATTR:{lspace:1,rspace:2,form:4},useMMLspacing:7,autoDefault:function(e,i){var n=this.def;if(!n){if("form"===e)return this.useMMLspacing&=~this.SPACE_ATTR.form,this.getForm();for(var a=this.data.join(""),s=[this.Get("form"),t.FORM.INFIX,t.FORM.POSTFIX,t.FORM.PREFIX],r=0,o=s.length;r=55296&&i<56320&&(i=(i-55296<<10)+(e.charCodeAt(1)-56320)+65536);for(var n=0,a=this.RANGES.length;n=0;t--)if(this.data[0]&&!this.data[t].isSpacelike())return this.data[t];return null},Core:function(){return this.isEmbellished()&&void 0!==this.core?this.data[this.core]:this},CoreMO:function(){return this.isEmbellished()&&void 0!==this.core?this.data[this.core].CoreMO():this},toString:function(){return this.inferred?"["+this.data.join(",")+"]":this.SUPER(arguments).toString.call(this)},setTeXclass:function(e){var i,n=this.data.length;if(!this.open&&!this.close||e&&e.fnOP){for(i=0;i0)&&e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t==this.den||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses}),t.msqrt=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"msqrt",inferRow:!0,linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses,adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return!0}}),t.mroot=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mroot",linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,adjustChild_displaystyle:function(t){return 1!==t&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel");return 1===t&&(e+=2),e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return 0===t||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses}),t.mstyle=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mstyle",isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,inferRow:!0,defaults:{scriptlevel:t.INHERIT,displaystyle:t.INHERIT,scriptsizemultiplier:Math.sqrt(.5),scriptminsize:"8pt",mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT,infixlinebreakstyle:t.LINEBREAKSTYLE.BEFORE,decimalseparator:"."},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.scriptlevel;if(null==e)e=this.Get("scriptlevel");else if(String(e).match(/^ *[-+]/)){e=this.Get("scriptlevel",null,!0)+parseInt(e)}return e},inheritFromMe:!0,noInherit:{mpadded:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,lspace:!0,voffset:!0},mtable:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,align:!0}},getRemoved:{fontfamily:"fontFamily",fontweight:"fontWeight",fontstyle:"fontStyle",fontsize:"fontSize"},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.merror=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"merror",inferRow:!0,linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD}),t.mpadded=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mpadded",inferRow:!0,isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,width:"",height:"",depth:"",lspace:0,voffset:0},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.mphantom=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mphantom",texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,inferRow:!0,isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.mfenced=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mfenced",defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,open:"(",close:")",separators:","},addFakeNodes:function(){var e=this.getValues("open","close","separators");if(e.open=e.open.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),e.close=e.close.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),e.separators=e.separators.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),""!==e.open&&(this.SetData("open",t.mo(e.open).With({fence:!0,form:t.FORM.PREFIX,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.OPEN})),this.data.open.useMMLspacing=0),""!==e.separators){for(;e.separators.length0)&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel");return t>0&&e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t===this.sub||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setBaseTeXclasses}),t.msub=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"msub"}),t.msup=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"msup",sub:2,sup:1}),t.mmultiscripts=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"mmultiscripts",adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t%2==1||this.Get("texprimestyle")}}),t.mprescripts=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mprescripts"}),t.none=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"none"}),t.munderover=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"munderover",base:0,under:1,over:2,sub:1,sup:2,ACCENTS:["","accentunder","accent"],linebreakContainer:!0,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,accent:t.AUTO,accentunder:t.AUTO,align:t.ALIGN.CENTER,texClass:t.AUTO,subscriptshift:"",superscriptshift:""},autoDefault:function(e){return"texClass"===e?this.isEmbellished()?this.CoreMO().Get(e):t.TEXCLASS.ORD:"accent"===e&&this.data[this.over]?this.data[this.over].CoreMO().Get("accent"):!("accentunder"!==e||!this.data[this.under])&&this.data[this.under].CoreMO().Get("accent")},adjustChild_displaystyle:function(t){return!(t>0)&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel"),i=this.data[this.base]&&!this.Get("displaystyle")&&this.data[this.base].CoreMO().Get("movablelimits");return t!=this.under||!i&&this.Get("accentunder")||e++,t!=this.over||!i&&this.Get("accent")||e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return!(t!==this.base||!this.data[this.over])||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setBaseTeXclasses}),t.munder=t.munderover.Subclass({type:"munder"}),t.mover=t.munderover.Subclass({type:"mover",over:1,under:2,sup:1,sub:2,ACCENTS:["","accent","accentunder"]}),t.mtable=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mtable",defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,align:t.ALIGN.AXIS,rowalign:t.ALIGN.BASELINE,columnalign:t.ALIGN.CENTER,groupalign:"{left}",alignmentscope:!0,columnwidth:t.WIDTH.AUTO,width:t.WIDTH.AUTO,rowspacing:"1ex",columnspacing:".8em",rowlines:t.LINES.NONE,columnlines:t.LINES.NONE,frame:t.LINES.NONE,framespacing:"0.4em 0.5ex",equalrows:!1,equalcolumns:!1,displaystyle:!1,side:t.SIDE.RIGHT,minlabelspacing:"0.8em",texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,useHeight:1},adjustChild_displaystyle:function(){return null!=this.displaystyle?this.displaystyle:this.defaults.displaystyle},inheritFromMe:!0,noInherit:{mover:{align:!0},munder:{align:!0},munderover:{align:!0},mtable:{align:!0,rowalign:!0,columnalign:!0,groupalign:!0,alignmentscope:!0,columnwidth:!0,width:!0,rowspacing:!0,columnspacing:!0,rowlines:!0,columnlines:!0,frame:!0,framespacing:!0,equalrows:!0,equalcolumns:!0,displaystyle:!0,side:!0,minlabelspacing:!0,texClass:!0,useHeight:1}},linebreakContainer:!0,Append:function(){for(var e=0,i=arguments.length;e>10),56320+(1023&t)))}}),t.xml=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"xml",Init:function(){return this.div=document.createElement("div"),this.SUPER(arguments).Init.apply(this,arguments)},Append:function(){for(var t=0,e=arguments.length;t":i.REL,"?":[1,1,e.CLOSE],"\\":i.ORD,"^":i.ORD11,_:i.ORD11,"|":[2,2,e.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"#":i.ORD,$:i.ORD,".":[0,3,e.PUNCT,{separator:!0}],"\u02b9":i.ORD,"\u0300":i.ACCENT,"\u0301":i.ACCENT,"\u0303":i.WIDEACCENT,"\u0304":i.ACCENT,"\u0306":i.ACCENT,"\u0307":i.ACCENT,"\u0308":i.ACCENT,"\u030c":i.ACCENT,"\u0332":i.WIDEACCENT,"\u0338":i.REL4,"\u2015":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2017":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2020":i.BIN3,"\u2021":i.BIN3,"\u20d7":i.ACCENT,"\u2111":i.ORD,"\u2113":i.ORD,"\u2118":i.ORD,"\u211c":i.ORD,"\u2205":i.ORD,"\u221e":i.ORD,"\u2305":i.BIN3,"\u2306":i.BIN3,"\u2322":i.REL4,"\u2323":i.REL4,"\u2329":i.OPEN,"\u232a":i.CLOSE,"\u23aa":i.ORD,"\u23af":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u23b0":i.OPEN,"\u23b1":i.CLOSE,"\u2500":i.ORD,"\u25ef":i.BIN3,"\u2660":i.ORD,"\u2661":i.ORD,"\u2662":i.ORD,"\u2663":i.ORD,"\u3008":i.OPEN,"\u3009":i.CLOSE,"\ufe37":i.WIDEACCENT,"\ufe38":i.WIDEACCENT}}},{OPTYPES:i});var n=t.mo.prototype.OPTABLE;n.infix["^"]=i.WIDEREL,n.infix._=i.WIDEREL,n.prefix["\u2223"]=i.OPEN,n.prefix["\u2225"]=i.OPEN,n.postfix["\u2223"]=i.CLOSE,n.postfix["\u2225"]=i.CLOSE}(MathJax.ElementJax.mml),MathJax.ElementJax.mml.loadComplete("jax.js")},315:function(){MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath=MathJax.InputJax({id:"AsciiMath",version:"2.7.2",directory:MathJax.InputJax.directory+"/AsciiMath",extensionDir:MathJax.InputJax.extensionDir+"/AsciiMath",config:{fixphi:!0,useMathMLspacing:!0,displaystyle:!0,decimalsign:"."}}),MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath.Register("math/asciimath"),MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath.loadComplete("config.js")},247:function(){var t,e;!function(t){var e,i=MathJax.Object.Subclass({firstChild:null,lastChild:null,Init:function(){this.childNodes=[]},appendChild:function(t){return t.parent&&t.parent.removeChild(t),this.lastChild&&(this.lastChild.nextSibling=t),this.firstChild||(this.firstChild=t),this.childNodes.push(t),t.parent=this,this.lastChild=t,t},removeChild:function(t){for(var e=0,i=this.childNodes.length;e=n-1&&(this.lastChild=t),this.childNodes[i]=t,t.nextSibling=e.nextSibling,e.nextSibling=e.parent=null,e},hasChildNodes:function(t){return this.childNodes.length>0},toString:function(){return"{"+this.childNodes.join("")+"}"}}),n={getElementById:!0,createElementNS:function(i,n){var a=e[n]();return"mo"===n&&t.config.useMathMLspacing&&(a.useMMLspacing=128),a},createTextNode:function(t){return e.chars(t).With({nodeValue:t})},createDocumentFragment:function(){return i()}},a={appName:"MathJax"},s="blue",r=!0,o=!0,l=".",u="Microsoft"==a.appName.slice(0,9);function h(t){return u?n.createElement(t):n.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",t)}var p="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML";function c(t){return u?n.createElement("m:"+t):n.createElementNS(p,t)}function d(t,e){var i;return i=u?n.createElement("m:"+t):n.createElementNS(p,t),e&&i.appendChild(e),i}var m=["\ud835\udc9c","\u212c","\ud835\udc9e","\ud835\udc9f","\u2130","\u2131","\ud835\udca2","\u210b","\u2110","\ud835\udca5","\ud835\udca6","\u2112","\u2133","\ud835\udca9","\ud835\udcaa","\ud835\udcab","\ud835\udcac","\u211b","\ud835\udcae","\ud835\udcaf","\ud835\udcb0","\ud835\udcb1","\ud835\udcb2","\ud835\udcb3","\ud835\udcb4","\ud835\udcb5","\ud835\udcb6","\ud835\udcb7","\ud835\udcb8","\ud835\udcb9","\u212f","\ud835\udcbb","\u210a","\ud835\udcbd","\ud835\udcbe","\ud835\udcbf","\ud835\udcc0","\ud835\udcc1","\ud835\udcc2","\ud835\udcc3","\u2134","\ud835\udcc5","\ud835\udcc6","\ud835\udcc7","\ud835\udcc8","\ud835\udcc9","\ud835\udcca","\ud835\udccb","\ud835\udccc","\ud835\udccd","\ud835\udcce","\ud835\udccf"],f=["\ud835\udd04","\ud835\udd05","\u212d","\ud835\udd07","\ud835\udd08","\ud835\udd09","\ud835\udd0a","\u210c","\u2111","\ud835\udd0d","\ud835\udd0e","\ud835\udd0f","\ud835\udd10","\ud835\udd11","\ud835\udd12","\ud835\udd13","\ud835\udd14","\u211c","\ud835\udd16","\ud835\udd17","\ud835\udd18","\ud835\udd19","\ud835\udd1a","\ud835\udd1b","\ud835\udd1c","\u2128","\ud835\udd1e","\ud835\udd1f","\ud835\udd20","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd22","\ud835\udd23","\ud835\udd24","\ud835\udd25","\ud835\udd26","\ud835\udd27","\ud835\udd28","\ud835\udd29","\ud835\udd2a","\ud835\udd2b","\ud835\udd2c","\ud835\udd2d","\ud835\udd2e","\ud835\udd2f","\ud835\udd30","\ud835\udd31","\ud835\udd32","\ud835\udd33","\ud835\udd34","\ud835\udd35","\ud835\udd36","\ud835\udd37"],g=["\ud835\udd38","\ud835\udd39","\u2102","\ud835\udd3b","\ud835\udd3c","\ud835\udd3d","\ud835\udd3e","\u210d","\ud835\udd40","\ud835\udd41","\ud835\udd42","\ud835\udd43","\ud835\udd44","\u2115","\ud835\udd46","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\ud835\udd4a","\ud835\udd4b","\ud835\udd4c","\ud835\udd4d","\ud835\udd4e","\ud835\udd4f","\ud835\udd50","\u2124","\ud835\udd52","\ud835\udd53","\ud835\udd54","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd56","\ud835\udd57","\ud835\udd58","\ud835\udd59","\ud835\udd5a","\ud835\udd5b","\ud835\udd5c","\ud835\udd5d","\ud835\udd5e","\ud835\udd5f","\ud835\udd60","\ud835\udd61","\ud835\udd62","\ud835\udd63","\ud835\udd64","\ud835\udd65","\ud835\udd66","\ud835\udd67","\ud835\udd68","\ud835\udd69","\ud835\udd6a","\ud835\udd6b"],y=0,E=1,x=2,T=3,C=4,b=5,S=6,I=7,N=8,A=9,v=10,R=15,O={input:'"',tag:"mtext",output:"mbox",tex:null,ttype:v},L=[{input:"alpha",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"beta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b2",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"chi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c7",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"delta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Delta",tag:"mo",output:"\u0394",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"epsi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b5",tex:"epsilon",ttype:y},{input:"varepsilon",tag:"mi",output:"\u025b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"eta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b7",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"gamma",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Gamma",tag:"mo",output:"\u0393",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"iota",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"kappa",tag:"mi",output:"\u03ba",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lambda",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Lambda",tag:"mo",output:"\u039b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lamda",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Lamda",tag:"mo",output:"\u039b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"mu",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bc",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"nu",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bd",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"omega",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Omega",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"phi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03d5",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"varphi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Phi",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"pi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Pi",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"psi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Psi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03a8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"rho",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"sigma",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Sigma",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"tau",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"theta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"vartheta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03d1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Theta",tag:"mo",output:"\u0398",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"upsilon",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c5",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"xi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03be",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Xi",tag:"mo",output:"\u039e",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"zeta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"*",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c5",tex:"cdot",ttype:y},{input:"**",tag:"mo",output:"\u2217",tex:"ast",ttype:y},{input:"***",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c6",tex:"star",ttype:y},{input:"//",tag:"mo",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"\\\\",tag:"mo",output:"\\",tex:"backslash",ttype:y},{input:"setminus",tag:"mo",output:"\\",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"xx",tag:"mo",output:"\xd7",tex:"times",ttype:y},{input:"|><",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c9",tex:"ltimes",ttype:y},{input:"><|",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ca",tex:"rtimes",ttype:y},{input:"|><|",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c8",tex:"bowtie",ttype:y},{input:"-:",tag:"mo",output:"\xf7",tex:"div",ttype:y},{input:"divide",tag:"mo",output:"-:",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"@",tag:"mo",output:"\u2218",tex:"circ",ttype:y},{input:"o+",tag:"mo",output:"\u2295",tex:"oplus",ttype:y},{input:"ox",tag:"mo",output:"\u2297",tex:"otimes",ttype:y},{input:"o.",tag:"mo",output:"\u2299",tex:"odot",ttype:y},{input:"sum",tag:"mo",output:"\u2211",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"prod",tag:"mo",output:"\u220f",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"^^",tag:"mo",output:"\u2227",tex:"wedge",ttype:y},{input:"^^^",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c0",tex:"bigwedge",ttype:I},{input:"vv",tag:"mo",output:"\u2228",tex:"vee",ttype:y},{input:"vvv",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c1",tex:"bigvee",ttype:I},{input:"nn",tag:"mo",output:"\u2229",tex:"cap",ttype:y},{input:"nnn",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c2",tex:"bigcap",ttype:I},{input:"uu",tag:"mo",output:"\u222a",tex:"cup",ttype:y},{input:"uuu",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c3",tex:"bigcup",ttype:I},{input:"!=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2260",tex:"ne",ttype:y},{input:":=",tag:"mo",output:":=",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lt",tag:"mo",output:"<",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"<=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2264",tex:"le",ttype:y},{input:"lt=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2264",tex:"leq",ttype:y},{input:"gt",tag:"mo",output:">",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:">=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2265",tex:"ge",ttype:y},{input:"gt=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2265",tex:"geq",ttype:y},{input:"-<",tag:"mo",output:"\u227a",tex:"prec",ttype:y},{input:"-lt",tag:"mo",output:"\u227a",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:">-",tag:"mo",output:"\u227b",tex:"succ",ttype:y},{input:"-<=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2aaf",tex:"preceq",ttype:y},{input:">-=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2ab0",tex:"succeq",ttype:y},{input:"in",tag:"mo",output:"\u2208",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"!in",tag:"mo",output:"\u2209",tex:"notin",ttype:y},{input:"sub",tag:"mo",output:"\u2282",tex:"subset",ttype:y},{input:"sup",tag:"mo",output:"\u2283",tex:"supset",ttype:y},{input:"sube",tag:"mo",output:"\u2286",tex:"subseteq",ttype:y},{input:"supe",tag:"mo",output:"\u2287",tex:"supseteq",ttype:y},{input:"-=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2261",tex:"equiv",ttype:y},{input:"~=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2245",tex:"cong",ttype:y},{input:"~~",tag:"mo",output:"\u2248",tex:"approx",ttype:y},{input:"~",tag:"mo",output:"\u223c",tex:"sim",ttype:y},{input:"prop",tag:"mo",output:"\u221d",tex:"propto",ttype:y},{input:"and",tag:"mtext",output:"and",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"or",tag:"mtext",output:"or",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"not",tag:"mo",output:"\xac",tex:"neg",ttype:y},{input:"=>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d2",tex:"implies",ttype:y},{input:"if",tag:"mo",output:"if",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"<=>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d4",tex:"iff",ttype:y},{input:"AA",tag:"mo",output:"\u2200",tex:"forall",ttype:y},{input:"EE",tag:"mo",output:"\u2203",tex:"exists",ttype:y},{input:"_|_",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a5",tex:"bot",ttype:y},{input:"TT",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a4",tex:"top",ttype:y},{input:"|--",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a2",tex:"vdash",ttype:y},{input:"|==",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a8",tex:"models",ttype:y},{input:"(",tag:"mo",output:"(",tex:"left(",ttype:C},{input:")",tag:"mo",output:")",tex:"right)",ttype:b},{input:"[",tag:"mo",output:"[",tex:"left[",ttype:C},{input:"]",tag:"mo",output:"]",tex:"right]",ttype:b},{input:"{",tag:"mo",output:"{",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:"}",tag:"mo",output:"}",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"|",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:A},{input:":|:",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"|:",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:":|",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"(:",tag:"mo",output:"\u2329",tex:"langle",ttype:C},{input:":)",tag:"mo",output:"\u232a",tex:"rangle",ttype:b},{input:"<<",tag:"mo",output:"\u2329",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:">>",tag:"mo",output:"\u232a",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"{:",tag:"mo",output:"{:",tex:null,ttype:C,invisible:!0},{input:":}",tag:"mo",output:":}",tex:null,ttype:b,invisible:!0},{input:"int",tag:"mo",output:"\u222b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"dx",tag:"mi",output:"{:d x:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dy",tag:"mi",output:"{:d y:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dz",tag:"mi",output:"{:d z:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dt",tag:"mi",output:"{:d t:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"oint",tag:"mo",output:"\u222e",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"del",tag:"mo",output:"\u2202",tex:"partial",ttype:y},{input:"grad",tag:"mo",output:"\u2207",tex:"nabla",ttype:y},{input:"+-",tag:"mo",output:"\xb1",tex:"pm",ttype:y},{input:"-+",tag:"mo",output:"\u2213",tex:"mp",ttype:y},{input:"O/",tag:"mo",output:"\u2205",tex:"emptyset",ttype:y},{input:"oo",tag:"mo",output:"\u221e",tex:"infty",ttype:y},{input:"aleph",tag:"mo",output:"\u2135",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"...",tag:"mo",output:"...",tex:"ldots",ttype:y},{input:":.",tag:"mo",output:"\u2234",tex:"therefore",ttype:y},{input:":'",tag:"mo",output:"\u2235",tex:"because",ttype:y},{input:"/_",tag:"mo",output:"\u2220",tex:"angle",ttype:y},{input:"/_\\",tag:"mo",output:"\u25b3",tex:"triangle",ttype:y},{input:"'",tag:"mo",output:"\u2032",tex:"prime",ttype:y},{input:"tilde",tag:"mover",output:"~",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"\\ ",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"frown",tag:"mo",output:"\u2322",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"quad",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"qquad",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0\xa0\xa0\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"cdots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ef",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"vdots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ee",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"ddots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22f1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"diamond",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"square",tag:"mo",output:"\u25a1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"|__",tag:"mo",output:"\u230a",tex:"lfloor",ttype:y},{input:"__|",tag:"mo",output:"\u230b",tex:"rfloor",ttype:y},{input:"|~",tag:"mo",output:"\u2308",tex:"lceiling",ttype:y},{input:"~|",tag:"mo",output:"\u2309",tex:"rceiling",ttype:y},{input:"CC",tag:"mo",output:"\u2102",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"NN",tag:"mo",output:"\u2115",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"QQ",tag:"mo",output:"\u211a",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"RR",tag:"mo",output:"\u211d",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"ZZ",tag:"mo",output:"\u2124",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"f",tag:"mi",output:"f",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"g",tag:"mi",output:"g",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lim",tag:"mo",output:"lim",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"Lim",tag:"mo",output:"Lim",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"sin",tag:"mo",output:"sin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cos",tag:"mo",output:"cos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"tan",tag:"mo",output:"tan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sinh",tag:"mo",output:"sinh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cosh",tag:"mo",output:"cosh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"tanh",tag:"mo",output:"tanh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cot",tag:"mo",output:"cot",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sec",tag:"mo",output:"sec",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"csc",tag:"mo",output:"csc",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arcsin",tag:"mo",output:"arcsin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arccos",tag:"mo",output:"arccos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arctan",tag:"mo",output:"arctan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"coth",tag:"mo",output:"coth",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sech",tag:"mo",output:"sech",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"csch",tag:"mo",output:"csch",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"exp",tag:"mo",output:"exp",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"abs",tag:"mo",output:"abs",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["|","|"]},{input:"norm",tag:"mo",output:"norm",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u2225","\u2225"]},{input:"floor",tag:"mo",output:"floor",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u230a","\u230b"]},{input:"ceil",tag:"mo",output:"ceil",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u2308","\u2309"]},{input:"log",tag:"mo",output:"log",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"ln",tag:"mo",output:"ln",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"det",tag:"mo",output:"det",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"dim",tag:"mo",output:"dim",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"mod",tag:"mo",output:"mod",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"gcd",tag:"mo",output:"gcd",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lcm",tag:"mo",output:"lcm",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lub",tag:"mo",output:"lub",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"glb",tag:"mo",output:"glb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"min",tag:"mo",output:"min",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"max",tag:"mo",output:"max",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"Sin",tag:"mo",output:"Sin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cos",tag:"mo",output:"Cos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Tan",tag:"mo",output:"Tan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arcsin",tag:"mo",output:"Arcsin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arccos",tag:"mo",output:"Arccos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arctan",tag:"mo",output:"Arctan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Sinh",tag:"mo",output:"Sinh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cosh",tag:"mo",output:"Cosh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Tanh",tag:"mo",output:"Tanh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cot",tag:"mo",output:"Cot",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Sec",tag:"mo",output:"Sec",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Csc",tag:"mo",output:"Csc",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Log",tag:"mo",output:"Log",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Ln",tag:"mo",output:"Ln",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Abs",tag:"mo",output:"abs",tex:null,ttype:E,notexcopy:!0,rewriteleftright:["|","|"]},{input:"uarr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2191",tex:"uparrow",ttype:y},{input:"darr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2193",tex:"downarrow",ttype:y},{input:"rarr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2192",tex:"rightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"->",tag:"mo",output:"\u2192",tex:"to",ttype:y},{input:">->",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a3",tex:"rightarrowtail",ttype:y},{input:"->>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a0",tex:"twoheadrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:">->>",tag:"mo",output:"\u2916",tex:"twoheadrightarrowtail",ttype:y},{input:"|->",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a6",tex:"mapsto",ttype:y},{input:"larr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2190",tex:"leftarrow",ttype:y},{input:"harr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2194",tex:"leftrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"rArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d2",tex:"Rightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"lArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d0",tex:"Leftarrow",ttype:y},{input:"hArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d4",tex:"Leftrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"sqrt",tag:"msqrt",output:"sqrt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"root",tag:"mroot",output:"root",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"frac",tag:"mfrac",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"/",tag:"mfrac",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"stackrel",tag:"mover",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"overset",tag:"mover",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"underset",tag:"munder",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"_",tag:"msub",output:"_",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"^",tag:"msup",output:"^",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"hat",tag:"mover",output:"^",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"bar",tag:"mover",output:"\xaf",tex:"overline",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"vec",tag:"mover",output:"\u2192",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"dot",tag:"mover",output:".",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ddot",tag:"mover",output:"..",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"overarc",tag:"mover",output:"\u23dc",tex:"overparen",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ul",tag:"munder",output:"\u0332",tex:"underline",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ubrace",tag:"munder",output:"\u23df",tex:"underbrace",ttype:R,acc:!0},{input:"obrace",tag:"mover",output:"\u23de",tex:"overbrace",ttype:R,acc:!0},{input:"text",tag:"mtext",output:"text",tex:null,ttype:v},{input:"mbox",tag:"mtext",output:"mbox",tex:null,ttype:v},{input:"color",tag:"mstyle",ttype:x},{input:"id",tag:"mrow",ttype:x},{input:"class",tag:"mrow",ttype:x},{input:"cancel",tag:"menclose",output:"cancel",tex:null,ttype:E},O,{input:"bb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"bold",output:"bb",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathbf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"bold",output:"mathbf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"sf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"sans-serif",output:"sf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathsf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"sans-serif",output:"mathsf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"bbb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"double-struck",output:"bbb",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:g},{input:"mathbb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"double-struck",output:"mathbb",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:g},{input:"cc",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"script",output:"cc",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:m},{input:"mathcal",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"script",output:"mathcal",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:m},{input:"tt",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"monospace",output:"tt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathtt",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"monospace",output:"mathtt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"fr",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"fraktur",output:"fr",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:f},{input:"mathfrak",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"fraktur",output:"mathfrak",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:f}];function M(t,e){return t.input>e.input?1:-1}var k,D,P,H=[];function w(){var t,e=L.length;for(t=0;t>1]=H[a];if(D=P,""!=s)return P=L[e].ttype,L[e];P=y,a=1,i=t.slice(0,1);for(var u=!0;"0"<=i&&i<="9"&&a<=t.length;)i=t.slice(a,a+1),a++;if(i==l&&"0"<=(i=t.slice(a,a+1))&&i<="9")for(u=!1,a++;"0"<=i&&i<="9"&&a<=t.length;)i=t.slice(a,a+1),a++;return u&&a>1||a>2?(i=t.slice(0,a-1),n="mn"):(a=2,n=("A">(i=t.slice(0,1))||i>"Z")&&("a">i||i>"z")?"mo":"mi"),"-"==i&&" "!==t.charAt(1)&&D==T?(P=T,{input:i,tag:n,output:i,ttype:E,func:!0}):{input:i,tag:n,output:i,ttype:y}}function j(t){var e;t.hasChildNodes()&&(!t.firstChild.hasChildNodes()||"mrow"!=t.nodeName&&"M:MROW"!=t.nodeName||"("!=(e=t.firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue)&&"["!=e&&"{"!=e||t.removeChild(t.firstChild),!t.lastChild.hasChildNodes()||"mrow"!=t.nodeName&&"M:MROW"!=t.nodeName||")"!=(e=t.lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue)&&"]"!=e&&"}"!=e||t.removeChild(t.lastChild))}function B(t){var e,i,a,s,r,o=n.createDocumentFragment();if(null==(e=U(t=J(t,0)))||e.ttype==b&&k>0)return[null,t];switch(e.ttype==N&&(e=U(t=e.output+J(t,e.input.length))),e.ttype){case I:case y:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];case C:return k++,a=G(t=J(t,e.input.length),!0),k--,"boolean"==typeof e.invisible&&e.invisible?i=d("mrow",a[0]):(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),(i=d("mrow",i)).appendChild(a[0])),[i,a[1]];case v:return e!=O&&(t=J(t,e.input.length)),-1==(s="{"==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf("}"):"("==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf(")"):"["==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf("]"):e==O?t.slice(1).indexOf('"')+1:0)&&(s=t.length)," "==(r=t.slice(1,s)).charAt(0)&&((i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i)),o.appendChild(d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(r)))," "==r.charAt(r.length-1)&&((i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i)),t=J(t,s+1),[d("mrow",o),t];case R:case E:if(null==(a=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0])return[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];if("boolean"==typeof e.func&&e.func)return"^"==(r=t.charAt(0))||"_"==r||"/"==r||"|"==r||","==r||1==e.input.length&&e.input.match(/\w/)&&"("!=r?[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t]:((i=d("mrow",d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)))).appendChild(a[0]),[i,a[1]]);if(j(a[0]),"sqrt"==e.input)return[d(e.tag,a[0]),a[1]];if(void 0!==e.rewriteleftright)return(i=d("mrow",d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.rewriteleftright[0])))).appendChild(a[0]),i.appendChild(d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.rewriteleftright[1]))),[i,a[1]];if("cancel"==e.input)return(i=d(e.tag,a[0])).setAttribute("notation","updiagonalstrike"),[i,a[1]];if("boolean"==typeof e.acc&&e.acc){i=d(e.tag,a[0]);var l=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output));return"vec"==e.input&&("mrow"==a[0].nodeName&&1==a[0].childNodes.length&&null!==a[0].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue&&1==a[0].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue.length||null!==a[0].firstChild.nodeValue&&1==a[0].firstChild.nodeValue.length)&&l.setAttribute("stretchy",!1),i.appendChild(l),[i,a[1]]}if(!u&&void 0!==e.codes)for(s=0;s64&&r.charCodeAt(p)<91?h+=e.codes[r.charCodeAt(p)-65]:r.charCodeAt(p)>96&&r.charCodeAt(p)<123?h+=e.codes[r.charCodeAt(p)-71]:h+=r.charAt(p);"mi"==a[0].nodeName?a[0]=d("mo").appendChild(n.createTextNode(h)):a[0].replaceChild(d("mo").appendChild(n.createTextNode(h)),a[0].childNodes[s])}return(i=d(e.tag,a[0])).setAttribute(e.atname,e.atval),[i,a[1]];case x:if(null==(a=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0])return[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.input)),t];j(a[0]);var c=B(a[1]);return null==c[0]?[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.input)),t]:(j(c[0]),["color","class","id"].indexOf(e.input)>=0?("{"==t.charAt(0)?s=t.indexOf("}"):"("==t.charAt(0)?s=t.indexOf(")"):"["==t.charAt(0)&&(s=t.indexOf("]")),r=t.slice(1,s),i=d(e.tag,c[0]),"color"===e.input?i.setAttribute("mathcolor",r):"class"===e.input?i.setAttribute("class",r):"id"===e.input&&i.setAttribute("id",r),[i,c[1]]):("root"!=e.input&&"stackrel"!=e.output||o.appendChild(c[0]),o.appendChild(a[0]),"frac"==e.input&&o.appendChild(c[0]),[d(e.tag,o),c[1]]));case T:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];case S:return t=J(t,e.input.length),(i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i),o.appendChild(d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output))),(i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i),[d("mrow",o),t];case A:return k++,a=G(t=J(t,e.input.length),!1),k--,r="",null!=a[0].lastChild&&(r=a[0].lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue),"|"==r&&","!==t.charAt(0)?(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),(i=d("mrow",i)).appendChild(a[0]),[i,a[1]]):(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u2223")),[i=d("mrow",i),t]);default:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t]}}function F(t){var e,i,a,s,r,o;if(i=U(t=J(t,0)),s=(r=B(t))[0],(e=U(t=r[1])).ttype==T&&"/"!=e.input){if(null==(r=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0]?r[0]=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u25a1")):j(r[0]),t=r[1],o=i.ttype==I||i.ttype==R,"_"==e.input)if("^"==(a=U(t)).input){var l=B(t=J(t,a.input.length));j(l[0]),t=l[1],(s=d(o?"munderover":"msubsup",s)).appendChild(r[0]),s.appendChild(l[0]),s=d("mrow",s)}else(s=d(o?"munder":"msub",s)).appendChild(r[0]);else"^"==e.input&&o?(s=d("mover",s)).appendChild(r[0]):(s=d(e.tag,s)).appendChild(r[0]);void 0!==i.func&&i.func&&(a=U(t)).ttype!=T&&a.ttype!=b&&(i.input.length>1||a.ttype==C)&&(r=F(t),(s=d("mrow",s)).appendChild(r[0]),t=r[1])}return[s,t]}function G(t,e){var i,a,s,r,o=n.createDocumentFragment();do{a=(s=F(t=J(t,0)))[0],(i=U(t=s[1])).ttype==T&&"/"==i.input?(null==(s=F(t=J(t,i.input.length)))[0]?s[0]=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u25a1")):j(s[0]),t=s[1],j(a),(a=d(i.tag,a)).appendChild(s[0]),o.appendChild(a),i=U(t)):null!=a&&o.appendChild(a)}while((i.ttype!=b&&(i.ttype!=A||e)||0==k)&&null!=i&&""!=i.output);if(i.ttype==b||i.ttype==A){var l=o.childNodes.length;if(l>0&&"mrow"==o.childNodes[l-1].nodeName&&o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild&&o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild.firstChild){var u=o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue;if(")"==u||"]"==u){var h=o.childNodes[l-1].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue;if("("==h&&")"==u&&"}"!=i.output||"["==h&&"]"==u){var p=[],c=!0,m=o.childNodes.length;for(r=0;c&&r1&&(c=p[r].length==p[r-2].length)}var g=[];if(c=c&&(p.length>1||p[0].length>0)){var y,E,x,C,S=n.createDocumentFragment();for(r=0;r2&&(o.removeChild(o.firstChild),o.removeChild(o.firstChild)),S.appendChild(d("mtr",y))}(a=d("mtable",S)).setAttribute("columnlines",g.join(" ")),"boolean"==typeof i.invisible&&i.invisible&&a.setAttribute("columnalign","left"),o.replaceChild(a,o.firstChild)}}}}t=J(t,i.input.length),"boolean"==typeof i.invisible&&i.invisible||(a=d("mo",n.createTextNode(i.output)),o.appendChild(a))}return[o,t]}function V(t,e){var i;return k=0,i=d("mstyle",G((t=(t=(t=t.replace(/ /g,"")).replace(/>/g,">")).replace(/</g,"<")).replace(/^\s+/g,""),!1)[0]),""!=s&&i.setAttribute("mathcolor",s),""!=z&&(i.setAttribute("fontsize",z),i.setAttribute("mathsize",z)),""!=W&&(i.setAttribute("fontfamily",W),i.setAttribute("mathvariant",W)),r&&i.setAttribute("displaystyle","true"),i=d("math",i),o&&i.setAttribute("title",t.replace(/\s+/g," ")),i}o=!1;var W="",z=(s="","");!function(){for(var t=0,e=L.length;t=n-1&&(this.lastChild=t),this.SetData(i,t),t.nextSibling=e.nextSibling,e.nextSibling=e.parent=null,e},hasChildNodes:function(t){return this.childNodes.length>0},setAttribute:function(t,e){this[t]=e}}),w()},Augment:function(t){for(var e in t)if(t.hasOwnProperty(e)){switch(e){case"displaystyle":r=t[e];break;case"decimal":decimal=t[e];break;case"parseMath":V=t[e];break;case"parseExpr":G=t[e];break;case"parseIexpr":F=t[e];break;case"parseSexpr":B=t[e];break;case"removeBrackets":j=t[e];break;case"getSymbol":U=t[e];break;case"position":X=t[e];break;case"removeCharsAndBlanks":J=t[e];break;case"createMmlNode":d=t[e];break;case"createElementMathML":c=t[e];break;case"createElementXHTML":h=t[e];break;case"initSymbols":w=t[e];break;case"refreshSymbols":_=t[e];break;case"compareNames":M=t[e]}this[e]=t[e]}},parseMath:V,parseExpr:G,parseIexpr:F,parseSexr:B,removeBrackets:j,getSymbol:U,position:X,removeCharsAndBlanks:J,createMmlNode:d,createElementMathML:c,createElementXHTML:h,initSymbols:w,refreshSymbols:_,compareNames:M,createDocumentFragment:i,document:n,define:function(t,e){L.push({input:t,tag:"mo",output:e,tex:null,ttype:N}),_()},newcommand:function(t,e){L.push({input:t,tag:"mo",output:e,tex:null,ttype:N}),_()},newsymbol:function(t){L.push(t),_()},symbols:L,names:H,TOKEN:{CONST:y,UNARY:E,BINARY:x,INFIX:T,LEFTBRACKET:C,RIGHTBRACKET:b,SPACE:S,UNDEROVER:I,DEFINITION:N,LEFTRIGHT:A,TEXT:v,UNARYUNDEROVER:R}}})}(MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath),(t=MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath).Augment({sourceMenuTitle:["AsciiMathInput","AsciiMath Input"],annotationEncoding:"text/x-asciimath",prefilterHooks:MathJax.Callback.Hooks(!0),postfilterHooks:MathJax.Callback.Hooks(!0),Translate:function(t){var i,n=MathJax.HTML.getScript(t),a={math:n,script:t},s=this.prefilterHooks.Execute(a);if(s)return s;n=a.math;try{i=this.AM.parseMath(n)}catch(t){if(!t.asciimathError)throw t;i=this.formatError(t,n)}return a.math=e(i),this.postfilterHooks.Execute(a),this.postfilterHooks.Execute(a)||a.math},formatError:function(t,i,n){var a=t.message.replace(/\n.*/,"");return MathJax.Hub.signal.Post(["AsciiMath Jax - parse error",a,i,n]),e.Error(a)},Error:function(t){throw MathJax.Hub.Insert(Error(t),{asciimathError:!0})},Startup:function(){e=MathJax.ElementJax.mml,this.AM.Init()}}),t.loadComplete("jax.js")},723:function(t,e){"use strict";MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},649:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractFindMath=MathJax._.core.FindMath.AbstractFindMath},309:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractInputJax=MathJax._.core.InputJax.AbstractInputJax},769:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.protoItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.protoItem,e.AbstractMathItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.AbstractMathItem,e.STATE=MathJax._.core.MathItem.STATE,e.newState=MathJax._.core.MathItem.newState},806:function(t,e){"use strict";e.g=MathJax._.core.MmlTree.MmlFactory.MmlFactory},77:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup},720:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.sortLength=MathJax._.util.string.sortLength,e.quotePattern=MathJax._.util.string.quotePattern,e.unicodeChars=MathJax._.util.string.unicodeChars,e.unicodeString=MathJax._.util.string.unicodeString,e.isPercent=MathJax._.util.string.isPercent,e.split=MathJax._.util.string.split}},e={};function i(n){var a=e[n];if(void 0!==a)return a.exports;var s=e[n]={exports:{}};return t[n].call(s.exports,s,s.exports,i),s.exports}i.g=function(){if("object"==typeof globalThis)return globalThis;try{return this||new Function("return this")()}catch(t){if("object"==typeof window)return window}}(),function(){"use strict";var t=i(723),e=i(306),n=i(884),a=i(577);MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("input/asciimath",e.q,"input"),(0,t.r8)({_:{input:{asciimath_ts:n,asciimath:{FindAsciiMath:a}}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.registerConstructor("asciimath",n.AsciiMath),MathJax.startup.useInput("asciimath"))}()}();����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692426889.044968
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/input/mml.js������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000034367�00000000000�020427� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,r,a,o,i={306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},236:function(t,e,r){var a,o=this&&this.__extends||(a=function(t,e){return a=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},a(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}a(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var a,o,i=r.call(t),n=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(a=i.next()).done;)n.push(a.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return n};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathML=void 0;var n=r(309),s=r(77),l=r(898),c=r(794),h=r(332),p=function(t){function e(e){void 0===e&&(e={});var r=this,a=i((0,s.separateOptions)(e,c.FindMathML.OPTIONS,h.MathMLCompile.OPTIONS),3),o=a[0],n=a[1],p=a[2];return(r=t.call(this,o)||this).findMathML=r.options.FindMathML||new c.FindMathML(n),r.mathml=r.options.MathMLCompile||new h.MathMLCompile(p),r.mmlFilters=new l.FunctionList,r}return o(e,t),e.prototype.setAdaptor=function(e){t.prototype.setAdaptor.call(this,e),this.findMathML.adaptor=e,this.mathml.adaptor=e},e.prototype.setMmlFactory=function(e){t.prototype.setMmlFactory.call(this,e),this.mathml.setMmlFactory(e)},Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"processStrings",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.compile=function(t,e){var r=t.start.node;if(!r||!t.end.node||this.options.forceReparse||"#text"===this.adaptor.kind(r)){var a=this.executeFilters(this.preFilters,t,e,(t.math||"").trim()),o=this.checkForErrors(this.adaptor.parse(a,"text/"+this.options.parseAs)),i=this.adaptor.body(o);1!==this.adaptor.childNodes(i).length&&this.error("MathML must consist of a single element"),r=this.adaptor.remove(this.adaptor.firstChild(i)),"math"!==this.adaptor.kind(r).replace(/^[a-z]+:/,"")&&this.error("MathML must be formed by a
## Installation
Currently tested with python 3.8.10/3.10.0 and opencv-contrib-python-headless 4.8.0.76 on an M1 Mac.
From PyPi:
```shell
pip install opencv-pg
```
From Github Repo:
```shell
pip install git+https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
```
### Note for Linux Users
**NOTE:** I no longer have access to anything but a Mac (as of `1.0.2`), so I can't confirm if the below still stands. It did in `1.0.1`.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (others currently untested), there may be missing links to xcb related shared objects.
tldr;
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
------
**Digging Deeper**
If you see errors about xcb, you can perform the following to help troubleshoot. In your terminal, make the following export:
```shell
export QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS=1
```
Run opencvpg again and validate the output. The final lines will likely mention details about files not found. Likely `libxcb-xinerama.so.0`.
Run the following:
```shell
cd your_venv/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/PySide2/Qt/plugins/platforms/
ldd libqxcb.so | grep "not found"
```
This will print any missing links. In our case, `libxcb-xinerama.so.0` showed up a couple times. Reinstalling the package as follows resolved the issue:
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
Once it’s working, you may want to disable that `QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS` env variable so it doesn’t throw extra garbage in your output.
## Usage
### Playground
To launch the OpenCV Playground with:
* The built-in image:
```shell
opencvpg
```
* An image of your choice:
```shell
opencvpg --image
```
* Without the documentation window:
```shell
opencvpg --no-docs
```
### Custom Pipeline
The following is an example of building a custom Pipeline.
```python
from opencv_pg import Pipeline, Window, launch_pipeline
from opencv_pg import support_transforms as supt
from opencv_pg import transforms as tf
if __name__ == '__main__':
my_image = '/path/to/image.png'
# Creates two windows
pipeline = Pipeline([
Window([
supt.LoadImage(my_image),
supt.CvtColor(),
tf.InRange(),
supt.BitwiseAnd(),
]),
Window([
tf.Canny(),
]),
])
launch_pipeline(pipeline)
```
Then run the file.
## Development
### Installation
To install in development mode:
```shell
git clone https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
pip install -e opencv-pg/[dev]
```
### Running Tests
```shell
cd tests
pytest
```
### Generating Docs
* Go into the top level `docs` directory
* run `sphinx-apidoc -f -o source/ ../src/opencv_pg`
* run `make html`
Output will be in the `docs/build/html/` directory.
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692427051.7198155
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/pyproject.toml����������������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000001657�00000000000�013306� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������[build-system]
build-backend = "flit_core.buildapi"
requires = ["flit_core >=3.2,<4"]
[project]
name = "opencv-pg"
description = "Qt6 GUI Application for realtime exploration of OpenCV functions"
version = "1.0.2"
readme = "README.md"
authors = []
requires-python = ">=3.7"
license = { file = "LICENSE.txt" }
dependencies = [
"pyside6==6.5.2",
"qtpy==2.3.1",
"opencv-contrib-python-headless==4.8.0.76",
"jinja2==3.1.2",
]
keywords = ["opencv", "cv2", "cv", "computer vision"]
[project.optional-dependencies]
dev = ["pytest==6.0.1", "flake8", "sphinx==3.2.1"]
[project.urls]
Homepage = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg"
Documentation = "https://opencv-pg.readthedocs.io/en/latest/"
Repository = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg"
Changelog = "https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md"
[project.scripts]
opencvpg = "opencv_pg.launcher:main"
opencvpg_docview = "opencv_pg.launcher:docview"
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692379427.5699644
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/.DS_Store�������������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�014612� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������������������������������������������������������������������������bwspblob���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������d�o�c�sbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������d�o�c�svSrnlong���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1640369016.170552
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/__init__.py�����������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000001062�00000000000�015240� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������from opencv_pg.pipeline_launcher import launch_pipeline
from jinja2 import Environment, PackageLoader, select_autoescape
env = Environment(
loader=PackageLoader("opencv_pg", "docs/source_docs"),
autoescape=select_autoescape(["html"]),
)
from opencv_pg.models.pipeline import Pipeline
from opencv_pg.models.window import Window
from opencv_pg.models.base_transform import BaseTransform
from opencv_pg.models import params
from opencv_pg.models.params import Param
from opencv_pg.models import transforms
from opencv_pg.models import support_transforms
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1706455
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/doc_viewer.py���������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000004227�00000000000�015635� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������from pathlib import Path
from qtpy.QtCore import Slot, QUrl
from qtpy.QtGui import QKeySequence
from qtpy.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QAction
from qtpy.QtWebEngineWidgets import QWebEngineView
from opencv_pg.docs import doc_writer
# Make sure rendered_docs folder exists
doc_writer._create_rendered_docs()
class MyWebView(QWebEngineView):
def contextMenuEvent(self, event):
self.parent().reload()
super().contextMenuEvent(event)
class DocWindow(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self, template_name):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("OpenCV DocViewer")
self._setup_window_dims()
self._add_statusbar(template_name)
self._add_menus()
self._load_webview(template_name)
self._template_name = template_name
def _load_webview(self, template_name):
"""Return a WebView widget"""
view = MyWebView(self)
doc_writer.render_local_doc(doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR, template_name)
doc_name = doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR.joinpath(template_name)
url = QUrl.fromLocalFile(str(doc_name))
view.load(url)
self.setCentralWidget(view)
view.show()
def reload(self):
print("RELOAD")
doc_writer.render_local_doc(doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR, self._template_name)
doc_writer.RENDERED_DIR.joinpath(self._template_name)
def _setup_window_dims(self):
"""Setup default window dimensions"""
# TODO: Figure out how to get screen geometry
# screen = QScreen()
# geometry = screen.availableGeometry()
width = 800
height = 600
self.resize(width, height)
def _add_statusbar(self, fname):
"""Create and add a status bar"""
self.status = self.statusBar()
self.status.showMessage(fname)
def _add_menus(self):
"""Create and add menubars"""
self.menu = self.menuBar()
self.menu.setNativeMenuBar(False)
self.file_menu = self.menu.addMenu("File")
exit_action = QAction("Exit", self)
exit_action.setShortcut(QKeySequence.Quit)
exit_action.triggered.connect(self.close)
self.file_menu.addAction(exit_action)
�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692379427.5692556
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/.DS_Store��������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�015542� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������� ����������������������������������������������������������������blob����bpli���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������j�sbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������j�svSrnlong�������
�r�e�n�d�e�r�e�d�_�d�o�c�svSrnlong�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E��� ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1707227
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/__init__.py������������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000000000�00000000000�016157� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1640369016.1708918
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/css/styles.css���������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000000471�00000000000�016707� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������body {
margin: 10px;
}
h1 {
font-weight: bold;
font-family: monospace;
}
refli {
margin: 0px 0;
}
li {
margin: 10px 0;
}
li ul li {
margin: 0px 0;
}
pre {
white-space: pre-wrap;
}
prmtr {
font-weight: bold;
font-family: monospace;
}
ptype {
font-style: italic;
}�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0401392
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/doc_writer.py����������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000002270�00000000000�016574� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������import logging
from pathlib import Path
from opencv_pg import env
from jinja2.exceptions import TemplateNotFound
log = logging.getLogger(__name__)
ROOT = Path(__file__)
RENDERED_DIR = ROOT.parent.joinpath("rendered_docs/")
def _create_rendered_docs():
"""Create rendered_docs folder if it doesn't exist"""
if not RENDERED_DIR.exists():
RENDERED_DIR.mkdir()
log.info("Created %s", RENDERED_DIR)
def render_local_doc(folder, doc_fname):
"""Renders template into a local file
Normally we would render content in the webview with `setHtml`, but there
seems to be a bug which doesn't load local resources when that method is
used. It works properly when loaded from a local file.
"""
try:
template = env.get_template(doc_fname)
html = template.render()
except TemplateNotFound:
template = env.get_template("error.html")
html = template.render(error=f"Template: {doc_fname} not found :(")
path = folder.joinpath(doc_fname)
with open(path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fout:
fout.write(html)
log.debug("Wrote Doc: %s", path)
# Create rendered docs folder if it doesn't exist
_create_rendered_docs()
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692389906.8380182
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/.DS_Store�����������������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�016156� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1��������������� �����������������������������������������������������������������j�a�xbwspbl���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������m�a�t�h�j�a�xbwspblob����bplist00�������������]ShowStatusBar[ShowToolbar[ShowTabView_��ContainerShowSidebar\WindowBounds[ShowSidebar� � _��{{58, 381}, {920, 436}} ��#/;R_klmno����������������
���������������������m�a�t�h�j�a�xlg1Scomp�����p�������m�a�t�h�j�a�xmoDDblob����p�@��G�A�����m�a�t�h�j�a�xmodDblob����p�@��G�A�����m�a�t�h�j�a�xph1Scomp�����s0������m�a�t�h�j�a�xvSrnlong������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E��� ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692389906.8391132
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/.DS_Store���������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014004�00000000000�017612� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������Bud1���������������
����������������������������������������������������������������lg1Scomp���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������a�1�1�ylg1Scomp������1������a�1�1�ymoDDblob�����n&��G�A�����a�1�1�ymodDblob�����n&��G�A�����a�1�1�yph1Scomp������P������a�d�a�p�t�o�r�slg1Scomp������Y������a�d�a�p�t�o�r�smoDDblob�����C���G�A�����a�d�a�p�t�o�r�smodDblob�����C���G�A�����a�d�a�p�t�o�r�sph1Scomp������`������i�n�p�u�tlg1Scomp������������i�n�p�u�tmoDDblob���������G�A�����i�n�p�u�tmodDblob���������G�A�����i�n�p�u�tph1Scomp�������������o�u�t�p�u�tlg1Scomp�������]�����o�u�t�p�u�tmoDDblob����2J���G�A�����o�u�t�p�u�tmodDblob����2J���G�A�����o�u�t�p�u�tph1Scomp�������������s�r�elg1Scomp�����<�������s�r�emoDDblob�����(A��G�A�����s�r�emodDblob�����(A��G�A�����s�r�eph1Scomp�����=`������u�ilg1Scomp�������������u�imoDDblob������,��G�A�����u�imodDblob������,��G�A�����u�iph1Scomp��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������� �������@�������������������������������������������������� �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������E���
���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������DSDB������������������������������� ���`������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������ �������@������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000032�00000000000�010210� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������26 mtime=1692426889.04051
������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/a11y/assistive-mml.js���������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000014474�00000000000�022050� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,i,o={62:function(t,e,i){var o,s=this&&this.__extends||(o=function(t,e){return o=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var i in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,i)&&(t[i]=e[i])},o(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function i(){this.constructor=t}o(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(i.prototype=e.prototype,new i)}),n=this&&this.__assign||function(){return n=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,i=1,o=arguments.length;i0)&&!(o=n.next()).done;)r.push(o.value)}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(i=n.return)&&i.call(n)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}return r},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,i){if(i||2===arguments.length)for(var o,s=0,n=e.length;s=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[o++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AssistiveMmlHandler=e.AssistiveMmlMathDocumentMixin=e.AssistiveMmlMathItemMixin=e.LimitedMmlVisitor=void 0;var p=i(769),c=i(433),u=i(77),h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return s(e,t),e.prototype.getAttributes=function(e){return t.prototype.getAttributes.call(this,e).replace(/ ?id=".*?"/,"")},e}(c.SerializedMmlVisitor);function m(t){return function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return s(e,t),e.prototype.assistiveMml=function(t,e){if(void 0===e&&(e=!1),!(this.state()>=p.STATE.ASSISTIVEMML)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableAssistiveMml||e)){var i=t.adaptor,o=t.toMML(this.root).replace(/\n */g,"").replace(//g,""),s=i.firstChild(i.body(i.parse(o,"text/html"))),n=i.node("mjx-assistive-mml",{unselectable:"on",display:this.display?"block":"inline"},[s]);i.setAttribute(i.firstChild(this.typesetRoot),"aria-hidden","true"),i.setStyle(this.typesetRoot,"position","relative"),i.append(this.typesetRoot,n)}this.state(p.STATE.ASSISTIVEMML)}},e}(t)}function M(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],i=0;i0)&&!(i=n.next()).done;)l.push(i.value)}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(o=n.return)&&o.call(n)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return l},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var i,r=0,n=e.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.ComplexityHandler=e.ComplexityMathDocumentMixin=e.ComplexityMathItemMixin=void 0;var p=o(769),c=o(511),u=o(175),h=o(77);function y(t,e){return function(t){function o(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return r(o,t),o.prototype.complexity=function(t,o){void 0===o&&(o=!1),this.state()>=p.STATE.COMPLEXITY||(this.isEscaped||!t.options.enableComplexity&&!o||(this.enrich(t,!0),e(this.root)),this.state(p.STATE.COMPLEXITY))},o}(t)}function d(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Collapse=void 0;var i=function(){function t(e){var o=this;this.cutoff={identifier:3,number:3,text:10,infixop:15,relseq:15,multirel:15,fenced:18,bigop:20,integral:20,fraction:12,sqrt:9,root:12,vector:15,matrix:15,cases:15,superscript:9,subscript:9,subsup:9,punctuated:{endpunct:t.NOCOLLAPSE,startpunct:t.NOCOLLAPSE,value:12}},this.marker={identifier:"x",number:"#",text:"...",appl:{"limit function":"lim",value:"f()"},fraction:"/",sqrt:"\u221a",root:"\u221a",superscript:"\u25fd\u02d9",subscript:"\u25fd.",subsup:"\u25fd:",vector:{binomial:"(:)",determinant:"|:|",value:"\u27e8:\u27e9"},matrix:{squarematrix:"[::]",rowvector:"\u27e8\u22ef\u27e9",columnvector:"\u27e8\u22ee\u27e9",determinant:"|::|",value:"(::)"},cases:"{:",infixop:{addition:"+",subtraction:"\u2212",multiplication:"\u22c5",implicit:"\u22c5",value:"+"},punctuated:{text:"...",value:","}},this.collapse=new Map([["fenced",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,1))>o.cutoff.fenced&&"leftright"===t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role")&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.getText(t.childNodes[0])+o.getText(t.childNodes[t.childNodes.length-1]))),e}],["appl",function(t,e){if(o.canUncollapse(t,2,2)){e=o.complexity.visitNode(t,!1);var i=o.marker.appl,r=i[t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role")]||i.value;e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["sqrt",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0))>o.cutoff.sqrt&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.sqrt)),e}],["root",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.sqrt&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.sqrt)),e}],["enclose",function(t,e){if(1===o.splitAttribute(t,"children").length){var i=o.canUncollapse(t,1);if(i){var r=i.getProperty("collapse-marker");o.unrecordCollapse(i),e=o.recordCollapse(t,o.complexity.visitNode(t,!1),r)}}return e}],["bigop",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.bigop||!t.isKind("mo")){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content").pop(),r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["integral",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.integral||!t.isKind("mo")){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content").pop(),r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["relseq",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.relseq){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content")[0],r=o.findChildText(t,i);e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["multirel",function(t,e){if(e>o.cutoff.relseq){var i=o.splitAttribute(t,"content")[0],r=o.findChildText(t,i)+"\u22ef";e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,r)}return e}],["superscript",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.superscript&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.superscript)),e}],["subscript",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,2))>o.cutoff.subscript&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.subscript)),e}],["subsup",function(t,e){return(e=o.uncollapseChild(e,t,0,3))>o.cutoff.subsup&&(e=o.recordCollapse(t,e,o.marker.subsup)),e}]]),this.idCount=0,this.complexity=e}return t.prototype.check=function(t,e){var o=t.attributes.get("data-semantic-type");return this.collapse.has(o)?this.collapse.get(o).call(this,t,e):this.cutoff.hasOwnProperty(o)?this.defaultCheck(t,e,o):e},t.prototype.defaultCheck=function(t,e,o){var i=t.attributes.get("data-semantic-role"),r=this.cutoff[o];if(e>("number"==typeof r?r:r[i]||r.value)){var n=this.marker[o]||"??",l="string"==typeof n?n:n[i]||n.value;e=this.recordCollapse(t,e,l)}return e},t.prototype.recordCollapse=function(t,e,o){return o="\u25c2"+o+"\u25b8",t.setProperty("collapse-marker",o),t.setProperty("collapse-complexity",e),o.length*this.complexity.complexity.text},t.prototype.unrecordCollapse=function(t){var e=t.getProperty("collapse-complexity");null!=e&&(t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",e),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"))},t.prototype.canUncollapse=function(t,e,o){if(void 0===o&&(o=1),this.splitAttribute(t,"children").length===o){var i=1===t.childNodes.length&&t.childNodes[0].isInferred?t.childNodes[0]:t;if(i&&i.childNodes[e]){var r=i.childNodes[e];if(r.getProperty("collapse-marker"))return r}}return null},t.prototype.uncollapseChild=function(t,e,o,i){void 0===i&&(i=1);var r=this.canUncollapse(e,o,i);return r&&(this.unrecordCollapse(r),r.parent!==e&&r.parent.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",void 0),t=this.complexity.visitNode(e,!1)),t},t.prototype.splitAttribute=function(t,e){return(t.attributes.get("data-semantic-"+e)||"").split(/,/)},t.prototype.getText=function(t){var e=this;return t.isToken?t.getText():t.childNodes.map((function(t){return e.getText(t)})).join("")},t.prototype.findChildText=function(t,e){var o=this.findChild(t,e);return this.getText(o.coreMO()||o)},t.prototype.findChild=function(t,e){var i,r;if(!t||t.attributes.get("data-semantic-id")===e)return t;if(!t.isToken)try{for(var n=o(t.childNodes),l=n.next();!l.done;l=n.next()){var s=l.value,a=this.findChild(s,e);if(a)return a}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}return null},t.prototype.makeCollapse=function(t){var e=[];t.walkTree((function(t){t.getProperty("collapse-marker")&&e.push(t)})),this.makeActions(e)},t.prototype.makeActions=function(t){var e,i;try{for(var r=o(t),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){var l=n.value;this.makeAction(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=r.return)&&i.call(r)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},t.prototype.makeId=function(){return"mjx-collapse-"+this.idCount++},t.prototype.makeAction=function(t){t.isKind("math")&&(t=this.addMrow(t));var e=this.complexity.factory,o=t.getProperty("collapse-marker"),i=t.parent,r=e.create("maction",{actiontype:"toggle",selection:2,"data-collapsible":!0,id:this.makeId(),"data-semantic-complexity":t.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity")},[e.create("mtext",{mathcolor:"blue"},[e.create("text").setText(o)])]);r.inheritAttributesFrom(t),t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",t.getProperty("collapse-complexity")),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),i.replaceChild(r,t),r.appendChild(t)},t.prototype.addMrow=function(t){var e,i,r=this.complexity.factory.create("mrow",null,t.childNodes[0].childNodes);t.childNodes[0].setChildren([r]);var n=t.attributes.getAllAttributes();try{for(var l=o(Object.keys(n)),s=l.next();!s.done;s=l.next()){var a=s.value;"data-semantic-"===a.substr(0,14)&&(r.attributes.set(a,n[a]),delete n[a])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return r.setProperty("collapse-marker",t.getProperty("collapse-marker")),r.setProperty("collapse-complexity",t.getProperty("collapse-complexity")),t.removeProperty("collapse-marker"),t.removeProperty("collapse-complexity"),r},t.NOCOLLAPSE=1e7,t}();e.Collapse=i},175:function(t,e,o){var i,r=this&&this.__extends||(i=function(t,e){return i=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},i(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}i(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)}),n=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,o=e&&t[e],i=0;if(o)return o.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&i>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[i++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.ComplexityVisitor=void 0;var l=o(176),s=o(850),a=o(77),p=function(t){function e(e,o){var i=t.call(this,e)||this;i.complexity={text:.5,token:.5,child:1,script:.8,sqrt:2,subsup:2,underover:2,fraction:2,enclose:2,action:2,phantom:0,xml:2,glyph:2};var r=i.constructor;return i.options=(0,a.userOptions)((0,a.defaultOptions)({},r.OPTIONS),o),i.collapse=new i.options.Collapse(i),i.factory=e,i}return r(e,t),e.prototype.visitTree=function(e){t.prototype.visitTree.call(this,e,!0),this.options.makeCollapsible&&this.collapse.makeCollapse(e)},e.prototype.visitNode=function(e,o){if(!e.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity"))return t.prototype.visitNode.call(this,e,o)},e.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var o;if(t.isToken){var i=t.getText();o=this.complexity.text*i.length+this.complexity.token}else o=this.childrenComplexity(t);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMfracNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)*this.complexity.script+this.complexity.fraction;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsqrtNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.sqrt;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMrootNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.sqrt-(1-this.complexity.script)*this.getComplexity(t.childNodes[1]);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMphantomNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.phantom,e)},e.prototype.visitMsNode=function(t,e){var o=(t.attributes.get("lquote")+t.getText()+t.attributes.get("rquote")).length*this.complexity.text;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsubsupNode=function(e,o){t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var i=e.childNodes[e.sub],r=e.childNodes[e.sup],n=e.childNodes[e.base],l=Math.max(i?this.getComplexity(i):0,r?this.getComplexity(r):0)*this.complexity.script;return l+=this.complexity.child*((i?1:0)+(r?1:0)),l+=n?this.getComplexity(n)+this.complexity.child:0,l+=this.complexity.subsup,this.setComplexity(e,l,o)},e.prototype.visitMsubNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMsubsupNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMsupNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMsubsupNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMunderoverNode=function(e,o){t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var i=e.childNodes[e.under],r=e.childNodes[e.over],n=e.childNodes[e.base],l=Math.max(i?this.getComplexity(i):0,r?this.getComplexity(r):0)*this.complexity.script;return n&&(l=Math.max(this.getComplexity(n),l)),l+=this.complexity.child*((i?1:0)+(r?1:0)+(n?1:0)),l+=this.complexity.underover,this.setComplexity(e,l,o)},e.prototype.visitMunderNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMunderoverNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMoverNode=function(t,e){return this.visitMunderoverNode(t,e)},e.prototype.visitMencloseNode=function(t,e){var o=this.childrenComplexity(t)+this.complexity.enclose;return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMactionNode=function(t,e){this.childrenComplexity(t);var o=this.getComplexity(t.selected);return this.setComplexity(t,o,e)},e.prototype.visitMsemanticsNode=function(t,e){var o=t.childNodes[0],i=0;return o&&(this.visitNode(o,!0),i=this.getComplexity(o)),this.setComplexity(t,i,e)},e.prototype.visitAnnotationNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.xml,e)},e.prototype.visitAnnotation_xmlNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.xml,e)},e.prototype.visitMglyphNode=function(t,e){return this.setComplexity(t,this.complexity.glyph,e)},e.prototype.getComplexity=function(t){var e=t.getProperty("collapsedComplexity");return null!=e?e:t.attributes.get("data-semantic-complexity")},e.prototype.setComplexity=function(t,e,o){return o&&(this.options.identifyCollapsible&&(e=this.collapse.check(t,e)),t.attributes.set("data-semantic-complexity",e)),e},e.prototype.childrenComplexity=function(e){var o,i;t.prototype.visitDefault.call(this,e,!0);var r=0;try{for(var l=n(e.childNodes),s=l.next();!s.done;s=l.next()){var a=s.value;r+=this.getComplexity(a)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return e.childNodes.length>1&&(r+=e.childNodes.length*this.complexity.child),r},e.OPTIONS={identifyCollapsible:!0,makeCollapsible:!0,Collapse:s.Collapse},e}(l.MmlVisitor);e.ComplexityVisitor=p},306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},511:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.EnrichedMathItemMixin=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichedMathItemMixin,e.EnrichedMathDocumentMixin=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichedMathDocumentMixin,e.EnrichHandler=MathJax._.a11y["semantic-enrich"].EnrichHandler},723:function(t,e){MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,e.PV=MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},769:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.protoItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.protoItem,e.AbstractMathItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.AbstractMathItem,e.STATE=MathJax._.core.MathItem.STATE,e.newState=MathJax._.core.MathItem.newState},176:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlVisitor=MathJax._.core.MmlTree.MmlVisitor.MmlVisitor},77:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup}},s={};function a(t){var e=s[t];if(void 0!==e)return e.exports;var o=s[t]={exports:{}};return l[t].call(o.exports,o,o.exports,a),o.exports}t=a(723),e=a(306),o=a(589),i=a(850),r=a(175),n=a(511),MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("a11y/complexity",e.q,"a11y"),(0,t.r8)({_:{a11y:{complexity_ts:o,complexity:{collapse:i,visitor:r},"semantic-enrich":n}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.extendHandler((function(t){return(0,o.ComplexityHandler)(t)})),(0,t.PV)(MathJax.config,"options",MathJax.config["a11y/complexity"]||{}))}();��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0411465
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/a11y/explorer.js��������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000106731�00000000000�021111� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,o,r,n,i,a,s,l={18:function(t,e,o){var r,n=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,o=1,r=arguments.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},u=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var o="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!o)return t;var r,n,i=o.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},h=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var r,n=0,i=e.length;n=f.STATE.EXPLORER)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableExplorer||o)){var r=this.typesetRoot,n=e(this.root);this.savedId&&(this.typesetRoot.setAttribute("sre-explorer-id",this.savedId),this.savedId=null),this.explorers=function(t,e,o){var r,n,i={};try{for(var a=c(Object.keys(S)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;i[l]=S[l](t,e,o)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return i}(t,r,n),this.attachExplorers(t)}this.state(f.STATE.EXPLORER)}},o.prototype.attachExplorers=function(t){var e,o,r,n;this.attached=[];var i=[];try{for(var a=c(Object.keys(this.explorers)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;(p=this.explorers[l])instanceof m.AbstractKeyExplorer&&(p.AddEvents(),p.stoppable=!1,i.unshift(p)),t.options.a11y[l]?(p.Attach(),this.attached.push(l)):p.Detach()}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}try{for(var u=c(i),h=u.next();!h.done;h=u.next()){var p;if((p=h.value).attached){p.stoppable=!0;break}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(n=u.return)&&n.call(u)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},o.prototype.rerender=function(e,o){var r,n;void 0===o&&(o=f.STATE.RERENDER),this.savedId=this.typesetRoot.getAttribute("sre-explorer-id"),this.refocus=window.document.activeElement===this.typesetRoot;try{for(var i=c(this.attached),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.explorers[s];l.active&&(this.restart.push(s),l.Stop())}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}t.prototype.rerender.call(this,e,o)},o.prototype.updateDocument=function(e){var o=this;t.prototype.updateDocument.call(this,e),this.refocus&&this.typesetRoot.focus(),this.restart.forEach((function(t){return o.explorers[t].Start()})),this.restart=[],this.refocus=!1},o}(t)}function O(t){var e;return e=function(t){function e(){for(var e=[],o=0;o0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},n=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,o){if(o||2===arguments.length)for(var r,n=0,i=e.length;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__importDefault||function(t){return t&&t.__esModule?t:{default:t}};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractExplorer=void 0;var s=a(o(712)),l=function(){function t(t,e,o){for(var r=[],n=3;n0&&n[n.length-1])||6!==i[0]&&2!==i[0])){a=0;continue}if(3===i[0]&&(!n||i[1]>n[0]&&i[1]0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.FlameHoverer=e.ContentHoverer=e.ValueHoverer=e.Hoverer=e.AbstractMouseExplorer=void 0;var a=o(367),s=o(724);o(712);var l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.events=t.prototype.Events.call(e).concat([["mouseover",e.MouseOver.bind(e)],["mouseout",e.MouseOut.bind(e)]]),e}return n(e,t),e.prototype.MouseOver=function(t){this.Start()},e.prototype.MouseOut=function(t){this.Stop()},e}(s.AbstractExplorer);e.AbstractMouseExplorer=l;var c=function(t){function e(e,o,r,n,i){var a=t.call(this,e,o,r)||this;return a.document=e,a.region=o,a.node=r,a.nodeQuery=n,a.nodeAccess=i,a}return n(e,t),e.prototype.MouseOut=function(e){e.clientX===this.coord[0]&&e.clientY===this.coord[1]||(this.highlighter.unhighlight(),this.region.Hide(),t.prototype.MouseOut.call(this,e))},e.prototype.MouseOver=function(e){t.prototype.MouseOver.call(this,e);var o=e.target;this.coord=[e.clientX,e.clientY];var r=i(this.getNode(o),2),n=r[0],a=r[1];n&&(this.highlighter.unhighlight(),this.highlighter.highlight([n]),this.region.Update(a),this.region.Show(n,this.highlighter))},e.prototype.getNode=function(t){for(var e=t;t&&t!==this.node;){if(this.nodeQuery(t))return[t,this.nodeAccess(t)];t=t.parentNode}for(t=e;t;){if(this.nodeQuery(t))return[t,this.nodeAccess(t)];var o=t.childNodes[0];t=o&&"defs"===o.tagName?t.childNodes[1]:o}return[null,null]},e}(l);e.Hoverer=c;var u=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.ValueHoverer=u;var h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.ContentHoverer=h;var p=function(t){function e(e,o,r){var n=t.call(this,e,new a.DummyRegion(e),r,(function(t){return n.highlighter.isMactionNode(t)}),(function(){}))||this;return n.document=e,n.node=r,n}return n(e,t),e}(c);e.FlameHoverer=p},367:function(t,e,o){var r,n,i,a,s=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var o in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,o)&&(t[o]=e[o])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function o(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(o.prototype=e.prototype,new o)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HoverRegion=e.LiveRegion=e.ToolTip=e.StringRegion=e.DummyRegion=e.AbstractRegion=void 0;var l=o(888),c=function(){function t(t){this.document=t,this.CLASS=this.constructor,this.AddStyles(),this.AddElement()}return t.prototype.AddStyles=function(){if(!this.CLASS.styleAdded){var t=this.document.adaptor.node("style");t.innerHTML=this.CLASS.style.cssText,this.document.adaptor.head(this.document.adaptor.document).appendChild(t),this.CLASS.styleAdded=!0}},t.prototype.AddElement=function(){var t=this.document.adaptor.node("div");t.classList.add(this.CLASS.className),t.style.backgroundColor="white",this.div=t,this.inner=this.document.adaptor.node("div"),this.div.appendChild(this.inner),this.document.adaptor.body(this.document.adaptor.document).appendChild(this.div)},t.prototype.Show=function(t,e){this.position(t),this.highlight(e),this.div.classList.add(this.CLASS.className+"_Show")},t.prototype.Hide=function(){this.div.classList.remove(this.CLASS.className+"_Show")},t.prototype.stackRegions=function(t){for(var e=t.getBoundingClientRect(),o=0,r=Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,n=this.document.adaptor.document.getElementsByClassName(this.CLASS.className+"_Show"),i=0,a=void 0;a=n[i];i++)a!==this.div&&(o=Math.max(a.getBoundingClientRect().bottom,o),r=Math.min(a.getBoundingClientRect().left,r));var s=(o||e.bottom+10)+window.pageYOffset,l=(r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,a,i=r.call(t),o=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)o.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return o},c=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,a=0,i=e.length;a=u.STATE.ENRICHED)){if(!this.isEscaped&&(t.options.enableEnrichment||n)){t.options.sre.speech!==y&&(y=t.options.sre.speech,h.mathjax.retryAfter(d.default.setupEngine(t.options.sre).then((function(){return d.default.sreReady()}))));var a=new t.options.MathItem("",e);try{var i=this.inputData.originalMml=r(this.root);a.math=this.serializeMml(d.default.toEnriched(i)),a.display=this.display,a.compile(t),this.root=a.root,this.inputData.enrichedMml=a.math}catch(e){t.options.enrichError(t,this,e)}}this.state(u.STATE.ENRICHED)}},n.prototype.attachSpeech=function(t){var e,r;if(!(this.state()>=u.STATE.ATTACHSPEECH)){var n=this.root.attributes.get("aria-label")||this.getSpeech(this.root);if(n){var a=t.adaptor,i=this.typesetRoot;a.setAttribute(i,"aria-label",n);try{for(var s=o(a.childNodes(i)),c=s.next();!c.done;c=s.next()){var l=c.value;a.setAttribute(l,"aria-hidden","true")}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(r=s.return)&&r.call(s)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}this.state(u.STATE.ATTACHSPEECH)}},n.prototype.getSpeech=function(t){var e,r,n=t.attributes;if(!n)return"";var a=n.getExplicit("data-semantic-speech");if(!n.getExplicit("data-semantic-parent")&&a)return a;try{for(var i=o(t.childNodes),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var c=s.value,l=this.getSpeech(c);if(null!=l)return l}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return""},n}(t)}function m(t,e){var r;return r=function(t){function r(){for(var r=[],n=0;n0&&i[i.length-1])||6!==o[0]&&2!==o[0])){s=0;continue}if(3===o[0]&&(!i||o[1]>i[0]&&o[1]delete e[t])),t.open.forEach((n=>e[n]=t[n]));const n=Object.keys(e);e.open=n},t.sortClose=function(e,t){if(e.length<=1)return e;const n=[];for(let r,i=0;r=t[i],e.length;i++)r.close&&r.close.length&&r.close.forEach((function(t){const r=e.indexOf(t);-1!==r&&(n.unshift(t),e.splice(r,1))}));return n};let a={},c=[];function l(e,t){const n=e[e.length-1];if(n){if(p(t)&&p(n)){if(void 0===n.join)return void(n.span=n.span.concat(t.span));const e=n.span.pop(),r=t.span.shift();return n.span.push(e+n.join+r),n.span=n.span.concat(t.span),void(n.join=t.join)}h(t)&&h(n)?n.pause=s(n.pause,t.pause):e.push(t)}else e.push(t)}function u(e,t){e.rate&&(t.rate=e.rate),e.pitch&&(t.pitch=e.pitch),e.volume&&(t.volume=e.volume)}function d(e){return"object"==typeof e&&e.open}function h(e){return"object"==typeof e&&1===Object.keys(e).length&&Object.keys(e)[0]===i.personalityProps.PAUSE}function p(e){const t=Object.keys(e);return"object"==typeof e&&(1===t.length&&"span"===t[0]||2===t.length&&("span"===t[0]&&"join"===t[1]||"span"===t[1]&&"join"===t[0]))}function f(e,t,n,r,a,c=!1){if(c){const c=e[e.length-1];let l;if(c&&(l=c[i.personalityProps.JOIN]),c&&!t.speech&&a&&h(c)){const e=i.personalityProps.PAUSE;c[e]=s(c[e],a[e]),a=null}if(c&&t.speech&&0===Object.keys(n).length&&p(c)){if(void 0!==l){const e=c.span.pop();t=new o.Span(e.speech+l+t.speech,e.attributes)}c.span.push(t),t=new o.Span("",{}),c[i.personalityProps.JOIN]=r}}0!==Object.keys(n).length&&e.push(n),t.speech&&e.push({span:[t],join:r}),a&&e.push(a)}function m(e,t){if(!t)return e;const n={};for(const r of i.personalityPropList){const i=e[r],o=t[r];if(!i&&!o||i&&o&&i===o)continue;const s=i||0;d(n)||(n.open=[],n.close=[]),i||n.close.push(r),o||n.open.push(r),o&&i&&(n.close.push(r),n.open.push(r)),t[r]=s,n[r]=s,a[r]?a[r].push(s):a[r]=[s]}if(d(n)){let e=n.close.slice();for(;e.length>0;){let i=c.pop();const o=(0,r.setdifference)(i,e);if(e=(0,r.setdifference)(e,i),i=o,0!==e.length){if(0!==i.length){n.close=n.close.concat(i),n.open=n.open.concat(i);for(let e,r=0;e=i[r];r++)n[e]=t[e]}}else 0!==i.length&&c.push(i)}c.push(n.open)}return n}t.personalityMarkup=function(e){a={},c=[];let t=[];const n={};for(let r,o=0;r=e[o];o++){let e=null;const o=r.descriptionSpan(),s=r.personality,a=s[i.personalityProps.JOIN];delete s[i.personalityProps.JOIN],void 0!==s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]&&(e={[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]:s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]},delete s[i.personalityProps.PAUSE]);f(t,o,m(s,n),a,e,!0)}return t=t.concat(function(){const e=[];for(let t=c.length-1;t>=0;t--){const n=c[t];if(n.length){const t={open:[],close:[]};for(let e=0;e"string"==typeof e?new l.Span(e,{}):e)),n=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return n?n.merge(t):e.join()},t.finalize=function(e){const t=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return t?t.finalize(e):e},t.error=function(e){const t=m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup);return t?t.error(e):""},t.registerRenderer=function(e,t){m.set(e,t)},t.isXml=function(){return m.get(r.default.getInstance().markup)instanceof p.XmlRenderer}},1292:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.LayoutRenderer=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4998),s=n(2599),a=n(4708);class c extends a.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return function(e){l="";const t=i.parseInput(`${e}`);return r.Debugger.getInstance().output(i.formatXml(t.toString())),l=p(t),l}(e)}pause(e){return""}prosodyElement(e,t){return e===o.personalityProps.LAYOUT?`<${t}>`:""}closeTag(e){return``}markup(e){const t=[];let n=[];for(const r of e){if(!r.layout){n.push(r);continue}t.push(this.processContent(n)),n=[];const e=r.layout;e.match(/^begin/)?t.push("<"+e.replace(/^begin/,"")+">"):e.match(/^end/)?t.push(""):console.warn("Something went wrong with layout markup: "+e)}return t.push(this.processContent(n)),t.join("")}processContent(e){const t=[],n=s.personalityMarkup(e);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)e.span?t.push(this.merge(e.span)):s.isPauseElement(e);return t.join("")}}t.LayoutRenderer=c;let l="";const u={TABLE:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(1).slice(0,-1)}));const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CASES:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(0,-1)}));const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CAYLEY:function(e){let t=S(e);t.forEach((e=>{e.cells=e.cells.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.width=e.width.slice(1).slice(0,-1),e.sep=e.sep+e.sep}));const[n,r]=b(t),i={lfence:"",rfence:"",cells:r.map((e=>"\u2810"+new Array(e).join("\u2812"))),width:r,height:1,sep:t[0].sep};return t.splice(1,0,i),t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},MATRIX:function(e){let t=S(e);const[n,r]=b(t);return t=N(t,r),E(t,n)},CELL:p,FENCE:p,ROW:p,FRACTION:function(e){const[t,n,,r,i]=Array.from(e.childNodes),o=d(n),s=d(r),a=m(o),c=m(s);let l=Math.max(a,c);const u=t+new Array(l+1).join("\u2812")+i;return l=u.length,`${C(o,l)}\n${u}\n${C(s,l)}`},NUMERATOR:T,DENOMINATOR:T};function d(e){const t=i.tagName(e),n=u[t];return n?n(e):e.textContent}function h(e,t){if(!e||!t)return e+t;const n=f(e),r=f(t),i=n-r;e=i<0?g(e,r,m(e)):e,t=i>0?g(t,n,m(t)):t;const o=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),s=t.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),a=[];for(let e=0;eMath.max(t.length,e)),0)}function g(e,t,n){return e=function(e,t){const n=t-f(e);return e+(n>0?new Array(n+1).join("\n"):"")}(e,t),function(e,t){const n=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),r=[];for(const e of n){const n=t-e.length;r.push(e+(n>0?new Array(n+1).join("\u2800"):""))}return r.join("\n")}(e,n)}function S(e){const t=Array.from(e.childNodes),n=[];for(const e of t)e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&n.push(_(e));return n}function b(e){const t=e.reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(t.height,e)),0),n=[];for(let t=0;te.width[t])).reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(e,t)),0));return[t,n]}function N(e,t){const n=[];for(const r of e){if(0===r.height)continue;const e=[];for(let n=0;ne.lfence+e.cells.join(e.sep)+e.rfence)).join("\n");const n=[];for(const t of e){const e=y(t.sep,t.height);let r=t.cells.shift();for(;t.cells.length;)r=h(r,e),r=h(r,t.cells.shift());r=h(y(t.lfence,t.height),r),r=h(r,y(t.rfence,t.height)),n.push(r),n.push(t.lfence+new Array(m(r)-3).join(t.sep)+t.rfence)}return n.slice(0,-1).join("\n")}function y(e,t){let n="";for(;t;)n+=e+"\n",t--;return n.slice(0,-1)}function A(e){return e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&"FENCE"===i.tagName(e)?d(e):""}function _(e){const t=Array.from(e.childNodes),n=A(t[0]),r=A(t[t.length-1]);n&&t.shift(),r&&t.pop();let o="";const s=[];for(const e of t){if(e.nodeType===i.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){o=e.textContent;continue}const t=d(e);s.push(t)}return{lfence:n,rfence:r,sep:o,cells:s,height:s.reduce(((e,t)=>Math.max(f(t),e)),0),width:s.map(m)}}function C(e,t){const n=(t-m(e))/2,[r,i]=Math.floor(n)===n?[n,n]:[Math.floor(n),Math.ceil(n)],o=e.split(/\r\n|\r|\n/),s=[],[a,c]=[new Array(r+1).join("\u2800"),new Array(i+1).join("\u2800")];for(const e of o)s.push(a+e+c);return s.join("\n")}function T(e){const t=e.firstChild,n=p(e);if(t&&t.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE){if("ENGLISH"===i.tagName(t))return"\u2830"+n;if("NUMBER"===i.tagName(t))return"\u283c"+n}return n}},9610:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MarkupRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(7086);class o extends i.AbstractAudioRenderer{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.ignoreElements=[r.personalityProps.LAYOUT],this.scaleFunction=null}setScaleFunction(e,t,n,r,i=0){this.scaleFunction=o=>{const s=(o-e)/(t-e),a=n*(1-s)+r*s;return+(Math.round(a+"e+"+i)+"e-"+i)}}applyScaleFunction(e){return this.scaleFunction?this.scaleFunction(e):e}ignoreElement(e){return-1!==this.ignoreElements.indexOf(e)}}t.MarkupRenderer=o},1674:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.PunctuationRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(7086),o=n(2599);class s extends i.AbstractAudioRenderer{markup(e){const t=o.personalityMarkup(e);let n="",i=null,s=!1;for(let e,a=0;e=t[a];a++)o.isMarkupElement(e)||(o.isPauseElement(e)?s&&(i=o.mergePause(i,e,Math.max)):(i&&(n+=this.pause(i[r.personalityProps.PAUSE]),i=null),n+=(s?this.getSeparator():"")+this.merge(e.span),s=!0));return n}pause(e){let t;return t="number"==typeof e?e<=250?"short":e<=500?"medium":"long":e,s.PAUSE_PUNCTUATION.get(t)||""}}t.PunctuationRenderer=s,s.PAUSE_PUNCTUATION=new Map([["short",","],["medium",";"],["long","."]])},8078:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SableRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4998),i=n(4708);class o extends i.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return''+this.getSeparator()+e+this.getSeparator()+""}pause(e){return''}prosodyElement(e,t){switch(t=this.applyScaleFunction(t),e){case r.personalityProps.PITCH:return'';case r.personalityProps.RATE:return'';case r.personalityProps.VOLUME:return'';default:return"<"+e.toUpperCase()+' VALUE="'+t+'">'}}closeTag(e){return""}}t.SableRenderer=o},1930:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Span=void 0;t.Span=class{constructor(e,t){this.speech=e,this.attributes=t}}},4115:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SsmlRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4708);class s extends o.XmlRenderer{finalize(e){return''+this.getSeparator()+e+this.getSeparator()+""}pause(e){return''}prosodyElement(e,t){const n=(t=Math.floor(this.applyScaleFunction(t)))<0?t.toString():"+"+t.toString();return"":'%">')}closeTag(e){return""}}t.SsmlRenderer=s},6123:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SsmlStepRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4115);class i extends r.SsmlRenderer{markup(e){return i.MARKS={},super.markup(e)}merge(e){const t=[];for(let n=0;n'),i.MARKS[o]=!0),1===r.speech.length&&r.speech.match(/[a-zA-Z]/)?t.push(''+r.speech+""):t.push(r.speech)}return t.join(this.getSeparator())}}t.SsmlStepRenderer=i,i.CHARACTER_ATTR="character",i.MARKS={}},8244:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.StringRenderer=void 0;const r=n(7086),i=n(2599);class o extends r.AbstractAudioRenderer{markup(e){let t="";const n=(0,i.personalityMarkup)(e).filter((e=>e.span));if(!n.length)return t;const r=n.length-1;for(let e,i=0;e=n[i];i++){if(e.span&&(t+=this.merge(e.span)),i>=r)continue;const n=e.join;t+=void 0===n?this.getSeparator():n}return t}}t.StringRenderer=o},4708:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.XmlRenderer=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(2599),o=n(9610);class s extends o.MarkupRenderer{markup(e){this.setScaleFunction(-2,2,-100,100,2);const t=i.personalityMarkup(e),n=[],o=[];for(let e,s=0;e=t[s];s++)if(e.span)n.push(this.merge(e.span));else if(i.isPauseElement(e))n.push(this.pause(e));else{if(e.close.length)for(let t=0;t{n.push(this.prosodyElement(t,e[t])),o.push(t)}))}}return n.join(" ")}}t.XmlRenderer=s},1426:function(e,t){function n(e,t){return e?t?e.filter((e=>t.indexOf(e)<0)):e:[]}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.union=t.setdifference=t.interleaveLists=t.removeEmpty=void 0,t.removeEmpty=function(e){return e.filter((e=>e))},t.interleaveLists=function(e,t){const n=[];for(;e.length||t.length;)e.length&&n.push(e.shift()),t.length&&n.push(t.shift());return n},t.setdifference=n,t.union=function(e,t){return e&&t?e.concat(n(t,e)):e||t||[]}},9501:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.loadScript=t.loadMapsForIE_=t.installWGXpath_=t.loadWGXpath_=t.mapsForIE=t.detectEdge=t.detectIE=void 0;const r=n(4755),i=n(5024);function o(e){c(r.default.WGXpath),s(e)}function s(e,t){let n=t||1;"undefined"==typeof wgxpath&&n<10?setTimeout((function(){s(e,n++)}),200):n>=10||(r.default.wgxpath=wgxpath,e?r.default.wgxpath.install({document:document}):r.default.wgxpath.install(),i.xpath.evaluate=document.evaluate,i.xpath.result=XPathResult,i.xpath.createNSResolver=document.createNSResolver)}function a(){c(r.default.mathmapsIePath)}function c(e){const t=r.default.document.createElement("script");t.type="text/javascript",t.src=e,r.default.document.head?r.default.document.head.appendChild(t):r.default.document.body.appendChild(t)}t.detectIE=function(){return"undefined"!=typeof window&&"ActiveXObject"in window&&"clipboardData"in window&&(a(),o(),!0)},t.detectEdge=function(){var e;return"undefined"!=typeof window&&"MSGestureEvent"in window&&null===(null===(e=window.chrome)||void 0===e?void 0:e.loadTimes)&&(document.evaluate=null,o(!0),!0)},t.mapsForIE=null,t.loadWGXpath_=o,t.installWGXpath_=s,t.loadMapsForIE_=a,t.loadScript=c},1984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Debugger=void 0;const r=n(4755);class i{constructor(){this.isActive_=!1,this.outputFunction_=console.info,this.stream_=null}static getInstance(){return i.instance=i.instance||new i,i.instance}init(e){e&&this.startDebugFile_(e),this.isActive_=!0}output(...e){this.isActive_&&this.output_(e)}generateOutput(e){this.isActive_&&this.output_(e.apply(e,[]))}exit(e=(()=>{})){this.isActive_&&this.stream_&&this.stream_.end("","",e)}startDebugFile_(e){this.stream_=r.default.fs.createWriteStream(e),this.outputFunction_=function(...e){this.stream_.write(e.join(" ")),this.stream_.write("\n")}.bind(this),this.stream_.on("error",function(e){console.info("Invalid log file. Debug information sent to console."),this.outputFunction_=console.info}.bind(this)),this.stream_.on("finish",(function(){console.info("Finalizing debug file.")}))}output_(e){this.outputFunction_.apply(console.info===this.outputFunction_?console:this.outputFunction_,["Speech Rule Engine Debugger:"].concat(e))}}t.Debugger=i},6671:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.serializeXml=t.cloneNode=t.tagName=t.querySelectorAll=t.querySelectorAllByAttrValue=t.querySelectorAllByAttr=t.formatXml=t.createTextNode=t.createElementNS=t.createElement=t.replaceNode=t.NodeType=t.parseInput=t.XML_ENTITIES=t.trimInput_=t.toArray=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4755),s=n(5024);function a(e){const t=[];for(let n=0,r=e.length;n[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]+<").trim()}function l(e,t){if(!t)return[!1,""];const n=e.match(/^<([^> ]+).*>/),r=t.match(/^<\/([^>]+)>(.*)/);return n&&r&&n[1]===r[1]?[!0,r[2]]:[!1,""]}t.toArray=a,t.trimInput_=c,t.XML_ENTITIES={"<":!0,">":!0,"&":!0,""":!0,"'":!0},t.parseInput=function(e){const t=new o.default.xmldom.DOMParser,n=c(e),a=!!n.match(/&(?!lt|gt|amp|quot|apos)\w+;/g);if(!n)throw new Error("Empty input!");try{const e=t.parseFromString(n,a?"text/html":"text/xml");return r.default.getInstance().mode===i.Mode.HTTP?(s.xpath.currentDocument=e,a?e.body.childNodes[0]:e.documentElement):e.documentElement}catch(e){throw new r.SREError("Illegal input: "+e.message)}},function(e){e[e.ELEMENT_NODE=1]="ELEMENT_NODE",e[e.ATTRIBUTE_NODE=2]="ATTRIBUTE_NODE",e[e.TEXT_NODE=3]="TEXT_NODE",e[e.CDATA_SECTION_NODE=4]="CDATA_SECTION_NODE",e[e.ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE=5]="ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE",e[e.ENTITY_NODE=6]="ENTITY_NODE",e[e.PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE=7]="PROCESSING_INSTRUCTION_NODE",e[e.COMMENT_NODE=8]="COMMENT_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_NODE=9]="DOCUMENT_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE=10]="DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE",e[e.DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE=11]="DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE",e[e.NOTATION_NODE=12]="NOTATION_NODE"}(t.NodeType||(t.NodeType={})),t.replaceNode=function(e,t){e.parentNode&&(e.parentNode.insertBefore(t,e),e.parentNode.removeChild(e))},t.createElement=function(e){return o.default.document.createElement(e)},t.createElementNS=function(e,t){return o.default.document.createElementNS(e,t)},t.createTextNode=function(e){return o.default.document.createTextNode(e)},t.formatXml=function(e){let t="",n=/(>)(<)(\/*)/g,r=0,i=(e=e.replace(n,"$1\r\n$2$3")).split("\r\n");for(n=/(\.)*(<)(\/*)/g,i=i.map((e=>e.replace(n,"$1\r\n$2$3").split("\r\n"))).reduce(((e,t)=>e.concat(t)),[]);i.length;){let e=i.shift();if(!e)continue;let n=0;if(e.match(/^<\w[^>/]*>[^>]+$/)){const t=l(e,i[0]);t[0]?t[1]?(e+=i.shift().slice(0,-t[1].length),t[1].trim()&&i.unshift(t[1])):e+=i.shift():n=1}else if(e.match(/^<\/\w/))0!==r&&(r-=1);else if(e.match(/^<\w[^>]*[^/]>.*$/))n=1;else if(e.match(/^<\w[^>]*\/>.+$/)){const t=e.indexOf(">")+1;e.slice(t).trim()&&i.unshift(),e=e.slice(0,t)}else n=0;t+=new Array(r+1).join(" ")+e+"\r\n",r+=n}return t},t.querySelectorAllByAttr=function(e,t){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(`[${t}]`)):s.evalXPath(`.//*[@${t}]`,e)},t.querySelectorAllByAttrValue=function(e,t,n){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(`[${t}="${n}"]`)):s.evalXPath(`.//*[@${t}="${n}"]`,e)},t.querySelectorAll=function(e,t){return e.querySelectorAll?a(e.querySelectorAll(t)):s.evalXPath(`.//${t}`,e)},t.tagName=function(e){return e.tagName.toUpperCase()},t.cloneNode=function(e){return e.cloneNode(!0)},t.serializeXml=function(e){return(new o.default.xmldom.XMLSerializer).serializeToString(e)}},4886:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.EnginePromise=t.SREError=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(4998),o=n(1984),s=n(4513);class a extends Error{constructor(e=""){super(),this.message=e,this.name="SRE Error"}}t.SREError=a;class c{constructor(){this.customLoader=null,this.parsers={},this.comparator=null,this.mode=i.Mode.SYNC,this.init=!0,this.delay=!1,this.comparators={},this.domain="mathspeak",this.style=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.STYLE],this._defaultLocale=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE],this.locale=this.defaultLocale,this.subiso="",this.modality=r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.MODALITY],this.speech=i.Speech.NONE,this.markup=i.Markup.NONE,this.walker="Table",this.structure=!1,this.ruleSets=[],this.strict=!1,this.isIE=!1,this.isEdge=!1,this.rate="100",this.pprint=!1,this.config=!1,this.rules="",this.prune="",this.evaluator=c.defaultEvaluator,this.defaultParser=new r.DynamicCstrParser(r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_ORDER),this.parser=this.defaultParser,this.dynamicCstr=r.DynamicCstr.defaultCstr()}set defaultLocale(e){this._defaultLocale=s.Variables.ensureLocale(e,this._defaultLocale)}get defaultLocale(){return this._defaultLocale}static getInstance(){return c.instance=c.instance||new c,c.instance}static defaultEvaluator(e,t){return e}static evaluateNode(e){return c.nodeEvaluator(e)}getRate(){const e=parseInt(this.rate,10);return isNaN(e)?100:e}setDynamicCstr(e){if(this.defaultLocale&&(r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE]=this.defaultLocale),e){const t=Object.keys(e);for(let n=0;n{void 0!==e[n]&&(t[n]=e[n])};return n("mode"),t.configurate(e),a.default.BINARY_FEATURES.forEach((n=>{void 0!==e[n]&&(t[n]=!!e[n])})),a.default.STRING_FEATURES.forEach(n),e.json&&(l.default.jsonPath=c.makePath(e.json)),e.xpath&&(l.default.WGXpath=e.xpath),t.setCustomLoader(e.custom),function(e){e.isIE=s.detectIE(),e.isEdge=s.detectEdge()}(t),i.setLocale(),t.setDynamicCstr(),t.init?(a.EnginePromise.promises.init=new Promise(((e,t)=>{setTimeout((()=>{e("init")}),10)})),t.init=!1,a.EnginePromise.get()):t.delay?(t.delay=!1,a.EnginePromise.get()):o.loadLocale()}))}},6988:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Event=t.EventType=t.Move=t.KeyCode=void 0,function(e){e[e.ENTER=13]="ENTER",e[e.ESC=27]="ESC",e[e.SPACE=32]="SPACE",e[e.PAGE_UP=33]="PAGE_UP",e[e.PAGE_DOWN=34]="PAGE_DOWN",e[e.END=35]="END",e[e.HOME=36]="HOME",e[e.LEFT=37]="LEFT",e[e.UP=38]="UP",e[e.RIGHT=39]="RIGHT",e[e.DOWN=40]="DOWN",e[e.TAB=9]="TAB",e[e.LESS=188]="LESS",e[e.GREATER=190]="GREATER",e[e.DASH=189]="DASH",e[e.ZERO=48]="ZERO",e[e.ONE=49]="ONE",e[e.TWO=50]="TWO",e[e.THREE=51]="THREE",e[e.FOUR=52]="FOUR",e[e.FIVE=53]="FIVE",e[e.SIX=54]="SIX",e[e.SEVEN=55]="SEVEN",e[e.EIGHT=56]="EIGHT",e[e.NINE=57]="NINE",e[e.A=65]="A",e[e.B=66]="B",e[e.C=67]="C",e[e.D=68]="D",e[e.E=69]="E",e[e.F=70]="F",e[e.G=71]="G",e[e.H=72]="H",e[e.I=73]="I",e[e.J=74]="J",e[e.K=75]="K",e[e.L=76]="L",e[e.M=77]="M",e[e.N=78]="N",e[e.O=79]="O",e[e.P=80]="P",e[e.Q=81]="Q",e[e.R=82]="R",e[e.S=83]="S",e[e.T=84]="T",e[e.U=85]="U",e[e.V=86]="V",e[e.W=87]="W",e[e.X=88]="X",e[e.Y=89]="Y",e[e.Z=90]="Z"}(t.KeyCode||(t.KeyCode={})),t.Move=new Map([[13,"ENTER"],[27,"ESC"],[32,"SPACE"],[33,"PAGE_UP"],[34,"PAGE_DOWN"],[35,"END"],[36,"HOME"],[37,"LEFT"],[38,"UP"],[39,"RIGHT"],[40,"DOWN"],[9,"TAB"],[188,"LESS"],[190,"GREATER"],[189,"DASH"],[48,"ZERO"],[49,"ONE"],[50,"TWO"],[51,"THREE"],[52,"FOUR"],[53,"FIVE"],[54,"SIX"],[55,"SEVEN"],[56,"EIGHT"],[57,"NINE"],[65,"A"],[66,"B"],[67,"C"],[68,"D"],[69,"E"],[70,"F"],[71,"G"],[72,"H"],[73,"I"],[74,"J"],[75,"K"],[76,"L"],[77,"M"],[78,"N"],[79,"O"],[80,"P"],[81,"Q"],[82,"R"],[83,"S"],[84,"T"],[85,"U"],[86,"V"],[87,"W"],[88,"X"],[89,"Y"],[90,"Z"]]),function(e){e.CLICK="click",e.DBLCLICK="dblclick",e.MOUSEDOWN="mousedown",e.MOUSEUP="mouseup",e.MOUSEOVER="mouseover",e.MOUSEOUT="mouseout",e.MOUSEMOVE="mousemove",e.SELECTSTART="selectstart",e.KEYPRESS="keypress",e.KEYDOWN="keydown",e.KEYUP="keyup",e.TOUCHSTART="touchstart",e.TOUCHMOVE="touchmove",e.TOUCHEND="touchend",e.TOUCHCANCEL="touchcancel"}(t.EventType||(t.EventType={}));t.Event=class{constructor(e,t,n){this.src=e,this.type=t,this.callback=n}add(){this.src.addEventListener(this.type,this.callback)}remove(){this.src.removeEventListener(this.type,this.callback)}}},7129:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localePath=t.makePath=void 0;const r=n(4755);function i(e){return e.match("/$")?e:e+"/"}t.makePath=i,t.localePath=function(e,t="json"){return i(r.default.jsonPath)+e+(t.match(/^\./)?t:"."+t)}},3539:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.KeyProcessor=t.Processor=void 0;const r=n(6988);class i{constructor(e,t){this.name=e,this.process=t.processor,this.postprocess=t.postprocessor||((e,t)=>e),this.processor=this.postprocess?function(e){return this.postprocess(this.process(e),e)}:this.process,this.print=t.print||i.stringify_,this.pprint=t.pprint||this.print}static stringify_(e){return e?e.toString():e}}t.Processor=i,i.LocalState={walker:null,speechGenerator:null,highlighter:null};class o extends i{constructor(e,t){super(e,t),this.key=t.key||o.getKey_}static getKey_(e){return"string"==typeof e?r.KeyCode[e.toUpperCase()]:e}}t.KeyProcessor=o},9615:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.keypress=t.output=t.print=t.process=t.set=void 0;const r=n(4253),i=n(7450),o=n(9009),s=n(4524),a=n(1939),c=n(7317),l=n(144),u=n(907),d=n(8835),h=n(6671),p=n(4886),f=n(4998),m=n(3539),g=n(5024),S=new Map;function b(e){S.set(e.name,e)}function N(e){const t=S.get(e);if(!t)throw new p.SREError("Unknown processor "+e);return t}function E(e,t){const n=N(e);try{return n.processor(t)}catch(e){throw new p.SREError("Processing error for expression "+t)}}function y(e,t){const n=N(e);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(t):n.print(t)}t.set=b,t.process=E,t.print=y,t.output=function(e,t){const n=N(e);try{const e=n.processor(t);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(e):n.print(e)}catch(e){throw new p.SREError("Processing error for expression "+t)}},t.keypress=function(e,t){const n=N(e),r=n instanceof m.KeyProcessor?n.key(t):t,i=n.processor(r);return p.default.getInstance().pprint?n.pprint(i):n.print(i)},b(new m.Processor("semantic",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e);return a.xmlTree(t)},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=p.default.getInstance().speech;if(n===f.Speech.NONE)return e;const i=h.cloneNode(e);let o=l.computeMarkup(i);if(n===f.Speech.SHALLOW)return e.setAttribute("speech",r.finalize(o)),e;const s=g.evalXPath(".//*[@id]",e),a=g.evalXPath(".//*[@id]",i);for(let e,t,n=0;e=s[n],t=a[n];n++)o=l.computeMarkup(t),e.setAttribute("speech",r.finalize(o));return e},pprint:function(e){return h.formatXml(e.toString())}})),b(new m.Processor("speech",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e),n=a.xmlTree(t),i=l.computeSpeech(n);return r.finalize(r.markup(i))},pprint:function(e){const t=e.toString();return r.isXml()?h.formatXml(t):t}})),b(new m.Processor("json",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e);return a.getTree(t).toJson()},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=p.default.getInstance().speech;if(n===f.Speech.NONE)return e;const i=h.parseInput(t),o=a.xmlTree(i),s=l.computeMarkup(o);if(n===f.Speech.SHALLOW)return e.stree.speech=r.finalize(s),e;const c=e=>{const t=g.evalXPath(`.//*[@id=${e.id}]`,o)[0],n=l.computeMarkup(t);e.speech=r.finalize(n),e.children&&e.children.forEach(c)};return c(e.stree),e},print:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e)},pprint:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e,null,2)}})),b(new m.Processor("description",{processor:function(e){const t=h.parseInput(e),n=a.xmlTree(t);return l.computeSpeech(n)},print:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e)},pprint:function(e){return JSON.stringify(e,null,2)}})),b(new m.Processor("enriched",{processor:function(e){return i.semanticMathmlSync(e)},postprocessor:function(e,t){const n=d.getSemanticRoot(e);let r;switch(p.default.getInstance().speech){case f.Speech.NONE:break;case f.Speech.SHALLOW:r=c.generator("Adhoc"),r.getSpeech(n,e);break;case f.Speech.DEEP:r=c.generator("Tree"),r.getSpeech(e,e)}return e},pprint:function(e){return h.formatXml(e.toString())}})),b(new m.Processor("walker",{processor:function(e){const t=c.generator("Node");m.Processor.LocalState.speechGenerator=t,t.setOptions({modality:p.default.getInstance().modality,locale:p.default.getInstance().locale,domain:p.default.getInstance().domain,style:p.default.getInstance().style}),m.Processor.LocalState.highlighter=o.highlighter({color:"black"},{color:"white"},{renderer:"NativeMML"});const n=E("enriched",e),r=y("enriched",n);return m.Processor.LocalState.walker=u.walker(p.default.getInstance().walker,n,t,m.Processor.LocalState.highlighter,r),m.Processor.LocalState.walker},print:function(e){return m.Processor.LocalState.walker.speech()}})),b(new m.KeyProcessor("move",{processor:function(e){if(!m.Processor.LocalState.walker)return null;return!1===m.Processor.LocalState.walker.move(e)?r.error(e):m.Processor.LocalState.walker.speech()}})),b(new m.Processor("number",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("ordinal",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("numericOrdinal",{processor:function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t)}})),b(new m.Processor("vulgar",{processor:function(e){const[t,n]=e.split("/").map((e=>parseInt(e,10)));return isNaN(t)||isNaN(n)?"":E("speech",`${t}${n}`)}}))},9037:function(e,t,n){var r=this&&this.__awaiter||function(e,t,n,r){return new(n||(n=Promise))((function(i,o){function s(e){try{c(r.next(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function a(e){try{c(r.throw(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function c(e){var t;e.done?i(e.value):(t=e.value,t instanceof n?t:new n((function(e){e(t)}))).then(s,a)}c((r=r.apply(e,t||[])).next())}))};Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localePath=t.exit=t.move=t.walk=t.processFile=t.file=t.vulgar=t.numericOrdinal=t.ordinal=t.number=t.toEnriched=t.toDescription=t.toJson=t.toSemantic=t.toSpeech=t.localeLoader=t.engineReady=t.engineSetup=t.setupEngine=t.version=void 0;const i=n(4886),o=n(985),s=n(4998),a=n(7129),c=n(9615),l=n(4755),u=n(4513),d=n(5659);function h(e){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return(0,o.setup)(e)}))}function p(e,t){return c.process(e,t)}function f(e,t,n){switch(i.default.getInstance().mode){case s.Mode.ASYNC:return function(e,t,n){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){const r=yield l.default.fs.promises.readFile(t,{encoding:"utf8"}),o=c.output(e,r);if(n)try{l.default.fs.promises.writeFile(n,o)}catch(e){throw new i.SREError("Can not write to file: "+n)}return o}))}(e,t,n);case s.Mode.SYNC:return function(e,t,n){const r=function(e){let t;try{t=l.default.fs.readFileSync(e,{encoding:"utf8"})}catch(t){throw new i.SREError("Can not open file: "+e)}return t}(t),o=c.output(e,r);if(n)try{l.default.fs.writeFileSync(n,o)}catch(e){throw new i.SREError("Can not write to file: "+n)}return o}(e,t,n);default:throw new i.SREError(`Can process files in ${i.default.getInstance().mode} mode`)}}t.version=u.Variables.VERSION,t.setupEngine=h,t.engineSetup=function(){const e=["mode"].concat(i.default.STRING_FEATURES,i.default.BINARY_FEATURES),t=i.default.getInstance(),n={};return e.forEach((function(e){n[e]=t[e]})),n.json=l.default.jsonPath,n.xpath=l.default.WGXpath,n.rules=t.ruleSets.slice(),n},t.engineReady=function(){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return h({}).then((()=>i.EnginePromise.getall()))}))},t.localeLoader=d.standardLoader,t.toSpeech=function(e){return p("speech",e)},t.toSemantic=function(e){return p("semantic",e)},t.toJson=function(e){return p("json",e)},t.toDescription=function(e){return p("description",e)},t.toEnriched=function(e){return p("enriched",e)},t.number=function(e){return p("number",e)},t.ordinal=function(e){return p("ordinal",e)},t.numericOrdinal=function(e){return p("numericOrdinal",e)},t.vulgar=function(e){return p("vulgar",e)},t.file={},t.file.toSpeech=function(e,t){return f("speech",e,t)},t.file.toSemantic=function(e,t){return f("semantic",e,t)},t.file.toJson=function(e,t){return f("json",e,t)},t.file.toDescription=function(e,t){return f("description",e,t)},t.file.toEnriched=function(e,t){return f("enriched",e,t)},t.processFile=f,t.walk=function(e){return c.output("walker",e)},t.move=function(e){return c.keypress("move",e)},t.exit=function(e){const t=e||0;i.EnginePromise.getall().then((()=>process.exit(t)))},t.localePath=a.localePath,l.default.documentSupported?h({mode:s.Mode.HTTP}).then((()=>h({}))):h({mode:s.Mode.SYNC}).then((()=>h({mode:s.Mode.ASYNC})))},4755:function(__unused_webpack_module,exports,__webpack_require__){var __dirname="/";Object.defineProperty(exports,"__esModule",{value:!0});const variables_1=__webpack_require__(4513);class SystemExternal{static extRequire(library){if("undefined"!=typeof process){const nodeRequire=eval("require");return nodeRequire(library)}return null}}exports.default=SystemExternal,SystemExternal.windowSupported=!("undefined"==typeof window),SystemExternal.documentSupported=SystemExternal.windowSupported&&!(void 0===window.document),SystemExternal.xmldom=SystemExternal.documentSupported?window:SystemExternal.extRequire("xmldom-sre"),SystemExternal.document=SystemExternal.documentSupported?window.document:(new SystemExternal.xmldom.DOMImplementation).createDocument("","",0),SystemExternal.xpath=SystemExternal.documentSupported?document:function(){const e={document:{},XPathResult:{}};return SystemExternal.extRequire("wicked-good-xpath").install(e),e.document.XPathResult=e.XPathResult,e.document}(),SystemExternal.mathmapsIePath="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/sre-mathmaps-ie@"+variables_1.Variables.VERSION+"mathmaps_ie.js",SystemExternal.commander=SystemExternal.documentSupported?null:SystemExternal.extRequire("commander"),SystemExternal.fs=SystemExternal.documentSupported?null:SystemExternal.extRequire("fs"),SystemExternal.url=variables_1.Variables.url,SystemExternal.jsonPath=(SystemExternal.documentSupported?SystemExternal.url:process.env.SRE_JSON_PATH||__webpack_require__.g.SRE_JSON_PATH||__dirname+"/mathmaps")+"/",SystemExternal.WGXpath=variables_1.Variables.WGXpath,SystemExternal.wgxpath=null},4513:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Variables=void 0;class n{static ensureLocale(e,t){return n.LOCALES.get(e)?e:(console.error(`Locale ${e} does not exist! Using ${n.LOCALES.get(t)} instead.`),t)}}t.Variables=n,n.VERSION="4.0.6",n.LOCALES=new Map([["ca","Catalan"],["da","Danish"],["de","German"],["en","English"],["es","Spanish"],["fr","French"],["hi","Hindi"],["it","Italian"],["nb","Bokm\xe5l"],["nn","Nynorsk"],["sv","Swedish"],["nemeth","Nemeth"]]),n.mathjaxVersion="3.2.1",n.url="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/speech-rule-engine@"+n.VERSION+"/lib/mathmaps",n.WGXpath="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/wicked-good-xpath@1.3.0/dist/wgxpath.install.js"},5024:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.updateEvaluator=t.evaluateString=t.evaluateBoolean=t.getLeafNodes=t.evalXPath=t.resolveNameSpace=t.xpath=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(4755);function s(){return"undefined"!=typeof XPathResult}t.xpath={currentDocument:null,evaluate:s()?document.evaluate:o.default.xpath.evaluate,result:s()?XPathResult:o.default.xpath.XPathResult,createNSResolver:s()?document.createNSResolver:o.default.xpath.createNSResolver};const a={xhtml:"http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",mathml:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML",mml:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML",svg:"http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"};function c(e){return a[e]||null}t.resolveNameSpace=c;class l{constructor(){this.lookupNamespaceURI=c}}function u(e,n,o){return r.default.getInstance().mode!==i.Mode.HTTP||r.default.getInstance().isIE||r.default.getInstance().isEdge?t.xpath.evaluate(e,n,new l,o,null):t.xpath.currentDocument.evaluate(e,n,c,o,null)}function d(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.ORDERED_NODE_ITERATOR_TYPE)}catch(e){return[]}const i=[];for(let e=r.iterateNext();e;e=r.iterateNext())i.push(e);return i}t.evalXPath=d,t.getLeafNodes=function(e){return d(".//*[count(*)=0]",e)},t.evaluateBoolean=function(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.BOOLEAN_TYPE)}catch(e){return!1}return r.booleanValue},t.evaluateString=function(e,n){let r;try{r=u(e,n,t.xpath.result.STRING_TYPE)}catch(e){return""}return r.stringValue},t.updateEvaluator=function(e){if(r.default.getInstance().mode!==i.Mode.HTTP)return;let n=e;for(;n&&!n.evaluate;)n=n.parentNode;n&&n.evaluate?t.xpath.currentDocument=n:e.ownerDocument&&(t.xpath.currentDocument=e.ownerDocument)}},9341:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractEnrichCase=void 0;t.AbstractEnrichCase=class{constructor(e){this.semantic=e}}},4306:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseBinomial=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!e.mathmlTree&&"line"===e.type&&"binomial"===e.role}getMathml(){if(!this.semantic.childNodes.length)return this.mml;const e=this.semantic.childNodes[0];if(this.mml=(0,o.walkTree)(e),this.mml.hasAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE)){const e=r.createElement("mrow");e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),r.replaceNode(this.mml,e),e.appendChild(this.mml),this.mml=e}return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseBinomial=a},8871:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseDoubleScript=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree||!e.childNodes.length)return!1;const t=r.tagName(e.mathmlTree),n=e.childNodes[0].role;return"MSUBSUP"===t&&"subsup"===n||"MUNDEROVER"===t&&"underover"===n}getMathml(){const e=this.semantic.childNodes[0],t=e.childNodes[0],n=this.semantic.childNodes[1],r=e.childNodes[1],i=o.walkTree(n),a=o.walkTree(t),c=o.walkTree(r);return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.CHILDREN,(0,s.makeIdList)([t,r,n])),[a,c,i].forEach((e=>o.getInnerNode(e).setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,this.mml.getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID)))),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE,e.role),o.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,[this.semantic.id,[e.id,t.id,r.id],n.id]),this.mml}}t.CaseDoubleScript=a},928:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseEmbellished=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9444),o=n(9341),s=n(8871),a=n(4308),c=n(439),l=n(8672),u=n(8171);class d extends o.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.fenced=null,this.fencedMml=null,this.fencedMmlNodes=[],this.ofence=null,this.ofenceMml=null,this.ofenceMap={},this.cfence=null,this.cfenceMml=null,this.cfenceMap={},this.parentCleanup=[]}static test(e){return!(!e.mathmlTree||!e.fencePointer||e.mathmlTree.getAttribute("data-semantic-type"))}static makeEmptyNode_(e){const t=r.createElement("mrow"),n=new i.SemanticNode(e);return n.type="empty",n.mathmlTree=t,n}static fencedMap_(e,t){t[e.id]=e.mathmlTree,e.embellished&&d.fencedMap_(e.childNodes[0],t)}getMathml(){this.getFenced_(),this.fencedMml=l.walkTree(this.fenced),this.getFencesMml_(),"empty"!==this.fenced.type||this.fencedMml.parentNode||(this.fencedMml.setAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),this.cfenceMml.parentNode.insertBefore(this.fencedMml,this.cfenceMml)),this.getFencedMml_();return this.rewrite_()}fencedElement(e){return"fenced"===e.type||"matrix"===e.type||"vector"===e.type}getFenced_(){let e=this.semantic;for(;!this.fencedElement(e);)e=e.childNodes[0];this.fenced=e.childNodes[0],this.ofence=e.contentNodes[0],this.cfence=e.contentNodes[1],d.fencedMap_(this.ofence,this.ofenceMap),d.fencedMap_(this.cfence,this.cfenceMap)}getFencedMml_(){let e=this.ofenceMml.nextSibling;for(e=e===this.fencedMml?e:this.fencedMml;e&&e!==this.cfenceMml;)this.fencedMmlNodes.push(e),e=e.nextSibling}getFencesMml_(){let e=this.semantic;const t=Object.keys(this.ofenceMap),n=Object.keys(this.cfenceMap);for(;!(this.ofenceMml&&this.cfenceMml||e===this.fenced);)-1===t.indexOf(e.fencePointer)||this.ofenceMml||(this.ofenceMml=e.mathmlTree),-1===n.indexOf(e.fencePointer)||this.cfenceMml||(this.cfenceMml=e.mathmlTree),e=e.childNodes[0];this.ofenceMml||(this.ofenceMml=this.ofence.mathmlTree),this.cfenceMml||(this.cfenceMml=this.cfence.mathmlTree),this.ofenceMml&&(this.ofenceMml=l.ascendNewNode(this.ofenceMml)),this.cfenceMml&&(this.cfenceMml=l.ascendNewNode(this.cfenceMml))}rewrite_(){let e=this.semantic,t=null;const n=this.introduceNewLayer_();for((0,u.setAttributes)(n,this.fenced.parent);!this.fencedElement(e);){const i=e.mathmlTree,o=this.specialCase_(e,i);if(o)e=o;else{(0,u.setAttributes)(i,e);const t=[];for(let n,r=1;n=e.childNodes[r];r++)t.push(l.walkTree(n));e=e.childNodes[0]}const s=r.createElement("dummy"),a=i.childNodes[0];r.replaceNode(i,s),r.replaceNode(n,i),r.replaceNode(i.childNodes[0],n),r.replaceNode(s,a),t||(t=i)}return l.walkTree(this.ofence),l.walkTree(this.cfence),this.cleanupParents_(),t||n}specialCase_(e,t){const n=r.tagName(t);let i,o=null;if("MSUBSUP"===n?(o=e.childNodes[0],i=s.CaseDoubleScript):"MMULTISCRIPTS"===n&&("superscript"===e.type||"subscript"===e.type?i=a.CaseMultiscripts:"tensor"===e.type&&(i=c.CaseTensor),o=i&&e.childNodes[0]&&"subsup"===e.childNodes[0].role?e.childNodes[0]:e),!o)return null;const l=o.childNodes[0],u=d.makeEmptyNode_(l.id);return o.childNodes[0]=u,t=new i(e).getMathml(),o.childNodes[0]=l,this.parentCleanup.push(t),o.childNodes[0]}introduceNewLayer_(){const e=this.fullFence(this.ofenceMml),t=this.fullFence(this.cfenceMml);let n=r.createElement("mrow");if(r.replaceNode(this.fencedMml,n),this.fencedMmlNodes.forEach((e=>n.appendChild(e))),n.insertBefore(e,this.fencedMml),n.appendChild(t),!n.parentNode){const e=r.createElement("mrow");for(;n.childNodes.length>0;)e.appendChild(n.childNodes[0]);n.appendChild(e),n=e}return n}fullFence(e){const t=this.fencedMml.parentNode;let n=e;for(;n.parentNode&&n.parentNode!==t;)n=n.parentNode;return n}cleanupParents_(){this.parentCleanup.forEach((function(e){const t=e.childNodes[1].getAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT);e.childNodes[0].setAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT,t)}))}}t.CaseEmbellished=d},9763:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseLimit=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree||!e.childNodes.length)return!1;const t=r.tagName(e.mathmlTree),n=e.type;return("limupper"===n||"limlower"===n)&&("MSUBSUP"===t||"MUNDEROVER"===t)||"limboth"===n&&("MSUB"===t||"MUNDER"===t||"MSUP"===t||"MOVER"===t)}static walkTree_(e){e&&o.walkTree(e)}getMathml(){const e=this.semantic.childNodes;return"limboth"!==this.semantic.type&&this.mml.childNodes.length>=3&&(this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer([this.mml],this.semantic)),(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),e[0].mathmlTree||(e[0].mathmlTree=this.semantic.mathmlTree),e.forEach(a.walkTree_),this.mml}}t.CaseLimit=a},7978:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseLine=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&"line"===e.type}getMathml(){return this.semantic.contentNodes.length&&i.walkTree(this.semantic.contentNodes[0]),this.semantic.childNodes.length&&i.walkTree(this.semantic.childNodes[0]),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseLine=s},2124:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseMultiindex=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static multiscriptIndex(e){return"punctuated"===e.type&&"dummy"===e.contentNodes[0].role?o.collapsePunctuated(e):(o.walkTree(e),e.id)}static createNone_(e){const t=r.createElement("none");return e&&(0,s.setAttributes)(t,e),t.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),t}completeMultiscript(e,t){const n=r.toArray(this.mml.childNodes).slice(1);let i=0;const c=e=>{for(let t,r=0;t=e[r];r++){const e=n[i];if(e&&t===parseInt(o.getInnerNode(e).getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID)))o.getInnerNode(e).setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,this.semantic.id.toString()),i++;else{const n=this.semantic.querySelectorAll((e=>e.id===t));this.mml.insertBefore(a.createNone_(n[0]),e||null)}}};c(e),n[i]&&"MPRESCRIPTS"!==r.tagName(n[i])?this.mml.insertBefore(n[i],r.createElement("mprescripts")):i++,c(t)}}t.CaseMultiindex=a},4308:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseMultiscripts=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7984),o=n(2124),s=n(8672),a=n(8171);class c extends o.CaseMultiindex{static test(e){if(!e.mathmlTree)return!1;return"MMULTISCRIPTS"===r.tagName(e.mathmlTree)&&("superscript"===e.type||"subscript"===e.type)}constructor(e){super(e)}getMathml(){let e,t,n;if((0,a.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.semantic.childNodes[0]&&"subsup"===this.semantic.childNodes[0].role){const r=this.semantic.childNodes[0];e=r.childNodes[0],t=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]),n=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(r.childNodes[1]);const c=[this.semantic.id,[r.id,e.id,n],t];s.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,c),this.mml.setAttribute(a.Attribute.TYPE,r.role),this.completeMultiscript(i.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(n,t),[])}else{e=this.semantic.childNodes[0],t=o.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]);const n=[this.semantic.id,e.id,t];s.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,n)}const r=i.SemanticSkeleton.collapsedLeafs(n||[],t),c=s.walkTree(e);return s.getInnerNode(c).setAttribute(a.Attribute.PARENT,this.semantic.id.toString()),r.unshift(e.id),this.mml.setAttribute(a.Attribute.CHILDREN,r.join(",")),this.mml}}t.CaseMultiscripts=c},5326:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseProof=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&("inference"===e.type||"premises"===e.type)}getMathml(){return this.semantic.childNodes.length?(this.semantic.contentNodes.forEach((function(e){i.walkTree(e),(0,o.setAttributes)(e.mathmlTree,e)})),this.semantic.childNodes.forEach((function(e){i.walkTree(e)})),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.getAttribute("data-semantic-id")===this.mml.getAttribute("data-semantic-parent")&&this.mml.removeAttribute("data-semantic-parent"),this.mml):this.mml}}t.CaseProof=s},6998:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseTable=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(9341),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.inner=[],this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return"matrix"===e.type||"vector"===e.type||"cases"===e.type}getMathml(){const e=o.cloneContentNode(this.semantic.contentNodes[0]),t=this.semantic.contentNodes[1]?o.cloneContentNode(this.semantic.contentNodes[1]):null;if(this.inner=this.semantic.childNodes.map(o.walkTree),this.mml)if("MFENCED"===r.tagName(this.mml)){const n=this.mml.childNodes;this.mml.insertBefore(e,n[0]||null),t&&this.mml.appendChild(t),this.mml=o.rewriteMfenced(this.mml)}else{const n=[e,this.mml];t&&n.push(t),this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer(n,this.semantic)}else this.mml=o.introduceNewLayer([e].concat(this.inner,[t]),this.semantic);return(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml}}t.CaseTable=a},439:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseTensor=void 0;const r=n(7984),i=n(2124),o=n(8672),s=n(8171);class a extends i.CaseMultiindex{static test(e){return!!e.mathmlTree&&"tensor"===e.type}constructor(e){super(e)}getMathml(){o.walkTree(this.semantic.childNodes[0]);const e=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[1]),t=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[2]),n=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[3]),a=i.CaseMultiindex.multiscriptIndex(this.semantic.childNodes[4]);(0,s.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic);const c=[this.semantic.id,this.semantic.childNodes[0].id,e,t,n,a];o.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,c);const l=r.SemanticSkeleton.collapsedLeafs(e,t,n,a);return l.unshift(this.semantic.childNodes[0].id),this.mml.setAttribute(s.Attribute.CHILDREN,l.join(",")),this.completeMultiscript(r.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(n,a),r.SemanticSkeleton.interleaveIds(e,t)),this.mml}}t.CaseTensor=a},598:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CaseText=void 0;const r=n(9341),i=n(8672),o=n(8171);class s extends r.AbstractEnrichCase{constructor(e){super(e),this.mml=e.mathmlTree}static test(e){return"punctuated"===e.type&&("text"===e.role||e.contentNodes.every((e=>"dummy"===e.role)))}getMathml(){const e=[],t=i.collapsePunctuated(this.semantic,e);return this.mml=i.introduceNewLayer(e,this.semantic),(0,o.setAttributes)(this.mml,this.semantic),this.mml.removeAttribute(o.Attribute.CONTENT),i.addCollapsedAttribute(this.mml,t),this.mml}}t.CaseText=s},7450:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.prepareMmlString=t.testTranslation__=t.semanticMathml=t.semanticMathmlSync=t.semanticMathmlNode=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4886),s=n(1939),a=n(8672),c=n(8171);function l(e){const t=i.cloneNode(e),n=s.getTree(t);return a.enrich(t,n)}function u(e){return l(i.parseInput(e))}function d(e){return e.match(/^"),e}n(7813),t.semanticMathmlNode=l,t.semanticMathmlSync=u,t.semanticMathml=function(e,t){o.EnginePromise.getall().then((()=>{const n=i.parseInput(e);t(l(n))}))},t.testTranslation__=function(e){r.Debugger.getInstance().init();const t=u(d(e)).toString();return(0,c.removeAttributePrefix)(t),r.Debugger.getInstance().exit(),t},t.prepareMmlString=d},8171:function(e,t){var n;function r(e){return e.map((function(e){return e.id})).join(",")}function i(e,t){const r=[];"mglyph"===t.role&&r.push("image"),t.attributes.href&&r.push("link"),r.length&&e.setAttribute(n.POSTFIX,r.join(" "))}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.addPrefix=t.removeAttributePrefix=t.setPostfix=t.setAttributes=t.makeIdList=t.EnrichAttributes=t.Attribute=t.Prefix=void 0,t.Prefix="data-semantic-",function(e){e.ADDED="data-semantic-added",e.ALTERNATIVE="data-semantic-alternative",e.CHILDREN="data-semantic-children",e.COLLAPSED="data-semantic-collapsed",e.CONTENT="data-semantic-content",e.EMBELLISHED="data-semantic-embellished",e.FENCEPOINTER="data-semantic-fencepointer",e.FONT="data-semantic-font",e.ID="data-semantic-id",e.ANNOTATION="data-semantic-annotation",e.OPERATOR="data-semantic-operator",e.OWNS="data-semantic-owns",e.PARENT="data-semantic-parent",e.POSTFIX="data-semantic-postfix",e.PREFIX="data-semantic-prefix",e.ROLE="data-semantic-role",e.SPEECH="data-semantic-speech",e.STRUCTURE="data-semantic-structure",e.TYPE="data-semantic-type"}(n=t.Attribute||(t.Attribute={})),t.EnrichAttributes=[n.ADDED,n.ALTERNATIVE,n.CHILDREN,n.COLLAPSED,n.CONTENT,n.EMBELLISHED,n.FENCEPOINTER,n.FONT,n.ID,n.ANNOTATION,n.OPERATOR,n.OWNS,n.PARENT,n.POSTFIX,n.PREFIX,n.ROLE,n.SPEECH,n.STRUCTURE,n.TYPE],t.makeIdList=r,t.setAttributes=function(e,o){e.setAttribute(n.TYPE,o.type);const s=o.allAttributes();for(let n,r=0;n=s[r];r++)e.setAttribute(t.Prefix+n[0].toLowerCase(),n[1]);o.childNodes.length&&e.setAttribute(n.CHILDREN,r(o.childNodes)),o.contentNodes.length&&e.setAttribute(n.CONTENT,r(o.contentNodes)),o.parent&&e.setAttribute(n.PARENT,o.parent.id.toString()),i(e,o)},t.setPostfix=i,t.removeAttributePrefix=function(e){return e.toString().replace(new RegExp(t.Prefix,"g"),"")},t.addPrefix=function(e){return t.Prefix+e}},9775:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.factory=t.getCase=void 0,t.getCase=function(e){for(let n,r=0;n=t.factory[r];r++)if(n.test(e))return n.constr(e);return null},t.factory=[]},7813:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4306),i=n(8871),o=n(928),s=n(9763),a=n(7978),c=n(4308),l=n(5326),u=n(6998),d=n(439),h=n(598);n(9775).factory.push({test:s.CaseLimit.test,constr:e=>new s.CaseLimit(e)},{test:o.CaseEmbellished.test,constr:e=>new o.CaseEmbellished(e)},{test:i.CaseDoubleScript.test,constr:e=>new i.CaseDoubleScript(e)},{test:d.CaseTensor.test,constr:e=>new d.CaseTensor(e)},{test:c.CaseMultiscripts.test,constr:e=>new c.CaseMultiscripts(e)},{test:a.CaseLine.test,constr:e=>new a.CaseLine(e)},{test:r.CaseBinomial.test,constr:e=>new r.CaseBinomial(e)},{test:l.CaseProof.test,constr:e=>new l.CaseProof(e)},{test:u.CaseTable.test,constr:e=>new u.CaseTable(e)},{test:h.CaseText.test,constr:e=>new h.CaseText(e)})},8672:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.printNodeList__=t.collapsePunctuated=t.formattedOutput_=t.formattedOutput=t.getInnerNode=t.setOperatorAttribute_=t.createInvisibleOperator_=t.rewriteMfenced=t.cloneContentNode=t.addCollapsedAttribute=t.parentNode_=t.isIgnorable_=t.unitChild_=t.descendNode_=t.ascendNewNode=t.validLca_=t.pathToRoot_=t.attachedElement_=t.prunePath_=t.mathmlLca_=t.lcaType=t.functionApplication_=t.isDescendant_=t.insertNewChild_=t.mergeChildren_=t.collectChildNodes_=t.collateChildNodes_=t.childrenSubset_=t.moveSemanticAttributes_=t.introduceLayerAboveLca=t.introduceNewLayer=t.walkTree=t.enrich=t.SETTINGS=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(6671),o=n(4886),s=n(4020),a=n(2721),c=n(7984),l=n(8901),u=n(8171),d=n(9775);function h(e){const t=(0,d.getCase)(e);let n;if(t)return n=t.getMathml(),I(n);if(1===e.mathml.length)return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 0"),n=e.mathml[0],u.setAttributes(n,e),e.childNodes.length&&(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 0.1"),e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){"empty"===e.type&&n.appendChild(h(e))}))),I(n);const i=e.contentNodes.map(F);k(e,i);const o=e.childNodes.map(h),s=c.SemanticSkeleton.combineContentChildren(e,i,o);if(n=e.mathmlTree,null===n)r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1"),n=p(s,e);else{const e=v(s);r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2"),e?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2.1"),n=e.parentNode):(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 2.2"),n=U(n))}return n=D(n),N(n,s,e),u.setAttributes(n,e),I(n)}function p(e,t){const n=C(e);let o=n.node;const s=n.type;if(s!==_.VALID||!l.hasEmptyTag(o))if(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1"),o=i.createElement("mrow"),s===_.PRUNED)r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.0"),o=f(o,n.node,e);else if(e[0]){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.1");const t=v(e),n=g(t.parentNode,e);i.replaceNode(t,o),n.forEach((function(e){o.appendChild(e)}))}return t.mathmlTree||(t.mathmlTree=o),o}function f(e,t,n){let o=L(t);if(l.hasMathTag(o)){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Walktree Case 1.1.0.0"),m(o,e),i.toArray(o.childNodes).forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)}));const t=e;e=o,o=t}const s=n.indexOf(t);return n[s]=o,i.replaceNode(o,e),e.appendChild(o),n.forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)})),e}function m(e,t){for(const n of u.EnrichAttributes)e.hasAttribute(n)&&(t.setAttribute(n,e.getAttribute(n)),e.removeAttribute(n))}function g(e,t){const n=i.toArray(e.childNodes);let r=1/0,o=-1/0;return t.forEach((function(e){const t=n.indexOf(e);-1!==t&&(r=Math.min(r,t),o=Math.max(o,t))})),n.slice(r,o+1)}function S(e,t,n){const r=[];let o=i.toArray(e.childNodes),s=!1;for(;o.length;){const e=o.shift();if(e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)){r.push(e);continue}const t=b(e);0!==t.length&&(1!==t.length?(s?e.setAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit",!0):s=!0,o=t.concat(o)):r.push(e))}const a=[],c=n.childNodes.map((function(e){return e.mathmlTree}));for(;c.length;){const e=c.pop();if(e){if(-1!==r.indexOf(e))break;-1!==t.indexOf(e)&&a.unshift(e)}}return r.concat(a)}function b(e){const t=[];let n=i.toArray(e.childNodes);for(;n.length;){const e=n.shift();e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&(e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)?t.push(e):n=i.toArray(e.childNodes).concat(n))}return t}function N(e,t,n){const r="implicit"===n.role&&a.flags.combine_juxtaposition?S(e,t,n):i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!r.length)return void t.forEach((function(t){e.appendChild(t)}));let o=0;for(;t.length;){const n=t[0];r[o]===n||A(r[o],n)?(t.shift(),o++):r[o]&&-1===t.indexOf(r[o])?o++:(y(n,e)||E(e,r[o],n),t.shift())}}function E(e,t,n){if(!t)return void e.insertBefore(n,null);let r=t,i=P(r);for(;i&&i.firstChild===r&&!r.hasAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit")&&i!==e;)r=i,i=P(r);i&&(i.insertBefore(n,r),r.removeAttribute("AuxiliaryImplicit"))}function y(e,t){if(!e)return!1;do{if((e=e.parentNode)===t)return!0}while(e);return!1}function A(e,t){const n=s.functionApplication();if(e&&t&&e.textContent&&t.textContent&&e.textContent===n&&t.textContent===n&&"true"===t.getAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED)){for(let n,r=0;n=e.attributes[r];r++)t.hasAttribute(n.nodeName)||t.setAttribute(n.nodeName,n.nodeValue);return i.replaceNode(e,t),!0}return!1}var _;function C(e){const t=v(e);if(!t)return{type:_.INVALID,node:null};const n=v(e.slice().reverse());if(t===n)return{type:_.VALID,node:t};const r=O(t),i=T(r,e),o=O(n,(function(e){return-1!==i.indexOf(e)})),s=o[0],a=i.indexOf(s);return-1===a?{type:_.INVALID,node:null}:{type:i.length!==r.length?_.PRUNED:M(i[a+1],o[1])?_.VALID:_.INVALID,node:s}}function T(e,t){let n=0;for(;e[n]&&-1===t.indexOf(e[n]);)n++;return e.slice(0,n+1)}function v(e){let t=0,n=null;for(;!n&&t!1),r=[e];for(;!n(e)&&!l.hasMathTag(e)&&e.parentNode;)e=P(e),r.unshift(e);return r}function M(e,t){return!(!e||!t||e.previousSibling||t.nextSibling)}function I(e){for(;!l.hasMathTag(e)&&R(e);)e=P(e);return e}function L(e){const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!t)return e;const n=t.filter((function(e){return e.nodeType===i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&!l.hasIgnoreTag(e)}));return 1===n.length&&l.hasEmptyTag(n[0])&&!n[0].hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)?L(n[0]):e}function R(e){const t=P(e);return!(!t||!l.hasEmptyTag(t))&&i.toArray(t.childNodes).every((function(t){return t===e||x(t)}))}function x(e){if(e.nodeType!==i.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE)return!0;if(!e||l.hasIgnoreTag(e))return!0;const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);return!(!l.hasEmptyTag(e)&&t.length||l.hasDisplayTag(e)||e.hasAttribute(u.Attribute.TYPE)||l.isOrphanedGlyph(e))&&i.toArray(e.childNodes).every(x)}function P(e){return e.parentNode}function F(e){if(e.mathml.length)return h(e);const n=t.SETTINGS.implicit?w(e):i.createElement("mrow");return e.mathml=[n],n}function D(e){if("MFENCED"!==i.tagName(e))return e;const t=i.createElement("mrow");for(let n,r=0;n=e.attributes[r];r++)-1===["open","close","separators"].indexOf(n.name)&&t.setAttribute(n.name,n.value);return i.toArray(e.childNodes).forEach((function(e){t.appendChild(e)})),i.replaceNode(e,t),t}function w(e){const t=i.createElement("mo"),n=i.createTextNode(e.textContent);return t.appendChild(n),u.setAttributes(t,e),t.setAttribute(u.Attribute.ADDED,"true"),t}function k(e,t){const n=e.type+(e.textContent?","+e.textContent:"");t.forEach((function(e){U(e).setAttribute(u.Attribute.OPERATOR,n)}))}function U(e){const t=i.toArray(e.childNodes);if(!t)return e;const n=t.filter((function(e){return!x(e)})),r=[];for(let e,t=0;e=n[t];t++)if(l.hasEmptyTag(e)){const t=U(e);t&&t!==e&&r.push(t)}else r.push(e);return 1===r.length?r[0]:e}function B(e,t,n,r){const i=r||!1;j(e,"Original MathML",i),j(n,"Semantic Tree",i),j(t,"Semantically enriched MathML",i)}function j(e,t,n){const r=i.formatXml(e.toString());n?console.info(t+":\n```html\n"+u.removeAttributePrefix(r)+"\n```\n"):console.info(r)}t.SETTINGS={collapsed:!0,implicit:!0},t.enrich=function(e,t){const n=i.cloneNode(e);return h(t.root),o.default.getInstance().structure&&e.setAttribute(u.Attribute.STRUCTURE,c.SemanticSkeleton.fromStructure(e,t).toString()),r.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((function(){return B(n,e,t,!0),[]})),e},t.walkTree=h,t.introduceNewLayer=p,t.introduceLayerAboveLca=f,t.moveSemanticAttributes_=m,t.childrenSubset_=g,t.collateChildNodes_=S,t.collectChildNodes_=b,t.mergeChildren_=N,t.insertNewChild_=E,t.isDescendant_=y,t.functionApplication_=A,function(e){e.VALID="valid",e.INVALID="invalid",e.PRUNED="pruned"}(_=t.lcaType||(t.lcaType={})),t.mathmlLca_=C,t.prunePath_=T,t.attachedElement_=v,t.pathToRoot_=O,t.validLca_=M,t.ascendNewNode=I,t.descendNode_=L,t.unitChild_=R,t.isIgnorable_=x,t.parentNode_=P,t.addCollapsedAttribute=function(e,t){const n=new c.SemanticSkeleton(t);e.setAttribute(u.Attribute.COLLAPSED,n.toString())},t.cloneContentNode=F,t.rewriteMfenced=D,t.createInvisibleOperator_=w,t.setOperatorAttribute_=k,t.getInnerNode=U,t.formattedOutput=B,t.formattedOutput_=j,t.collapsePunctuated=function(e,t){const n=!!t,r=t||[],i=e.parent,o=e.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e.id}));o.unshift("c");const s=[e.id,o];for(let t,o=0;t=e.childNodes[o];o++){const e=h(t);r.push(e);const o=U(e);i&&!n&&o.setAttribute(u.Attribute.PARENT,i.id.toString()),s.push(t.id)}return s},t.printNodeList__=function(e,t){console.info(e),i.toArray(t).forEach((function(e){console.info(e.toString())})),console.info("<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<")}},7228:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(5024),i=n(8171);class o{constructor(){this.color=null,this.mactionName="",this.currentHighlights=[]}highlight(e){this.currentHighlights.push(e.map((e=>{const t=this.highlightNode(e);return this.setHighlighted(e),t})))}highlightAll(e){const t=this.getMactionNodes(e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)this.highlight([e])}unhighlight(){const e=this.currentHighlights.pop();e&&e.forEach((e=>{this.isHighlighted(e.node)&&(this.unhighlightNode(e),this.unsetHighlighted(e.node))}))}unhighlightAll(){for(;this.currentHighlights.length>0;)this.unhighlight()}setColor(e){this.color=e}colorString(){return this.color.rgba()}addEvents(e,t){const n=this.getMactionNodes(e);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)for(const n in t)e.addEventListener(n,t[n])}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByClassName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){const t=e.className||e.getAttribute("class");return!!t&&!!t.match(new RegExp(this.mactionName))}isHighlighted(e){return e.hasAttribute(o.ATTR)}setHighlighted(e){e.setAttribute(o.ATTR,"true")}unsetHighlighted(e){e.removeAttribute(o.ATTR)}colorizeAll(e){r.evalXPath(`.//*[@${i.Attribute.ID}]`,e).forEach((e=>this.colorize(e)))}uncolorizeAll(e){r.evalXPath(`.//*[@${i.Attribute.ID}]`,e).forEach((e=>this.uncolorize(e)))}colorize(e){const t=(0,i.addPrefix)("foreground");e.hasAttribute(t)&&(e.setAttribute(t+"-old",e.style.color),e.style.color=e.getAttribute(t))}uncolorize(e){const t=(0,i.addPrefix)("foreground")+"-old";e.hasAttribute(t)&&(e.style.color=e.getAttribute(t))}}t.AbstractHighlighter=o,o.ATTR="sre-highlight"},7567:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ChtmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(9400);class i extends r.CssHighlighter{constructor(){super()}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName.toUpperCase()===this.mactionName.toUpperCase()}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}}t.ChtmlHighlighter=i},1123:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ContrastPicker=t.ColorPicker=void 0;const n={red:{red:255,green:0,blue:0},green:{red:0,green:255,blue:0},blue:{red:0,green:0,blue:255},yellow:{red:255,green:255,blue:0},cyan:{red:0,green:255,blue:255},magenta:{red:255,green:0,blue:255},white:{red:255,green:255,blue:255},black:{red:0,green:0,blue:0}};function r(e,t){const r=e||{color:t};let i=Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,"color")?n[r.color]:r;return i||(i=n[t]),i.alpha=Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(r,"alpha")?r.alpha:1,function(e){const t=e=>(e=Math.max(e,0),e=Math.min(255,e),Math.round(e));return e.red=t(e.red),e.green=t(e.green),e.blue=t(e.blue),e.alpha=Math.max(e.alpha,0),e.alpha=Math.min(1,e.alpha),e}(i)}class i{constructor(e,t){this.foreground=r(t,i.DEFAULT_FOREGROUND_),this.background=r(e,i.DEFAULT_BACKGROUND_)}static toHex(e){const t=e.toString(16);return 1===t.length?"0"+t:t}rgba(){const e=function(e){return"rgba("+e.red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+","+e.alpha+")"};return{background:e(this.background),foreground:e(this.foreground)}}rgb(){const e=function(e){return"rgb("+e.red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+")"};return{background:e(this.background),alphaback:this.background.alpha.toString(),foreground:e(this.foreground),alphafore:this.foreground.alpha.toString()}}hex(){const e=function(e){return"#"+i.toHex(e.red)+i.toHex(e.green)+i.toHex(e.blue)};return{background:e(this.background),alphaback:this.background.alpha.toString(),foreground:e(this.foreground),alphafore:this.foreground.alpha.toString()}}}t.ColorPicker=i,i.DEFAULT_BACKGROUND_="blue",i.DEFAULT_FOREGROUND_="black";t.ContrastPicker=class{constructor(){this.hue=10,this.sat=100,this.light=50,this.incr=50}generate(){return t=function(e,t,n){t=t>1?t/100:t,n=n>1?n/100:n;const r=(1-Math.abs(2*n-1))*t,i=r*(1-Math.abs(e/60%2-1)),o=n-r/2;let s=0,a=0,c=0;return 0<=e&&e<60?[s,a,c]=[r,i,0]:60<=e&&e<120?[s,a,c]=[i,r,0]:120<=e&&e<180?[s,a,c]=[0,r,i]:180<=e&&e<240?[s,a,c]=[0,i,r]:240<=e&&e<300?[s,a,c]=[i,0,r]:300<=e&&e<360&&([s,a,c]=[r,0,i]),{red:s+o,green:a+o,blue:c+o}}(this.hue,this.sat,this.light),"rgb("+(e={red:Math.round(255*t.red),green:Math.round(255*t.green),blue:Math.round(255*t.blue)}).red+","+e.green+","+e.blue+")";var e,t}increment(){this.hue=(this.hue+this.incr)%360}}},9400:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CssHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(7228);class i extends r.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="mjx-maction"}highlightNode(e){const t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},n=this.colorString();return e.style.backgroundColor=n.background,e.style.color=n.foreground,t}unhighlightNode(e){e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,e.node.style.color=e.foreground}}t.CssHighlighter=i},9009:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.highlighterMapping_=t.addEvents=t.highlighter=void 0;const r=n(7567),i=n(1123),o=n(9400),s=n(7872),a=n(3711),c=n(4662),l=n(3507),u=n(280);t.highlighter=function(e,n,r){const o=new i.ColorPicker(e,n),s="NativeMML"===r.renderer&&"Safari"===r.browser?"MML-CSS":"SVG"===r.renderer&&"v3"===r.browser?"SVG-V3":r.renderer,a=new(t.highlighterMapping_[s]||t.highlighterMapping_.NativeMML);return a.setColor(o),a},t.addEvents=function(e,n,r){const i=t.highlighterMapping_[r.renderer];i&&(new i).addEvents(e,n)},t.highlighterMapping_={SVG:l.SvgHighlighter,"SVG-V3":u.SvgV3Highlighter,NativeMML:c.MmlHighlighter,"HTML-CSS":s.HtmlHighlighter,"MML-CSS":a.MmlCssHighlighter,CommonHTML:o.CssHighlighter,CHTML:r.ChtmlHighlighter}},7872:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.HtmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7228);class o extends i.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){const t={node:e,foreground:e.style.color,position:e.style.position},n=this.color.rgb();e.style.color=n.foreground,e.style.position="relative";const i=e.bbox;if(i&&i.w){const o=.05,s=0,a=r.createElement("span"),c=parseFloat(e.style.paddingLeft||"0");a.style.backgroundColor=n.background,a.style.opacity=n.alphaback.toString(),a.style.display="inline-block",a.style.height=i.h+i.d+2*o+"em",a.style.verticalAlign=-i.d+"em",a.style.marginTop=a.style.marginBottom=-o+"em",a.style.width=i.w+2*s+"em",a.style.marginLeft=c-s+"em",a.style.marginRight=-i.w-s-c+"em",e.parentNode.insertBefore(a,e),t.box=a}return t}unhighlightNode(e){const t=e.node;t.style.color=e.foreground,t.style.position=e.position,e.box&&e.box.parentNode.removeChild(e.box)}}t.HtmlHighlighter=o},3711:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MmlCssHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(9400);class i extends r.CssHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName===this.mactionName}}t.MmlCssHighlighter=i},4662:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MmlHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(7228);class i extends r.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){let t=e.getAttribute("style");return t+=";background-color: "+this.colorString().background,t+=";color: "+this.colorString().foreground,e.setAttribute("style",t),{node:e}}unhighlightNode(e){let t=e.node.getAttribute("style");t=t.replace(";background-color: "+this.colorString().background,""),t=t.replace(";color: "+this.colorString().foreground,""),e.node.setAttribute("style",t)}colorString(){return this.color.rgba()}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(e.getElementsByTagName(this.mactionName))}isMactionNode(e){return e.tagName===this.mactionName}}t.MmlHighlighter=i},3507:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SvgHighlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(7228);class o extends i.AbstractHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="mjx-svg-maction"}highlightNode(e){let t;if(this.isHighlighted(e))return t={node:e.previousSibling||e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},t;if("svg"===e.tagName){const t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color};return e.style.backgroundColor=this.colorString().background,e.style.color=this.colorString().foreground,t}const n=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","rect");let o;if("use"===e.nodeName){const t=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","g");e.parentNode.insertBefore(t,e),t.appendChild(e),o=t.getBBox(),t.parentNode.replaceChild(e,t)}else o=e.getBBox();n.setAttribute("x",(o.x-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("y",(o.y-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("width",(o.width+80).toString()),n.setAttribute("height",(o.height+80).toString());const s=e.getAttribute("transform");return s&&n.setAttribute("transform",s),n.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().background),n.setAttribute(i.AbstractHighlighter.ATTR,"true"),e.parentNode.insertBefore(n,e),t={node:n,foreground:e.getAttribute("fill")},e.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().foreground),t}setHighlighted(e){"svg"===e.tagName&&super.setHighlighted(e)}unhighlightNode(e){if("background"in e)return e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,void(e.node.style.color=e.foreground);e.foreground?e.node.nextSibling.setAttribute("fill",e.foreground):e.node.nextSibling.removeAttribute("fill"),e.node.parentNode.removeChild(e.node)}isMactionNode(e){let t=e.className||e.getAttribute("class");return t=void 0!==t.baseVal?t.baseVal:t,!!t&&!!t.match(new RegExp(this.mactionName))}}t.SvgHighlighter=o},280:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SvgV3Highlighter=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(5024),o=n(7228),s=n(1123),a=n(3507);class c extends a.SvgHighlighter{constructor(){super(),this.mactionName="maction"}highlightNode(e){let t;if(this.isHighlighted(e))return t={node:e,background:this.colorString().background,foreground:this.colorString().foreground},t;if("svg"===e.tagName||"MJX-CONTAINER"===e.tagName)return t={node:e,background:e.style.backgroundColor,foreground:e.style.color},e.style.backgroundColor=this.colorString().background,e.style.color=this.colorString().foreground,t;const n=r.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/2000/svg","rect");n.setAttribute("sre-highlighter-added","true");const i=e.getBBox();n.setAttribute("x",(i.x-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("y",(i.y-40).toString()),n.setAttribute("width",(i.width+80).toString()),n.setAttribute("height",(i.height+80).toString());const a=e.getAttribute("transform");if(a&&n.setAttribute("transform",a),n.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().background),e.setAttribute(o.AbstractHighlighter.ATTR,"true"),e.parentNode.insertBefore(n,e),t={node:e,foreground:e.getAttribute("fill")},"rect"===e.nodeName){const t=new s.ColorPicker({alpha:0,color:"black"});e.setAttribute("fill",t.rgba().foreground)}else e.setAttribute("fill",this.colorString().foreground);return t}unhighlightNode(e){const t=e.node.previousSibling;if(t&&t.hasAttribute("sre-highlighter-added"))return e.foreground?e.node.setAttribute("fill",e.foreground):e.node.removeAttribute("fill"),void e.node.parentNode.removeChild(t);e.node.style.backgroundColor=e.background,e.node.style.color=e.foreground}isMactionNode(e){return e.getAttribute("data-mml-node")===this.mactionName}getMactionNodes(e){return Array.from(i.evalXPath(`.//*[@data-mml-node="${this.mactionName}"]`,e))}}t.SvgV3Highlighter=c},1473:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.StaticTrieNode=t.AbstractTrieNode=void 0;const r=n(1984),i=n(9259);class o{constructor(e,t){this.constraint=e,this.test=t,this.children_={},this.kind=i.TrieNodeKind.ROOT}getConstraint(){return this.constraint}getKind(){return this.kind}applyTest(e){return this.test(e)}addChild(e){const t=e.getConstraint(),n=this.children_[t];return this.children_[t]=e,n}getChild(e){return this.children_[e]}getChildren(){const e=[];for(const t in this.children_)e.push(this.children_[t]);return e}findChildren(e){const t=[];for(const n in this.children_){const r=this.children_[n];r.applyTest(e)&&t.push(r)}return t}removeChild(e){delete this.children_[e]}toString(){return this.constraint}}t.AbstractTrieNode=o;t.StaticTrieNode=class extends o{constructor(e,t){super(e,t),this.rule_=null,this.kind=i.TrieNodeKind.STATIC}getRule(){return this.rule_}setRule(e){this.rule_&&r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Replacing rule "+this.rule_+" with "+e),this.rule_=e}toString(){return this.getRule()?this.constraint+"\n==> "+this.getRule().action:this.constraint}}},2803:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Trie=void 0;const r=n(9259),i=n(9146);class o{constructor(){this.root=(0,i.getNode)(r.TrieNodeKind.ROOT,"",null)}static collectRules_(e){const t=[];let n=[e];for(;n.length;){const e=n.shift();if(e.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.QUERY||e.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.BOOLEAN){const n=e.getRule();n&&t.unshift(n)}n=n.concat(e.getChildren())}return t}static printWithDepth_(e,t,n){n+=new Array(t+2).join(t.toString())+": "+e.toString()+"\n";const r=e.getChildren();for(let e,i=0;e=r[i];i++)n=o.printWithDepth_(e,t+1,n);return n}static order_(e){const t=e.getChildren();if(!t.length)return 0;const n=Math.max.apply(null,t.map(o.order_));return Math.max(t.length,n)}addRule(e){let t=this.root;const n=e.context,i=e.dynamicCstr.getValues();for(let e=0,o=i.length;e{t.getKind()===r.TrieNodeKind.DYNAMIC&&-1===e.indexOf(t.getConstraint())||i.push(t)}))}n=i.slice()}for(;n.length;){const t=n.shift();if(t.getRule){const e=t.getRule();e&&i.push(e)}const r=t.findChildren(e);n=n.concat(r)}return i}hasSubtrie(e){let t=this.root;for(let n=0,r=e.length;n!0)),this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.ROOT}}t.RootTrieNode=u;class d extends a.AbstractTrieNode{constructor(e){super(e,(t=>t===e)),this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.DYNAMIC}}t.DynamicTrieNode=d;const h={"=":(e,t)=>e===t,"!=":(e,t)=>e!==t,"<":(e,t)=>e":(e,t)=>e>t,"<=":(e,t)=>e<=t,">=":(e,t)=>e>=t};function p(e){if(e.match(/^self::\*$/))return e=>!0;if(e.match(/^self::\w+$/)){const t=e.slice(6).toUpperCase();return e=>e.tagName&&r.tagName(e)===t}if(e.match(/^self::\w+:\w+$/)){const t=e.split(":"),n=i.resolveNameSpace(t[2]);if(!n)return null;const r=t[3].toUpperCase();return e=>e.localName&&e.localName.toUpperCase()===r&&e.namespaceURI===n}if(e.match(/^@\w+$/)){const t=e.slice(1);return e=>e.hasAttribute&&e.hasAttribute(t)}if(e.match(/^@\w+="[\w\d ]+"$/)){const t=e.split("="),n=t[0].slice(1),r=t[1].slice(1,-1);return e=>e.hasAttribute&&e.hasAttribute(n)&&e.getAttribute(n)===r}if(e.match(/^@\w+!="[\w\d ]+"$/)){const t=e.split("!="),n=t[0].slice(1),r=t[1].slice(1,-1);return e=>!e.hasAttribute||!e.hasAttribute(n)||e.getAttribute(n)!==r}if(e.match(/^contains\(\s*@grammar\s*,\s*"[\w\d ]+"\s*\)$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1];return e=>!!o.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter(t)}if(e.match(/^not\(\s*contains\(\s*@grammar\s*,\s*"[\w\d ]+"\s*\)\s*\)$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1];return e=>!o.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter(t)}if(e.match(/^name\(\.\.\/\.\.\)="\w+"$/)){const t=e.split('"')[1].toUpperCase();return e=>{var n,i;return(null===(i=null===(n=e.parentNode)||void 0===n?void 0:n.parentNode)||void 0===i?void 0:i.tagName)&&r.tagName(e.parentNode.parentNode)===t}}if(e.match(/^count\(preceding-sibling::\*\)=\d+$/)){const t=e.split("="),n=parseInt(t[1],10);return e=>{var t;return(null===(t=e.parentNode)||void 0===t?void 0:t.childNodes[n])===e}}if(e.match(/^.+\[@category!?=".+"\]$/)){let[,t,n,r]=e.match(/^(.+)\[@category(!?=)"(.+)"\]$/);const o=r.match(/^unit:(.+)$/);let a="";return o&&(r=o[1],a=":unit"),e=>{const o=i.evalXPath(t,e)[0];if(o){const e=s.lookupCategory(o.textContent+a);return"="===n?e===r:e!==r}return!1}}if(e.match(/^string-length\(.+\)\W+\d+/)){const[,t,n,r]=e.match(/^string-length\((.+)\)(\W+)(\d+)/),o=h[n]||h["="],s=parseInt(r,10);return e=>{const n=i.evalXPath(t,e)[0];return!!n&&o(Array.from(n.textContent).length,s)}}return null}t.constraintTest_=p;class f extends c.StaticTrieNode{constructor(e,t){super(e,p(e)),this.context=t,this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.QUERY}applyTest(e){return this.test?this.test(e):this.context.applyQuery(e,this.constraint)===e}}t.QueryTrieNode=f;class m extends c.StaticTrieNode{constructor(e,t){super(e,p(e)),this.context=t,this.kind=l.TrieNodeKind.BOOLEAN}applyTest(e){return this.test?this.test(e):this.context.applyConstraint(e,this.constraint)}}t.BooleanTrieNode=m},2371:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.completeLocale=t.getLocale=t.setLocale=t.locales=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4513),o=n(1058),s=n(8597),a=n(9883),c=n(2523),l=n(3938),u=n(9139),d=n(1547),h=n(346),p=n(13),f=n(6238),m=n(2913),g=n(3305),S=n(9770),b=n(4524);function N(){const e=i.Variables.ensureLocale(r.default.getInstance().locale,r.default.getInstance().defaultLocale);return r.default.getInstance().locale=e,t.locales[e]()}t.locales={ca:s.ca,da:a.da,de:c.de,en:l.en,es:u.es,fr:d.fr,hi:h.hi,it:p.it,nb:f.nb,nn:g.nn,sv:S.sv,nemeth:m.nemeth},t.setLocale=function(){const e=N();if(function(e){const t=r.default.getInstance().subiso;-1===e.SUBISO.all.indexOf(t)&&(r.default.getInstance().subiso=e.SUBISO.default);e.SUBISO.current=r.default.getInstance().subiso}(e),e){for(const t of Object.getOwnPropertyNames(e))b.LOCALE[t]=e[t];for(const[t,n]of Object.entries(e.CORRECTIONS))o.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection(t,n)}},t.getLocale=N,t.completeLocale=function(e){const n=t.locales[e.locale];if(!n)return void console.error("Locale "+e.locale+" does not exist!");const r=e.kind.toUpperCase(),i=e.messages;if(!i)return;const o=n();for(const[e,t]of Object.entries(i))o[r][e]=t}},4524:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.createLocale=t.LOCALE=void 0;const r=n(4277);function i(){return{FUNCTIONS:(0,r.FUNCTIONS)(),MESSAGES:(0,r.MESSAGES)(),ALPHABETS:(0,r.ALPHABETS)(),NUMBERS:(0,r.NUMBERS)(),COMBINERS:{},CORRECTIONS:{},SUBISO:(0,r.SUBISO)()}}t.LOCALE=i(),t.createLocale=i},3319:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.localeFontCombiner=t.extractString=t.localEnclose=t.localRole=t.localFont=t.combinePostfixIndex=t.nestingToString=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(9385);function o(e,t){return void 0===e?t:"string"==typeof e?e:e[0]}t.nestingToString=function(e){switch(e){case 1:return r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ONCE||"";case 2:return r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.TWICE;default:return e.toString()}},t.combinePostfixIndex=function(e,t){return e===r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX||e===r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.INDEX?e:e+" "+t},t.localFont=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.font[e],e)},t.localRole=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.role[e],e)},t.localEnclose=function(e){return o(r.LOCALE.MESSAGES.enclose[e],e)},t.extractString=o,t.localeFontCombiner=function(e){return"string"==typeof e?{font:e,combiner:r.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.combiner}:{font:e[0],combiner:r.LOCALE.COMBINERS[e[1]]||i.Combiners[e[1]]||r.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.combiner}}},8597:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ca=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(165),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e="sans serif "+(n?n+" "+e:e),t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.ca=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.sansserif=a,e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=i.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>e+n,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e+" "),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*os$/.test(e)?e+"sos":/.*s$/.test(e)?e+"os":/.*ga$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"gues":/.*\xe7a$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ces":/.*ca$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ques":/.*ja$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ges":/.*qua$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-3)+"q\xfces":/.*a$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"es":/.*(e|i)$/.test(e)?e+"ns":/.*\xed$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ins":e+"s",e.FUNCTIONS.si=(e,t)=>(t.match(/^metre/)&&(e=e.replace(/a$/,"\xe0").replace(/o$/,"\xf2").replace(/i$/,"\xed")),e+t),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e}()),c}},9883:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.da=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(5571),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.da=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=t=>t===e.ALPHABETS.capPrefix.default?RegExp("^"+t+" "):RegExp(" "+t+"$"),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.postfixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e}()),a}},2523:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.de=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(3319),o=n(4524),s=n(757),a=function(e,t,n){return"s"===n&&(t=t.split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"")})).join(" "),n=""),e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?t+" "+e:e},c=function(e,t,n){return e=n&&"s"!==n?n+" "+e:e,t?e+" "+t:e};let l=null;t.de=function(){return l||(l=function(){const e=(0,o.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.COMBINERS.germanPostfix=c,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=t=>t>1?e.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t)+"fach":"",e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=(e,t)=>{const n=t?t+"wurzel":"";return e.replace("Wurzel",n)},e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>{const r=(t?t+" ":"")+(e=n.match(/exponent$/)?e+"r":e);return n.match(/ /)?n.replace(/ /," "+r+" "):r+" "+n},e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=function(e){return e=e.split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"(|s)")})).join(" "),new RegExp("((^"+e+" )|( "+e+"$))")},e.CORRECTIONS.correctOne=e=>e.replace(/^eins$/,"ein"),e.CORRECTIONS.localFontNumber=e=>(0,i.localFont)(e).split(" ").map((function(e){return e.replace(/s$/,"")})).join(" "),e.CORRECTIONS.lowercase=e=>e.toLowerCase(),e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>{const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("case"),n=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("plural");return"dative"===t?{der:"dem",die:n?"den":"der",das:"dem"}[e]:e},e.CORRECTIONS.masculine=e=>"dative"===r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("case")?e+"n":e,e}()),l}},3938:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.en=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(4524),o=n(3319),s=n(166),a=n(9385);let c=null;t.en=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=o.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*s$/.test(e)?e:e+"s",e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=s.default.numberToWords,e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("noArticle")?"":e,e}()),c}},9139:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.es=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(6154),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e="sans serif "+(n?n+" "+e:e),t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.es=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.sansserif=a,e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=i.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>e+n,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e+" "),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*(a|e|i|o|u)$/.test(e)?e+"s":/.*z$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ces":/.*c$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-1)+"ques":/.*g$/.test(e)?e+"ues":/.*\u00f3n$/.test(e)?e.slice(0,-2)+"ones":e+"es",e.FUNCTIONS.si=(e,t)=>(t.match(/^metro/)&&(e=e.replace(/a$/,"\xe1").replace(/o$/,"\xf3").replace(/i$/,"\xed")),e+t),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e}()),c}},1547:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.fr=void 0;const r=n(1058),i=n(4524),o=n(3319),s=n(4394),a=n(9385);let c=null;t.fr=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=s.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=o.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=o.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction=(e,t,n)=>n.replace(/ $/g,"")+t+e,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>n+" "+e,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp(" (en |)"+e+"$"),e.FUNCTIONS.plural=e=>/.*s$/.test(e)?e:e+"s",e.CORRECTIONS.article=e=>r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("noArticle")?"":e,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=a.Combiners.romanceCombiner,e.SUBISO={default:"fr",current:"fr",all:["fr","be","ch"]},e}()),c}},346:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.hi=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(1779),o=n(9385),s=n(3319);let a=null;t.hi=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=i.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=o.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=s.nestingToString,e}()),a}},13:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.it=void 0;const r=n(3319),i=n(4524),o=n(5952),s=n(9385),a=function(e,t,n){return e.match(/^[a-zA-Z]$/)&&(t=t.replace("cerchiato","cerchiata")),e=n?e+" "+n:e,t?e+" "+t:e};let c=null;t.it=function(){return c||(c=function(){const e=(0,i.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.COMBINERS.italianPostfix=a,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=r.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex=r.combinePostfixIndex,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction=(e,t,n)=>n.replace(/ $/g,"")+t+e,e.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical=(e,t,n)=>n+" "+e,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp(" (en |)"+e+"$"),e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.romanceCombiner,e}()),c}},6238:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nb=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(984),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.nb=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e}()),a}},2913:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nemeth=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3669),o=n(9385),s=function(e){return e.match(RegExp("^"+h.ALPHABETS.languagePrefix.english))?e.slice(1):e},a=function(e,t,n){return e=s(e),t?e+t:e},c=function(e,t,n){return t+s(e)},l=function(e,t,n){return t+(n||"")+(e=s(e))+"\u283b"},u=function(e,t,n){return t+(n||"")+(e=s(e))+"\u283b\u283b"},d=function(e,t,n){return t+(e=s(e))+"\u283e"};let h=null;t.nemeth=function(){return h||(h=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=i.default,e.COMBINERS={postfixCombiner:a,germanCombiner:c,embellishCombiner:l,doubleEmbellishCombiner:u,parensCombiner:d},e.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth=e=>!1,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=e=>RegExp("^"+e),e.FUNCTIONS.si=o.identityTransformer,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=(e,t,n)=>t?t+n+e:s(e),e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans={default:i.default.numberToWords},e}()),h}},3305:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.nn=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(984),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.nn=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.SUBISO={default:"",current:"",all:["","alt"]},e}()),a}},9770:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.sv=void 0;const r=n(4524),i=n(3319),o=n(6416),s=n(9385);let a=null;t.sv=function(){return a||(a=function(){const e=(0,r.createLocale)();return e.NUMBERS=o.default,e.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth=i.nestingToString,e.FUNCTIONS.fontRegexp=function(e){return new RegExp("((^"+e+" )|( "+e+"$))")},e.ALPHABETS.combiner=s.Combiners.prefixCombiner,e.ALPHABETS.digitTrans.default=o.default.numberToWords,e.CORRECTIONS.correctOne=e=>e.replace(/^ett$/,"en"),e}()),a}},4277:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SUBISO=t.FUNCTIONS=t.ALPHABETS=t.NUMBERS=t.MESSAGES=void 0;const r=n(9385);t.MESSAGES=function(){return{MS:{},MSroots:{},font:{},embellish:{},role:{},enclose:{},navigate:{},regexp:{},unitTimes:""}},t.NUMBERS=function(){return{zero:"zero",ones:[],tens:[],large:[],special:{},wordOrdinal:r.identityTransformer,numericOrdinal:r.identityTransformer,numberToWords:r.identityTransformer,numberToOrdinal:r.pluralCase,vulgarSep:" ",numSep:" "}},t.ALPHABETS=function(){return{latinSmall:[],latinCap:[],greekSmall:[],greekCap:[],capPrefix:{default:""},smallPrefix:{default:""},digitPrefix:{default:""},languagePrefix:{},digitTrans:{default:r.identityTransformer,mathspeak:r.identityTransformer,clearspeak:r.identityTransformer},letterTrans:{default:r.identityTransformer},combiner:(e,t,n)=>e}},t.FUNCTIONS=function(){return{fracNestDepth:e=>r.vulgarFractionSmall(e,10,100),radicalNestDepth:e=>"",combineRootIndex:function(e,t){return e},combineNestedFraction:r.Combiners.identityCombiner,combineNestedRadical:r.Combiners.identityCombiner,fontRegexp:function(e){return new RegExp("^"+e.split(/ |-/).join("( |-)")+"( |-)")},si:r.siCombiner,plural:r.identityTransformer}},t.SUBISO=function(){return{default:"",current:"",all:[]}}},165:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){const t=e%1e3,n=Math.floor(t/100),r=n?1===n?"cent":a.ones[n]+"-cents":"",i=function(e){const t=e%100;if(t<20)return a.ones[t];const n=Math.floor(t/10),r=a.tens[n],i=a.ones[t%10];return r&&i?r+(2===n?"-i-":"-")+i:r||i}(t%100);return r&&i?r+a.numSep+i:r||i}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%(t>1?1e6:1e3);if(r){let e=a.large[t];if(t)if(1===t)n=(1===r?"":i(r)+a.numSep)+e+(n?a.numSep+n:"");else{const t=o(r);e=1===r?e:e.replace(/\u00f3$/,"ons"),n=t+a.numSep+e+(n?a.numSep+n:"")}else n=i(r)}e=Math.floor(e/(t>1?1e6:1e3)),t++}return n}function s(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("f"===t?"a":"n")}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.numericOrdinal=s,a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(e>1999)return s(e);if(e<=10)return a.special.onesOrdinals[e-1];const n=o(e);return n.match(/mil$/)?n.replace(/mil$/,"mil\xb7l\xe8sima"):n.match(/u$/)?n.replace(/u$/,"vena"):n.match(/a$/)?n.replace(/a$/,"ena"):n+(n.match(/e$/)?"na":"ena")},t.default=a},5571:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?t?"et":"en":e}function i(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,i="",o=a.ones[Math.floor(n/100)];if(i+=o?r(o,!0)+" hundrede":"",n%=100,n)if(i+=i?" og ":"",o=t?a.special.smallOrdinals[n]:a.ones[n],o)i+=o;else{const e=t?a.special.tensOrdinals[Math.floor(n/10)]:a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)];o=a.ones[n%10],i+=o?r(o)+"og"+e:e}return i}function o(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,o="";for(;e>0;){const s=e%1e3;if(s){const e=i(s,t&&!n);if(n){const t=a.large[n],i=s>1?"er":"";o=r(e,n<=1)+" "+t+i+(o?" og ":"")+o}else o=r(e)+o}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return o}function s(e){if(e%100)return o(e,!0);const t=o(e);return t.match(/e$/)?t:t+"e"}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return 1===e?t?"hel":"hele":2===e?t?"halv":"halve":s(e)+(t?"dele":"del")},t.default=a},757:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?t?"eine":"ein":e}function i(e){let t=e%1e3,n="",i=a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)];if(n+=i?r(i)+"hundert":"",t%=100,t)if(n+=n?a.numSep:"",i=a.ones[t],i)n+=i;else{const e=a.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];i=a.ones[t%10],n+=i?r(i)+"und"+e:e}return n}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const s=i(e%1e3);if(t){const e=a.large[t],i=t>1&&o>1?e.match(/e$/)?"n":"en":"";n=r(s,t>1)+e+i+n}else n=r(s,t>1)+n}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/ein$/,"eins")}function s(e){if(1===e)return"erste";if(3===e)return"dritte";if(7===e)return"siebte";if(8===e)return"achte";return o(e)+(e<19?"te":"ste")}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return 1===e?"eintel":2===e?t?"halbe":"halb":s(e)+"l"},t.default=a},166:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";return n+=s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+s.numSep+"hundred":"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]||s.tens[Math.floor(t/10)]+(t%10?s.numSep+s.ones[t%10]:"")),n}function i(e){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){e%1e3&&(n=r(e%1e3)+(t?"-"+s.large[t]+"-":"")+n),e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}function o(e){let t=i(e);return t.match(/one$/)?t=t.slice(0,-3)+"first":t.match(/two$/)?t=t.slice(0,-3)+"second":t.match(/three$/)?t=t.slice(0,-5)+"third":t.match(/five$/)?t=t.slice(0,-4)+"fifth":t.match(/eight$/)?t=t.slice(0,-5)+"eighth":t.match(/nine$/)?t=t.slice(0,-4)+"ninth":t.match(/twelve$/)?t=t.slice(0,-6)+"twelfth":t.match(/ty$/)?t=t.slice(0,-2)+"tieth":t+="th",t}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=e%100,n=e.toString();if(t>10&&t<20)return n+"th";switch(e%10){case 1:return n+"st";case 2:return n+"nd";case 3:return n+"rd";default:return n+"th"}},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(1===e)return t?"oneths":"oneth";if(2===e)return t?"halves":"half";const n=o(e);return t?n+"s":n},t.default=s},6154:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){const t=e%1e3,n=Math.floor(t/100),r=o.special.hundreds[n],i=function(e){const t=e%100;if(t<30)return o.ones[t];const n=o.tens[Math.floor(t/10)],r=o.ones[t%10];return n&&r?n+" y "+r:n||r}(t%100);return 1===n?i?r+"to "+i:r:r&&i?r+" "+i:r||i}const o=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();o.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("f"===t?"a":"o")},o.numberToWords=function(e){if(0===e)return o.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%1e3;if(r){let e=o.large[t];const s=i(r);t?1===r?(e=e.match("/^mil( |$)/")?e:"un "+e,n=e+(n?" "+n:"")):(e=e.replace(/\u00f3n$/,"ones"),n=i(r)+" "+e+(n?" "+n:"")):n=s}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n},o.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(e>1999)return e.toString()+"a";if(e<=12)return o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1];const n=[];if(e>=1e3&&(e-=1e3,n.push("mil\xe9sima")),!e)return n.join(" ");let r=0;return r=Math.floor(e/100),r>0&&(n.push(o.special.hundredsOrdinals[r-1]),e%=100),e<=12?n.push(o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1]):(r=Math.floor(e/10),r>0&&(n.push(o.special.tensOrdinals[r-1]),e%=10),e>0&&n.push(o.special.onesOrdinals[e-1])),n.join(" ")},t.default=o},4394:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4886),i=n(1058),o=n(4277);function s(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";if(n+=u.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?u.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+"-cent":"",t%=100,t){n+=n?"-":"";let e=u.ones[t];if(e)n+=e;else{const r=u.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];r.match(/-dix$/)?(e=u.ones[t%10+10],n+=r.replace(/-dix$/,"")+"-"+e):n+=r+(t%10?"-"+u.ones[t%10]:"")}}const r=n.match(/s-\w+$/);return r?n.replace(/s-\w+$/,r[0].slice(1)):n.replace(/-un$/,"-et-un")}function a(e){if(0===e)return u.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();u.special["tens-"+r.default.getInstance().subiso]&&(u.tens=u.special["tens-"+r.default.getInstance().subiso]);let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){const r=e%1e3;if(r){let e=u.large[t];const i=s(r);if(e&&e.match(/^mille /)){const r=e.replace(/^mille /,"");n=n.match(RegExp(r))?i+(t?"-mille-":"")+n:n.match(RegExp(r.replace(/s$/,"")))?i+(t?"-mille-":"")+n.replace(r.replace(/s$/,""),r):i+(t?"-"+e+"-":"")+n}else e=1===r&&e?e.replace(/s$/,""):e,n=i+(t?"-"+e+"-":"")+n}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}const c={1:"uni\xe8me",2:"demi",3:"tiers",4:"quart"};function l(e){if(1===e)return"premi\xe8re";let t=a(e);return t.match(/^neuf$/)?t=t.slice(0,-1)+"v":t.match(/cinq$/)?t+="u":t.match(/trois$/)?t+="":(t.match(/e$/)||t.match(/s$/))&&(t=t.slice(0,-1)),t+="i\xe8me",t}const u=(0,o.NUMBERS)();u.wordOrdinal=l,u.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=i.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return 1===e?e.toString()+("m"===t?"er":"re"):e.toString()+"e"},u.numberToWords=a,u.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){const n=c[e]||l(e);return 3===e?n:t?n+"s":n},t.default=u},1779:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,32))return e.toString();let t=0,n="";const r=function(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";return n+=s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?s.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+s.numSep+s.special.hundred:"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]),n}(e%1e3);if(!(e=Math.floor(e/1e3)))return r;for(;e>0;){const r=e%100;r&&(n=s.ones[r]+s.numSep+s.large[t]+(n?s.numSep+n:"")),e=Math.floor(e/100),t++}return r?n+s.numSep+r:n}function o(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");if(e<=0)return e.toString();if(e<10)return"f"===t?s.special.ordinalsFeminine[e]:s.special.ordinalsMasculine[e];return i(e)+("f"===t?"\u0935\u0940\u0902":"\u0935\u093e\u0901")}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e>0&&e<10?"f"===t?s.special.simpleSmallOrdinalsFeminine[e]:s.special.simpleSmallOrdinalsMasculine[e]:e.toString().split("").map((function(e){const t=parseInt(e,10);return isNaN(t)?"":s.special.simpleNumbers[t]})).join("")+("f"===t?"\u0935\u0940\u0902":"\u0935\u093e\u0901")},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return e<=10?s.special.smallDenominators[e]:o(e)+" \u0905\u0902\u0936"},t.default=s},5952:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1058);function i(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";if(n+=a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]?a.ones[Math.floor(t/100)]+a.numSep+"cento":"",t%=100,t){n+=n?a.numSep:"";const e=a.ones[t];if(e)n+=e;else{let e=a.tens[Math.floor(t/10)];const r=t%10;1!==r&&8!==r||(e=e.slice(0,-1)),n+=e,n+=r?a.numSep+a.ones[t%10]:""}}return n}function o(e){if(0===e)return a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();if(1===e&&r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("fraction"))return"un";let t=0,n="";for(;e>0;){e%1e3&&(n=i(e%1e3)+(t?"-"+a.large[t]+"-":"")+n),e=Math.floor(e/1e3),t++}return n.replace(/-$/,"")}function s(e){const t="m"===r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender")?"o":"a";let n=a.special.onesOrdinals[e];return n?n.slice(0,-1)+t:(n=o(e),n.slice(0,-1)+"esim"+t)}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=r.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("gender");return e.toString()+("m"===t?"o":"a")},a.numberToWords=o,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(2===e)return t?"mezzi":"mezzo";const n=s(e);if(!t)return n;const r=n.match(/o$/)?"i":"e";return n.slice(0,-1)+r},t.default=a},3669:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){return e.toString().split("").map((function(e){return i.ones[parseInt(e,10)]})).join("")}const i=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();i.numberToWords=r,i.numberToOrdinal=r,t.default=i},984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(4886);function i(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,r="";const i=Math.floor(n/100),s=a.ones[i];if(r+=s?(1===i?"":s)+"hundre":"",n%=100,n){if(r+=r?"og":"",t){const e=a.special.smallOrdinals[n];if(e)return r+e;if(n%10)return r+a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)]+a.special.smallOrdinals[n%10]}r+=a.ones[n]||a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)]+(n%10?a.ones[n%10]:"")}return t?o(r):r}function o(e){const t=a.special.endOrdinal[0];return"a"===t&&e.match(/en$/)?e.slice(0,-2)+a.special.endOrdinal:e.match(/(d|n)$/)||e.match(/hundre$/)?e+"de":e.match(/i$/)?e+a.special.endOrdinal:"a"===t&&e.match(/e$/)?e.slice(0,-1)+a.special.endOrdinal:(e.match(/e$/),e+"nde")}function s(e){return u(e,!0)}const a=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();function c(e,t=!1){return e===a.ones[1]?"ein"===e?"eitt ":t?"et":"ett":e}function l(e,t=!1){let n=e%1e3,r="",i=a.ones[Math.floor(n/100)];if(r+=i?c(i)+"hundre":"",n%=100,n){if(r+=r?"og":"",t){const e=a.special.smallOrdinals[n];if(e)return r+e}if(i=a.ones[n],i)r+=i;else{const e=a.tens[Math.floor(n/10)];i=a.ones[n%10],r+=i?i+"og"+e:e}}return t?o(r):r}function u(e,t=!1){const n="alt"===r.default.getInstance().subiso?function(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return t?a.special.smallOrdinals[0]:a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,r="";for(;e>0;){const i=e%1e3;if(i){const o=l(e%1e3,!n&&t);!n&&t&&(t=!t),r=(1===n?c(o,!0):o)+(n>1?a.numSep:"")+(n?a.large[n]+(n>1&&i>1?"er":""):"")+(n>1&&r?a.numSep:"")+r}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return t?r+(r.match(/tusen$/)?"de":"te"):r}(e,t):function(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return t?a.special.smallOrdinals[0]:a.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,r="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const s=i(e%1e3,!n&&t);!n&&t&&(t=!t),r=s+(n?" "+a.large[n]+(n>1&&o>1?"er":"")+(r?" ":""):"")+r}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return t?r+(r.match(/tusen$/)?"de":"te"):r}(e,t);return n}a.wordOrdinal=s,a.numericOrdinal=function(e){return e.toString()+"."},a.numberToWords=u,a.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){return s(e)},t.default=a},6416:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});function r(e){let t=e%1e3,n="";const r=Math.floor(t/100);return n+=s.ones[r]?(1===r?"":s.ones[r]+s.numSep)+"hundra":"",t%=100,t&&(n+=n?s.numSep:"",n+=s.ones[t]||s.tens[Math.floor(t/10)]+(t%10?s.numSep+s.ones[t%10]:"")),n}function i(e,t=!1){if(0===e)return s.zero;if(e>=Math.pow(10,36))return e.toString();let n=0,i="";for(;e>0;){const o=e%1e3;if(o){const a=s.large[n],c=o>1&&n>1&&!t?"er":"";i=(1===n&&1===o?"":(n>1&&1===o?"en":r(e%1e3))+(n>1?" ":""))+(n?a+c+(n>1?" ":""):"")+i}e=Math.floor(e/1e3),n++}return i.replace(/ $/,"")}function o(e){let t=i(e,!0);return t.match(/^noll$/)?t="nollte":t.match(/ett$/)?t=t.replace(/ett$/,"f\xf6rsta"):t.match(/tv\xe5$/)?t=t.replace(/tv\xe5$/,"andra"):t.match(/tre$/)?t=t.replace(/tre$/,"tredje"):t.match(/fyra$/)?t=t.replace(/fyra$/,"fj\xe4rde"):t.match(/fem$/)?t=t.replace(/fem$/,"femte"):t.match(/sex$/)?t=t.replace(/sex$/,"sj\xe4tte"):t.match(/sju$/)?t=t.replace(/sju$/,"sjunde"):t.match(/\xe5tta$/)?t=t.replace(/\xe5tta$/,"\xe5ttonde"):t.match(/nio$/)?t=t.replace(/nio$/,"nionde"):t.match(/tio$/)?t=t.replace(/tio$/,"tionde"):t.match(/elva$/)?t=t.replace(/elva$/,"elfte"):t.match(/tolv$/)?t=t.replace(/tolv$/,"tolfte"):t.match(/tusen$/)?t=t.replace(/tusen$/,"tusonde"):t.match(/jard$/)||t.match(/jon$/)?t+="te":t+="de",t}const s=(0,n(4277).NUMBERS)();s.wordOrdinal=o,s.numericOrdinal=function(e){const t=e.toString();return t.match(/11$|12$/)?t+":e":t+(t.match(/1$|2$/)?":a":":e")},s.numberToWords=i,s.numberToOrdinal=function(e,t){if(1===e)return"hel";if(2===e)return t?"halva":"halv";let n=o(e);return n=n.match(/de$/)?n.replace(/de$/,""):n,n+(t?"delar":"del")},t.default=s},9385:function(e,t){function n(e,t=""){if(!e.childNodes||!e.childNodes[0]||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes||e.childNodes[0].childNodes.length<2||"number"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName||"integer"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].getAttribute("role")||"number"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].tagName||"integer"!==e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role"))return{convertible:!1,content:e.textContent};const n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent,r=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent,i=Number(n),o=Number(r);return isNaN(i)||isNaN(o)?{convertible:!1,content:`${r} ${t} ${n}`}:{convertible:!0,enumerator:o,denominator:i}}Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.vulgarFractionSmall=t.convertVulgarFraction=t.Combiners=t.siCombiner=t.identityTransformer=t.pluralCase=void 0,t.pluralCase=function(e,t){return e.toString()},t.identityTransformer=function(e){return e.toString()},t.siCombiner=function(e,t){return e+t.toLowerCase()},t.Combiners={},t.Combiners.identityCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e+t+n},t.Combiners.prefixCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?t+" "+e:e},t.Combiners.postfixCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?n+" "+e:e,t?e+" "+t:e},t.Combiners.romanceCombiner=function(e,t,n){return e=n?e+" "+n:e,t?e+" "+t:e},t.convertVulgarFraction=n,t.vulgarFractionSmall=function(e,t,r){const i=n(e);if(i.convertible){const e=i.enumerator,n=i.denominator;return e>0&&e0&&n{const s=this.parseCstr(t.toString().replace(i,""));this.addRule(new o.SpeechRule(e,s,r,n))}))}getFullPreconditions(e){const t=this.preconditions.get(e);return t||!this.inherits?t:this.inherits.getFullPreconditions(e)}definePrecondition(e,t,n,...r){const i=this.parsePrecondition(n,r),o=this.parseCstr(t);i&&o?(i.rank=this.rank++,this.preconditions.set(e,new c(o,i))):console.error(`Precondition Error: ${n}, (${t})`)}inheritRules(){if(!this.inherits||!this.inherits.getSpeechRules().length)return;const e=new RegExp("^\\w+\\.\\w+\\."+(this.domain?"\\w+\\.":""));this.inherits.getSpeechRules().forEach((t=>{const n=this.parseCstr(t.dynamicCstr.toString().replace(e,""));this.addRule(new o.SpeechRule(t.name,n,t.precondition,t.action))}))}ignoreRules(e,...t){let n=this.findAllRules((t=>t.name===e));if(!t.length)return void n.forEach(this.deleteRule.bind(this));let r=[];for(const e of t){const t=this.parseCstr(e);for(const e of n)t.equal(e.dynamicCstr)?this.deleteRule(e):r.push(e);n=r,r=[]}}parsePrecondition_(e){const t=this.context.customGenerators.lookup(e);return t?t():[e]}}t.BaseRuleStore=a;class c{constructor(e,t){this.base=e,this._conditions=[],this.constraints=[],this.allCstr={},this.constraints.push(e),this.addCondition(e,t)}get conditions(){return this._conditions}addConstraint(e){if(this.constraints.filter((t=>t.equal(e))).length)return;this.constraints.push(e);const t=[];for(const[n,r]of this.conditions)this.base.equal(n)&&t.push([e,r]);this._conditions=this._conditions.concat(t)}addBaseCondition(e){this.addCondition(this.base,e)}addFullCondition(e){this.constraints.forEach((t=>this.addCondition(t,e)))}addCondition(e,t){const n=e.toString()+" "+t.toString();this.allCstr.condStr||(this.allCstr[n]=!0,this._conditions.push([e,t]))}}t.Condition=c},1462:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.BrailleStore=void 0;const r=n(4036),i=n(7478);class o extends i.MathStore{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.modality="braille",this.customTranscriptions={"\u22ca":"\u2808\u2821\u2833"}}evaluateString(e){const t=[],n=Array.from(e);for(let e=0;ee.push(this.getProperty(t).slice()))),e}toString(){const e=[];return this.order.forEach((t=>e.push(t+": "+this.getProperty(t).toString()))),e.join("\n")}}t.DynamicProperties=r;class i extends r{constructor(e,t){const n={};for(const[t,r]of Object.entries(e))n[t]=[r];super(n,t),this.components=e}static createCstr(...e){const t=i.DEFAULT_ORDER,n={};for(let r=0,i=e.length,o=t.length;r{const n=t.indexOf(e);return-1!==n&&t.splice(n,1)}))}getComponents(){return this.components}getValue(e){return this.components[e]}getValues(){return this.order.map((e=>this.getValue(e)))}allProperties(){const e=super.allProperties();for(let t,n,r=0;t=e[r],n=this.order[r];r++){const e=this.getValue(n);-1===t.indexOf(e)&&t.unshift(e)}return e}toString(){return this.getValues().join(".")}equal(e){const t=e.getAxes();if(this.order.length!==t.length)return!1;for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++){const t=this.getValue(n);if(!t||e.getValue(n)!==t)return!1}return!0}}t.DynamicCstr=i,i.DEFAULT_ORDER=[n.LOCALE,n.MODALITY,n.DOMAIN,n.STYLE,n.TOPIC],i.BASE_LOCALE="base",i.DEFAULT_VALUE="default",i.DEFAULT_VALUES={[n.LOCALE]:"en",[n.DOMAIN]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.STYLE]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.TOPIC]:i.DEFAULT_VALUE,[n.MODALITY]:"speech"};t.DynamicCstrParser=class{constructor(e){this.order=e}parse(e){const t=e.split("."),n={};if(t.length>this.order.length)throw new Error("Invalid dynamic constraint: "+n);let r=0;for(let e,i=0;e=this.order[i],t.length;i++,r++){const r=t.shift();n[e]=r}return new i(n,this.order.slice(0,r))}};t.DefaultComparator=class{constructor(e,t=new r(e.getProperties(),e.getOrder())){this.reference=e,this.fallback=t,this.order=this.reference.getOrder()}getReference(){return this.reference}setReference(e,t){this.reference=e,this.fallback=t||new r(e.getProperties(),e.getOrder()),this.order=this.reference.getOrder()}match(e){const t=e.getAxes();return t.length===this.reference.getAxes().length&&t.every((t=>{const n=e.getValue(t);return n===this.reference.getValue(t)||-1!==this.fallback.getProperty(t).indexOf(n)}))}compare(e,t){let n=!1;for(let r,i=0;r=this.order[i];i++){const i=e.getValue(r),o=t.getValue(r);if(!n){const e=this.reference.getValue(r);if(e===i&&e!==o)return-1;if(e===o&&e!==i)return 1;if(e===i&&e===o)continue;e!==i&&e!==o&&(n=!0)}const s=this.fallback.getProperty(r),a=s.indexOf(i),c=s.indexOf(o);if(a!h.equal(e.cstr))),c.push(m),this.rules.set(t,c),p.setReference(f)}lookupRule(e,t){let n=this.getRules(t.getValue(i.Axis.LOCALE));return n=n.filter((function(e){return o.testDynamicConstraints_(t,e)})),1===n.length?n[0]:n.length?n.sort(((e,t)=>r.default.getInstance().comparator.compare(e.cstr,t.cstr)))[0]:null}}t.MathSimpleStore=o},7478:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MathStore=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(4524),o=n(4036),s=n(1970),a=n(7039);class c extends s.BaseRuleStore{constructor(){super(),this.annotators=[],this.parseMethods.Alias=this.defineAlias,this.parseMethods.SpecializedRule=this.defineSpecializedRule,this.parseMethods.Specialized=this.defineSpecialized}initialize(){this.initialized||(this.annotations(),this.initialized=!0)}annotations(){for(let e,t=0;e=this.annotators[t];t++)(0,o.activate)(this.domain,e)}defineAlias(e,t,...n){const r=this.parsePrecondition(t,n);if(!r)return void console.error(`Precondition Error: ${t} ${n}`);const i=this.preconditions.get(e);i?i.addFullCondition(r):console.error(`Alias Error: No precondition by the name of ${e}`)}defineRulesAlias(e,t,...n){const r=this.findAllRules((function(t){return t.name===e}));if(0===r.length)throw new a.OutputError("Rule with name "+e+" does not exist.");const i=[];r.forEach((e=>{(e=>{const t=e.dynamicCstr.toString(),n=e.action.toString();for(let e,r=0;e=i[r];r++)if(e.action===n&&e.cstr===t)return!1;return i.push({cstr:t,action:n}),!0})(e)&&this.addAlias_(e,t,n)}))}defineSpecializedRule(e,t,n,r){const i=this.parseCstr(t),o=this.findRule((t=>t.name===e&&i.equal(t.dynamicCstr))),s=this.parseCstr(n);if(!o&&r)throw new a.OutputError("Rule named "+e+" with style "+t+" does not exist.");const c=r?a.Action.fromString(r):o.action,l=new a.SpeechRule(o.name,s,o.precondition,c);this.addRule(l)}defineSpecialized(e,t,n){const r=this.parseCstr(n);if(!r)return void console.error(`Dynamic Constraint Error: ${n}`);const i=this.preconditions.get(e);i?i.addConstraint(r):console.error(`Alias Error: No precondition by the name of ${e}`)}evaluateString(e){const t=[];if(e.match(/^\s+$/))return t;let n=this.matchNumber_(e);if(n&&n.length===e.length)return t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n.number)),t;const o=r.removeEmpty(e.replace(/\s/g," ").split(" "));for(let e,r=0;e=o[r];r++)if(1===e.length)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e));else if(e.match(new RegExp("^["+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.TEXT+"]+$")))t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e));else{let r=e;for(;r;){n=this.matchNumber_(r);const e=r.match(new RegExp("^["+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.TEXT+"]+"));if(n)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n.number)),r=r.substring(n.length);else if(e)t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(e[0])),r=r.substring(e[0].length);else{const e=Array.from(r),n=e[0];t.push(this.evaluateCharacter(n)),r=e.slice(1).join("")}}}return t}parse(e){super.parse(e),this.annotators=e.annotators||[]}addAlias_(e,t,n){const r=this.parsePrecondition(t,n),i=new a.SpeechRule(e.name,e.dynamicCstr,r,e.action);i.name=e.name,this.addRule(i)}matchNumber_(e){const t=e.match(new RegExp("^"+i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.NUMBER)),n=e.match(new RegExp("^"+c.regexp.NUMBER));if(!t&&!n)return null;const r=n&&n[0]===e;if(t&&t[0]===e||!r)return t?{number:t[0],length:t[0].length}:null;return{number:n[0].replace(new RegExp(c.regexp.DIGIT_GROUP,"g"),"X").replace(new RegExp(c.regexp.DECIMAL_MARK,"g"),i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.DECIMAL_MARK).replace(/X/g,i.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.DIGIT_GROUP.replace(/\\/g,"")),length:n[0].length}}}t.MathStore=c,c.regexp={NUMBER:"((\\d{1,3})(?=(,| ))((,| )\\d{3})*(\\.\\d+)?)|^\\d*\\.\\d+|^\\d+",DECIMAL_MARK:"\\.",DIGIT_GROUP:","}},7039:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.OutputError=t.Precondition=t.Action=t.Component=t.ActionType=t.SpeechRule=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(1058);var o;function s(e){switch(e){case"[n]":return o.NODE;case"[m]":return o.MULTI;case"[t]":return o.TEXT;case"[p]":return o.PERSONALITY;default:throw"Parse error: "+e}}t.SpeechRule=class{constructor(e,t,n,r){this.name=e,this.dynamicCstr=t,this.precondition=n,this.action=r,this.context=null}toString(){return this.name+" | "+this.dynamicCstr.toString()+" | "+this.precondition.toString()+" ==> "+this.action.toString()}},function(e){e.NODE="NODE",e.MULTI="MULTI",e.TEXT="TEXT",e.PERSONALITY="PERSONALITY"}(o=t.ActionType||(t.ActionType={}));class a{constructor({type:e,content:t,attributes:n,grammar:r}){this.type=e,this.content=t,this.attributes=n,this.grammar=r}static grammarFromString(e){return i.Grammar.parseInput(e)}static fromString(e){const t={type:s(e.substring(0,3))};let n=e.slice(3).trim();if(!n)throw new u("Missing content.");switch(t.type){case o.TEXT:if('"'===n[0]){const e=d(n,"\\(")[0].trim();if('"'!==e.slice(-1))throw new u("Invalid string syntax.");t.content=e,n=n.slice(e.length).trim(),-1===n.indexOf("(")&&(n="");break}case o.NODE:case o.MULTI:{const e=n.indexOf(" (");if(-1===e){t.content=n.trim(),n="";break}t.content=n.substring(0,e).trim(),n=n.slice(e).trim()}}if(n){const e=a.attributesFromString(n);e.grammar&&(t.grammar=e.grammar,delete e.grammar),Object.keys(e).length&&(t.attributes=e)}return new a(t)}static attributesFromString(e){if("("!==e[0]||")"!==e.slice(-1))throw new u("Invalid attribute expression: "+e);const t={},n=d(e.slice(1,-1),",");for(let e=0,r=n.length;e0?"("+e.join(", ")+")":""}getAttributes(){const e=[];for(const t in this.attributes){const n=this.attributes[t];"true"===n?e.push(t):e.push(t+":"+n)}return e}}t.Component=a;class c{constructor(e){this.components=e}static fromString(e){const t=d(e,";").filter((function(e){return e.match(/\S/)})).map((function(e){return e.trim()})),n=[];for(let e=0,r=t.length;e0?n[0]:null}applyConstraint(e,t){return!!this.applyQuery(e,t)||r.evaluateBoolean(t,e)}constructString(e,t){if(!t)return"";if('"'===t.charAt(0))return t.slice(1,-1);const n=this.customStrings.lookup(t);return n?n(e):r.evaluateString(t,e)}parse(e){const t=Array.isArray(e)?e:Object.entries(e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++){switch(e[0].slice(0,3)){case"CQF":this.customQueries.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CSF":this.customStrings.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CTF":this.contextFunctions.add(e[0],e[1]);break;case"CGF":this.customGenerators.add(e[0],e[1]);break;default:console.error("FunctionError: Invalid function name "+e[0])}}}}},6060:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.storeFactory=t.SpeechRuleEngine=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(1984),o=n(6671),s=n(4886),a=n(4998),c=n(5024),l=n(7278),u=n(9805),d=n(1462),h=n(8310),p=n(1058),f=n(7478),m=n(7039),g=n(2803);class S{constructor(){this.trie=null,this.evaluators_={},this.trie=new g.Trie}static getInstance(){return S.instance=S.instance||new S,S.instance}static debugSpeechRule(e,t){const n=e.precondition,r=e.context.applyQuery(t,n.query);i.Debugger.getInstance().output(n.query,r?r.toString():r),n.constraints.forEach((n=>i.Debugger.getInstance().output(n,e.context.applyConstraint(t,n))))}static debugNamedSpeechRule(e,t){const n=S.getInstance().trie.collectRules().filter((t=>t.name==e));for(let r,o=0;r=n[o];o++)i.Debugger.getInstance().output("Rule",e,"DynamicCstr:",r.dynamicCstr.toString(),"number",o),S.debugSpeechRule(r,t)}evaluateNode(e){(0,c.updateEvaluator)(e);const t=(new Date).getTime();let n=[];try{n=this.evaluateNode_(e)}catch(e){console.error("Something went wrong computing speech."),i.Debugger.getInstance().output(e)}const r=(new Date).getTime();return i.Debugger.getInstance().output("Time:",r-t),n}toString(){return this.trie.collectRules().map((e=>e.toString())).join("\n")}runInSetting(e,t){const n=s.default.getInstance(),r={};for(const t in e)r[t]=n[t],n[t]=e[t];n.setDynamicCstr();const i=t();for(const e in r)n[e]=r[e];return n.setDynamicCstr(),i}addStore(e){const t=N(e);"abstract"!==t.kind&&t.getSpeechRules().forEach((e=>this.trie.addRule(e))),this.addEvaluator(t)}processGrammar(e,t,n){const r={};for(const i in n){const o=n[i];r[i]="string"==typeof o?e.constructString(t,o):o}p.Grammar.getInstance().pushState(r)}addEvaluator(e){const t=e.evaluateDefault.bind(e),n=this.evaluators_[e.locale];if(n)return void(n[e.modality]=t);const r={};r[e.modality]=t,this.evaluators_[e.locale]=r}getEvaluator(e,t){const n=this.evaluators_[e]||this.evaluators_[h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.LOCALE]];return n[t]||n[h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY]]}enumerate(e){return this.trie.enumerate(e)}evaluateNode_(e){return e?(this.updateConstraint_(),this.evaluateTree_(e)):[]}evaluateTree_(e){const t=s.default.getInstance();let n;i.Debugger.getInstance().output(t.mode!==a.Mode.HTTP?e.toString():e),p.Grammar.getInstance().setAttribute(e);const o=this.lookupRule(e,t.dynamicCstr);if(!o)return t.strict?[]:(n=this.getEvaluator(t.locale,t.modality)(e),e.attributes&&this.addPersonality_(n,{},!1,e),n);i.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((()=>["Apply Rule:",o.name,o.dynamicCstr.toString(),(t.mode,a.Mode.HTTP,e).toString()]));const l=o.context,u=o.action.components;n=[];for(let t,i=0;t=u[i];i++){let i=[];const o=t.content||"",a=t.attributes||{};let u=!1;t.grammar&&this.processGrammar(l,e,t.grammar);let d=null;if(a.engine){d=s.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr.getComponents();const e=p.Grammar.parseInput(a.engine);s.default.getInstance().setDynamicCstr(e)}switch(t.type){case m.ActionType.NODE:{const t=l.applyQuery(e,o);t&&(i=this.evaluateTree_(t))}break;case m.ActionType.MULTI:{u=!0;const t=l.applySelector(e,o);t.length>0&&(i=this.evaluateNodeList_(l,t,a.sepFunc,l.constructString(e,a.separator),a.ctxtFunc,l.constructString(e,a.context)))}break;case m.ActionType.TEXT:{const t=a.span,n={};if(t){const r=(0,c.evalXPath)(t,e);r.length&&(n.extid=r[0].getAttribute("extid"))}const s=l.constructString(e,o);(s||""===s)&&(i=Array.isArray(s)?s.map((function(e){return r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:e.speech,attributes:e.attributes},{adjust:!0})})):[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:s,attributes:n},{adjust:!0})])}break;case m.ActionType.PERSONALITY:default:i=[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:o})]}i[0]&&!u&&(a.context&&(i[0].context=l.constructString(e,a.context)+(i[0].context||"")),a.annotation&&(i[0].annotation=a.annotation)),this.addLayout(i,a,u),t.grammar&&p.Grammar.getInstance().popState(),n=n.concat(this.addPersonality_(i,a,u,e)),d&&s.default.getInstance().setDynamicCstr(d)}return n}evaluateNodeList_(e,t,n,i,o,s){if(!t.length)return[];const a=i||"",c=s||"",l=e.contextFunctions.lookup(o),u=l?l(t,c):function(){return c},d=e.contextFunctions.lookup(n),h=d?d(t,a):function(){return[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:a},{translate:!0})]};let p=[];for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++){const r=this.evaluateTree_(e);if(r.length>0&&(r[0].context=u()+(r[0].context||""),p=p.concat(r),n=0;t--){const r=n[t].name;!e.attributes[r]&&r.match(/^ext/)&&(e.attributes[r]=n[t].value)}}}addRelativePersonality_(e,t){if(!e.personality)return e.personality=t,e;const n=e.personality;for(const e in t)n[e]&&"number"==typeof n[e]&&"number"==typeof t[e]?n[e]=n[e]+t[e]:n[e]||(n[e]=t[e]);return e}updateConstraint_(){const e=s.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr,t=s.default.getInstance().strict,n=this.trie,r={};let i=e.getValue(h.Axis.LOCALE),o=e.getValue(h.Axis.MODALITY),a=e.getValue(h.Axis.DOMAIN);n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(a=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.DOMAIN],n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(o=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY],n.hasSubtrie([i,o,a])||(i=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.LOCALE]))),r[h.Axis.LOCALE]=[i],r[h.Axis.MODALITY]=["summary"!==o?o:h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.MODALITY]],r[h.Axis.DOMAIN]=["speech"!==o?h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[h.Axis.DOMAIN]:a];const c=e.getOrder();for(let n,i=0;n=c[i];i++)if(!r[n]){const i=e.getValue(n),o=this.makeSet_(i,e.preference),s=h.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[n];t||i===s||o.push(s),r[n]=o}e.updateProperties(r)}makeSet_(e,t){return t&&Object.keys(t).length?e.split(":"):[e]}lookupRule(e,t){if(!e||e.nodeType!==o.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE&&e.nodeType!==o.NodeType.TEXT_NODE)return null;const n=this.lookupRules(e,t);return n.length>0?this.pickMostConstraint_(t,n):null}lookupRules(e,t){return this.trie.lookupRules(e,t.allProperties())}pickMostConstraint_(e,t){const n=s.default.getInstance().comparator;return t.sort((function(e,t){return n.compare(e.dynamicCstr,t.dynamicCstr)||t.precondition.priority-e.precondition.priority||t.precondition.constraints.length-e.precondition.constraints.length||t.precondition.rank-e.precondition.rank})),i.Debugger.getInstance().generateOutput((()=>t.map((e=>e.name+"("+e.dynamicCstr.toString()+")"))).bind(this)),t[0]}}t.SpeechRuleEngine=S;const b=new Map;function N(e){const t=`${e.locale}.${e.modality}.${e.domain}`;if("actions"===e.kind){const n=b.get(t);return n.parse(e),n}u.init(),e&&!e.functions&&(e.functions=l.getStore(e.locale,e.modality,e.domain));const n="braille"===e.modality?new d.BrailleStore:new f.MathStore;return b.set(t,n),e.inherits&&(n.inherits=b.get(`${e.inherits}.${e.modality}.${e.domain}`)),n.parse(e),n.initialize(),n}t.storeFactory=N,s.default.nodeEvaluator=S.getInstance().evaluateNode.bind(S.getInstance())},3686:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.CustomGenerators=t.ContextFunctions=t.CustomStrings=t.CustomQueries=void 0;class n{constructor(e,t){this.prefix=e,this.store=t}add(e,t){this.checkCustomFunctionSyntax_(e)&&(this.store[e]=t)}addStore(e){const t=Object.keys(e.store);for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++)this.add(n,e.store[n])}lookup(e){return this.store[e]}checkCustomFunctionSyntax_(e){const t=new RegExp("^"+this.prefix);return!!e.match(t)||(console.error("FunctionError: Invalid function name. Expected prefix "+this.prefix),!1)}}t.CustomQueries=class extends n{constructor(){super("CQF",{})}};t.CustomStrings=class extends n{constructor(){super("CSF",{})}};t.ContextFunctions=class extends n{constructor(){super("CTF",{})}};t.CustomGenerators=class extends n{constructor(){super("CGF",{})}}},931:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.contentIterator=t.pauseSeparator=t.nodeCounter=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(5024),o=n(4886);t.nodeCounter=function(e,t){const n=e.length;let r=0,i=t;return t||(i=""),function(){return r0?i.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=n.shift(),i=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!e)return i;const s=o.default.evaluateNode(e);return i.concat(s)}}},1939:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getTreeFromString=t.getTree=t.xmlTree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(1784);function o(e){return new i.SemanticTree(e)}t.xmlTree=function(e){return o(e).xml()},t.getTree=o,t.getTreeFromString=function(e){return o(r.parseInput(e))}},4036:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.annotate=t.activate=t.register=t.visitors=t.annotators=void 0;const r=n(241);t.annotators=new Map,t.visitors=new Map,t.register=function(e){const n=e.domain+":"+e.name;e instanceof r.SemanticAnnotator?t.annotators.set(n,e):t.visitors.set(n,e)},t.activate=function(e,n){const r=e+":"+n,i=t.annotators.get(r)||t.visitors.get(r);i&&(i.active=!0)},t.annotate=function(e){for(const n of t.annotators.values())n.active&&n.annotate(e);for(const n of t.visitors.values())n.active&&n.visit(e,Object.assign({},n.def))}},241:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticVisitor=t.SemanticAnnotator=void 0;t.SemanticAnnotator=class{constructor(e,t,n){this.domain=e,this.name=t,this.func=n,this.active=!1}annotate(e){e.childNodes.forEach(this.annotate.bind(this)),e.addAnnotation(this.domain,this.func(e))}};t.SemanticVisitor=class{constructor(e,t,n,r={}){this.domain=e,this.name=t,this.func=n,this.def=r,this.active=!1}visit(e,t){let n=this.func(e,t);e.addAnnotation(this.domain,n[0]);for(let t,r=0;t=e.childNodes[r];r++)n=this.visit(t,n[1]);return n}}},4020:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.lookupSecondary=t.isEmbellishedType=t.isMatchingFence=t.functionApplication=t.invisibleComma=t.invisiblePlus=t.invisibleTimes=t.lookupMeaning=t.lookupRole=t.lookupType=t.equal=t.allLettersRegExp=void 0;const n=String.fromCodePoint(8291),r=["\uff0c","\ufe50",",",n],i=["\xaf","\u2012","\u2013","\u2014","\u2015","\ufe58","-","\u207b","\u208b","\u2212","\u2796","\ufe63","\uff0d","\u2010","\u2011","\u203e","_"],o=["~","\u0303","\u223c","\u02dc","\u223d","\u02f7","\u0334","\u0330"],s={"(":")","[":"]","{":"}","\u2045":"\u2046","\u2329":"\u232a","\u2768":"\u2769","\u276a":"\u276b","\u276c":"\u276d","\u276e":"\u276f","\u2770":"\u2771","\u2772":"\u2773","\u2774":"\u2775","\u27c5":"\u27c6","\u27e6":"\u27e7","\u27e8":"\u27e9","\u27ea":"\u27eb","\u27ec":"\u27ed","\u27ee":"\u27ef","\u2983":"\u2984","\u2985":"\u2986","\u2987":"\u2988","\u2989":"\u298a","\u298b":"\u298c","\u298d":"\u298e","\u298f":"\u2990","\u2991":"\u2992","\u2993":"\u2994","\u2995":"\u2996","\u2997":"\u2998","\u29d8":"\u29d9","\u29da":"\u29db","\u29fc":"\u29fd","\u2e22":"\u2e23","\u2e24":"\u2e25","\u2e26":"\u2e27","\u2e28":"\u2e29","\u3008":"\u3009","\u300a":"\u300b","\u300c":"\u300d","\u300e":"\u300f","\u3010":"\u3011","\u3014":"\u3015","\u3016":"\u3017","\u3018":"\u3019","\u301a":"\u301b","\u301d":"\u301e","\ufd3e":"\ufd3f","\ufe17":"\ufe18","\ufe59":"\ufe5a","\ufe5b":"\ufe5c","\ufe5d":"\ufe5e","\uff08":"\uff09","\uff3b":"\uff3d","\uff5b":"\uff5d","\uff5f":"\uff60","\uff62":"\uff63","\u2308":"\u2309","\u230a":"\u230b","\u230c":"\u230d","\u230e":"\u230f","\u231c":"\u231d","\u231e":"\u231f","\u239b":"\u239e","\u239c":"\u239f","\u239d":"\u23a0","\u23a1":"\u23a4","\u23a2":"\u23a5","\u23a3":"\u23a6","\u23a7":"\u23ab","\u23a8":"\u23ac","\u23a9":"\u23ad","\u23b0":"\u23b1","\u23b8":"\u23b9"},a={"\u23b4":"\u23b5","\u23dc":"\u23dd","\u23de":"\u23df","\u23e0":"\u23e1","\ufe35":"\ufe36","\ufe37":"\ufe38","\ufe39":"\ufe3a","\ufe3b":"\ufe3c","\ufe3d":"\ufe3e","\ufe3f":"\ufe40","\ufe41":"\ufe42","\ufe43":"\ufe44","\ufe47":"\ufe48"},c=Object.keys(s),l=Object.values(s);l.push("\u301f");const u=Object.keys(a),d=Object.values(a),h=["|","\xa6","\u2223","\u23d0","\u23b8","\u23b9","\u2758","\uff5c","\uffe4","\ufe31","\ufe32"],p=["\u2016","\u2225","\u2980","\u2af4"],f=["A","B","C","D","E","F","G","H","I","J","K","L","M","N","O","P","Q","R","S","T","U","V","W","X","Y","Z"],m=["a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","i","j","k","l","m","n","o","p","q","r","s","t","u","v","w","x","y","z","\u0131","\u0237"],g=["\uff21","\uff22","\uff23","\uff24","\uff25","\uff26","\uff27","\uff28","\uff29","\uff2a","\uff2b","\uff2c","\uff2d","\uff2e","\uff2f","\uff30","\uff31","\uff32","\uff33","\uff34","\uff35","\uff36","\uff37","\uff38","\uff39","\uff3a"],S=["\uff41","\uff42","\uff43","\uff44","\uff45","\uff46","\uff47","\uff48","\uff49","\uff4a","\uff4b","\uff4c","\uff4d","\uff4e","\uff4f","\uff50","\uff51","\uff52","\uff53","\uff54","\uff55","\uff56","\uff57","\uff58","\uff59","\uff5a"],b=["\ud835\udc00","\ud835\udc01","\ud835\udc02","\ud835\udc03","\ud835\udc04","\ud835\udc05","\ud835\udc06","\ud835\udc07","\ud835\udc08","\ud835\udc09","\ud835\udc0a","\ud835\udc0b","\ud835\udc0c","\ud835\udc0d","\ud835\udc0e","\ud835\udc0f","\ud835\udc10","\ud835\udc11","\ud835\udc12","\ud835\udc13","\ud835\udc14","\ud835\udc15","\ud835\udc16","\ud835\udc17","\ud835\udc18","\ud835\udc19"],N=["\ud835\udc1a","\ud835\udc1b","\ud835\udc1c","\ud835\udc1d","\ud835\udc1e","\ud835\udc1f","\ud835\udc20","\ud835\udc21","\ud835\udc22","\ud835\udc23","\ud835\udc24","\ud835\udc25","\ud835\udc26","\ud835\udc27","\ud835\udc28","\ud835\udc29","\ud835\udc2a","\ud835\udc2b","\ud835\udc2c","\ud835\udc2d","\ud835\udc2e","\ud835\udc2f","\ud835\udc30","\ud835\udc31","\ud835\udc32","\ud835\udc33"],E=["\ud835\udc34","\ud835\udc35","\ud835\udc36","\ud835\udc37","\ud835\udc38","\ud835\udc39","\ud835\udc3a","\ud835\udc3b","\ud835\udc3c","\ud835\udc3d","\ud835\udc3e","\ud835\udc3f","\ud835\udc40","\ud835\udc41","\ud835\udc42","\ud835\udc43","\ud835\udc44","\ud835\udc45","\ud835\udc46","\ud835\udc47","\ud835\udc48","\ud835\udc49","\ud835\udc4a","\ud835\udc4b","\ud835\udc4c","\ud835\udc4d"],y=["\ud835\udc4e","\ud835\udc4f","\ud835\udc50","\ud835\udc51","\ud835\udc52","\ud835\udc53","\ud835\udc54","\u210e","\ud835\udc56","\ud835\udc57","\ud835\udc58","\ud835\udc59","\ud835\udc5a","\ud835\udc5b","\ud835\udc5c","\ud835\udc5d","\ud835\udc5e","\ud835\udc5f","\ud835\udc60","\ud835\udc61","\ud835\udc62","\ud835\udc63","\ud835\udc64","\ud835\udc65","\ud835\udc66","\ud835\udc67","\ud835\udea4","\ud835\udea5"],A=["\ud835\udc68","\ud835\udc69","\ud835\udc6a","\ud835\udc6b","\ud835\udc6c","\ud835\udc6d","\ud835\udc6e","\ud835\udc6f","\ud835\udc70","\ud835\udc71","\ud835\udc72","\ud835\udc73","\ud835\udc74","\ud835\udc75","\ud835\udc76","\ud835\udc77","\ud835\udc78","\ud835\udc79","\ud835\udc7a","\ud835\udc7b","\ud835\udc7c","\ud835\udc7d","\ud835\udc7e","\ud835\udc7f","\ud835\udc80","\ud835\udc81"],_=["\ud835\udc82","\ud835\udc83","\ud835\udc84","\ud835\udc85","\ud835\udc86","\ud835\udc87","\ud835\udc88","\ud835\udc89","\ud835\udc8a","\ud835\udc8b","\ud835\udc8c","\ud835\udc8d","\ud835\udc8e","\ud835\udc8f","\ud835\udc90","\ud835\udc91","\ud835\udc92","\ud835\udc93","\ud835\udc94","\ud835\udc95","\ud835\udc96","\ud835\udc97","\ud835\udc98","\ud835\udc99","\ud835\udc9a","\ud835\udc9b"],C=["\ud835\udc9c","\u212c","\ud835\udc9e","\ud835\udc9f","\u2130","\u2131","\ud835\udca2","\u210b","\u2110","\ud835\udca5","\ud835\udca6","\u2112","\u2133","\ud835\udca9","\ud835\udcaa","\ud835\udcab","\ud835\udcac","\u211b","\ud835\udcae","\ud835\udcaf","\ud835\udcb0","\ud835\udcb1","\ud835\udcb2","\ud835\udcb3","\ud835\udcb4","\ud835\udcb5","\u2118"],T=["\ud835\udcb6","\ud835\udcb7","\ud835\udcb8","\ud835\udcb9","\u212f","\ud835\udcbb","\u210a","\ud835\udcbd","\ud835\udcbe","\ud835\udcbf","\ud835\udcc0","\ud835\udcc1","\ud835\udcc2","\ud835\udcc3","\u2134","\ud835\udcc5","\ud835\udcc6","\ud835\udcc7","\ud835\udcc8","\ud835\udcc9","\ud835\udcca","\ud835\udccb","\ud835\udccc","\ud835\udccd","\ud835\udcce","\ud835\udccf","\u2113"],v=["\ud835\udcd0","\ud835\udcd1","\ud835\udcd2","\ud835\udcd3","\ud835\udcd4","\ud835\udcd5","\ud835\udcd6","\ud835\udcd7","\ud835\udcd8","\ud835\udcd9","\ud835\udcda","\ud835\udcdb","\ud835\udcdc","\ud835\udcdd","\ud835\udcde","\ud835\udcdf","\ud835\udce0","\ud835\udce1","\ud835\udce2","\ud835\udce3","\ud835\udce4","\ud835\udce5","\ud835\udce6","\ud835\udce7","\ud835\udce8","\ud835\udce9"],O=["\ud835\udcea","\ud835\udceb","\ud835\udcec","\ud835\udced","\ud835\udcee","\ud835\udcef","\ud835\udcf0","\ud835\udcf1","\ud835\udcf2","\ud835\udcf3","\ud835\udcf4","\ud835\udcf5","\ud835\udcf6","\ud835\udcf7","\ud835\udcf8","\ud835\udcf9","\ud835\udcfa","\ud835\udcfb","\ud835\udcfc","\ud835\udcfd","\ud835\udcfe","\ud835\udcff","\ud835\udd00","\ud835\udd01","\ud835\udd02","\ud835\udd03"],M=["\ud835\udd04","\ud835\udd05","\u212d","\ud835\udd07","\ud835\udd08","\ud835\udd09","\ud835\udd0a","\u210c","\u2111","\ud835\udd0d","\ud835\udd0e","\ud835\udd0f","\ud835\udd10","\ud835\udd11","\ud835\udd12","\ud835\udd13","\ud835\udd14","\u211c","\ud835\udd16","\ud835\udd17","\ud835\udd18","\ud835\udd19","\ud835\udd1a","\ud835\udd1b","\ud835\udd1c","\u2128"],I=["\ud835\udd1e","\ud835\udd1f","\ud835\udd20","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd22","\ud835\udd23","\ud835\udd24","\ud835\udd25","\ud835\udd26","\ud835\udd27","\ud835\udd28","\ud835\udd29","\ud835\udd2a","\ud835\udd2b","\ud835\udd2c","\ud835\udd2d","\ud835\udd2e","\ud835\udd2f","\ud835\udd30","\ud835\udd31","\ud835\udd32","\ud835\udd33","\ud835\udd34","\ud835\udd35","\ud835\udd36","\ud835\udd37"],L=["\ud835\udd38","\ud835\udd39","\u2102","\ud835\udd3b","\ud835\udd3c","\ud835\udd3d","\ud835\udd3e","\u210d","\ud835\udd40","\ud835\udd41","\ud835\udd42","\ud835\udd43","\ud835\udd44","\u2115","\ud835\udd46","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\ud835\udd4a","\ud835\udd4b","\ud835\udd4c","\ud835\udd4d","\ud835\udd4e","\ud835\udd4f","\ud835\udd50","\u2124"],R=["\ud835\udd52","\ud835\udd53","\ud835\udd54","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd56","\ud835\udd57","\ud835\udd58","\ud835\udd59","\ud835\udd5a","\ud835\udd5b","\ud835\udd5c","\ud835\udd5d","\ud835\udd5e","\ud835\udd5f","\ud835\udd60","\ud835\udd61","\ud835\udd62","\ud835\udd63","\ud835\udd64","\ud835\udd65","\ud835\udd66","\ud835\udd67","\ud835\udd68","\ud835\udd69","\ud835\udd6a","\ud835\udd6b"],x=["\ud835\udd6c","\ud835\udd6d","\ud835\udd6e","\ud835\udd6f","\ud835\udd70","\ud835\udd71","\ud835\udd72","\ud835\udd73","\ud835\udd74","\ud835\udd75","\ud835\udd76","\ud835\udd77","\ud835\udd78","\ud835\udd79","\ud835\udd7a","\ud835\udd7b","\ud835\udd7c","\ud835\udd7d","\ud835\udd7e","\ud835\udd7f","\ud835\udd80","\ud835\udd81","\ud835\udd82","\ud835\udd83","\ud835\udd84","\ud835\udd85"],P=["\ud835\udd86","\ud835\udd87","\ud835\udd88","\ud835\udd89","\ud835\udd8a","\ud835\udd8b","\ud835\udd8c","\ud835\udd8d","\ud835\udd8e","\ud835\udd8f","\ud835\udd90","\ud835\udd91","\ud835\udd92","\ud835\udd93","\ud835\udd94","\ud835\udd95","\ud835\udd96","\ud835\udd97","\ud835\udd98","\ud835\udd99","\ud835\udd9a","\ud835\udd9b","\ud835\udd9c","\ud835\udd9d","\ud835\udd9e","\ud835\udd9f"],F=["\ud835\udda0","\ud835\udda1","\ud835\udda2","\ud835\udda3","\ud835\udda4","\ud835\udda5","\ud835\udda6","\ud835\udda7","\ud835\udda8","\ud835\udda9","\ud835\uddaa","\ud835\uddab","\ud835\uddac","\ud835\uddad","\ud835\uddae","\ud835\uddaf","\ud835\uddb0","\ud835\uddb1","\ud835\uddb2","\ud835\uddb3","\ud835\uddb4","\ud835\uddb5","\ud835\uddb6","\ud835\uddb7","\ud835\uddb8","\ud835\uddb9"],D=["\ud835\uddba","\ud835\uddbb","\ud835\uddbc","\ud835\uddbd","\ud835\uddbe","\ud835\uddbf","\ud835\uddc0","\ud835\uddc1","\ud835\uddc2","\ud835\uddc3","\ud835\uddc4","\ud835\uddc5","\ud835\uddc6","\ud835\uddc7","\ud835\uddc8","\ud835\uddc9","\ud835\uddca","\ud835\uddcb","\ud835\uddcc","\ud835\uddcd","\ud835\uddce","\ud835\uddcf","\ud835\uddd0","\ud835\uddd1","\ud835\uddd2","\ud835\uddd3"],w=["\ud835\uddd4","\ud835\uddd5","\ud835\uddd6","\ud835\uddd7","\ud835\uddd8","\ud835\uddd9","\ud835\uddda","\ud835\udddb","\ud835\udddc","\ud835\udddd","\ud835\uddde","\ud835\udddf","\ud835\udde0","\ud835\udde1","\ud835\udde2","\ud835\udde3","\ud835\udde4","\ud835\udde5","\ud835\udde6","\ud835\udde7","\ud835\udde8","\ud835\udde9","\ud835\uddea","\ud835\uddeb","\ud835\uddec","\ud835\udded"],k=["\ud835\uddee","\ud835\uddef","\ud835\uddf0","\ud835\uddf1","\ud835\uddf2","\ud835\uddf3","\ud835\uddf4","\ud835\uddf5","\ud835\uddf6","\ud835\uddf7","\ud835\uddf8","\ud835\uddf9","\ud835\uddfa","\ud835\uddfb","\ud835\uddfc","\ud835\uddfd","\ud835\uddfe","\ud835\uddff","\ud835\ude00","\ud835\ude01","\ud835\ude02","\ud835\ude03","\ud835\ude04","\ud835\ude05","\ud835\ude06","\ud835\ude07"],U=["\ud835\ude08","\ud835\ude09","\ud835\ude0a","\ud835\ude0b","\ud835\ude0c","\ud835\ude0d","\ud835\ude0e","\ud835\ude0f","\ud835\ude10","\ud835\ude11","\ud835\ude12","\ud835\ude13","\ud835\ude14","\ud835\ude15","\ud835\ude16","\ud835\ude17","\ud835\ude18","\ud835\ude19","\ud835\ude1a","\ud835\ude1b","\ud835\ude1c","\ud835\ude1d","\ud835\ude1e","\ud835\ude1f","\ud835\ude20","\ud835\ude21"],B=["\ud835\ude22","\ud835\ude23","\ud835\ude24","\ud835\ude25","\ud835\ude26","\ud835\ude27","\ud835\ude28","\ud835\ude29","\ud835\ude2a","\ud835\ude2b","\ud835\ude2c","\ud835\ude2d","\ud835\ude2e","\ud835\ude2f","\ud835\ude30","\ud835\ude31","\ud835\ude32","\ud835\ude33","\ud835\ude34","\ud835\ude35","\ud835\ude36","\ud835\ude37","\ud835\ude38","\ud835\ude39","\ud835\ude3a","\ud835\ude3b"],j=["\ud835\ude3c","\ud835\ude3d","\ud835\ude3e","\ud835\ude3f","\ud835\ude40","\ud835\ude41","\ud835\ude42","\ud835\ude43","\ud835\ude44","\ud835\ude45","\ud835\ude46","\ud835\ude47","\ud835\ude48","\ud835\ude49","\ud835\ude4a","\ud835\ude4b","\ud835\ude4c","\ud835\ude4d","\ud835\ude4e","\ud835\ude4f","\ud835\ude50","\ud835\ude51","\ud835\ude52","\ud835\ude53","\ud835\ude54","\ud835\ude55"],G=["\ud835\ude56","\ud835\ude57","\ud835\ude58","\ud835\ude59","\ud835\ude5a","\ud835\ude5b","\ud835\ude5c","\ud835\ude5d","\ud835\ude5e","\ud835\ude5f","\ud835\ude60","\ud835\ude61","\ud835\ude62","\ud835\ude63","\ud835\ude64","\ud835\ude65","\ud835\ude66","\ud835\ude67","\ud835\ude68","\ud835\ude69","\ud835\ude6a","\ud835\ude6b","\ud835\ude6c","\ud835\ude6d","\ud835\ude6e","\ud835\ude6f"],V=["\ud835\ude70","\ud835\ude71","\ud835\ude72","\ud835\ude73","\ud835\ude74","\ud835\ude75","\ud835\ude76","\ud835\ude77","\ud835\ude78","\ud835\ude79","\ud835\ude7a","\ud835\ude7b","\ud835\ude7c","\ud835\ude7d","\ud835\ude7e","\ud835\ude7f","\ud835\ude80","\ud835\ude81","\ud835\ude82","\ud835\ude83","\ud835\ude84","\ud835\ude85","\ud835\ude86","\ud835\ude87","\ud835\ude88","\ud835\ude89"],$=["\ud835\ude8a","\ud835\ude8b","\ud835\ude8c","\ud835\ude8d","\ud835\ude8e","\ud835\ude8f","\ud835\ude90","\ud835\ude91","\ud835\ude92","\ud835\ude93","\ud835\ude94","\ud835\ude95","\ud835\ude96","\ud835\ude97","\ud835\ude98","\ud835\ude99","\ud835\ude9a","\ud835\ude9b","\ud835\ude9c","\ud835\ude9d","\ud835\ude9e","\ud835\ude9f","\ud835\udea0","\ud835\udea1","\ud835\udea2","\ud835\udea3"],H=["\u2145","\u2146","\u2147","\u2148","\u2149"],W=["\u0391","\u0392","\u0393","\u0394","\u0395","\u0396","\u0397","\u0398","\u0399","\u039a","\u039b","\u039c","\u039d","\u039e","\u039f","\u03a0","\u03a1","\u03a3","\u03a4","\u03a5","\u03a6","\u03a7","\u03a8","\u03a9"],X=["\u03b1","\u03b2","\u03b3","\u03b4","\u03b5","\u03b6","\u03b7","\u03b8","\u03b9","\u03ba","\u03bb","\u03bc","\u03bd","\u03be","\u03bf","\u03c0","\u03c1","\u03c2","\u03c3","\u03c4","\u03c5","\u03c6","\u03c7","\u03c8","\u03c9"],q=["\ud835\udea8","\ud835\udea9","\ud835\udeaa","\ud835\udeab","\ud835\udeac","\ud835\udead","\ud835\udeae","\ud835\udeaf","\ud835\udeb0","\ud835\udeb1","\ud835\udeb2","\ud835\udeb3","\ud835\udeb4","\ud835\udeb5","\ud835\udeb6","\ud835\udeb7","\ud835\udeb8","\ud835\udeba","\ud835\udebb","\ud835\udebc","\ud835\udebd","\ud835\udebe","\ud835\udebf","\ud835\udec0"],Y=["\ud835\udec2","\ud835\udec3","\ud835\udec4","\ud835\udec5","\ud835\udec6","\ud835\udec7","\ud835\udec8","\ud835\udec9","\ud835\udeca","\ud835\udecb","\ud835\udecc","\ud835\udecd","\ud835\udece","\ud835\udecf","\ud835\uded0","\ud835\uded1","\ud835\uded2","\ud835\uded3","\ud835\uded4","\ud835\uded5","\ud835\uded6","\ud835\uded7","\ud835\uded8","\ud835\uded9","\ud835\udeda"],K=["\ud835\udee2","\ud835\udee3","\ud835\udee4","\ud835\udee5","\ud835\udee6","\ud835\udee7","\ud835\udee8","\ud835\udee9","\ud835\udeea","\ud835\udeeb","\ud835\udeec","\ud835\udeed","\ud835\udeee","\ud835\udeef","\ud835\udef0","\ud835\udef1","\ud835\udef2","\ud835\udef4","\ud835\udef5","\ud835\udef6","\ud835\udef7","\ud835\udef8","\ud835\udef9","\ud835\udefa"],z=["\ud835\udefc","\ud835\udefd","\ud835\udefe","\ud835\udeff","\ud835\udf00","\ud835\udf01","\ud835\udf02","\ud835\udf03","\ud835\udf04","\ud835\udf05","\ud835\udf06","\ud835\udf07","\ud835\udf08","\ud835\udf09","\ud835\udf0a","\ud835\udf0b","\ud835\udf0c","\ud835\udf0d","\ud835\udf0e","\ud835\udf0f","\ud835\udf10","\ud835\udf11","\ud835\udf12","\ud835\udf13","\ud835\udf14"],J=["\ud835\udf1c","\ud835\udf1d","\ud835\udf1e","\ud835\udf1f","\ud835\udf20","\ud835\udf21","\ud835\udf22","\ud835\udf23","\ud835\udf24","\ud835\udf25","\ud835\udf26","\ud835\udf27","\ud835\udf28","\ud835\udf29","\ud835\udf2a","\ud835\udf2b","\ud835\udf2c","\ud835\udf2e","\ud835\udf2f","\ud835\udf30","\ud835\udf31","\ud835\udf32","\ud835\udf33","\ud835\udf34"],Q=["\ud835\udf36","\ud835\udf37","\ud835\udf38","\ud835\udf39","\ud835\udf3a","\ud835\udf3b","\ud835\udf3c","\ud835\udf3d","\ud835\udf3e","\ud835\udf3f","\ud835\udf40","\ud835\udf41","\ud835\udf42","\ud835\udf43","\ud835\udf44","\ud835\udf45","\ud835\udf46","\ud835\udf47","\ud835\udf48","\ud835\udf49","\ud835\udf4a","\ud835\udf4b","\ud835\udf4c","\ud835\udf4d","\ud835\udf4e"],Z=["\ud835\udf56","\ud835\udf57","\ud835\udf58","\ud835\udf59","\ud835\udf5a","\ud835\udf5b","\ud835\udf5c","\ud835\udf5d","\ud835\udf5e","\ud835\udf5f","\ud835\udf60","\ud835\udf61","\ud835\udf62","\ud835\udf63","\ud835\udf64","\ud835\udf65","\ud835\udf66","\ud835\udf68","\ud835\udf69","\ud835\udf6a","\ud835\udf6b","\ud835\udf6c","\ud835\udf6d","\ud835\udf6e"],ee=["\ud835\udf70","\ud835\udf71","\ud835\udf72","\ud835\udf73","\ud835\udf74","\ud835\udf75","\ud835\udf76","\ud835\udf77","\ud835\udf78","\ud835\udf79","\ud835\udf7a","\ud835\udf7b","\ud835\udf7c","\ud835\udf7d","\ud835\udf7e","\ud835\udf7f","\ud835\udf80","\ud835\udf81","\ud835\udf82","\ud835\udf83","\ud835\udf84","\ud835\udf85","\ud835\udf86","\ud835\udf87","\ud835\udf88"],te=["\ud835\udf90","\ud835\udf91","\ud835\udf92","\ud835\udf93","\ud835\udf94","\ud835\udf95","\ud835\udf96","\ud835\udf97","\ud835\udf98","\ud835\udf99","\ud835\udf9a","\ud835\udf9b","\ud835\udf9c","\ud835\udf9d","\ud835\udf9e","\ud835\udf9f","\ud835\udfa0","\ud835\udfa2","\ud835\udfa3","\ud835\udfa4","\ud835\udfa5","\ud835\udfa6","\ud835\udfa7","\ud835\udfa8"],ne=["\ud835\udfaa","\ud835\udfab","\ud835\udfac","\ud835\udfad","\ud835\udfae","\ud835\udfaf","\ud835\udfb0","\ud835\udfb1","\ud835\udfb2","\ud835\udfb3","\ud835\udfb4","\ud835\udfb5","\ud835\udfb6","\ud835\udfb7","\ud835\udfb8","\ud835\udfb9","\ud835\udfba","\ud835\udfbb","\ud835\udfbc","\ud835\udfbd","\ud835\udfbe","\ud835\udfbf","\ud835\udfc0","\ud835\udfc1","\ud835\udfc2"],re=["\u213c","\u213d","\u213e","\u213f"],ie=["\u03d0","\u03d1","\u03d5","\u03d6","\u03d7","\u03f0","\u03f1","\u03f5","\u03f6","\u03f4"],oe=["\ud835\udedc","\ud835\udedd","\ud835\udede","\ud835\udedf","\ud835\udee0","\ud835\udee1"],se=["\ud835\udf16","\ud835\udf17","\ud835\udf18","\ud835\udf19","\ud835\udf1a","\ud835\udf1b"],ae=["\ud835\udf8a","\ud835\udf8b","\ud835\udf8c","\ud835\udf8d","\ud835\udf8e","\ud835\udf8f"],ce=["\u2135","\u2136","\u2137","\u2138"],le=f.concat(m,g,S,b,N,E,A,_,y,C,T,v,O,M,I,L,R,x,P,F,D,w,k,U,B,j,G,V,$,H,W,X,q,Y,K,z,J,Q,Z,ee,re,ie,te,ne,oe,se,ae,ce);t.allLettersRegExp=new RegExp(le.join("|"));const ue=["+","\xb1","\u2213","\u2214","\u2227","\u2228","\u2229","\u222a","\u228c","\u228d","\u228e","\u2293","\u2294","\u229d","\u229e","\u22a4","\u22a5","\u22ba","\u22bb","\u22bc","\u22c4","\u22ce","\u22cf","\u22d2","\u22d3","\u2a5e","\u2295","\u22d4"],de=String.fromCodePoint(8292);ue.push(de);const he=["\u2020","\u2021","\u2210","\u2217","\u2218","\u2219","\u2240","\u229a","\u229b","\u22a0","\u22a1","\u22c5","\u22c6","\u22c7","\u22c8","\u22c9","\u22ca","\u22cb","\u22cc","\u25cb","\xb7","*","\u2297","\u2299"],pe=String.fromCodePoint(8290);he.push(pe);const fe=String.fromCodePoint(8289),me=["\xbc","\xbd","\xbe","\u2150","\u2151","\u2152","\u2153","\u2154","\u2155","\u2156","\u2157","\u2158","\u2159","\u215a","\u215b","\u215c","\u215d","\u215e","\u215f","\u2189"],ge=["\xb2","\xb3","\xb9","\u2070","\u2074","\u2075","\u2076","\u2077","\u2078","\u2079"].concat(["\u2080","\u2081","\u2082","\u2083","\u2084","\u2085","\u2086","\u2087","\u2088","\u2089"],["\u2460","\u2461","\u2462","\u2463","\u2464","\u2465","\u2466","\u2467","\u2468","\u2469","\u246a","\u246b","\u246c","\u246d","\u246e","\u246f","\u2470","\u2471","\u2472","\u2473","\u24ea","\u24eb","\u24ec","\u24ed","\u24ee","\u24ef","\u24f0","\u24f1","\u24f2","\u24f3","\u24f4","\u24f5","\u24f6","\u24f7","\u24f8","\u24f9","\u24fa","\u24fb","\u24fc","\u24fd","\u24fe","\u24ff","\u2776","\u2777","\u2778","\u2779","\u277a","\u277b","\u277c","\u277d","\u277e","\u277f","\u2780","\u2781","\u2782","\u2783","\u2784","\u2785","\u2786","\u2787","\u2788","\u2789","\u278a","\u278b","\u278c","\u278d","\u278e","\u278f","\u2790","\u2791","\u2792","\u2793","\u3248","\u3249","\u324a","\u324b","\u324c","\u324d","\u324e","\u324f","\u3251","\u3252","\u3253","\u3254","\u3255","\u3256","\u3257","\u3258","\u3259","\u325a","\u325b","\u325c","\u325d","\u325e","\u325f","\u32b1","\u32b2","\u32b3","\u32b4","\u32b5","\u32b6","\u32b7","\u32b8","\u32b9","\u32ba","\u32bb","\u32bc","\u32bd","\u32be","\u32bf"],["\u2474","\u2475","\u2476","\u2477","\u2478","\u2479","\u247a","\u247b","\u247c","\u247d","\u247e","\u247f","\u2480","\u2481","\u2482","\u2483","\u2484","\u2485","\u2486","\u2487"],["\u2488","\u2489","\u248a","\u248b","\u248c","\u248d","\u248e","\u248f","\u2490","\u2491","\u2492","\u2493","\u2494","\u2495","\u2496","\u2497","\u2498","\u2499","\u249a","\u249b","\ud83c\udd00","\ud83c\udd01","\ud83c\udd02","\ud83c\udd03","\ud83c\udd04","\ud83c\udd05","\ud83c\udd06","\ud83c\udd07","\ud83c\udd08","\ud83c\udd09","\ud83c\udd0a"]),Se=["cos","cot","csc","sec","sin","tan","arccos","arccot","arccsc","arcsec","arcsin","arctan","arc cos","arc cot","arc csc","arc sec","arc sin","arc tan"].concat(["cosh","coth","csch","sech","sinh","tanh","arcosh","arcoth","arcsch","arsech","arsinh","artanh","arccosh","arccoth","arccsch","arcsech","arcsinh","arctanh"],["deg","det","dim","hom","ker","Tr","tr"],["log","ln","lg","exp","expt","gcd","gcd","arg","im","re","Pr"]),be=[{set:["!",'"',"#","%","&",";","?","@","\\","\xa1","\xa7","\xb6","\xbf","\u2017","\u2020","\u2021","\u2022","\u2023","\u2024","\u2025","\u2027","\u2030","\u2031","\u2038","\u203b","\u203c","\u203d","\u203e","\u2041","\u2042","\u2043","\u2047","\u2048","\u2049","\u204b","\u204c","\u204d","\u204e","\u204f","\u2050","\u2051","\u2053","\u2055","\u2056","\u2058","\u2059","\u205a","\u205b","\u205c","\u205d","\u205e","\ufe10","\ufe14","\ufe15","\ufe16","\ufe30","\ufe45","\ufe46","\ufe49","\ufe4a","\ufe4b","\ufe4c","\ufe54","\ufe56","\ufe57","\ufe5f","\ufe60","\ufe61","\ufe68","\ufe6a","\ufe6b","\uff01","\uff02","\uff03","\uff05","\uff06","\uff07","\uff0a","\uff0f","\uff1b","\uff1f","\uff20","\uff3c"],type:"punctuation",role:"unknown"},{set:["\ufe13",":","\uff1a","\ufe55"],type:"punctuation",role:"colon"},{set:r,type:"punctuation",role:"comma"},{set:["\u2026","\u22ee","\u22ef","\u22f0","\u22f1","\ufe19"],type:"punctuation",role:"ellipsis"},{set:[".","\ufe52","\uff0e"],type:"punctuation",role:"fullstop"},{set:i,type:"operator",role:"dash"},{set:o,type:"operator",role:"tilde"},{set:["'","\u2032","\u2033","\u2034","\u2035","\u2036","\u2037","\u2057","\u02b9","\u02ba"],type:"punctuation",role:"prime"},{set:["\xb0"],type:"punctuation",role:"degree"},{set:c,type:"fence",role:"open"},{set:l,type:"fence",role:"close"},{set:u,type:"fence",role:"top"},{set:d,type:"fence",role:"bottom"},{set:h,type:"fence",role:"neutral"},{set:p,type:"fence",role:"metric"},{set:m,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:f,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:S,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:g,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"normal"},{set:N,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold"},{set:b,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold"},{set:y,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"italic"},{set:E,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"italic"},{set:_,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:A,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:T,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"script"},{set:C,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"script"},{set:O,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-script"},{set:v,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-script"},{set:I,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"fraktur"},{set:M,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"fraktur"},{set:R,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:L,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:P,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-fraktur"},{set:x,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"bold-fraktur"},{set:D,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif"},{set:F,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif"},{set:k,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:w,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:B,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-italic"},{set:U,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-italic"},{set:G,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:j,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:$,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"monospace"},{set:V,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"monospace"},{set:H,type:"identifier",role:"latinletter",font:"double-struck-italic"},{set:X,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:W,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:Y,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:q,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:z,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:K,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:Q,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:J,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold-italic"},{set:ee,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:Z,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:te,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:ne,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold-italic"},{set:re,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"double-struck"},{set:ie,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"normal"},{set:oe,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"bold"},{set:se,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"italic"},{set:ae,type:"identifier",role:"greekletter",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:ce,type:"identifier",role:"otherletter",font:"normal"},{set:["0","1","2","3","4","5","6","7","8","9"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"normal"},{set:["\uff10","\uff11","\uff12","\uff13","\uff14","\uff15","\uff16","\uff17","\uff18","\uff19"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"normal"},{set:["\ud835\udfce","\ud835\udfcf","\ud835\udfd0","\ud835\udfd1","\ud835\udfd2","\ud835\udfd3","\ud835\udfd4","\ud835\udfd5","\ud835\udfd6","\ud835\udfd7"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"bold"},{set:["\ud835\udfd8","\ud835\udfd9","\ud835\udfda","\ud835\udfdb","\ud835\udfdc","\ud835\udfdd","\ud835\udfde","\ud835\udfdf","\ud835\udfe0","\ud835\udfe1"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"double-struck"},{set:["\ud835\udfe2","\ud835\udfe3","\ud835\udfe4","\ud835\udfe5","\ud835\udfe6","\ud835\udfe7","\ud835\udfe8","\ud835\udfe9","\ud835\udfea","\ud835\udfeb"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"sans-serif"},{set:["\ud835\udfec","\ud835\udfed","\ud835\udfee","\ud835\udfef","\ud835\udff0","\ud835\udff1","\ud835\udff2","\ud835\udff3","\ud835\udff4","\ud835\udff5"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:["\ud835\udff6","\ud835\udff7","\ud835\udff8","\ud835\udff9","\ud835\udffa","\ud835\udffb","\ud835\udffc","\ud835\udffd","\ud835\udffe","\ud835\udfff"],type:"number",role:"integer",font:"monospace"},{set:me,type:"number",role:"float"},{set:ge,type:"number",role:"othernumber"},{set:ue,type:"operator",role:"addition"},{set:he,type:"operator",role:"multiplication"},{set:["\xaf","-","\u2052","\u207b","\u208b","\u2212","\u2216","\u2238","\u2242","\u2296","\u229f","\u2796","\u2a29","\u2a2a","\u2a2b","\u2a2c","\u2a3a","\u2a41","\ufe63","\uff0d","\u2010","\u2011"],type:"operator",role:"subtraction"},{set:["/","\xf7","\u2044","\u2215","\u2298","\u27cc","\u29bc","\u2a38"],type:"operator",role:"division"},{set:["\u2200","\u2203","\u2206","\u2207","\u2202","\u2201","\u2204"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator"},{set:["\ud835\udec1","\ud835\udedb","\ud835\udfca","\ud835\udfcb"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"bold"},{set:["\ud835\udefb","\ud835\udf15"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"italic"},{set:["\ud835\udf6f","\ud835\udf89"],type:"operator",role:"prefix operator",font:"sans-serif-bold"},{set:["=","~","\u207c","\u208c","\u223c","\u223d","\u2243","\u2245","\u2248","\u224a","\u224b","\u224c","\u224d","\u224e","\u2251","\u2252","\u2253","\u2254","\u2255","\u2256","\u2257","\u2258","\u2259","\u225a","\u225b","\u225c","\u225d","\u225e","\u225f","\u2261","\u2263","\u29e4","\u2a66","\u2a6e","\u2a6f","\u2a70","\u2a71","\u2a72","\u2a73","\u2a74","\u2a75","\u2a76","\u2a77","\u2a78","\u22d5","\u2a6d","\u2a6a","\u2a6b","\u2a6c","\ufe66","\uff1d","\u2a6c","\u229c","\u2237"],type:"relation",role:"equality"},{set:["<",">","\u2241","\u2242","\u2244","\u2246","\u2247","\u2249","\u224f","\u2250","\u2260","\u2262","\u2264","\u2265","\u2266","\u2267","\u2268","\u2269","\u226a","\u226b","\u226c","\u226d","\u226e","\u226f","\u2270","\u2271","\u2272","\u2273","\u2274","\u2275","\u2276","\u2277","\u2278","\u2279","\u227a","\u227b","\u227c","\u227d","\u227e","\u227f","\u2280","\u2281","\u22d6","\u22d7","\u22d8","\u22d9","\u22da","\u22db","\u22dc","\u22dd","\u22de","\u22df","\u22e0","\u22e1","\u22e6","\u22e7","\u22e8","\u22e9","\u2a79","\u2a7a","\u2a7b","\u2a7c","\u2a7d","\u2a7e","\u2a7f","\u2a80","\u2a81","\u2a82","\u2a83","\u2a84","\u2a85","\u2a86","\u2a87","\u2a88","\u2a89","\u2a8a","\u2a8b","\u2a8c","\u2a8d","\u2a8e","\u2a8f","\u2a90","\u2a91","\u2a92","\u2a93","\u2a94","\u2a95","\u2a96","\u2a97","\u2a98","\u2a99","\u2a9a","\u2a9b","\u2a9c","\u2a9d","\u2a9e","\u2a9f","\u2aa0","\u2aa1","\u2aa2","\u2aa3","\u2aa4","\u2aa5","\u2aa6","\u2aa7","\u2aa8","\u2aa9","\u2aaa","\u2aab","\u2aac","\u2aad","\u2aae","\u2aaf","\u2ab0","\u2ab1","\u2ab2","\u2ab3","\u2ab4","\u2ab5","\u2ab6","\u2ab7","\u2ab8","\u2ab9","\u2aba","\u2abb","\u2abc","\u2af7","\u2af8","\u2af9","\u2afa","\u29c0","\u29c1","\ufe64","\ufe65","\uff1c","\uff1e"],type:"relation",role:"inequality"},{set:["\u22e2","\u22e3","\u22e4","\u22e5","\u2282","\u2283","\u2284","\u2285","\u2286","\u2287","\u2288","\u2289","\u228a","\u228b","\u228f","\u2290","\u2291","\u2292","\u2abd","\u2abe","\u2abf","\u2ac0","\u2ac1","\u2ac2","\u2ac3","\u2ac4","\u2ac5","\u2ac6","\u2ac7","\u2ac8","\u2ac9","\u2aca","\u2acb","\u2acc","\u2acd","\u2ace","\u2acf","\u2ad0","\u2ad1","\u2ad2","\u2ad3","\u2ad4","\u2ad5","\u2ad6","\u2ad7","\u2ad8","\u22d0","\u22d1","\u22ea","\u22eb","\u22ec","\u22ed","\u22b2","\u22b3","\u22b4","\u22b5"],type:"relation",role:"set"},{set:["\u22a2","\u22a3","\u22a6","\u22a7","\u22a8","\u22a9","\u22aa","\u22ab","\u22ac","\u22ad","\u22ae","\u22af","\u2ade","\u2adf","\u2ae0","\u2ae1","\u2ae2","\u2ae3","\u2ae4","\u2ae5","\u2ae6","\u2ae7","\u2ae8","\u2ae9","\u2aea","\u2aeb","\u2aec","\u2aed"],type:"relation",role:"unknown"},{set:["\u2190","\u2191","\u2192","\u2193","\u2194","\u2195","\u2196","\u2197","\u2198","\u2199","\u219a","\u219b","\u219c","\u219d","\u219e","\u219f","\u21a0","\u21a1","\u21a2","\u21a3","\u21a4","\u21a5","\u21a6","\u21a7","\u21a8","\u21a9","\u21aa","\u21ab","\u21ac","\u21ad","\u21ae","\u21af","\u21b0","\u21b1","\u21b2","\u21b3","\u21b4","\u21b5","\u21b6","\u21b7","\u21b8","\u21b9","\u21ba","\u21bb","\u21c4","\u21c5","\u21c6","\u21c7","\u21c8","\u21c9","\u21ca","\u21cd","\u21ce","\u21cf","\u21d0","\u21d1","\u21d2","\u21d3","\u21d4","\u21d5","\u21d6","\u21d7","\u21d8","\u21d9","\u21da","\u21db","\u21dc","\u21dd","\u21de","\u21df","\u21e0","\u21e1","\u21e2","\u21e3","\u21e4","\u21e5","\u21e6","\u21e7","\u21e8","\u21e9","\u21ea","\u21eb","\u21ec","\u21ed","\u21ee","\u21ef","\u21f0","\u21f1","\u21f2","\u21f3","\u21f4","\u21f5","\u21f6","\u21f7","\u21f8","\u21f9","\u21fa","\u21fb","\u21fc","\u21fd","\u21fe","\u21ff","\u2301","\u2303","\u2304","\u2324","\u238b","\u2794","\u2798","\u2799","\u279a","\u279b","\u279c","\u279d","\u279e","\u279f","\u27a0","\u27a1","\u27a2","\u27a3","\u27a4","\u27a5","\u27a6","\u27a7","\u27a8","\u27a9","\u27aa","\u27ab","\u27ac","\u27ad","\u27ae","\u27af","\u27b1","\u27b2","\u27b3","\u27b4","\u27b5","\u27b6","\u27b7","\u27b8","\u27b9","\u27ba","\u27bb","\u27bc","\u27bd","\u27be","\u27f0","\u27f1","\u27f2","\u27f3","\u27f4","\u27f5","\u27f6","\u27f7","\u27f8","\u27f9","\u27fa","\u27fb","\u27fc","\u27fd","\u27fe","\u27ff","\u2900","\u2901","\u2902","\u2903","\u2904","\u2905","\u2906","\u2907","\u2908","\u2909","\u290a","\u290b","\u290c","\u290d","\u290e","\u290f","\u2910","\u2911","\u2912","\u2913","\u2914","\u2915","\u2916","\u2917","\u2918","\u2919","\u291a","\u291b","\u291c","\u291d","\u291e","\u291f","\u2920","\u2921","\u2922","\u2923","\u2924","\u2925","\u2926","\u2927","\u2928","\u2929","\u292a","\u292d","\u292e","\u292f","\u2930","\u2931","\u2932","\u2933","\u2934","\u2935","\u2936","\u2937","\u2938","\u2939","\u293a","\u293b","\u293c","\u293d","\u293e","\u293f","\u2940","\u2941","\u2942","\u2943","\u2944","\u2945","\u2946","\u2947","\u2948","\u2949","\u2970","\u2971","\u2972","\u2973","\u2974","\u2975","\u2976","\u2977","\u2978","\u2979","\u297a","\u297b","\u29b3","\u29b4","\u29bd","\u29ea","\u29ec","\u29ed","\u2a17","\u2b00","\u2b01","\u2b02","\u2b03","\u2b04","\u2b05","\u2b06","\u2b07","\u2b08","\u2b09","\u2b0a","\u2b0b","\u2b0c","\u2b0d","\u2b0e","\u2b0f","\u2b10","\u2b11","\u2b30","\u2b31","\u2b32","\u2b33","\u2b34","\u2b35","\u2b36","\u2b37","\u2b38","\u2b39","\u2b3a","\u2b3b","\u2b3c","\u2b3d","\u2b3e","\u2b3f","\u2b40","\u2b41","\u2b42","\u2b43","\u2b44","\u2b45","\u2b46","\u2b47","\u2b48","\u2b49","\u2b4a","\u2b4b","\u2b4c","\uffe9","\uffea","\uffeb","\uffec","\u21bc","\u21bd","\u21be","\u21bf","\u21c0","\u21c1","\u21c2","\u21c3","\u21cb","\u21cc","\u294a","\u294b","\u294c","\u294d","\u294e","\u294f","\u2950","\u2951","\u2952","\u2953","\u2954","\u2955","\u2956","\u2957","\u2958","\u2959","\u295a","\u295b","\u295c","\u295d","\u295e","\u295f","\u2960","\u2961","\u2962","\u2963","\u2964","\u2965","\u2966","\u2967","\u2968","\u2969","\u296a","\u296b","\u296c","\u296d","\u296e","\u296f","\u297c","\u297d","\u297e","\u297f"],type:"relation",role:"arrow"},{set:["\u2208","\u220a","\u22f2","\u22f3","\u22f4","\u22f5","\u22f6","\u22f7","\u22f8","\u22f9","\u22ff"],type:"operator",role:"element"},{set:["\u2209"],type:"operator",role:"nonelement"},{set:["\u220b","\u220d","\u22fa","\u22fb","\u22fc","\u22fd","\u22fe"],type:"operator",role:"reelement"},{set:["\u220c"],type:"operator",role:"renonelement"},{set:["\u2140","\u220f","\u2210","\u2211","\u22c0","\u22c1","\u22c2","\u22c3","\u2a00","\u2a01","\u2a02","\u2a03","\u2a04","\u2a05","\u2a06","\u2a07","\u2a08","\u2a09","\u2a0a","\u2a0b","\u2afc","\u2aff"],type:"largeop",role:"sum"},{set:["\u222b","\u222c","\u222d","\u222e","\u222f","\u2230","\u2231","\u2232","\u2233","\u2a0c","\u2a0d","\u2a0e","\u2a0f","\u2a10","\u2a11","\u2a12","\u2a13","\u2a14","\u2a15","\u2a16","\u2a17","\u2a18","\u2a19","\u2a1a","\u2a1b","\u2a1c"],type:"largeop",role:"integral"},{set:["\u221f","\u2220","\u2221","\u2222","\u22be","\u22bf","\u25b3","\u25b7","\u25bd","\u25c1"],type:"operator",role:"geometry"},{set:["inf","lim","liminf","limsup","max","min","sup","injlim","projlim","inj lim","proj lim"],type:"function",role:"limit function"},{set:Se,type:"function",role:"prefix function"},{set:["mod","rem"],type:"operator",role:"prefix function"}],Ne=function(){const e={};for(let t,n=0;t=be[n];n++)t.set.forEach((function(n){e[n]={role:t.role||"unknown",type:t.type||"unknown",font:t.font||"unknown"}}));return e}();t.equal=function(e,t){return e.type===t.type&&e.role===t.role&&e.font===t.font},t.lookupType=function(e){var t;return(null===(t=Ne[e])||void 0===t?void 0:t.type)||"unknown"},t.lookupRole=function(e){var t;return(null===(t=Ne[e])||void 0===t?void 0:t.role)||"unknown"},t.lookupMeaning=function(e){return Ne[e]||{role:"unknown",type:"unknown",font:"unknown"}},t.invisibleTimes=function(){return pe},t.invisiblePlus=function(){return de},t.invisibleComma=function(){return n},t.functionApplication=function(){return fe},t.isMatchingFence=function(e,t){return-1!==h.indexOf(e)||-1!==p.indexOf(e)?e===t:s[e]===t||a[e]===t},t.isEmbellishedType=function(e){return"operator"===e||"relation"===e||"fence"===e||"punctuation"===e};const Ee=new Map;function ye(e,t){return`${e} ${t}`}function Ae(e,t,n=""){for(const r of t)Ee.set(ye(e,r),n||e)}Ae("d",["d","\u2146","\uff44","\ud835\udc1d","\ud835\udc51","\ud835\udcb9","\ud835\udced","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd89","\ud835\uddbd","\ud835\uddf1","\ud835\ude25","\ud835\ude8d"]),Ae("bar",i),Ae("tilde",o),t.lookupSecondary=function(e,t){return Ee.get(ye(e,t))}},7405:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMeaningCollator=t.SemanticNodeCollator=t.SemanticDefault=void 0;const r=n(4020),i=n(178);class o{constructor(){this.map={}}static key(e,t){return t?e+":"+t:e}add(e,t){this.map[o.key(e,t.font)]=t}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e.meaning())}retrieve(e,t){return this.map[o.key(e,t)]}retrieveNode(e){return this.retrieve(e.textContent,e.font)}size(){return Object.keys(this.map).length}}t.SemanticDefault=o;class s{constructor(){this.map={}}add(e,t){const n=this.map[e];n?n.push(t):this.map[e]=[t]}retrieve(e,t){return this.map[o.key(e,t)]}retrieveNode(e){return this.retrieve(e.textContent,e.font)}copy(){const e=this.copyCollator();for(const t in this.map)e.map[t]=this.map[t];return e}minimize(){for(const e in this.map)1===this.map[e].length&&delete this.map[e]}minimalCollator(){const e=this.copy();for(const t in e.map)1===e.map[t].length&&delete e.map[t];return e}isMultiValued(){for(const e in this.map)if(this.map[e].length>1)return!0;return!1}isEmpty(){return!Object.keys(this.map).length}}class a extends s{copyCollator(){return new a}add(e,t){const n=o.key(e,t.font);super.add(n,t)}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e)}toString(){const e=[];for(const t in this.map){const n=Array(t.length+3).join(" "),r=this.map[t],i=[];for(let e,t=0;e=r[t];t++)i.push(e.toString());e.push(t+": "+i.join("\n"+n))}return e.join("\n")}collateMeaning(){const e=new c;for(const t in this.map)e.map[t]=this.map[t].map((function(e){return e.meaning()}));return e}}t.SemanticNodeCollator=a;class c extends s{copyCollator(){return new c}add(e,t){const n=this.retrieve(e,t.font);if(!n||!n.find((function(e){return r.equal(e,t)}))){const n=o.key(e,t.font);super.add(n,t)}}addNode(e){this.add(e.textContent,e.meaning())}toString(){const e=[];for(const t in this.map){const n=Array(t.length+3).join(" "),r=this.map[t],i=[];for(let e,t=0;e=r[t];t++)i.push("{type: "+e.type+", role: "+e.role+", font: "+e.font+"}");e.push(t+": "+i.join("\n"+n))}return e.join("\n")}reduce(){for(const e in this.map)1!==this.map[e].length&&(this.map[e]=(0,i.reduce)(this.map[e]))}default(){const e=new o;for(const t in this.map)1===this.map[t].length&&(e.map[t]=this.map[t][0]);return e}newDefault(){const e=this.default();this.reduce();const t=this.default();return e.size()!==t.size()?t:null}}t.SemanticMeaningCollator=c},5958:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMultiHeuristic=t.SemanticTreeHeuristic=t.SemanticAbstractHeuristic=void 0;class n{constructor(e,t,n=(e=>!1)){this.name=e,this.apply=t,this.applicable=n}}t.SemanticAbstractHeuristic=n;t.SemanticTreeHeuristic=class extends n{};t.SemanticMultiHeuristic=class extends n{}},2721:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.lookup=t.run=t.add=t.blacklist=t.flags=t.updateFactory=t.factory=void 0,t.factory=null,t.updateFactory=function(e){t.factory=e};const n=new Map;function r(e){return n.get(e)}t.flags={combine_juxtaposition:!0,convert_juxtaposition:!0,multioperator:!0},t.blacklist={},t.add=function(e){const r=e.name;n.set(r,e),t.flags[r]||(t.flags[r]=!1)},t.run=function(e,n,i){const o=r(e);return o&&!t.blacklist[e]&&(t.flags[e]||o.applicable(n))?o.apply(n):i?i(n):n},t.lookup=r},7103:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(1984),i=n(4886),o=n(4020),s=n(2721),a=n(5958),c=n(6161),l=n(7793),u=n(8901);function d(e,t,n){let r=null;if(!e.length)return r;const i=n[n.length-1],o=i&&i.length,s=t&&t.length,a=l.default.getInstance();if(o&&s){if("infixop"===t[0].type&&"implicit"===t[0].role)return r=e.pop(),i.push(a.postfixNode_(i.pop(),e)),r;r=e.shift();const n=a.prefixNode_(t.shift(),e);return t.unshift(n),r}return o?(i.push(a.postfixNode_(i.pop(),e)),r):(s&&t.unshift(a.prefixNode_(t.shift(),e)),r)}function h(e,t,n){if(!t.length)return e;const i=e.pop(),o=t.shift(),a=n.shift();if(c.isImplicitOp(o)){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 2");const s=(i?[i,o]:[o]).concat(a);return h(e.concat(s),t,n)}if(!i)return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 3"),h([o].concat(a),t,n);const l=a.shift();if(!l){r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 9");const a=s.factory.makeBranchNode("infixop",[i,t.shift()],[o],o.textContent);return a.role="implicit",s.run("combine_juxtaposition",a),t.unshift(a),h(e,t,n)}if(c.isOperator(i)||c.isOperator(l))return r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 4"),h(e.concat([i,o,l]).concat(a),t,n);let u=null;return c.isImplicitOp(i)&&c.isImplicitOp(l)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 5"),i.contentNodes.push(o),i.contentNodes=i.contentNodes.concat(l.contentNodes),i.childNodes.push(l),i.childNodes=i.childNodes.concat(l.childNodes),l.childNodes.forEach((e=>e.parent=i)),o.parent=i,i.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),i.addMathmlNodes(l.mathml),u=i):c.isImplicitOp(i)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 6"),i.contentNodes.push(o),i.childNodes.push(l),l.parent=i,o.parent=i,i.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),i.addMathmlNodes(l.mathml),u=i):c.isImplicitOp(l)?(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 7"),l.contentNodes.unshift(o),l.childNodes.unshift(i),i.parent=l,o.parent=l,l.addMathmlNodes(o.mathml),l.addMathmlNodes(i.mathml),u=l):(r.Debugger.getInstance().output("Juxta Heuristic Case 8"),u=s.factory.makeBranchNode("infixop",[i,l],[o],o.textContent),u.role="implicit"),e.push(u),h(e.concat(a),t,n)}s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("combine_juxtaposition",(function(e){for(let t,n=e.childNodes.length-1;t=e.childNodes[n];n--)c.isImplicitOp(t)&&!t.nobreaking&&(e.childNodes.splice(n,1,...t.childNodes),e.contentNodes.splice(n,0,...t.contentNodes),t.childNodes.concat(t.contentNodes).forEach((function(t){t.parent=e})),e.addMathmlNodes(t.mathml));return e}))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("propagateSimpleFunction",(e=>("infixop"!==e.type&&"fraction"!==e.type||!e.childNodes.every(c.isSimpleFunction)||(e.role="composed function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("simpleNamedFunction",(e=>("unit"!==e.role&&-1!==["f","g","h","F","G","H"].indexOf(e.textContent)&&(e.role="simple function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("propagateComposedFunction",(e=>("fenced"===e.type&&"composed function"===e.childNodes[0].role&&(e.role="composed function"),e)),(e=>"clearspeak"===i.default.getInstance().domain))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("multioperator",(e=>{if("unknown"!==e.role||e.textContent.length<=1)return;const t=[...e.textContent].map(o.lookupMeaning).reduce((function(e,t){return e&&t.role&&"unknown"!==t.role&&t.role!==e?"unknown"===e?t.role:null:e}),"unknown");t&&(e.role=t)}))),s.add(new a.SemanticMultiHeuristic("convert_juxtaposition",(e=>{let t=u.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===o.invisibleTimes()&&"operator"===e.type}));t=t.rel.length?function(e){const t=[],n=[];let r=e.comp.shift(),i=null,o=[];for(;e.comp.length;)if(o=[],r.length)i&&t.push(i),n.push(r),i=e.rel.shift(),r=e.comp.shift();else{for(i&&o.push(i);!r.length&&e.comp.length;)r=e.comp.shift(),o.push(e.rel.shift());i=d(o,r,n)}o.length||r.length?(t.push(i),n.push(r)):(o.push(i),d(o,r,n));return{rel:t,comp:n}}(t):t,e=t.comp[0];for(let n,r,i=1;n=t.comp[i],r=t.rel[i-1];i++)e.push(r),e=e.concat(n);return t=u.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===o.invisibleTimes()&&("operator"===e.type||"infixop"===e.type)})),t.rel.length?h(t.comp.shift(),t.rel,t.comp):e}))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("simple2prefix",(e=>(e.textContent.length>1&&!e.textContent[0].match(/[A-Z]/)&&(e.role="prefix function"),e)),(e=>"braille"===i.default.getInstance().modality&&"identifier"===e.type))),s.add(new a.SemanticTreeHeuristic("detect_cycle",(e=>{e.type="matrix",e.role="cycle";const t=e.childNodes[0];return t.type="row",t.role="cycle",t.textContent="",t.contentNodes=[],e}),(e=>"fenced"===e.type&&"infixop"===e.childNodes[0].type&&"implicit"===e.childNodes[0].role&&e.childNodes[0].childNodes.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type}))&&e.childNodes[0].contentNodes.every((function(e){return"space"===e.role})))))},8122:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticMathml=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(6098),o=n(6161),s=n(7793),a=n(8901);class c extends i.SemanticAbstractParser{constructor(){super("MathML"),this.parseMap_={SEMANTICS:this.semantics_.bind(this),MATH:this.rows_.bind(this),MROW:this.rows_.bind(this),MPADDED:this.rows_.bind(this),MSTYLE:this.rows_.bind(this),MFRAC:this.fraction_.bind(this),MSUB:this.limits_.bind(this),MSUP:this.limits_.bind(this),MSUBSUP:this.limits_.bind(this),MOVER:this.limits_.bind(this),MUNDER:this.limits_.bind(this),MUNDEROVER:this.limits_.bind(this),MROOT:this.root_.bind(this),MSQRT:this.sqrt_.bind(this),MTABLE:this.table_.bind(this),MLABELEDTR:this.tableLabeledRow_.bind(this),MTR:this.tableRow_.bind(this),MTD:this.tableCell_.bind(this),MS:this.text_.bind(this),MTEXT:this.text_.bind(this),MSPACE:this.space_.bind(this),"ANNOTATION-XML":this.text_.bind(this),MI:this.identifier_.bind(this),MN:this.number_.bind(this),MO:this.operator_.bind(this),MFENCED:this.fenced_.bind(this),MENCLOSE:this.enclosed_.bind(this),MMULTISCRIPTS:this.multiscripts_.bind(this),ANNOTATION:this.empty_.bind(this),NONE:this.empty_.bind(this),MACTION:this.action_.bind(this)};const e={type:"identifier",role:"numbersetletter",font:"double-struck"};["C","H","N","P","Q","R","Z","\u2102","\u210d","\u2115","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\u2124"].forEach((t=>this.getFactory().defaultMap.add(t,e)).bind(this))}static getAttribute_(e,t,n){if(!e.hasAttribute(t))return n;const r=e.getAttribute(t);return r.match(/^\s*$/)?null:r}parse(e){s.default.getInstance().setNodeFactory(this.getFactory());const t=r.toArray(e.childNodes),n=r.tagName(e),i=this.parseMap_[n],o=(i||this.dummy_.bind(this))(e,t);return a.addAttributes(o,e),-1!==["MATH","MROW","MPADDED","MSTYLE","SEMANTICS"].indexOf(n)||(o.mathml.unshift(e),o.mathmlTree=e),o}semantics_(e,t){return t.length?this.parse(t[0]):this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode()}rows_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("semantics");if(n&&n.match("bspr_"))return s.default.proof(e,n,this.parseList.bind(this));let r;return 1===(t=a.purgeNodes(t)).length?(r=this.parse(t[0]),"empty"!==r.type||r.mathmlTree||(r.mathmlTree=e)):r=s.default.getInstance().row(this.parseList(t)),r.mathml.unshift(e),r}fraction_(e,t){if(!t.length)return this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode();const n=this.parse(t[0]),r=t[1]?this.parse(t[1]):this.getFactory().makeEmptyNode();return s.default.getInstance().fractionLikeNode(n,r,e.getAttribute("linethickness"),"true"===e.getAttribute("bevelled"))}limits_(e,t){return s.default.getInstance().limitNode(r.tagName(e),this.parseList(t))}root_(e,t){return t[1]?this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("root",[this.parse(t[1]),this.parse(t[0])],[]):this.sqrt_(e,t)}sqrt_(e,t){const n=this.parseList(a.purgeNodes(t));return this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("sqrt",[s.default.getInstance().row(n)],[])}table_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("semantics");if(n&&n.match("bspr_"))return s.default.proof(e,n,this.parseList.bind(this));const r=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("table",this.parseList(t),[]);return r.mathmlTree=e,s.default.tableToMultiline(r),r}tableRow_(e,t){const n=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("row",this.parseList(t),[]);return n.role="table",n}tableLabeledRow_(e,t){if(!t.length)return this.tableRow_(e,t);const n=this.parse(t[0]);n.role="label";const r=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("row",this.parseList(t.slice(1)),[n]);return r.role="table",r}tableCell_(e,t){const n=this.parseList(a.purgeNodes(t));let r;r=n.length?1===n.length&&o.isType(n[0],"empty")?n:[s.default.getInstance().row(n)]:[];const i=this.getFactory().makeBranchNode("cell",r,[]);return i.role="table",i}space_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute("width"),i=n&&n.match(/[a-z]*$/);if(!i)return this.empty_(e,t);const o=i[0],a=parseFloat(n.slice(0,i.index)),c={cm:.4,pc:.5,em:.5,ex:1,in:.15,pt:5,mm:5}[o];if(!c||isNaN(a)||a1?this.parse(t[1]):this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e)}dummy_(e,t){const n=this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e);return n.role=e.tagName,n.textContent=e.textContent,n}leaf_(e,t){if(1===t.length&&t[0].nodeType!==r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){const n=this.getFactory().makeUnprocessed(e);return n.role=t[0].tagName,a.addAttributes(n,t[0]),n}return this.getFactory().makeLeafNode(e.textContent,s.default.getInstance().font(e.getAttribute("mathvariant")))}}t.SemanticMathml=c},9444:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticNode=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(4020),o=n(8901);class s{constructor(e){this.id=e,this.mathml=[],this.parent=null,this.type="unknown",this.role="unknown",this.font="unknown",this.embellished=null,this.fencePointer="",this.childNodes=[],this.textContent="",this.mathmlTree=null,this.contentNodes=[],this.annotation={},this.attributes={},this.nobreaking=!1}static fromXml(e){const t=parseInt(e.getAttribute("id"),10),n=new s(t);return n.type=e.tagName,s.setAttribute(n,e,"role"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"font"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"embellished"),s.setAttribute(n,e,"fencepointer","fencePointer"),e.getAttribute("annotation")&&n.parseAnnotation(e.getAttribute("annotation")),o.addAttributes(n,e),s.processChildren(n,e),n}static setAttribute(e,t,n,r){r=r||n;const i=t.getAttribute(n);i&&(e[r]=i)}static processChildren(e,t){for(const n of r.toArray(t.childNodes)){if(n.nodeType===r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE){e.textContent=n.textContent;continue}const t=r.toArray(n.childNodes).map(s.fromXml);t.forEach((t=>t.parent=e)),"CONTENT"===r.tagName(n)?e.contentNodes=t:e.childNodes=t}}querySelectorAll(e){let t=[];for(let n,r=0;n=this.childNodes[r];r++)t=t.concat(n.querySelectorAll(e));for(let n,r=0;n=this.contentNodes[r];r++)t=t.concat(n.querySelectorAll(e));return e(this)&&t.unshift(this),t}xml(e,t){const n=function(n,r){const i=r.map((function(n){return n.xml(e,t)})),o=e.createElementNS("",n);for(let e,t=0;e=i[t];t++)o.appendChild(e);return o},r=e.createElementNS("",this.type);return t||this.xmlAttributes(r),r.textContent=this.textContent,this.contentNodes.length>0&&r.appendChild(n("content",this.contentNodes)),this.childNodes.length>0&&r.appendChild(n("children",this.childNodes)),r}toString(e=!1){const t=r.parseInput("");return r.serializeXml(this.xml(t,e))}allAttributes(){const e=[];return e.push(["role",this.role]),"unknown"!==this.font&&e.push(["font",this.font]),Object.keys(this.annotation).length&&e.push(["annotation",this.xmlAnnotation()]),this.embellished&&e.push(["embellished",this.embellished]),this.fencePointer&&e.push(["fencepointer",this.fencePointer]),e.push(["id",this.id.toString()]),e}xmlAnnotation(){const e=[];for(const t in this.annotation)this.annotation[t].forEach((function(n){e.push(t+":"+n)}));return e.join(";")}toJson(){const e={};e.type=this.type;const t=this.allAttributes();for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++)e[n[0]]=n[1].toString();return this.textContent&&(e.$t=this.textContent),this.childNodes.length&&(e.children=this.childNodes.map((function(e){return e.toJson()}))),this.contentNodes.length&&(e.content=this.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e.toJson()}))),e}updateContent(e,t){const n=t?e.replace(/^[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]*/,"").replace(/[ \f\n\r\t\v\u200b]*$/,""):e.trim();if(e=e&&!n?e:n,this.textContent===e)return;const r=(0,i.lookupMeaning)(e);this.textContent=e,this.role=r.role,this.type=r.type,this.font=r.font}addMathmlNodes(e){for(let t,n=0;t=e[n];n++)-1===this.mathml.indexOf(t)&&this.mathml.push(t)}appendChild(e){this.childNodes.push(e),this.addMathmlNodes(e.mathml),e.parent=this}replaceChild(e,t){const n=this.childNodes.indexOf(e);if(-1===n)return;e.parent=null,t.parent=this,this.childNodes[n]=t;const r=e.mathml.filter((function(e){return-1===t.mathml.indexOf(e)})),i=t.mathml.filter((function(t){return-1===e.mathml.indexOf(t)}));this.removeMathmlNodes(r),this.addMathmlNodes(i)}appendContentNode(e){e&&(this.contentNodes.push(e),this.addMathmlNodes(e.mathml),e.parent=this)}removeContentNode(e){if(e){const t=this.contentNodes.indexOf(e);-1!==t&&this.contentNodes.slice(t,1)}}equals(e){if(!e)return!1;if(this.type!==e.type||this.role!==e.role||this.textContent!==e.textContent||this.childNodes.length!==e.childNodes.length||this.contentNodes.length!==e.contentNodes.length)return!1;for(let t,n,r=0;t=this.childNodes[r],n=e.childNodes[r];r++)if(!t.equals(n))return!1;for(let t,n,r=0;t=this.contentNodes[r],n=e.contentNodes[r];r++)if(!t.equals(n))return!1;return!0}displayTree(){console.info(this.displayTree_(0))}addAnnotation(e,t){t&&this.addAnnotation_(e,t)}getAnnotation(e){const t=this.annotation[e];return t||[]}hasAnnotation(e,t){const n=this.annotation[e];return!!n&&-1!==n.indexOf(t)}parseAnnotation(e){const t=e.split(";");for(let e=0,n=t.length;e1)return!1;const n=t[0];if("infixop"===n.type){if("implicit"!==n.role)return!1;if(n.childNodes.some((e=>o(e,"infixop"))))return!1}return!0},t.isPrefixFunctionBoundary=function(e){return l(e)&&!a(e,"division")||o(e,"appl")||c(e)},t.isBigOpBoundary=function(e){return l(e)||c(e)},t.isIntegralDxBoundary=function(e,t){return!!t&&o(t,"identifier")&&r.lookupSecondary("d",e.textContent)},t.isIntegralDxBoundarySingle=function(e){if(o(e,"identifier")){const t=e.textContent[0];return t&&e.textContent[1]&&r.lookupSecondary("d",t)}return!1},t.isGeneralFunctionBoundary=c,t.isEmbellished=function(e){return e.embellished?e.embellished:r.isEmbellishedType(e.type)?e.type:null},t.isOperator=l,t.isRelation=u,t.isPunctuation=d,t.isFence=h,t.isElligibleEmbellishedFence=function(e){return!(!e||!h(e))&&(!e.embellished||p(e))},t.isTableOrMultiline=f,t.tableIsMatrixOrVector=function(e){return!!e&&m(e)&&f(e.childNodes[0])},t.isFencedElement=m,t.tableIsCases=function(e,t){return t.length>0&&a(t[t.length-1],"openfence")},t.tableIsMultiline=function(e){return e.childNodes.every((function(e){return e.childNodes.length<=1}))},t.lineIsLabelled=function(e){return o(e,"line")&&e.contentNodes.length&&a(e.contentNodes[0],"label")},t.isBinomial=function(e){return 2===e.childNodes.length},t.isLimitBase=function e(t){return o(t,"largeop")||o(t,"limboth")||o(t,"limlower")||o(t,"limupper")||o(t,"function")&&a(t,"limit function")||(o(t,"overscore")||o(t,"underscore"))&&e(t.childNodes[0])},t.isSimpleFunctionHead=function(e){return"identifier"===e.type||"latinletter"===e.role||"greekletter"===e.role||"otherletter"===e.role},t.singlePunctAtPosition=function(e,t,n){return 1===t.length&&("punctuation"===e[n].type||"punctuation"===e[n].embellished)&&e[n]===t[0]},t.isSimpleFunction=function(e){return o(e,"identifier")&&a(e,"simple function")},t.isLeftBrace=g,t.isRightBrace=S,t.isSetNode=function(e){return g(e.contentNodes[0])&&S(e.contentNodes[1])},t.illegalSingleton_=["punctuation","punctuated","relseq","multirel","table","multiline","cases","inference"],t.scriptedElement_=["limupper","limlower","limboth","subscript","superscript","underscore","overscore","tensor"],t.isSingletonSetContent=function e(n){const r=n.type;return-1===t.illegalSingleton_.indexOf(r)&&("infixop"!==r||"implicit"===n.role)&&("fenced"===r?"leftright"!==n.role||e(n.childNodes[0]):-1===t.scriptedElement_.indexOf(r)||e(n.childNodes[0]))},t.isNumber=b,t.isUnitCounter=function(e){return b(e)||"vulgar"===e.role||"mixed"===e.role},t.isPureUnit=function(e){const t=e.childNodes;return"unit"===e.role&&(!t.length||"unit"===t[0].role)},t.isImplicit=function(e){return"implicit"===e.role||"unit"===e.role&&!!e.contentNodes.length&&e.contentNodes[0].textContent===r.invisibleTimes()},t.isImplicitOp=function(e){return"infixop"===e.type&&"implicit"===e.role},t.isNeutralFence=N,t.compareNeutralFences=function(e,t){return N(e)&&N(t)&&(0,i.getEmbellishedInner)(e).textContent===(0,i.getEmbellishedInner)(t).textContent},t.elligibleLeftNeutral=function(e){return!!N(e)&&(!e.embellished||"superscript"!==e.type&&"subscript"!==e.type&&("tensor"!==e.type||"empty"===e.childNodes[3].type&&"empty"===e.childNodes[4].type))},t.elligibleRightNeutral=function(e){return!!N(e)&&(!e.embellished||("tensor"!==e.type||"empty"===e.childNodes[1].type&&"empty"===e.childNodes[2].type))},t.isMembership=function(e){return["element","nonelement","reelement","renonelement"].includes(e.role)}},7793:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0});const r=n(6671),i=n(4020),o=n(2721),s=n(4790),a=n(6161),c=n(8901);class l{constructor(){this.funcAppls={},this.factory_=new s.SemanticNodeFactory,o.updateFactory(this.factory_)}static getInstance(){return l.instance=l.instance||new l,l.instance}static tableToMultiline(e){if(a.tableIsMultiline(e)){e.type="multiline";for(let t,n=0;t=e.childNodes[n];n++)l.rowToLine_(t,"multiline");1===e.childNodes.length&&!a.lineIsLabelled(e.childNodes[0])&&a.isFencedElement(e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0])&&l.tableToMatrixOrVector_(l.rewriteFencedLine_(e)),l.binomialForm_(e),l.classifyMultiline(e)}else l.classifyTable(e)}static number(e){"unknown"!==e.type&&"identifier"!==e.type||(e.type="number"),l.numberRole_(e),l.exprFont_(e)}static classifyMultiline(e){let t=0;const n=e.childNodes.length;let r;for(;t=n)return;const i=r.childNodes[0].role;"unknown"!==i&&e.childNodes.every((function(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];return!t||t.role===i&&(a.isType(t,"relation")||a.isType(t,"relseq"))}))&&(e.role=i)}static classifyTable(e){const t=l.computeColumns_(e);l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"equality")||l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"inequality",["equality"])||l.classifyByColumns_(e,t,"arrow")||l.detectCaleyTable(e)}static detectCaleyTable(e){if(!e.mathmlTree)return!1;const t=e.mathmlTree,n=t.getAttribute("columnlines"),r=t.getAttribute("rowlines");return!(!n||!r)&&(!(!l.cayleySpacing(n)||!l.cayleySpacing(r))&&(e.role="cayley",!0))}static cayleySpacing(e){const t=e.split(" ");return("solid"===t[0]||"dashed"===t[0])&&t.slice(1).every((e=>"none"===e))}static proof(e,t,n){const r=l.separateSemantics(t);return l.getInstance().proof(e,r,n)}static findSemantics(e,t,n){const r=null==n?null:n,i=l.getSemantics(e);return!!i&&(!!i[t]&&(null==r||i[t]===r))}static getSemantics(e){const t=e.getAttribute("semantics");return t?l.separateSemantics(t):null}static removePrefix(e){const[,...t]=e.split("_");return t.join("_")}static separateSemantics(e){const t={};return e.split(";").forEach((function(e){const[n,r]=e.split(":");t[l.removePrefix(n)]=r})),t}static matchSpaces_(e,t){for(let n,r=0;n=t[r];r++){const t=e[r].mathmlTree,i=e[r+1].mathmlTree;if(!t||!i)continue;const o=t.nextSibling;if(!o||o===i)continue;const s=l.getSpacer_(o);s&&(n.mathml.push(s),n.mathmlTree=s,n.role="space")}}static getSpacer_(e){if("MSPACE"===r.tagName(e))return e;for(;c.hasEmptyTag(e)&&1===e.childNodes.length;)if(e=e.childNodes[0],"MSPACE"===r.tagName(e))return e;return null}static fenceToPunct_(e){const t=l.FENCE_TO_PUNCT_[e.role];if(t){for(;e.embellished;)e.embellished="punctuation",a.isRole(e,"subsup")||a.isRole(e,"underover")||(e.role=t),e=e.childNodes[0];e.type="punctuation",e.role=t}}static classifyFunction_(e,t){if("appl"===e.type||"bigop"===e.type||"integral"===e.type)return"";if(t[0]&&t[0].textContent===i.functionApplication()){l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id]=t.shift();let n="simple function";return o.run("simple2prefix",e),"prefix function"!==e.role&&"limit function"!==e.role||(n=e.role),l.propagateFunctionRole_(e,n),"prefix"}const n=l.CLASSIFY_FUNCTION_[e.role];return n||(a.isSimpleFunctionHead(e)?"simple":"")}static propagateFunctionRole_(e,t){if(e){if("infixop"===e.type)return;a.isRole(e,"subsup")||a.isRole(e,"underover")||(e.role=t),l.propagateFunctionRole_(e.childNodes[0],t)}}static getFunctionOp_(e,t){if(t(e))return e;for(let n,r=0;n=e.childNodes[r];r++){const e=l.getFunctionOp_(n,t);if(e)return e}return null}static tableToMatrixOrVector_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];a.isType(t,"multiline")?l.tableToVector_(e):l.tableToMatrix_(e),e.contentNodes.forEach(t.appendContentNode.bind(t));for(let e,n=0;e=t.childNodes[n];n++)l.assignRoleToRow_(e,l.getComponentRoles_(t));return t.parent=null,t}static tableToVector_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];t.type="vector",1!==t.childNodes.length?l.binomialForm_(t):l.tableToSquare_(e)}static binomialForm_(e){a.isBinomial(e)&&(e.role="binomial",e.childNodes[0].role="binomial",e.childNodes[1].role="binomial")}static tableToMatrix_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];t.type="matrix",t.childNodes&&t.childNodes.length>0&&t.childNodes[0].childNodes&&t.childNodes.length===t.childNodes[0].childNodes.length?l.tableToSquare_(e):t.childNodes&&1===t.childNodes.length&&(t.role="rowvector")}static tableToSquare_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0];a.isNeutralFence(e)?t.role="determinant":t.role="squarematrix"}static getComponentRoles_(e){const t=e.role;return t&&"unknown"!==t?t:e.type.toLowerCase()||"unknown"}static tableToCases_(e,t){for(let t,n=0;t=e.childNodes[n];n++)l.assignRoleToRow_(t,"cases");return e.type="cases",e.appendContentNode(t),a.tableIsMultiline(e)&&l.binomialForm_(e),e}static rewriteFencedLine_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0],n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],r=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes[0];return n.parent=e.parent,e.parent=n,r.parent=t,n.childNodes=[e],t.childNodes=[r],n}static rowToLine_(e,t){const n=t||"unknown";a.isType(e,"row")&&(e.type="line",e.role=n,1===e.childNodes.length&&a.isType(e.childNodes[0],"cell")&&(e.childNodes=e.childNodes[0].childNodes,e.childNodes.forEach((function(t){t.parent=e}))))}static assignRoleToRow_(e,t){a.isType(e,"line")?e.role=t:a.isType(e,"row")&&(e.role=t,e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){a.isType(e,"cell")&&(e.role=t)})))}static nextSeparatorFunction_(e){let t;if(e){if(e.match(/^\s+$/))return null;t=e.replace(/\s/g,"").split("").filter((function(e){return e}))}else t=[","];return function(){return t.length>1?t.shift():t[0]}}static numberRole_(e){if("unknown"!==e.role)return;const t=[...e.textContent].filter((e=>e.match(/[^\s]/))),n=t.map(i.lookupMeaning);if(n.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type&&"integer"===e.role||"punctuation"===e.type&&"comma"===e.role})))return e.role="integer",void("0"===t[0]&&e.addAnnotation("general","basenumber"));n.every((function(e){return"number"===e.type&&"integer"===e.role||"punctuation"===e.type}))?e.role="float":e.role="othernumber"}static exprFont_(e){if("unknown"!==e.font)return;const t=[...e.textContent].map(i.lookupMeaning).reduce((function(e,t){return e&&t.font&&"unknown"!==t.font&&t.font!==e?"unknown"===e?t.font:null:e}),"unknown");t&&(e.font=t)}static purgeFences_(e){const t=e.rel,n=e.comp,r=[],i=[];for(;t.length>0;){const e=t.shift();let o=n.shift();a.isElligibleEmbellishedFence(e)?(r.push(e),i.push(o)):(l.fenceToPunct_(e),o.push(e),o=o.concat(n.shift()),n.unshift(o))}return i.push(n.shift()),{rel:r,comp:i}}static rewriteFencedNode_(e){const t=e.contentNodes[0],n=e.contentNodes[1];let r=l.rewriteFence_(e,t);return e.contentNodes[0]=r.fence,r=l.rewriteFence_(r.node,n),e.contentNodes[1]=r.fence,e.contentNodes[0].parent=e,e.contentNodes[1].parent=e,r.node.parent=null,r.node}static rewriteFence_(e,t){if(!t.embellished)return{node:e,fence:t};const n=t.childNodes[0],r=l.rewriteFence_(e,n);return a.isType(t,"superscript")||a.isType(t,"subscript")||a.isType(t,"tensor")?(a.isRole(t,"subsup")||(t.role=e.role),n!==r.node&&(t.replaceChild(n,r.node),n.parent=e),l.propagateFencePointer_(t,n),{node:t,fence:r.fence}):(t.replaceChild(n,r.fence),t.mathmlTree&&-1===t.mathml.indexOf(t.mathmlTree)&&t.mathml.push(t.mathmlTree),{node:r.node,fence:t})}static propagateFencePointer_(e,t){e.fencePointer=t.fencePointer||t.id.toString(),e.embellished=null}static classifyByColumns_(e,t,n,r){return!!(3===t.length&&l.testColumns_(t,1,(e=>l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))||2===t.length&&(l.testColumns_(t,1,(e=>l.isEndRelation_(e,n)||l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))||l.testColumns_(t,0,(e=>l.isEndRelation_(e,n,!0)||l.isPureRelation_(e,n)))))&&(e.role=n,!0)}static isEndRelation_(e,t,n){const r=n?e.childNodes.length-1:0;return a.isType(e,"relseq")&&a.isRole(e,t)&&a.isType(e.childNodes[r],"empty")}static isPureRelation_(e,t){return a.isType(e,"relation")&&a.isRole(e,t)}static computeColumns_(e){const t=[];for(let n,r=0;n=e.childNodes[r];r++)for(let e,r=0;e=n.childNodes[r];r++){t[r]?t[r].push(e):t[r]=[e]}return t}static testColumns_(e,t,n){const r=e[t];return!!r&&(r.some((function(e){return e.childNodes.length&&n(e.childNodes[0])}))&&r.every((function(e){return!e.childNodes.length||n(e.childNodes[0])})))}setNodeFactory(e){l.getInstance().factory_=e,o.updateFactory(l.getInstance().factory_)}getNodeFactory(){return l.getInstance().factory_}identifierNode(e,t,n){if("MathML-Unit"===n)e.type="identifier",e.role="unit";else if(!t&&1===e.textContent.length&&("integer"===e.role||"latinletter"===e.role||"greekletter"===e.role)&&"normal"===e.font)return e.font="italic",o.run("simpleNamedFunction",e);return"unknown"===e.type&&(e.type="identifier"),l.exprFont_(e),o.run("simpleNamedFunction",e)}implicitNode(e){if(e=l.getInstance().getMixedNumbers_(e),1===(e=l.getInstance().combineUnits_(e)).length)return e[0];const t=l.getInstance().implicitNode_(e);return o.run("combine_juxtaposition",t)}text(e,t){return l.exprFont_(e),e.type="text","MS"===t?(e.role="string",e):"MSPACE"===t||e.textContent.match(/^\s*$/)?(e.role="space",e):e}row(e){return 0===(e=e.filter((function(e){return!a.isType(e,"empty")}))).length?l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode():(e=l.getInstance().getFencesInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().tablesInRow(e),e=l.getInstance().getPunctuationInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().getTextInRow_(e),e=l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e),l.getInstance().relationsInRow_(e))}limitNode(e,t){if(!t.length)return l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();let n,r=t[0],i="unknown";if(!t[1])return r;if(a.isLimitBase(r)){n=l.MML_TO_LIMIT_[e];const o=n.length;if(i=n.type,t=t.slice(0,n.length+1),1===o&&a.isAccent(t[1])||2===o&&a.isAccent(t[1])&&a.isAccent(t[2]))return n=l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_[e],l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,t,n.type,n.length,n.accent);if(2===o){if(a.isAccent(t[1]))return r=l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,[r,t[1]],{MSUBSUP:"subscript",MUNDEROVER:"underscore"}[e],1,!0),t[2]?l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,[r,t[2]],null,"limupper"):r;if(t[2]&&a.isAccent(t[2]))return r=l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,[r,t[2]],{MSUBSUP:"superscript",MUNDEROVER:"overscore"}[e],1,!0),l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,[r,t[1]],null,"limlower");t[o]||(i="limlower")}return l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(r,t,null,i)}return n=l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_[e],l.getInstance().accentNode_(r,t,n.type,n.length,n.accent)}tablesInRow(e){let t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.tableIsMatrixOrVector),n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++)n=n.concat(t.comp.shift()),n.push(l.tableToMatrixOrVector_(e));n=n.concat(t.comp.shift()),t=c.partitionNodes(n,a.isTableOrMultiline),n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const r=t.comp.shift();a.tableIsCases(e,r)&&l.tableToCases_(e,r.pop()),n=n.concat(r),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp.shift())}mfenced(e,t,n,r){if(n&&r.length>0){const e=l.nextSeparatorFunction_(n),t=[r.shift()];r.forEach((n=>{t.push(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e())),t.push(n)})),r=t}return e&&t?l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e),l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(t),r):(e&&r.unshift(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(e)),t&&r.push(l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(t)),l.getInstance().row(r))}fractionLikeNode(e,t,n,r){let i;if(!r&&c.isZeroLength(n)){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("line",[e],[]),r=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("line",[t],[]);return i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("multiline",[n,r],[]),l.binomialForm_(i),l.classifyMultiline(i),i}return i=l.getInstance().fractionNode_(e,t),r&&i.addAnnotation("general","bevelled"),i}tensor(e,t,n,r,i){const o=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("tensor",[e,l.getInstance().scriptNode_(t,"leftsub"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(n,"leftsuper"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(r,"rightsub"),l.getInstance().scriptNode_(i,"rightsuper")],[]);return o.role=e.role,o.embellished=a.isEmbellished(e),o}pseudoTensor(e,t,n){const r=e=>!a.isType(e,"empty"),i=t.filter(r).length,o=n.filter(r).length;if(!i&&!o)return e;const s=i?o?"MSUBSUP":"MSUB":"MSUP",c=[e];return i&&c.push(l.getInstance().scriptNode_(t,"rightsub",!0)),o&&c.push(l.getInstance().scriptNode_(n,"rightsuper",!0)),l.getInstance().limitNode(s,c)}font(e){const t=l.MATHJAX_FONTS[e];return t||e}proof(e,t,n){if(t.inference||t.axiom||console.log("Noise"),t.axiom){const t=l.getInstance().cleanInference(e.childNodes),r=t.length?l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",n(t),[]):l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();return r.role="axiom",r.mathmlTree=e,r}const r=l.getInstance().inference(e,t,n);return t.proof&&(r.role="proof",r.childNodes[0].role="final"),r}inference(e,t,n){if(t.inferenceRule){const t=l.getInstance().getFormulas(e,[],n);return l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",[t.conclusion,t.premises],[])}const i=t.labelledRule,o=r.toArray(e.childNodes),s=[];"left"!==i&&"both"!==i||s.push(l.getInstance().getLabel(e,o,n,"left")),"right"!==i&&"both"!==i||s.push(l.getInstance().getLabel(e,o,n,"right"));const a=l.getInstance().getFormulas(e,o,n),c=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("inference",[a.conclusion,a.premises],s);return c.mathmlTree=e,c}getLabel(e,t,n,i){const o=l.getInstance().findNestedRow(t,"prooflabel",i),s=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("rulelabel",n(r.toArray(o.childNodes)),[]);return s.role=i,s.mathmlTree=o,s}getFormulas(e,t,n){const i=t.length?l.getInstance().findNestedRow(t,"inferenceRule"):e,o="up"===l.getSemantics(i).inferenceRule,s=o?i.childNodes[1]:i.childNodes[0],a=o?i.childNodes[0]:i.childNodes[1],c=s.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],u=r.toArray(c.childNodes[0].childNodes),d=[];let h=1;for(const e of u)h%2&&d.push(e.childNodes[0]),h++;const p=n(d),f=n(r.toArray(a.childNodes[0].childNodes))[0],m=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("premises",p,[]);m.mathmlTree=c;const g=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("conclusion",[f],[]);return g.mathmlTree=a.childNodes[0].childNodes[0],{conclusion:g,premises:m}}findNestedRow(e,t,n){return l.getInstance().findNestedRow_(e,t,0,n)}cleanInference(e){return r.toArray(e).filter((function(e){return"MSPACE"!==r.tagName(e)}))}operatorNode(e){return"unknown"===e.type&&(e.type="operator"),o.run("multioperator",e)}implicitNode_(e){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeMultipleContentNodes(e.length-1,i.invisibleTimes());l.matchSpaces_(e,t);const n=l.getInstance().infixNode_(e,t[0]);return n.role="implicit",t.forEach((function(e){e.parent=n})),n.contentNodes=t,n}infixNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("infixop",e,[t],c.getEmbellishedInner(t).textContent);return n.role=t.role,o.run("propagateSimpleFunction",n)}explicitMixed_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return e.textContent===i.invisiblePlus()}));if(!t.rel.length)return e;let n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const i=t.comp[r],o=t.comp[r+1],s=i.length-1;if(i[s]&&o[0]&&a.isType(i[s],"number")&&!a.isRole(i[s],"mixed")&&a.isType(o[0],"fraction")){const e=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("number",[i[s],o[0]],[]);e.role="mixed",n=n.concat(i.slice(0,s)),n.push(e),o.shift()}else n=n.concat(i),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp[t.comp.length-1])}concatNode_(e,t,n){if(0===t.length)return e;const r=t.map((function(e){return c.getEmbellishedInner(e).textContent})).join(" "),i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(n,[e],t,r);return t.length>1&&(i.role="multiop"),i}prefixNode_(e,t){const n=c.partitionNodes(t,(e=>a.isRole(e,"subtraction")));let r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(e,n.comp.pop(),"prefixop");for(1===r.contentNodes.length&&"addition"===r.contentNodes[0].role&&"+"===r.contentNodes[0].textContent&&(r.role="positive");n.rel.length>0;)r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(r,[n.rel.pop()],"prefixop"),r.role="negative",r=l.getInstance().concatNode_(r,n.comp.pop(),"prefixop");return r}postfixNode_(e,t){return t.length?l.getInstance().concatNode_(e,t,"postfixop"):e}combineUnits_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return!a.isRole(e,"unit")}));if(e.length===t.rel.length)return t.rel;const n=[];let r,i;do{const e=t.comp.shift();r=t.rel.shift();let o=null;i=n.pop(),i&&(e.length&&a.isUnitCounter(i)?e.unshift(i):n.push(i)),1===e.length&&(o=e.pop()),e.length>1&&(o=l.getInstance().implicitNode_(e),o.role="unit"),o&&n.push(o),r&&n.push(r)}while(r);return n}getMixedNumbers_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(e){return a.isType(e,"fraction")&&a.isRole(e,"vulgar")}));if(!t.rel.length)return e;let n=[];for(let e,r=0;e=t.rel[r];r++){const i=t.comp[r],o=i.length-1;if(i[o]&&a.isType(i[o],"number")&&(a.isRole(i[o],"integer")||a.isRole(i[o],"float"))){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("number",[i[o],e],[]);t.role="mixed",n=n.concat(i.slice(0,o)),n.push(t)}else n=n.concat(i),n.push(e)}return n.concat(t.comp[t.comp.length-1])}getTextInRow_(e){if(e.length<=1)return e;const t=c.partitionNodes(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"text")));if(0===t.rel.length)return e;const n=[];let r=t.comp[0];r.length>0&&n.push(l.getInstance().row(r));for(let e,i=0;e=t.rel[i];i++)n.push(e),r=t.comp[i+1],r.length>0&&n.push(l.getInstance().row(r));return[l.getInstance().dummyNode_(n)]}relationsInRow_(e){const t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.isRelation),n=t.rel[0];if(!n)return l.getInstance().operationsInRow_(e);if(1===e.length)return e[0];const r=t.comp.map(l.getInstance().operationsInRow_);let i;return t.rel.some((function(e){return!e.equals(n)}))?(i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("multirel",r,t.rel),t.rel.every((function(e){return e.role===n.role}))&&(i.role=n.role),i):(i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("relseq",r,t.rel,c.getEmbellishedInner(n).textContent),i.role=n.role,i)}operationsInRow_(e){if(0===e.length)return l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();if(1===(e=l.getInstance().explicitMixed_(e)).length)return e[0];const t=[];for(;e.length>0&&a.isOperator(e[0]);)t.push(e.shift());if(0===e.length)return l.getInstance().prefixNode_(t.pop(),t);if(1===e.length)return l.getInstance().prefixNode_(e[0],t);e=o.run("convert_juxtaposition",e);const n=c.sliceNodes(e,a.isOperator),r=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(l.getInstance().implicitNode(n.head),t);return n.div?l.getInstance().operationsTree_(n.tail,r,n.div):r}operationsTree_(e,t,n,r){const i=r||[];if(0===e.length){if(i.unshift(n),"infixop"===t.type){const e=l.getInstance().postfixNode_(t.childNodes.pop(),i);return t.appendChild(e),t}return l.getInstance().postfixNode_(t,i)}const o=c.sliceNodes(e,a.isOperator);if(0===o.head.length)return i.push(o.div),l.getInstance().operationsTree_(o.tail,t,n,i);const s=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(l.getInstance().implicitNode(o.head),i),u=l.getInstance().appendOperand_(t,n,s);return o.div?l.getInstance().operationsTree_(o.tail,u,o.div,[]):u}appendOperand_(e,t,n){if("infixop"!==e.type)return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t);const r=l.getInstance().appendDivisionOp_(e,t,n);return r||(l.getInstance().appendExistingOperator_(e,t,n)?e:"multiplication"===t.role?l.getInstance().appendMultiplicativeOp_(e,t,n):l.getInstance().appendAdditiveOp_(e,t,n))}appendDivisionOp_(e,t,n){return"division"===t.role?a.isImplicit(e)?l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t):l.getInstance().appendLastOperand_(e,t,n):"division"===e.role?l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t):null}appendLastOperand_(e,t,n){let r=e,i=e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];for(;i&&"infixop"===i.type&&!a.isImplicit(i);)r=i,i=r.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];const o=l.getInstance().infixNode_([r.childNodes.pop(),n],t);return r.appendChild(o),e}appendMultiplicativeOp_(e,t,n){if(a.isImplicit(e))return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t);let r=e,i=e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];for(;i&&"infixop"===i.type&&!a.isImplicit(i);)r=i,i=r.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1];const o=l.getInstance().infixNode_([r.childNodes.pop(),n],t);return r.appendChild(o),e}appendAdditiveOp_(e,t,n){return l.getInstance().infixNode_([e,n],t)}appendExistingOperator_(e,t,n){return!(!e||"infixop"!==e.type||a.isImplicit(e))&&(e.contentNodes[0].equals(t)?(e.appendContentNode(t),e.appendChild(n),!0):l.getInstance().appendExistingOperator_(e.childNodes[e.childNodes.length-1],t,n))}getFencesInRow_(e){let t=c.partitionNodes(e,a.isFence);t=l.purgeFences_(t);const n=t.comp.shift();return l.getInstance().fences_(t.rel,t.comp,[],[n])}fences_(e,t,n,r){if(0===e.length&&0===n.length)return r[0];const i=e=>a.isRole(e,"open");if(0===e.length){const e=r.shift();for(;n.length>0;){if(i(n[0])){const t=n.shift();l.fenceToPunct_(t),e.push(t)}else{const t=c.sliceNodes(n,i),o=t.head.length-1,s=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(t.head,r.slice(0,o));r=r.slice(o),e.push(...s),t.div&&t.tail.unshift(t.div),n=t.tail}e.push(...r.shift())}return e}const o=n[n.length-1],s=e[0].role;if("open"===s||a.isNeutralFence(e[0])&&(!o||!a.compareNeutralFences(e[0],o))){n.push(e.shift());const i=t.shift();return i&&r.push(i),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&"close"===s&&"open"===o.role){const i=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(n.pop(),e.shift(),r.pop());return r.push(r.pop().concat([i],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&a.compareNeutralFences(e[0],o)){if(!a.elligibleLeftNeutral(o)||!a.elligibleRightNeutral(e[0])){n.push(e.shift());const i=t.shift();return i&&r.push(i),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}const i=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(n.pop(),e.shift(),r.pop());return r.push(r.pop().concat([i],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}if(o&&"close"===s&&a.isNeutralFence(o)&&n.some(i)){const o=c.sliceNodes(n,i,!0),s=r.pop(),a=r.length-o.tail.length+1,u=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(o.tail,r.slice(a));r=r.slice(0,a);const d=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(o.div,e.shift(),r.pop().concat(u,s));return r.push(r.pop().concat([d],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,o.head,r)}const u=e.shift();return l.fenceToPunct_(u),r.push(r.pop().concat([u],t.shift())),l.getInstance().fences_(e,t,n,r)}neutralFences_(e,t){if(0===e.length)return e;if(1===e.length)return l.fenceToPunct_(e[0]),e;const n=e.shift();if(!a.elligibleLeftNeutral(n)){l.fenceToPunct_(n);const r=t.shift();return r.unshift(n),r.concat(l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t))}const r=c.sliceNodes(e,(function(e){return a.compareNeutralFences(e,n)}));if(!r.div){l.fenceToPunct_(n);const r=t.shift();return r.unshift(n),r.concat(l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t))}if(!a.elligibleRightNeutral(r.div))return l.fenceToPunct_(r.div),e.unshift(n),l.getInstance().neutralFences_(e,t);const i=l.getInstance().combineFencedContent_(n,r.div,r.head,t);if(r.tail.length>0){const e=i.shift(),t=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(r.tail,i);return e.concat(t)}return i[0]}combineFencedContent_(e,t,n,r){if(0===n.length){const n=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,r.shift());return r.length>0?r[0].unshift(n):r=[[n]],r}const i=r.shift(),o=n.length-1,s=r.slice(0,o),a=(r=r.slice(o)).shift(),c=l.getInstance().neutralFences_(n,s);i.push(...c),i.push(...a);const u=l.getInstance().horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,i);return r.length>0?r[0].unshift(u):r=[[u]],r}horizontalFencedNode_(e,t,n){const r=l.getInstance().row(n);let i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("fenced",[r],[e,t]);return"open"===e.role?(l.getInstance().classifyHorizontalFence_(i),i=o.run("propagateComposedFunction",i)):i.role=e.role,i=o.run("detect_cycle",i),l.rewriteFencedNode_(i)}classifyHorizontalFence_(e){e.role="leftright";const t=e.childNodes;if(!a.isSetNode(e)||t.length>1)return;if(0===t.length||"empty"===t[0].type)return void(e.role="set empty");const n=t[0].type;if(1===t.length&&a.isSingletonSetContent(t[0]))return void(e.role="set singleton");const r=t[0].role;if("punctuated"===n&&"sequence"===r){if("comma"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role)return 1!==t[0].contentNodes.length||"vbar"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role&&"colon"!==t[0].contentNodes[0].role?void 0:(e.role="set extended",void l.getInstance().setExtension_(e));e.role="set collection"}}setExtension_(e){const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0];t&&"infixop"===t.type&&1===t.contentNodes.length&&a.isMembership(t.contentNodes[0])&&(t.addAnnotation("set","intensional"),t.contentNodes[0].addAnnotation("set","intensional"))}getPunctuationInRow_(e){if(e.length<=1)return e;const t=e=>{const t=e.type;return"punctuation"===t||"text"===t||"operator"===t||"relation"===t},n=c.partitionNodes(e,(function(n){if(!a.isPunctuation(n))return!1;if(a.isPunctuation(n)&&!a.isRole(n,"ellipsis"))return!0;const r=e.indexOf(n);if(0===r)return!e[1]||!t(e[1]);const i=e[r-1];if(r===e.length-1)return!t(i);const o=e[r+1];return!t(i)||!t(o)}));if(0===n.rel.length)return e;const r=[];let i=n.comp.shift();i.length>0&&r.push(l.getInstance().row(i));let o=0;for(;n.comp.length>0;)r.push(n.rel[o++]),i=n.comp.shift(),i.length>0&&r.push(l.getInstance().row(i));return[l.getInstance().punctuatedNode_(r,n.rel)]}punctuatedNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("punctuated",e,t);if(t.length===e.length){const e=t[0].role;if("unknown"!==e&&t.every((function(t){return t.role===e})))return n.role=e,n}return a.singlePunctAtPosition(e,t,0)?n.role="startpunct":a.singlePunctAtPosition(e,t,e.length-1)?n.role="endpunct":t.every((e=>a.isRole(e,"dummy")))?n.role="text":t.every((e=>a.isRole(e,"space")))?n.role="space":n.role="sequence",n}dummyNode_(e){const t=l.getInstance().factory_.makeMultipleContentNodes(e.length-1,i.invisibleComma());return t.forEach((function(e){e.role="dummy"})),l.getInstance().punctuatedNode_(e,t)}accentRole_(e,t){if(!a.isAccent(e))return!1;const n=e.textContent,r=i.lookupSecondary("bar",n)||i.lookupSecondary("tilde",n)||e.role;return e.role="underscore"===t?"underaccent":"overaccent",e.addAnnotation("accent",r),!0}accentNode_(e,t,n,r,i){const o=(t=t.slice(0,r+1))[1],s=t[2];let a;if(!i&&s&&(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("subscript",[e,o],[]),a.role="subsup",t=[a,s],n="superscript"),i){const r=l.getInstance().accentRole_(o,n);if(s){l.getInstance().accentRole_(s,"overscore")&&!r?(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("overscore",[e,s],[]),t=[a,o],n="underscore"):(a=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("underscore",[e,o],[]),t=[a,s],n="overscore"),a.role="underover"}}return l.getInstance().makeLimitNode_(e,t,a,n)}makeLimitNode_(e,t,n,r){if("limupper"===r&&"limlower"===e.type)return e.childNodes.push(t[1]),t[1].parent=e,e.type="limboth",e;if("limlower"===r&&"limupper"===e.type)return e.childNodes.splice(1,-1,t[1]),t[1].parent=e,e.type="limboth",e;const i=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(r,t,[]),o=a.isEmbellished(e);return n&&(n.embellished=o),i.embellished=o,i.role=e.role,i}getFunctionsInRow_(e,t){const n=t||[];if(0===e.length)return n;const r=e.shift(),i=l.classifyFunction_(r,e);if(!i)return n.push(r),l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e,n);const o=l.getInstance().getFunctionsInRow_(e,[]),s=l.getInstance().getFunctionArgs_(r,o,i);return n.concat(s)}getFunctionArgs_(e,t,n){let r,i,o;switch(n){case"integral":{const n=l.getInstance().getIntegralArgs_(t);if(!n.intvar&&!n.integrand.length)return n.rest.unshift(e),n.rest;const r=l.getInstance().row(n.integrand);return o=l.getInstance().integralNode_(e,r,n.intvar),n.rest.unshift(o),n.rest}case"prefix":if(t[0]&&"fenced"===t[0].type){const n=t.shift();return a.isNeutralFence(n)||(n.role="leftright"),o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,n),t.unshift(o),t}if(r=c.sliceNodes(t,a.isPrefixFunctionBoundary),r.head.length)i=l.getInstance().row(r.head),r.div&&r.tail.unshift(r.div);else{if(!r.div||!a.isType(r.div,"appl"))return t.unshift(e),t;i=r.div}return o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,i),r.tail.unshift(o),r.tail;case"bigop":return r=c.sliceNodes(t,a.isBigOpBoundary),r.head.length?(i=l.getInstance().row(r.head),o=l.getInstance().bigOpNode_(e,i),r.div&&r.tail.unshift(r.div),r.tail.unshift(o),r.tail):(t.unshift(e),t);default:{if(0===t.length)return[e];const n=t[0];return"fenced"===n.type&&!a.isNeutralFence(n)&&a.isSimpleFunctionScope(n)?(n.role="leftright",l.propagateFunctionRole_(e,"simple function"),o=l.getInstance().functionNode_(e,t.shift()),t.unshift(o),t):(t.unshift(e),t)}}}getIntegralArgs_(e,t=[]){if(0===e.length)return{integrand:t,intvar:null,rest:e};const n=e[0];if(a.isGeneralFunctionBoundary(n))return{integrand:t,intvar:null,rest:e};if(a.isIntegralDxBoundarySingle(n))return n.role="integral",{integrand:t,intvar:n,rest:e.slice(1)};if(e[1]&&a.isIntegralDxBoundary(n,e[1])){const r=l.getInstance().prefixNode_(e[1],[n]);return r.role="integral",{integrand:t,intvar:r,rest:e.slice(2)}}return t.push(e.shift()),l.getInstance().getIntegralArgs_(e,t)}functionNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeContentNode(i.functionApplication()),r=l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id];r&&(n.mathmlTree=r.mathmlTree,n.mathml=r.mathml,n.annotation=r.annotation,n.attributes=r.attributes,delete l.getInstance().funcAppls[e.id]),n.type="punctuation",n.role="application";const o=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(function(e){return a.isType(e,"function")||a.isType(e,"identifier")&&a.isRole(e,"simple function")}));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("appl",[e,t],o,[n])}bigOpNode_(e,t){const n=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"largeop")));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("bigop",[e,t],n,[])}integralNode_(e,t,n){t=t||l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode(),n=n||l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();const r=l.getFunctionOp_(e,(e=>a.isType(e,"largeop")));return l.getInstance().functionalNode_("integral",[e,t,n],r,[])}functionalNode_(e,t,n,r){const i=t[0];let o;n&&(o=n.parent,r.push(n));const s=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode(e,t,r);return s.role=i.role,o&&(n.parent=o),s}fractionNode_(e,t){const n=l.getInstance().factory_.makeBranchNode("fraction",[e,t],[]);return n.role=n.childNodes.every((function(e){return a.isType(e,"number")&&a.isRole(e,"integer")}))?"vulgar":n.childNodes.every(a.isPureUnit)?"unit":"division",o.run("propagateSimpleFunction",n)}scriptNode_(e,t,n){let r;switch(e.length){case 0:r=l.getInstance().factory_.makeEmptyNode();break;case 1:if(r=e[0],n)return r;break;default:r=l.getInstance().dummyNode_(e)}return r.role=t,r}findNestedRow_(e,t,n,i){if(n>3)return null;for(let o,s=0;o=e[s];s++){const e=r.tagName(o);if("MSPACE"!==e){if("MROW"===e)return l.getInstance().findNestedRow_(r.toArray(o.childNodes),t,n+1,i);if(l.findSemantics(o,t,i))return o}}return null}}t.default=l,l.FENCE_TO_PUNCT_={metric:"metric",neutral:"vbar",open:"openfence",close:"closefence"},l.MML_TO_LIMIT_={MSUB:{type:"limlower",length:1},MUNDER:{type:"limlower",length:1},MSUP:{type:"limupper",length:1},MOVER:{type:"limupper",length:1},MSUBSUP:{type:"limboth",length:2},MUNDEROVER:{type:"limboth",length:2}},l.MML_TO_BOUNDS_={MSUB:{type:"subscript",length:1,accent:!1},MSUP:{type:"superscript",length:1,accent:!1},MSUBSUP:{type:"subscript",length:2,accent:!1},MUNDER:{type:"underscore",length:1,accent:!0},MOVER:{type:"overscore",length:1,accent:!0},MUNDEROVER:{type:"underscore",length:2,accent:!0}},l.CLASSIFY_FUNCTION_={integral:"integral",sum:"bigop","prefix function":"prefix","limit function":"prefix","simple function":"prefix","composed function":"prefix"},l.MATHJAX_FONTS={"-tex-caligraphic":"caligraphic","-tex-caligraphic-bold":"caligraphic-bold","-tex-calligraphic":"caligraphic","-tex-calligraphic-bold":"caligraphic-bold","-tex-oldstyle":"oldstyle","-tex-oldstyle-bold":"oldstyle-bold","-tex-mathit":"italic"}},7984:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticSkeleton=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(5024),o=n(8171);class s{constructor(e){this.parents=null,this.levelsMap=null,e=0===e?e:e||[],this.array=e}static fromTree(e){return s.fromNode(e.root)}static fromNode(e){return new s(s.fromNode_(e))}static fromString(e){return new s(s.fromString_(e))}static simpleCollapseStructure(e){return"number"==typeof e}static contentCollapseStructure(e){return!!e&&!s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)&&"c"===e[0]}static interleaveIds(e,t){return r.interleaveLists(s.collapsedLeafs(e),s.collapsedLeafs(t))}static collapsedLeafs(...e){return e.reduce(((e,t)=>{return e.concat((n=t,s.simpleCollapseStructure(n)?[n]:s.contentCollapseStructure(n[1])?n.slice(2):n.slice(1)));var n}),[])}static fromStructure(e,t){return new s(s.tree_(e,t.root))}static combineContentChildren(e,t,n){switch(e.type){case"relseq":case"infixop":case"multirel":return r.interleaveLists(n,t);case"prefixop":return t.concat(n);case"postfixop":return n.concat(t);case"fenced":return n.unshift(t[0]),n.push(t[1]),n;case"appl":return[n[0],t[0],n[1]];case"root":return[n[1],n[0]];case"row":case"line":return t.length&&n.unshift(t[0]),n;default:return n}}static makeSexp_(e){return s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?e.toString():s.contentCollapseStructure(e)?"(c "+e.slice(1).map(s.makeSexp_).join(" ")+")":"("+e.map(s.makeSexp_).join(" ")+")"}static fromString_(e){let t=e.replace(/\(/g,"[");return t=t.replace(/\)/g,"]"),t=t.replace(/ /g,","),t=t.replace(/c/g,'"c"'),JSON.parse(t)}static fromNode_(e){if(!e)return[];const t=e.contentNodes;let n;t.length&&(n=t.map(s.fromNode_),n.unshift("c"));const r=e.childNodes;if(!r.length)return t.length?[e.id,n]:e.id;const i=r.map(s.fromNode_);return t.length&&i.unshift(n),i.unshift(e.id),i}static tree_(e,t){if(!t)return[];if(!t.childNodes.length)return t.id;const n=t.id,r=[n],a=i.evalXPath(`.//self::*[@${o.Attribute.ID}=${n}]`,e)[0],c=s.combineContentChildren(t,t.contentNodes.map((function(e){return e})),t.childNodes.map((function(e){return e})));a&&s.addOwns_(a,c);for(let t,n=0;t=c[n];n++)r.push(s.tree_(e,t));return r}static addOwns_(e,t){const n=e.getAttribute(o.Attribute.COLLAPSED),r=n?s.realLeafs_(s.fromString(n).array):t.map((e=>e.id));e.setAttribute(o.Attribute.OWNS,r.join(" "))}static realLeafs_(e){if(s.simpleCollapseStructure(e))return[e];if(s.contentCollapseStructure(e))return[];let t=[];for(let n=1;ns.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?e:s.contentCollapseStructure(e)?e[1]:e[0]))}subtreeNodes(e){if(!this.isRoot(e))return[];const t=(e,n)=>{s.simpleCollapseStructure(e)?n.push(e):(s.contentCollapseStructure(e)&&(e=e.slice(1)),e.forEach((e=>t(e,n))))},n=this.levelsMap[e],r=[];return t(n.slice(1),r),r}}t.SemanticSkeleton=s},1784:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SemanticTree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(4036),o=n(241),s=n(8122),a=n(9444),c=n(6161);n(7103);class l{constructor(e){this.mathml=e,this.parser=new s.SemanticMathml,this.root=this.parser.parse(e),this.collator=this.parser.getFactory().leafMap.collateMeaning();const t=this.collator.newDefault();t&&(this.parser=new s.SemanticMathml,this.parser.getFactory().defaultMap=t,this.root=this.parser.parse(e)),u.visit(this.root,{}),(0,i.annotate)(this.root)}static empty(){const e=r.parseInput(""),t=new l(e);return t.mathml=e,t}static fromNode(e,t){const n=l.empty();return n.root=e,t&&(n.mathml=t),n}static fromRoot(e,t){let n=e;for(;n.parent;)n=n.parent;const r=l.fromNode(n);return t&&(r.mathml=t),r}static fromXml(e){const t=l.empty();return e.childNodes[0]&&(t.root=a.SemanticNode.fromXml(e.childNodes[0])),t}xml(e){const t=r.parseInput(""),n=this.root.xml(t.ownerDocument,e);return t.appendChild(n),t}toString(e){return r.serializeXml(this.xml(e))}formatXml(e){const t=this.toString(e);return r.formatXml(t)}displayTree(){this.root.displayTree()}replaceNode(e,t){const n=e.parent;n?n.replaceChild(e,t):this.root=t}toJson(){const e={};return e.stree=this.root.toJson(),e}}t.SemanticTree=l;const u=new o.SemanticVisitor("general","unit",((e,t)=>{if("infixop"===e.type&&("multiplication"===e.role||"implicit"===e.role)){const t=e.childNodes;t.length&&(c.isPureUnit(t[0])||c.isUnitCounter(t[0]))&&e.childNodes.slice(1).every(c.isPureUnit)&&(e.role="unit")}return!1}))},8901:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.partitionNodes=t.sliceNodes=t.getEmbellishedInner=t.addAttributes=t.isZeroLength=t.purgeNodes=t.isOrphanedGlyph=t.hasDisplayTag=t.hasEmptyTag=t.hasIgnoreTag=t.hasLeafTag=t.hasMathTag=t.directSpeechKeys=t.DISPLAYTAGS=t.EMPTYTAGS=t.IGNORETAGS=t.LEAFTAGS=void 0;const r=n(6671);function i(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.LEAFTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))}function o(e,t,n){n&&e.reverse();const r=[];for(let i,o=0;i=e[o];o++){if(t(i))return n?{head:e.slice(o+1).reverse(),div:i,tail:r.reverse()}:{head:r,div:i,tail:e.slice(o+1)};r.push(i)}return n?{head:[],div:null,tail:r.reverse()}:{head:r,div:null,tail:[]}}t.LEAFTAGS=["MO","MI","MN","MTEXT","MS","MSPACE"],t.IGNORETAGS=["MERROR","MPHANTOM","MALIGNGROUP","MALIGNMARK","MPRESCRIPTS","ANNOTATION","ANNOTATION-XML"],t.EMPTYTAGS=["MATH","MROW","MPADDED","MACTION","NONE","MSTYLE","SEMANTICS"],t.DISPLAYTAGS=["MROOT","MSQRT"],t.directSpeechKeys=["aria-label","exact-speech","alt"],t.hasMathTag=function(e){return!!e&&"MATH"===r.tagName(e)},t.hasLeafTag=i,t.hasIgnoreTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.IGNORETAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.hasEmptyTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.EMPTYTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.hasDisplayTag=function(e){return!!e&&-1!==t.DISPLAYTAGS.indexOf(r.tagName(e))},t.isOrphanedGlyph=function(e){return!!e&&"MGLYPH"===r.tagName(e)&&!i(e.parentNode)},t.purgeNodes=function(e){const n=[];for(let i,o=0;i=e[o];o++){if(i.nodeType!==r.NodeType.ELEMENT_NODE)continue;const e=r.tagName(i);-1===t.IGNORETAGS.indexOf(e)&&(-1!==t.EMPTYTAGS.indexOf(e)&&0===i.childNodes.length||n.push(i))}return n},t.isZeroLength=function(e){if(!e)return!1;if(-1!==["negativeveryverythinmathspace","negativeverythinmathspace","negativethinmathspace","negativemediummathspace","negativethickmathspace","negativeverythickmathspace","negativeveryverythickmathspace"].indexOf(e))return!0;const t=e.match(/[0-9.]+/);return!!t&&0===parseFloat(t[0])},t.addAttributes=function(e,n){if(n.hasAttributes()){const r=n.attributes;for(let n=r.length-1;n>=0;n--){const i=r[n].name;i.match(/^ext/)&&(e.attributes[i]=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0),-1!==t.directSpeechKeys.indexOf(i)&&(e.attributes["ext-speech"]=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0),i.match(/texclass$/)&&(e.attributes.texclass=r[n].value),"href"===i&&(e.attributes.href=r[n].value,e.nobreaking=!0)}}},t.getEmbellishedInner=function e(t){return t&&t.embellished&&t.childNodes.length>0?e(t.childNodes[0]):t},t.sliceNodes=o,t.partitionNodes=function(e,t){let n=e;const r=[],i=[];let s=null;do{s=o(n,t),i.push(s.head),r.push(s.div),n=s.tail}while(s.div);return r.pop(),{rel:r,comp:i}}},9135:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(985),i=n(8171),o=n(1848),s=n(144);t.AbstractSpeechGenerator=class{constructor(){this.modality=i.addPrefix("speech"),this.rebuilt_=null,this.options_={}}getRebuilt(){return this.rebuilt_}setRebuilt(e){this.rebuilt_=e}setOptions(e){this.options_=e||{},this.modality=i.addPrefix(this.options_.modality||"speech")}getOptions(){return this.options_}start(){}end(){}generateSpeech(e,t){return this.rebuilt_||(this.rebuilt_=new o.RebuildStree(t)),(0,r.setup)(this.options_),s.computeMarkup(this.getRebuilt().xml)}}},3153:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AdhocSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135);class i extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){const n=this.generateSpeech(e,t);return e.setAttribute(this.modality,n),n}}t.AdhocSpeechGenerator=i},6281:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ColorGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8171),i=n(1123),o=n(1848),s=n(8835),a=n(9135);class c extends a.AbstractSpeechGenerator{constructor(){super(...arguments),this.modality=(0,r.addPrefix)("foreground"),this.contrast=new i.ContrastPicker}static visitStree_(e,t,n){if(e.childNodes.length){if(e.contentNodes.length&&("punctuated"===e.type&&e.contentNodes.forEach((e=>n[e.id]=!0)),"implicit"!==e.role&&t.push(e.contentNodes.map((e=>e.id)))),e.childNodes.length){if("implicit"===e.role){const r=[];let i=[];for(const t of e.childNodes){const e=[];c.visitStree_(t,e,n),e.length<=2&&r.push(e.shift()),i=i.concat(e)}return t.push(r),void i.forEach((e=>t.push(e)))}e.childNodes.forEach((e=>c.visitStree_(e,t,n)))}}else n[e.id]||t.push(e.id)}getSpeech(e,t){return s.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}generateSpeech(e,t){return this.getRebuilt()||this.setRebuilt(new o.RebuildStree(e)),this.colorLeaves_(e),s.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}colorLeaves_(e){const t=[];c.visitStree_(this.getRebuilt().streeRoot,t,{});for(const n of t){const t=this.contrast.generate();let r=!1;r=Array.isArray(n)?n.map((n=>this.colorLeave_(e,n,t))).reduce(((e,t)=>e||t),!1):this.colorLeave_(e,n.toString(),t),r&&this.contrast.increment()}}colorLeave_(e,t,n){const r=s.getBySemanticId(e,t);return!!r&&(r.setAttribute(this.modality,n),!0)}}t.ColorGenerator=c},1565:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DirectSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8835),i=n(9135);class o extends i.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return r.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}}t.DirectSpeechGenerator=o},7721:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DummySpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135);class i extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return""}}t.DummySpeechGenerator=i},1558:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.NodeSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8835),i=n(7486);class o extends i.TreeSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return super.getSpeech(e,t),r.getAttribute(e,this.modality)}}t.NodeSpeechGenerator=o},7317:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.generatorMapping_=t.generator=void 0;const r=n(3153),i=n(6281),o=n(1565),s=n(7721),a=n(1558),c=n(5778),l=n(7486);t.generator=function(e){return(t.generatorMapping_[e]||t.generatorMapping_.Direct)()},t.generatorMapping_={Adhoc:()=>new r.AdhocSpeechGenerator,Color:()=>new i.ColorGenerator,Direct:()=>new o.DirectSpeechGenerator,Dummy:()=>new s.DummySpeechGenerator,Node:()=>new a.NodeSpeechGenerator,Summary:()=>new c.SummarySpeechGenerator,Tree:()=>new l.TreeSpeechGenerator}},144:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.computeSummary_=t.retrieveSummary=t.connectAllMactions=t.connectMactions=t.nodeAtPosition_=t.computePrefix_=t.retrievePrefix=t.addPrefix=t.addModality=t.addSpeech=t.recomputeMarkup=t.computeMarkup=t.recomputeSpeech=t.computeSpeech=void 0;const r=n(4253),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(8171),a=n(6060),c=n(1784),l=n(8835);function u(e){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(e)}function d(e){return u(c.SemanticTree.fromNode(e).xml())}function h(e){const t=d(e);return r.markup(t)}function p(e){const t=f(e);return r.markup(t)}function f(e){const t=c.SemanticTree.fromRoot(e),n=o.evalXPath('.//*[@id="'+e.id+'"]',t.xml());let r=n[0];return n.length>1&&(r=m(e,n)||r),r?a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().runInSetting({modality:"prefix",domain:"default",style:"default",strict:!0,speech:!0},(function(){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(r)})):[]}function m(e,t){const n=t[0];if(!e.parent)return n;const r=[];for(;e;)r.push(e.id),e=e.parent;const i=function(e,t){for(;t.length&&t.shift().toString()===e.getAttribute("id")&&e.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode;)e=e.parentNode.parentNode;return!t.length};for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if(i(e,r.slice()))return e;return n}function g(e){return e?a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().runInSetting({modality:"summary",strict:!1,speech:!0},(function(){return a.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().evaluateNode(e)})):[]}t.computeSpeech=u,t.recomputeSpeech=d,t.computeMarkup=function(e){const t=u(e);return r.markup(t)},t.recomputeMarkup=h,t.addSpeech=function(e,t,n){const o=i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",t.id.toString())[0],a=o?r.markup(u(o)):h(t);e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.SPEECH,a)},t.addModality=function(e,t,n){const r=h(t);e.setAttribute(n,r)},t.addPrefix=function(e,t){const n=p(t);n&&e.setAttribute(s.Attribute.PREFIX,n)},t.retrievePrefix=p,t.computePrefix_=f,t.nodeAtPosition_=m,t.connectMactions=function(e,t,n){const r=i.querySelectorAll(t,"maction");for(let t,o=0;t=r[o];o++){const r=t.getAttribute("id"),o=i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(e,"id",r)[0];if(!o)continue;const a=t.childNodes[1],c=a.getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID);let u=l.getBySemanticId(e,c);if(u&&"dummy"!==u.getAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE))continue;if(u=o.childNodes[0],u.getAttribute("sre-highlighter-added"))continue;const d=a.getAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT);d&&u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.PARENT,d),u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.TYPE,"dummy"),u.setAttribute(s.Attribute.ID,c);i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",c)[0].setAttribute("alternative",c)}},t.connectAllMactions=function(e,t){const n=i.querySelectorAll(e,"maction");for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++){const n=e.childNodes[1].getAttribute(s.Attribute.ID);i.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(t,"id",n)[0].setAttribute("alternative",n)}},t.retrieveSummary=function(e){const t=g(e);return r.markup(t)},t.computeSummary_=g},5778:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SummarySpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(9135),i=n(144);class o extends r.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){return i.connectAllMactions(t,this.getRebuilt().xml),this.generateSpeech(e,t)}}t.SummarySpeechGenerator=o},7486:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.TreeSpeechGenerator=void 0;const r=n(8171),i=n(8835),o=n(9135),s=n(144);class a extends o.AbstractSpeechGenerator{getSpeech(e,t){const n=this.generateSpeech(e,t),o=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict;for(const n in o){const a=o[n],c=i.getBySemanticId(t,n),l=i.getBySemanticId(e,n);c&&l&&(this.modality&&this.modality!==r.Attribute.SPEECH?s.addModality(l,a,this.modality):s.addSpeech(l,a,this.getRebuilt().xml),this.modality===r.Attribute.SPEECH&&s.addPrefix(l,a))}return n}}t.TreeSpeechGenerator=a},650:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.INTERVALS=t.makeLetter=t.numberRules=t.alphabetRules=t.getFont=t.makeInterval=t.generate=t.makeDomains_=t.Domains_=t.Base=t.Embellish=t.Font=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(2371),o=n(4524),s=n(3319),a=n(4161);var c,l,u;function d(){const e=o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS,n=(e,t)=>{const n={};return Object.keys(e).forEach((e=>n[e]=!0)),Object.keys(t).forEach((e=>n[e]=!0)),Object.keys(n)};t.Domains_.small=n(e.smallPrefix,e.letterTrans),t.Domains_.capital=n(e.capPrefix,e.letterTrans),t.Domains_.digit=n(e.digitPrefix,e.digitTrans)}function h(e){const t=e.toString(16).toUpperCase();return t.length>3?t:("000"+t).slice(-4)}function p([e,t],n){const r=parseInt(e,16),i=parseInt(t,16),o=[];for(let e=r;e<=i;e++){let t=h(e);!1!==n[t]&&(t=n[t]||t,o.push(t))}return o}function f(e){const t="normal"===e||"fullwidth"===e?"":o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.font[e]||o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.embellish[e]||"";return(0,s.localeFontCombiner)(t)}function m(e,n,r,i,s,a){const c=f(i);for(let i,l,u,d=0;i=e[d],l=n[d],u=r[d];d++){const e=a?o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.capPrefix:o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.smallPrefix,n=a?t.Domains_.capital:t.Domains_.small;S(c.combiner,i,l,u,c.font,e,s,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.letterTrans,n)}}function g(e,n,r,i,s){const a=f(r);for(let r,c,l=0;r=e[l],c=n[l];l++){const e=o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.digitPrefix,n=l+s;S(a.combiner,r,c,n,a.font,e,i,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS.digitTrans,t.Domains_.digit)}}function S(e,t,n,r,i,o,s,c,l){for(let u,d=0;u=l[d];d++){const l=u in c?c[u]:c.default,d=u in o?o[u]:o.default;a.defineRule(t.toString(),u,"default",s,n,e(l(r),i,d))}}!function(e){e.BOLD="bold",e.BOLDFRAKTUR="bold-fraktur",e.BOLDITALIC="bold-italic",e.BOLDSCRIPT="bold-script",e.DOUBLESTRUCK="double-struck",e.FULLWIDTH="fullwidth",e.FRAKTUR="fraktur",e.ITALIC="italic",e.MONOSPACE="monospace",e.NORMAL="normal",e.SCRIPT="script",e.SANSSERIF="sans-serif",e.SANSSERIFITALIC="sans-serif-italic",e.SANSSERIFBOLD="sans-serif-bold",e.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC="sans-serif-bold-italic"}(c=t.Font||(t.Font={})),function(e){e.SUPER="super",e.SUB="sub",e.CIRCLED="circled",e.PARENTHESIZED="parenthesized",e.PERIOD="period",e.NEGATIVECIRCLED="negative-circled",e.DOUBLECIRCLED="double-circled",e.CIRCLEDSANSSERIF="circled-sans-serif",e.NEGATIVECIRCLEDSANSSERIF="negative-circled-sans-serif",e.COMMA="comma",e.SQUARED="squared",e.NEGATIVESQUARED="negative-squared"}(l=t.Embellish||(t.Embellish={})),function(e){e.LATINCAP="latinCap",e.LATINSMALL="latinSmall",e.GREEKCAP="greekCap",e.GREEKSMALL="greekSmall",e.DIGIT="digit"}(u=t.Base||(t.Base={})),t.Domains_={small:["default"],capital:["default"],digit:["default"]},t.makeDomains_=d,t.generate=function(e){const n=r.default.getInstance().locale;r.default.getInstance().locale=e,i.setLocale(),a.addSymbolRules({locale:e}),d();const s=t.INTERVALS;for(let e,t=0;e=s[t];t++){const t=p(e.interval,e.subst),n=t.map((function(e){return String.fromCodePoint(parseInt(e,16))}));if("offset"in e)g(t,n,e.font,e.category,e.offset||0);else{m(t,n,o.LOCALE.ALPHABETS[e.base],e.font,e.category,!!e.capital)}}r.default.getInstance().locale=n,i.setLocale()},t.makeInterval=p,t.getFont=f,t.alphabetRules=m,t.numberRules=g,t.makeLetter=S,t.INTERVALS=[{interval:["1D400","1D419"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D41A","1D433"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D56C","1D585"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDFRAKTUR},{interval:["1D586","1D59F"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDFRAKTUR},{interval:["1D468","1D481"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D482","1D49B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D4D0","1D4E9"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDSCRIPT},{interval:["1D4EA","1D503"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDSCRIPT},{interval:["1D538","1D551"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D53A":"2102","1D53F":"210D","1D545":"2115","1D547":"2119","1D548":"211A","1D549":"211D","1D551":"2124"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D552","1D56B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D504","1D51D"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D506":"212D","1D50B":"210C","1D50C":"2111","1D515":"211C","1D51D":"2128"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.FRAKTUR},{interval:["1D51E","1D537"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.FRAKTUR},{interval:["FF21","FF3A"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["FF41","FF5A"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["1D434","1D44D"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D44E","1D467"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{"1D455":"210E"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D670","1D689"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["1D68A","1D6A3"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["0041","005A"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["0061","007A"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["1D49C","1D4B5"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{"1D49D":"212C","1D4A0":"2130","1D4A1":"2131","1D4A3":"210B","1D4A4":"2110","1D4A7":"2112","1D4A8":"2133","1D4AD":"211B"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SCRIPT},{interval:["1D4B6","1D4CF"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{"1D4BA":"212F","1D4BC":"210A","1D4C4":"2134"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SCRIPT},{interval:["1D5A0","1D5B9"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D5BA","1D5D3"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D608","1D621"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFITALIC},{interval:["1D622","1D63B"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFITALIC},{interval:["1D5D4","1D5ED"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D5EE","1D607"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D63C","1D655"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D656","1D66F"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["0391","03A9"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{"03A2":"03F4"},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["03B0","03D0"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{"03B0":"2207","03CA":"2202","03CB":"03F5","03CC":"03D1","03CD":"03F0","03CE":"03D5","03CF":"03F1","03D0":"03D6"},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["1D6A8","1D6C0"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D6C1","1D6E1"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D6E2","1D6FA"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D6FB","1D71B"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.ITALIC},{interval:["1D71C","1D734"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D735","1D755"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.BOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D756","1D76E"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D76F","1D78F"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D790","1D7A8"],base:u.GREEKCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"Lu",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["1D7A9","1D7C9"],base:u.GREEKSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"Ll",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLDITALIC},{interval:["0030","0039"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.NORMAL},{interval:["2070","2079"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2071:"00B9",2072:"00B2",2073:"00B3"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.SUPER},{interval:["2080","2089"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.SUB},{interval:["245F","2473"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{"245F":"24EA"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["3251","325F"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:21,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["32B1","32BF"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:36,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["2474","2487"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:1,category:"No",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["2487","249B"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2487:"1F100"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.PERIOD},{interval:["2775","277F"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2775:"24FF"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED},{interval:["24EB","24F4"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:11,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED},{interval:["24F5","24FE"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:1,category:"No",font:l.DOUBLECIRCLED},{interval:["277F","2789"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{"277F":"1F10B"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.CIRCLEDSANSSERIF},{interval:["2789","2793"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{2789:"1F10C"},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLEDSANSSERIF},{interval:["FF10","FF19"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.FULLWIDTH},{interval:["1D7CE","1D7D7"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.BOLD},{interval:["1D7D8","1D7E1"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.DOUBLESTRUCK},{interval:["1D7E2","1D7EB"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.SANSSERIF},{interval:["1D7EC","1D7F5"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.SANSSERIFBOLD},{interval:["1D7F6","1D7FF"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"Nd",font:c.MONOSPACE},{interval:["1F101","1F10A"],base:u.DIGIT,subst:{},offset:0,category:"No",font:l.COMMA},{interval:["24B6","24CF"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["24D0","24E9"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"So",font:l.CIRCLED},{interval:["1F110","1F129"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["249C","24B5"],base:u.LATINSMALL,subst:{},capital:!1,category:"So",font:l.PARENTHESIZED},{interval:["1F130","1F149"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.SQUARED},{interval:["1F170","1F189"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.NEGATIVESQUARED},{interval:["1F150","1F169"],base:u.LATINCAP,subst:{},capital:!0,category:"So",font:l.NEGATIVECIRCLED}]},3955:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Parser=t.Comparator=t.ClearspeakPreferences=void 0;const r=n(4886),i=n(4998),o=n(8310),s=n(8310),a=n(4161),c=n(6060);class l extends o.DynamicCstr{constructor(e,t){super(e),this.preference=t}static comparator(){return new d(r.default.getInstance().dynamicCstr,s.DynamicProperties.createProp([o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.LOCALE]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.MODALITY]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.DOMAIN]],[o.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[s.Axis.STYLE]]))}static fromPreference(e){const t=e.split(":"),n={},r=u.getProperties(),i=Object.keys(r);for(let e,o=0;e=t[o];o++){const t=e.split("_");if(-1===i.indexOf(t[0]))continue;const o=t[1];o&&o!==l.AUTO&&-1!==r[t[0]].indexOf(o)&&(n[t[0]]=t[1])}return n}static toPreference(e){const t=Object.keys(e),n=[];for(let r=0;rs?-1:o0&&t<20&&n>0&&n<11}function _(e){return i.default.getInstance().style===e}function C(e){if(!e.hasAttribute("annotation"))return!1;const t=e.getAttribute("annotation");return!!/clearspeak:simple$|clearspeak:simple;/.exec(t)}function T(e){if(C(e))return!0;if("subscript"!==e.tagName)return!1;const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes,n=t[1];return"identifier"===t[0].tagName&&(v(n)||"infixop"===n.tagName&&n.hasAttribute("role")&&"implicit"===n.getAttribute("role")&&O(n))}function v(e){return"number"===e.tagName&&e.hasAttribute("role")&&"integer"===e.getAttribute("role")}function O(e){return o.evalXPath("children/*",e).every((e=>v(e)||"identifier"===e.tagName))}function M(e){return"text"===e.type||"punctuated"===e.type&&"text"===e.role&&E(e.childNodes[0])&&I(e.childNodes.slice(1))||"identifier"===e.type&&"unit"===e.role||"infixop"===e.type&&("implicit"===e.role||"unit"===e.role)}function I(e){for(let t=0;t10?s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t):s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(t)},t.NESTING_DEPTH=null,t.nestingDepth=function(e){let n=0;const r=e.textContent,i="open"===e.getAttribute("role")?0:1;let o=e.parentNode;for(;o;)"fenced"===o.tagName&&o.childNodes[0].childNodes[i].textContent===r&&n++,o=o.parentNode;return t.NESTING_DEPTH=n>1?s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(n):"",t.NESTING_DEPTH},t.matchingFences=function(e){const t=e.previousSibling;let n,r;return t?(n=t,r=e):(n=e,r=e.nextSibling),r&&(0,h.isMatchingFence)(n.textContent,r.textContent)?[e]:[]},t.insertNesting=L,c.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection("insertNesting",L),t.fencedArguments=function(e){const t=r.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes),n=o.evalXPath("../../children/*",e),i=t.indexOf(e);return x(n[i])||x(n[i+1])?[e]:[]},t.simpleArguments=function(e){const t=r.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes),n=o.evalXPath("../../children/*",e),i=t.indexOf(e);return R(n[i])&&n[i+1]&&(R(n[i+1])||"root"===n[i+1].tagName||"sqrt"===n[i+1].tagName||"superscript"===n[i+1].tagName&&n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0]&&("number"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName||"identifier"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].tagName)&&("2"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent||"3"===n[i+1].childNodes[0].childNodes[1].textContent))?[e]:[]},t.simpleFactor_=R,t.fencedFactor_=x,t.layoutFactor_=P,t.wordOrdinal=function(e){return s.LOCALE.NUMBERS.wordOrdinal(parseInt(e.textContent,10))}},5659:function(e,t,n){var r=this&&this.__awaiter||function(e,t,n,r){return new(n||(n=Promise))((function(i,o){function s(e){try{c(r.next(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function a(e){try{c(r.throw(e))}catch(e){o(e)}}function c(e){var t;e.done?i(e.value):(t=e.value,t instanceof n?t:new n((function(e){e(t)}))).then(s,a)}c((r=r.apply(e,t||[])).next())}))};Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.loadAjax=t.loadFileSync=t.loadFile=t.parseMaps=t.retrieveFiles=t.standardLoader=t.loadLocale=t.store=void 0;const i=n(9501),o=n(4886),s=n(4998),a=n(7129),c=n(4755),l=n(8310),u=n(4161),d=n(6060),h=n(2371),p=n(650);t.store=u;const f={functions:u.addFunctionRules,symbols:u.addSymbolRules,units:u.addUnitRules,si:u.setSiPrefixes};let m=!1;function g(e=o.default.getInstance().locale){o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]||(o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!1,!1],function(e){if(o.default.getInstance().isIE&&o.default.getInstance().mode===s.Mode.HTTP)return void y(e);b(e)}(e))}function S(){switch(o.default.getInstance().mode){case s.Mode.ASYNC:return A;case s.Mode.HTTP:return C;case s.Mode.SYNC:default:return _}}function b(e){const t=o.default.getInstance().customLoader?o.default.getInstance().customLoader:S(),n=new Promise((n=>{t(e).then((t=>{N(t),o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!0,!0],n(e)}),(t=>{o.EnginePromise.loaded[e]=[!0,!1],console.error(`Unable to load locale: ${e}`),o.default.getInstance().locale=o.default.getInstance().defaultLocale,n(e)}))}));o.EnginePromise.promises[e]=n}function N(e){E(JSON.parse(e))}function E(e,t){let n=!0;for(let r,i=0;r=Object.keys(e)[i];i++){const i=r.split("/");t&&t!==i[0]||("rules"===i[1]?d.SpeechRuleEngine.getInstance().addStore(e[r]):"messages"===i[1]?(0,h.completeLocale)(e[r]):(n&&(p.generate(i[0]),n=!1),e[r].forEach(f[i[1]])))}}function y(e,t){let n=t||1;i.mapsForIE?E(i.mapsForIE,e):n<=5&&setTimeout((()=>y(e,n++)).bind(this),300)}function A(e){const t=a.localePath(e);return new Promise(((e,n)=>{c.default.fs.readFile(t,"utf8",((t,r)=>{if(t)return n(t);e(r)}))}))}function _(e){const t=a.localePath(e);return new Promise(((e,n)=>{let r="{}";try{r=c.default.fs.readFileSync(t,"utf8")}catch(e){return n(e)}e(r)}))}function C(e){const t=a.localePath(e),n=new XMLHttpRequest;return new Promise(((e,r)=>{n.onreadystatechange=function(){if(4===n.readyState){const t=n.status;0===t||t>=200&&t<400?e(n.responseText):r(t)}},n.open("GET",t,!0),n.send()}))}t.loadLocale=function(e=o.default.getInstance().locale){return r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return m||(g(l.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE),m=!0),o.EnginePromise.promises[l.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE].then((()=>r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){const t=o.default.getInstance().defaultLocale;return t?(g(t),o.EnginePromise.promises[t].then((()=>r(this,void 0,void 0,(function*(){return g(e),o.EnginePromise.promises[e]}))))):(g(e),o.EnginePromise.promises[e])}))))}))},t.standardLoader=S,t.retrieveFiles=b,t.parseMaps=N,t.loadFile=A,t.loadFileSync=_,t.loadAjax=C},3784:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.leftSubscriptBrief=t.leftSuperscriptBrief=t.leftSubscriptVerbose=t.leftSuperscriptVerbose=t.baselineBrief=t.baselineVerbose=void 0;const r=n(3269);t.baselineVerbose=function(e){return r.baselineVerbose(e).replace(/-$/,"")},t.baselineBrief=function(e){return r.baselineBrief(e).replace(/-$/,"")},t.leftSuperscriptVerbose=function(e){return r.superscriptVerbose(e).replace(/^exposant/,"exposant gauche")},t.leftSubscriptVerbose=function(e){return r.subscriptVerbose(e).replace(/^indice/,"indice gauche")},t.leftSuperscriptBrief=function(e){return r.superscriptBrief(e).replace(/^sup/,"sup gauche")},t.leftSubscriptBrief=function(e){return r.subscriptBrief(e).replace(/^sub/,"sub gauche")}},4972:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.MathspeakRules=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(931),o=n(3784),s=n(3269),a=n(2110),c=n(7278),l=n(9771);t.MathspeakRules=function(){c.addStore(r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak","",{CQFspaceoutNumber:s.spaceoutNumber,CQFspaceoutIdentifier:s.spaceoutIdentifier,CSFspaceoutText:s.spaceoutText,CSFopenFracVerbose:s.openingFractionVerbose,CSFcloseFracVerbose:s.closingFractionVerbose,CSFoverFracVerbose:s.overFractionVerbose,CSFopenFracBrief:s.openingFractionBrief,CSFcloseFracBrief:s.closingFractionBrief,CSFopenFracSbrief:s.openingFractionSbrief,CSFcloseFracSbrief:s.closingFractionSbrief,CSFoverFracSbrief:s.overFractionSbrief,CSFvulgarFraction:a.vulgarFraction,CQFvulgarFractionSmall:s.isSmallVulgarFraction,CSFopenRadicalVerbose:s.openingRadicalVerbose,CSFcloseRadicalVerbose:s.closingRadicalVerbose,CSFindexRadicalVerbose:s.indexRadicalVerbose,CSFopenRadicalBrief:s.openingRadicalBrief,CSFcloseRadicalBrief:s.closingRadicalBrief,CSFindexRadicalBrief:s.indexRadicalBrief,CSFopenRadicalSbrief:s.openingRadicalSbrief,CSFindexRadicalSbrief:s.indexRadicalSbrief,CQFisSmallRoot:s.smallRoot,CSFsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFbaselineVerbose:s.baselineVerbose,CSFbaselineBrief:s.baselineBrief,CSFleftsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFleftsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFrightsuperscriptVerbose:s.superscriptVerbose,CSFrightsubscriptVerbose:s.subscriptVerbose,CSFleftsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFleftsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFrightsuperscriptBrief:s.superscriptBrief,CSFrightsubscriptBrief:s.subscriptBrief,CSFunderscript:s.nestedUnderscript,CSFoverscript:s.nestedOverscript,CSFendscripts:s.endscripts,CTFordinalCounter:a.ordinalCounter,CTFwordCounter:a.wordCounter,CTFcontentIterator:i.contentIterator,CQFdetIsSimple:s.determinantIsSimple,CSFRemoveParens:s.removeParens,CQFresetNesting:s.resetNestingDepth,CGFbaselineConstraint:s.generateBaselineConstraint,CGFtensorRules:s.generateTensorRules}),c.addStore("es.speech.mathspeak",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CTFunitMultipliers:l.unitMultipliers,CQFoneLeft:l.oneLeft}),c.addStore("fr.speech.mathspeak",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CSFbaselineVerbose:o.baselineVerbose,CSFbaselineBrief:o.baselineBrief,CSFleftsuperscriptVerbose:o.leftSuperscriptVerbose,CSFleftsubscriptVerbose:o.leftSubscriptVerbose,CSFleftsuperscriptBrief:o.leftSuperscriptBrief,CSFleftsubscriptBrief:o.leftSubscriptBrief})}},3269:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.smallRoot=t.generateTensorRules=t.removeParens=t.generateBaselineConstraint=t.determinantIsSimple=t.nestedOverscript=t.endscripts=t.overscoreNestingDepth=t.nestedUnderscript=t.underscoreNestingDepth=t.indexRadicalSbrief=t.openingRadicalSbrief=t.indexRadicalBrief=t.closingRadicalBrief=t.openingRadicalBrief=t.indexRadicalVerbose=t.closingRadicalVerbose=t.openingRadicalVerbose=t.getRootIndex=t.nestedRadical=t.radicalNestingDepth=t.baselineBrief=t.baselineVerbose=t.superscriptBrief=t.superscriptVerbose=t.subscriptBrief=t.subscriptVerbose=t.nestedSubSuper=t.isSmallVulgarFraction=t.overFractionSbrief=t.closingFractionSbrief=t.openingFractionSbrief=t.closingFractionBrief=t.openingFractionBrief=t.overFractionVerbose=t.closingFractionVerbose=t.openingFractionVerbose=t.nestedFraction=t.fractionNestingDepth=t.computeNestingDepth_=t.containsAttr=t.getNestingDepth=t.resetNestingDepth=t.nestingBarriers=t.spaceoutIdentifier=t.spaceoutNumber=t.spaceoutNodes=t.spaceoutText=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(4524),a=n(7793);let c={};function l(e,t){const n=Array.from(e.textContent),r=[],i=a.default.getInstance(),o=e.ownerDocument;for(let e,s=0;e=n[s];s++){const n=i.getNodeFactory().makeLeafNode(e,"unknown"),s=i.identifierNode(n,"unknown","");t(s),r.push(s.xml(o))}return r}function u(e,n,o,s,a,l){s=s||t.nestingBarriers,a=a||{},l=l||function(e){return!1};const u=i.serializeXml(n);if(c[e]||(c[e]={}),c[e][u])return c[e][u];if(l(n)||o.indexOf(n.tagName)<0)return 0;const d=h(n,o,r.setdifference(s,o),a,l,0);return c[e][u]=d,d}function d(e,t){if(!e.attributes)return!1;const n=i.toArray(e.attributes);for(let e,r=0;e=n[r];r++)if(t[e.nodeName]===e.nodeValue)return!0;return!1}function h(e,t,n,r,o,s){if(o(e)||n.indexOf(e.tagName)>-1||d(e,r))return s;if(t.indexOf(e.tagName)>-1&&s++,!e.childNodes||0===e.childNodes.length)return s;const a=i.toArray(e.childNodes);return Math.max.apply(null,a.map((function(e){return h(e,t,n,r,o,s)})))}function p(e){return u("fraction",e,["fraction"],t.nestingBarriers,{},s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth)}function f(e,t,n){const r=p(e),i=Array(r).fill(t);return n&&i.push(n),i.join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_FRAC)}function m(e,t,n){for(;e.parentNode;){const r=e.parentNode,i=r.parentNode;if(!i)break;const o=e.getAttribute&&e.getAttribute("role");("subscript"===i.tagName&&e===r.childNodes[1]||"tensor"===i.tagName&&o&&("leftsub"===o||"rightsub"===o))&&(t=n.sub+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_SUBSUPER+t),("superscript"===i.tagName&&e===r.childNodes[1]||"tensor"===i.tagName&&o&&("leftsuper"===o||"rightsuper"===o))&&(t=n.sup+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.regexp.JOINER_SUBSUPER+t),e=i}return t.trim()}function g(e){return u("radical",e,["sqrt","root"],t.nestingBarriers,{})}function S(e,t,n){const r=g(e),i=b(e);return n=i?s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineRootIndex(n,i):n,1===r?n:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedRadical(t,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(r-1),n)}function b(e){const t="sqrt"===e.tagName?"2":o.evalXPath("children/*[1]",e)[0].textContent.trim();return s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MSroots[t]||""}function N(e){return u("underscore",e,["underscore"],t.nestingBarriers,{},(function(e){return e.tagName&&"underscore"===e.tagName&&"underaccent"===e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role")}))}function E(e){return u("overscore",e,["overscore"],t.nestingBarriers,{},(function(e){return e.tagName&&"overscore"===e.tagName&&"overaccent"===e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("role")}))}t.spaceoutText=function(e){return Array.from(e.textContent).join(" ")},t.spaceoutNodes=l,t.spaceoutNumber=function(e){return l(e,(function(e){e.textContent.match(/\W/)||(e.type="number")}))},t.spaceoutIdentifier=function(e){return l(e,(function(e){e.font="unknown",e.type="identifier"}))},t.nestingBarriers=["cases","cell","integral","line","matrix","multiline","overscore","root","row","sqrt","subscript","superscript","table","underscore","vector"],t.resetNestingDepth=function(e){return c={},[e]},t.getNestingDepth=u,t.containsAttr=d,t.computeNestingDepth_=h,t.fractionNestingDepth=p,t.nestedFraction=f,t.openingFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.START,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_V)},t.closingFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.END,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_V)},t.overFractionVerbose=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER)},t.openingFractionBrief=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.START,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_B)},t.closingFractionBrief=function(e){return f(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.END,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_B)},t.openingFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_S:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_S)},t.closingFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDFRAC:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDFRAC)},t.overFractionSbrief=function(e){const t=p(e);return 1===t?s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER:s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.combineNestedFraction(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_FRAC,s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.radicalNestDepth(t-1),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER)},t.isSmallVulgarFraction=function(e){return s.LOCALE.FUNCTIONS.fracNestDepth(e)?[e]:[]},t.nestedSubSuper=m,t.subscriptVerbose=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUBSCRIPT,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.subscriptBrief=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.superscriptVerbose=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPERSCRIPT,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.superscriptBrief=function(e){return m(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})},t.baselineVerbose=function(e){const t=m(e,"",{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB});return t?t.replace(new RegExp(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB+"$"),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUBSCRIPT).replace(new RegExp(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER+"$"),s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPERSCRIPT):s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.BASELINE},t.baselineBrief=function(e){return m(e,"",{sup:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUP,sub:s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB})||s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.BASE},t.radicalNestingDepth=g,t.nestedRadical=S,t.getRootIndex=b,t.openingRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadicalVerbose=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.openingRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadicalBrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.openingRadicalSbrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOT)},t.indexRadicalSbrief=function(e){return S(e,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NEST_ROOT,s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.INDEX)},t.underscoreNestingDepth=N,t.nestedUnderscript=function(e){const t=N(e);return Array(t).join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.UNDER)+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.UNDERSCRIPT},t.overscoreNestingDepth=E,t.endscripts=function(e){return s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDSCRIPTS},t.nestedOverscript=function(e){const t=E(e);return Array(t).join(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.OVER)+s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.OVERSCRIPT},t.determinantIsSimple=function(e){if("matrix"!==e.tagName||"determinant"!==e.getAttribute("role"))return[];const t=o.evalXPath("children/row/children/cell/children/*",e);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if("number"!==e.tagName){if("identifier"===e.tagName){const t=e.getAttribute("role");if("latinletter"===t||"greekletter"===t||"otherletter"===t)continue}return[]}return[e]},t.generateBaselineConstraint=function(){const e=e=>e.map((e=>"ancestor::"+e)),t=e=>"not("+e+")",n=t(e(["subscript","superscript","tensor"]).join(" or ")),r=e(["relseq","multrel"]),i=e(["fraction","punctuation","fenced","sqrt","root"]);let o=[];for(let e,t=0;e=i[t];t++)o=o.concat(r.map((function(t){return e+"/"+t})));return[["ancestor::*/following-sibling::*",n,t(o.join(" | "))].join(" and ")]},t.removeParens=function(e){if(!e.childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes.length)return"";const t=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent;return t.match(/^\(.+\)$/)?t.slice(1,-1):t};const y=new Map([[3,"CSFleftsuperscript"],[4,"CSFleftsubscript"],[2,"CSFbaseline"],[1,"CSFrightsubscript"],[0,"CSFrightsuperscript"]]),A=new Map([[4,2],[3,3],[2,1],[1,4],[0,5]]);function _(e){const t=[];let n="",r="",i=parseInt(e,2);for(let e=0;e<5;e++){const o="children/*["+A.get(e)+"]";if(1&i){const t=y.get(e%5);n="[t] "+t+"Verbose; [n] "+o+";"+n,r="[t] "+t+"Brief; [n] "+o+";"+r}else t.unshift("name("+o+')="empty"');i>>=1}return[t,n,r]}t.generateTensorRules=function(e,t=!0){const n=["11111","11110","11101","11100","10111","10110","10101","10100","01111","01110","01101","01100"];for(let r,i=0;r=n[i];i++){let n="tensor"+r,[i,o,s]=_(r);e.defineRule(n,"default",o,"self::tensor",...i),t&&(e.defineRule(n,"brief",s,"self::tensor",...i),e.defineRule(n,"sbrief",s,"self::tensor",...i));const a=y.get(2);o+="; [t]"+a+"Verbose",s+="; [t]"+a+"Brief",n+="-baseline";const c="((.//*[not(*)])[last()]/@id)!=(((.//ancestor::fraction|ancestor::root|ancestor::sqrt|ancestor::cell|ancestor::line|ancestor::stree)[1]//*[not(*)])[last()]/@id)";e.defineRule(n,"default",o,"self::tensor",c,...i),t&&(e.defineRule(n,"brief",s,"self::tensor",c,...i),e.defineRule(n,"sbrief",s,"self::tensor",c,...i))}},t.smallRoot=function(e){let t=Object.keys(s.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MSroots).length;if(!t)return[];if(t++,!e.childNodes||0===e.childNodes.length||!e.childNodes[0].childNodes)return[];const n=e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].textContent;if(!/^\d+$/.test(n))return[];const r=parseInt(n,10);return r>1&&r<=t?[e]:[]}},9570:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.implicitIterator=t.relationIterator=t.propagateNumber=t.checkParent_=t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_=t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_=t.enlargeFence=t.indexRadical=t.closingRadical=t.openingRadical=t.radicalNestingDepth=t.nestedRadical=t.overBevelledFraction=t.overFraction=t.closingFraction=t.openingFraction=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(6671),o=n(5024),s=n(1058),a=n(4886),c=n(4036),l=n(241),u=n(4524),d=n(3269);function h(e,t){const n=p(e);return 1===n?t:new Array(n).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.NESTED)+t}function p(e,t){const n=t||0;return e.parentNode?p(e.parentNode,"root"===e.tagName||"sqrt"===e.tagName?n+1:n):n}function f(e){const t="\u2820";if(1===e.length)return t+e;const n=e.split("");return n.every((function(e){return"\u2833"===e}))?t+n.join(t):e.slice(0,-1)+t+e.slice(-1)}function m(e,n){const r=e.parent;if(!r)return!1;const i=r.type;return-1!==t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_.indexOf(i)||"prefixop"===i&&"negative"===r.role&&!n.script||"prefixop"===i&&"geometry"===r.role||!("punctuated"!==i||n.enclosed&&"text"!==r.role)}function g(e,n){return e.childNodes.length?(-1!==t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_.indexOf(e.type)&&(n.script=!0),"fenced"===e.type?(n.number=!1,n.enclosed=!0,["",n]):(m(e,n)&&(n.number=!0,n.enclosed=!1),["",n])):(m(e,n)&&(n.number=!0,n.script=!1,n.enclosed=!1),[n.number?"number":"",{number:!1,enclosed:n.enclosed,script:n.script}])}t.openingFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_START},t.closingFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_END},t.overFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_OVER},t.overBevelledFraction=function(e){const t=d.fractionNestingDepth(e);return new Array(t).join(u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_REPEAT)+"\u2838"+u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRACTION_OVER},t.nestedRadical=h,t.radicalNestingDepth=p,t.openingRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.STARTROOT)},t.closingRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ENDROOT)},t.indexRadical=function(e){return h(e,u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.ROOTINDEX)},t.enlargeFence=f,s.Grammar.getInstance().setCorrection("enlargeFence",f),t.NUMBER_PROPAGATORS_=["multirel","relseq","appl","row","line"],t.NUMBER_INHIBITORS_=["subscript","superscript","overscore","underscore"],t.checkParent_=m,t.propagateNumber=g,(0,c.register)(new l.SemanticVisitor("nemeth","number",g,{number:!0})),t.relationIterator=function(e,t){const n=e.slice(0);let s,c=!0;return s=e.length>0?o.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=s.shift(),o=n.shift(),l=n[0],h=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!e)return h;const p=o?d.nestedSubSuper(o,"",{sup:u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUPER,sub:u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.SUB}):"",f=o&&"EMPTY"!==i.tagName(o)||c&&e.parentNode.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode.previousSibling?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"+p},{})]:[],m=l&&"EMPTY"!==i.tagName(l)||!s.length&&e.parentNode.parentNode&&e.parentNode.parentNode.nextSibling?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"},{})]:[],g=a.default.evaluateNode(e);return c=!1,h.concat(f,g,m)}},t.implicitIterator=function(e,t){const n=e.slice(0);let s;return s=e.length>0?o.evalXPath("../../content/*",e[0]):[],function(){const e=n.shift(),o=n[0],a=s.shift(),c=t?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:t},{translate:!0})]:[];if(!a)return c;const l=e&&"NUMBER"===i.tagName(e),u=o&&"NUMBER"===i.tagName(o);return c.concat(l&&u&&"space"===a.getAttribute("role")?[r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:"\u2800"},{})]:[])}}},2110:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.ordinalPosition=t.vulgarFraction=t.wordCounter=t.ordinalCounter=void 0;const r=n(1930),i=n(6671),o=n(4524),s=n(9385);t.ordinalCounter=function(e,t){let n=0;return function(){return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(++n)+" "+t}},t.wordCounter=function(e,t){let n=0;return function(){return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToOrdinal(++n,!1)+" "+t}},t.vulgarFraction=function(e){const t=(0,s.convertVulgarFraction)(e,o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.MS.FRAC_OVER);return t.convertible&&t.enumerator&&t.denominator?[new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToWords(t.enumerator),{extid:e.childNodes[0].childNodes[0].getAttribute("extid"),separator:""}),new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.vulgarSep,{separator:""}),new r.Span(o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numberToOrdinal(t.denominator,1!==t.enumerator),{extid:e.childNodes[0].childNodes[1].getAttribute("extid")})]:[new r.Span(t.content||"",{extid:e.getAttribute("extid")})]},t.ordinalPosition=function(e){const t=i.toArray(e.parentNode.childNodes);return o.LOCALE.NUMBERS.numericOrdinal(t.indexOf(e)+1).toString()}},3724:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.BrailleRules=t.OtherRules=t.PrefixRules=void 0;const r=n(8310),i=n(931),o=n(3269),s=n(9570),a=n(2110),c=n(7278);t.PrefixRules=function(){c.addStore("en.prefix.default","",{CSFordinalPosition:a.ordinalPosition})},t.OtherRules=function(){c.addStore("en.speech.chromevox","",{CTFnodeCounter:i.nodeCounter,CTFcontentIterator:i.contentIterator}),c.addStore("en.speech.emacspeak","en.speech.chromevox",{CQFvulgarFractionSmall:o.isSmallVulgarFraction,CSFvulgarFraction:a.vulgarFraction})},t.BrailleRules=function(){c.addStore("nemeth.braille.default",r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE+".speech.mathspeak",{CSFopenFraction:s.openingFraction,CSFcloseFraction:s.closingFraction,CSFoverFraction:s.overFraction,CSFoverBevFraction:s.overBevelledFraction,CSFopenRadical:s.openingRadical,CSFcloseRadical:s.closingRadical,CSFindexRadical:s.indexRadical,CSFsubscript:o.subscriptVerbose,CSFsuperscript:o.superscriptVerbose,CSFbaseline:o.baselineVerbose,CGFtensorRules:e=>o.generateTensorRules(e,!1),CTFrelationIterator:s.relationIterator,CTFimplicitIterator:s.implicitIterator})}},9805:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.init=t.INIT_=void 0;const r=n(127),i=n(4972),o=n(3724);t.INIT_=!1,t.init=function(){t.INIT_||((0,i.MathspeakRules)(),(0,r.ClearspeakRules)(),(0,o.PrefixRules)(),(0,o.OtherRules)(),(0,o.BrailleRules)(),t.INIT_=!0)}},7278:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getStore=t.addStore=t.funcStore=void 0;const r=n(8310);t.funcStore=new Map,t.addStore=function(e,n,r){const i={};if(n){const e=t.funcStore.get(n)||{};Object.assign(i,e)}t.funcStore.set(e,Object.assign(i,r))},t.getStore=function(e,n,i){return t.funcStore.get([e,n,i].join("."))||t.funcStore.get([r.DynamicCstr.DEFAULT_VALUES[r.Axis.LOCALE],n,i].join("."))||t.funcStore.get([r.DynamicCstr.BASE_LOCALE,n,i].join("."))||{}}},9771:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.oneLeft=t.leftMostUnit=t.rightMostUnit=t.unitMultipliers=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(5024),o=n(4524);t.unitMultipliers=function(e,t){const n=e;let i=0;return function(){const e=r.AuditoryDescription.create({text:a(n[i])&&c(n[i+1])?o.LOCALE.MESSAGES.unitTimes:""},{});return i++,[e]}};const s=["superscript","subscript","overscore","underscore"];function a(e){for(;e;){if("unit"===e.getAttribute("role"))return!0;const t=e.tagName,n=i.evalXPath("children/*",e);e=-1!==s.indexOf(t)?n[0]:n[n.length-1]}return!1}function c(e){for(;e;){if("unit"===e.getAttribute("role"))return!0;e=i.evalXPath("children/*",e)[0]}return!1}t.rightMostUnit=a,t.leftMostUnit=c,t.oneLeft=function(e){for(;e;){if("number"===e.tagName&&"1"===e.textContent)return[e];if("infixop"!==e.tagName||"multiplication"!==e.getAttribute("role")&&"implicit"!==e.getAttribute("role"))return[];e=i.evalXPath("children/*",e)[0]}return[]}},4660:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.AbstractWalker=void 0;const r=n(4148),i=n(4253),o=n(6671),s=n(4998),a=n(985),c=n(6988),l=n(8171),u=n(4524),d=n(1058),h=n(7984),p=n(7317),f=n(144),m=n(3955),g=n(5658),S=n(1848),b=n(8119),N=n(8835),E=n(5024);class y{constructor(e,t,n,r){this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.modifier=!1,this.keyMapping=new Map([[c.KeyCode.UP,this.up.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.DOWN,this.down.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.RIGHT,this.right.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.LEFT,this.left.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.TAB,this.repeat.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.DASH,this.expand.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.SPACE,this.depth.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.HOME,this.home.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.X,this.summary.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.Z,this.detail.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.V,this.virtualize.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.P,this.previous.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.U,this.undo.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.LESS,this.previousRules.bind(this)],[c.KeyCode.GREATER,this.nextRules.bind(this)]]),this.cursors=[],this.xml_=null,this.rebuilt_=null,this.focus_=null,this.active_=!1,this.node.id?this.id=this.node.id:this.node.hasAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR)?this.id=this.node.getAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR):(this.node.setAttribute(y.SRE_ID_ATTR,y.ID_COUNTER.toString()),this.id=y.ID_COUNTER++),this.rootNode=N.getSemanticRoot(e),this.rootId=this.rootNode.getAttribute(l.Attribute.ID),this.xmlString_=r,this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.ENTER}getXml(){return this.xml_||(this.xml_=o.parseInput(this.xmlString_)),this.xml_}getRebuilt(){return this.rebuilt_||this.rebuildStree(),this.rebuilt_}isActive(){return this.active_}activate(){this.isActive()||(this.generator.start(),this.toggleActive_())}deactivate(){this.isActive()&&(b.WalkerState.setState(this.id,this.primaryId()),this.generator.end(),this.toggleActive_())}getFocus(e=!1){return this.focus_||(this.focus_=this.singletonFocus(this.rootId)),e&&this.updateFocus(),this.focus_}setFocus(e){this.focus_=e}getDepth(){return this.levels.depth()-1}isSpeech(){return this.generator.modality===l.Attribute.SPEECH}focusDomNodes(){return this.getFocus().getDomNodes()}focusSemanticNodes(){return this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes()}speech(){const e=this.focusDomNodes();if(!e.length)return"";const t=this.specialMove();if(null!==t)return t;switch(this.moved){case b.WalkerMoves.DEPTH:return this.depth_();case b.WalkerMoves.SUMMARY:return this.summary_();case b.WalkerMoves.DETAIL:return this.detail_();default:{const t=[],n=this.focusSemanticNodes();for(let r=0,i=e.length;r0}restoreState(){if(!this.highlighter)return;const e=b.WalkerState.getState(this.id);if(!e)return;let t=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict[e];const n=[];for(;t;)n.push(t.id),t=t.parent;for(n.pop();n.length>0;){this.down();const e=n.pop(),t=this.findFocusOnLevel(e);if(!t)break;this.setFocus(t)}this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.ENTER}updateFocus(){this.setFocus(g.Focus.factory(this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes().map((e=>e.id.toString())),this.getRebuilt(),this.node))}rebuildStree(){this.rebuilt_=new S.RebuildStree(this.getXml()),this.rootId=this.rebuilt_.stree.root.id.toString(),this.generator.setRebuilt(this.rebuilt_),this.skeleton=h.SemanticSkeleton.fromTree(this.rebuilt_.stree),this.skeleton.populate(),this.focus_=this.singletonFocus(this.rootId),this.levels=this.initLevels(),f.connectMactions(this.node,this.getXml(),this.rebuilt_.xml)}previousLevel(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary();return e?N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.PARENT):this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().parent.id.toString()}nextLevel(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary();let t,n;if(e){t=N.splitAttribute(N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.CHILDREN)),n=N.splitAttribute(N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.CONTENT));const r=N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.TYPE),i=N.getAttribute(e,l.Attribute.ROLE);return this.combineContentChildren(r,i,n,t)}const r=e=>e.id.toString(),i=this.getRebuilt().nodeDict[this.primaryId()];return t=i.childNodes.map(r),n=i.contentNodes.map(r),0===t.length?[]:this.combineContentChildren(i.type,i.role,n,t)}singletonFocus(e){this.getRebuilt();const t=this.retrieveVisuals(e);return this.focusFromId(e,t)}retrieveVisuals(e){if(!this.skeleton)return[e];const t=parseInt(e,10),n=this.skeleton.subtreeNodes(t);if(!n.length)return[e];n.unshift(t);const r={},i=[];E.updateEvaluator(this.getXml());for(const e of n)r[e]||(i.push(e.toString()),r[e]=!0,this.subtreeIds(e,r));return i}subtreeIds(e,t){const n=E.evalXPath(`//*[@data-semantic-id="${e}"]`,this.getXml());E.evalXPath("*//@data-semantic-id",n[0]).forEach((e=>t[parseInt(e.textContent,10)]=!0))}focusFromId(e,t){return g.Focus.factory(e,t,this.getRebuilt(),this.node)}summary(){return this.moved=this.isSpeech()?b.WalkerMoves.SUMMARY:b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone()}detail(){return this.moved=this.isSpeech()?b.WalkerMoves.DETAIL:b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone()}specialMove(){return null}virtualize(e){return this.cursors.push({focus:this.getFocus(),levels:this.levels,undo:e||!this.cursors.length}),this.levels=this.levels.clone(),this.getFocus().clone()}previous(){const e=this.cursors.pop();return e?(this.levels=e.levels,e.focus):this.getFocus()}undo(){let e;do{e=this.cursors.pop()}while(e&&!e.undo);return e?(this.levels=e.levels,e.focus):this.getFocus()}update(e){this.generator.setOptions(e),(0,a.setup)(e).then((()=>p.generator("Tree").getSpeech(this.node,this.getXml())))}nextRules(){const e=this.generator.getOptions();return"speech"!==e.modality?this.getFocus():(s.DOMAIN_TO_STYLES[e.domain]=e.style,e.domain="mathspeak"===e.domain?"clearspeak":"mathspeak",e.style=s.DOMAIN_TO_STYLES[e.domain],this.update(e),this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone())}nextStyle(e,t){if("mathspeak"===e){const e=["default","brief","sbrief"],n=e.indexOf(t);return-1===n?t:n>=e.length-1?e[0]:e[n+1]}if("clearspeak"===e){const e=m.ClearspeakPreferences.getLocalePreferences().en;if(!e)return"default";const n=m.ClearspeakPreferences.relevantPreferences(this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary()),r=m.ClearspeakPreferences.findPreference(t,n),i=e[n].map((function(e){return e.split("_")[1]})),o=i.indexOf(r);if(-1===o)return t;const s=o>=i.length-1?i[0]:i[o+1];return m.ClearspeakPreferences.addPreference(t,n,s)}return t}previousRules(){const e=this.generator.getOptions();return"speech"!==e.modality?this.getFocus():(e.style=this.nextStyle(e.domain,e.style),this.update(e),this.moved=b.WalkerMoves.REPEAT,this.getFocus().clone())}refocus(){let e,t=this.getFocus();for(;!t.getNodes().length;){e=this.levels.peek();const n=this.up();if(!n)break;this.setFocus(n),t=this.getFocus(!0)}this.levels.push(e),this.setFocus(t)}toggleActive_(){this.active_=!this.active_}mergePrefix_(e,t=[]){const n=this.isSpeech()?this.prefix_():"";n&&e.unshift(n);const r=this.isSpeech()?this.postfix_():"";return r&&e.push(r),i.finalize(i.merge(t.concat(e)))}prefix_(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomNodes(),t=this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes();return e[0]?N.getAttribute(e[0],l.Attribute.PREFIX):f.retrievePrefix(t[0])}postfix_(){const e=this.getFocus().getDomNodes();return e[0]?N.getAttribute(e[0],l.Attribute.POSTFIX):""}depth_(){const e=d.Grammar.getInstance().getParameter("depth");d.Grammar.getInstance().setParameter("depth",!0);const t=this.getFocus().getDomPrimary(),n=this.expandable(t)?u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.EXPANDABLE:this.collapsible(t)?u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.COLLAPSIBLE:"",o=u.LOCALE.MESSAGES.navigate.LEVEL+" "+this.getDepth(),s=this.getFocus().getSemanticNodes(),a=f.retrievePrefix(s[0]),c=[new r.AuditoryDescription({text:o,personality:{}}),new r.AuditoryDescription({text:a,personality:{}}),new r.AuditoryDescription({text:n,personality:{}})];return d.Grammar.getInstance().setParameter("depth",e),i.finalize(i.markup(c))}actionable_(e){const t=null==e?void 0:e.parentNode;return t&&this.highlighter.isMactionNode(t)?t:null}summary_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),t=this.getRebuilt().xml.getAttribute("id")===e?this.getRebuilt().xml:o.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",e)[0],n=f.retrieveSummary(t);return this.mergePrefix_([n])}detail_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary().id.toString(),t=this.getRebuilt().xml.getAttribute("id")===e?this.getRebuilt().xml:o.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",e)[0],n=t.getAttribute("alternative");t.removeAttribute("alternative");const r=f.computeMarkup(t),i=this.mergePrefix_([r]);return t.setAttribute("alternative",n),i}}t.AbstractWalker=y,y.ID_COUNTER=0,y.SRE_ID_ATTR="sre-explorer-id"},4296:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.DummyWalker=void 0;const r=n(4660);class i extends r.AbstractWalker{up(){return null}down(){return null}left(){return null}right(){return null}repeat(){return null}depth(){return null}home(){return null}getDepth(){return 0}initLevels(){return null}combineContentChildren(e,t,n,r){return[]}findFocusOnLevel(e){return null}}t.DummyWalker=i},5658:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.Focus=void 0;const r=n(8835);class i{constructor(e,t){this.nodes=e,this.primary=t,this.domNodes=[],this.domPrimary_=null,this.allNodes=[]}static factory(e,t,n,o){const s=e=>r.getBySemanticId(o,e),a=n.nodeDict,c=s(e),l=t.map(s),u=t.map((function(e){return a[e]})),d=new i(u,a[e]);return d.domNodes=l,d.domPrimary_=c,d.allNodes=i.generateAllVisibleNodes_(t,l,a,o),d}static generateAllVisibleNodes_(e,t,n,o){const s=e=>r.getBySemanticId(o,e);let a=[];for(let r=0,c=e.length;r=t.length?null:t[e]}depth(){return this.level_.length}clone(){const e=new n;return e.level_=this.level_.slice(0),e}toString(){let e="";for(let t,n=0;t=this.level_[n];n++)e+="\n"+t.map((function(e){return e.toString()}));return e}}t.Levels=n},1848:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.RebuildStree=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(8171),o=n(4020),s=n(4790),a=n(7793),c=n(7984),l=n(1784),u=n(8901),d=n(8835);class h{constructor(e){this.mathml=e,this.factory=new s.SemanticNodeFactory,this.nodeDict={},this.mmlRoot=d.getSemanticRoot(e),this.streeRoot=this.assembleTree(this.mmlRoot),this.stree=l.SemanticTree.fromNode(this.streeRoot,this.mathml),this.xml=this.stree.xml(),a.default.getInstance().setNodeFactory(this.factory)}static addAttributes(e,t,n){n&&1===t.childNodes.length&&t.childNodes[0].nodeType!==r.NodeType.TEXT_NODE&&u.addAttributes(e,t.childNodes[0]),u.addAttributes(e,t)}static textContent(e,t,n){if(!n&&t.textContent)return void(e.textContent=t.textContent);const r=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(t,i.Attribute.OPERATOR));r.length>1&&(e.textContent=r[1])}static isPunctuated(e){return!c.SemanticSkeleton.simpleCollapseStructure(e)&&e[1]&&c.SemanticSkeleton.contentCollapseStructure(e[1])}getTree(){return this.stree}assembleTree(e){const t=this.makeNode(e),n=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.CHILDREN)),r=d.splitAttribute(d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.CONTENT));if(h.addAttributes(t,e,!(n.length||r.length)),0===r.length&&0===n.length)return h.textContent(t,e),t;if(r.length>0){const e=d.getBySemanticId(this.mathml,r[0]);e&&h.textContent(t,e,!0)}t.contentNodes=r.map((e=>this.setParent(e,t))),t.childNodes=n.map((e=>this.setParent(e,t)));const o=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.COLLAPSED);return o?this.postProcess(t,o):t}makeNode(e){const t=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.TYPE),n=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ROLE),r=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.FONT),o=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ANNOTATION)||"",s=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.ID),a=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.EMBELLISHED),c=d.getAttribute(e,i.Attribute.FENCEPOINTER),l=this.createNode(parseInt(s,10));return l.type=t,l.role=n,l.font=r||"unknown",l.parseAnnotation(o),c&&(l.fencePointer=c),a&&(l.embellished=a),l}makePunctuation(e){const t=this.createNode(e);return t.updateContent((0,o.invisibleComma)()),t.role="dummy",t}makePunctuated(e,t,n){const r=this.createNode(t[0]);r.type="punctuated",r.embellished=e.embellished,r.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,r.role=n;const i=t.splice(1,1)[0].slice(1);r.contentNodes=i.map(this.makePunctuation.bind(this)),this.collapsedChildren_(t)}makeEmpty(e,t,n){const r=this.createNode(t);r.type="empty",r.embellished=e.embellished,r.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,r.role=n}makeIndex(e,t,n){if(h.isPunctuated(t))return this.makePunctuated(e,t,n),void(t=t[0]);c.SemanticSkeleton.simpleCollapseStructure(t)&&!this.nodeDict[t.toString()]&&this.makeEmpty(e,t,n)}postProcess(e,t){const n=c.SemanticSkeleton.fromString(t).array;if("subsup"===e.type){const t=this.createNode(n[1][0]);return t.type="subscript",t.role="subsup",e.type="superscript",t.embellished=e.embellished,t.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,this.makeIndex(e,n[1][2],"rightsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e}if("subscript"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsub"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("superscript"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("tensor"===e.type)return this.makeIndex(e,n[2],"leftsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[3],"leftsuper"),this.makeIndex(e,n[4],"rightsub"),this.makeIndex(e,n[5],"rightsuper"),this.collapsedChildren_(n),e;if("punctuated"===e.type){if(h.isPunctuated(n)){const t=n.splice(1,1)[0].slice(1);e.contentNodes=t.map(this.makePunctuation.bind(this))}return e}if("underover"===e.type){const t=this.createNode(n[1][0]);return"overaccent"===e.childNodes[1].role?(t.type="overscore",e.type="underscore"):(t.type="underscore",e.type="overscore"),t.role="underover",t.embellished=e.embellished,t.fencePointer=e.fencePointer,this.collapsedChildren_(n),e}return e}createNode(e){const t=this.factory.makeNode(e);return this.nodeDict[e.toString()]=t,t}collapsedChildren_(e){const t=e=>{const n=this.nodeDict[e[0]];n.childNodes=[];for(let r=1,i=e.length;rt.getSemanticPrimary().id===e))}}t.SemanticWalker=o},3531:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.SyntaxWalker=void 0;const r=n(1426),i=n(4660),o=n(1497);class s extends i.AbstractWalker{constructor(e,t,n,r){super(e,t,n,r),this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.levels=null,this.restoreState()}initLevels(){const e=new o.Levels;return e.push([this.primaryId()]),e}up(){super.up();const e=this.previousLevel();return e?(this.levels.pop(),this.singletonFocus(e)):null}down(){super.down();const e=this.nextLevel();if(0===e.length)return null;const t=this.singletonFocus(e[0]);return t&&this.levels.push(e),t}combineContentChildren(e,t,n,i){switch(e){case"relseq":case"infixop":case"multirel":return(0,r.interleaveLists)(i,n);case"prefixop":return n.concat(i);case"postfixop":return i.concat(n);case"matrix":case"vector":case"fenced":return i.unshift(n[0]),i.push(n[1]),i;case"cases":return i.unshift(n[0]),i;case"punctuated":return"text"===t?(0,r.interleaveLists)(i,n):i;case"appl":return[i[0],n[0],i[1]];case"root":return[i[1],i[0]];default:return i}}left(){super.left();const e=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId());if(null===e)return null;const t=this.levels.get(e-1);return t?this.singletonFocus(t):null}right(){super.right();const e=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId());if(null===e)return null;const t=this.levels.get(e+1);return t?this.singletonFocus(t):null}findFocusOnLevel(e){return this.singletonFocus(e.toString())}focusDomNodes(){return[this.getFocus().getDomPrimary()]}focusSemanticNodes(){return[this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary()]}}t.SyntaxWalker=s},4051:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.TableWalker=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(6988),o=n(3531),s=n(8119);class a extends o.SyntaxWalker{constructor(e,t,n,r){super(e,t,n,r),this.node=e,this.generator=t,this.highlighter=n,this.firstJump=null,this.key_=null,this.row_=0,this.currentTable_=null,this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.ZERO,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.ONE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.TWO,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.THREE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.FOUR,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.FIVE,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.SIX,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.SEVEN,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.EIGHT,this.jumpCell.bind(this)),this.keyMapping.set(i.KeyCode.NINE,this.jumpCell.bind(this))}move(e){this.key_=e;const t=super.move(e);return this.modifier=!1,t}up(){return this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.UP,this.eligibleCell_()?this.verticalMove_(!1):super.up()}down(){return this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.DOWN,this.eligibleCell_()?this.verticalMove_(!0):super.down()}jumpCell(){if(!this.isInTable_()||null===this.key_)return this.getFocus();if(this.moved===s.WalkerMoves.ROW){this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.CELL;const e=this.key_-i.KeyCode.ZERO;return this.isLegalJump_(this.row_,e)?this.jumpCell_(this.row_,e):this.getFocus()}const e=this.key_-i.KeyCode.ZERO;return e>this.currentTable_.childNodes.length?this.getFocus():(this.row_=e,this.moved=s.WalkerMoves.ROW,this.getFocus().clone())}undo(){const e=super.undo();return e===this.firstJump&&(this.firstJump=null),e}eligibleCell_(){const e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary();return this.modifier&&"cell"===e.type&&-1!==a.ELIGIBLE_CELL_ROLES.indexOf(e.role)}verticalMove_(e){const t=this.previousLevel();if(!t)return null;const n=this.getFocus(),r=this.levels.indexOf(this.primaryId()),i=this.levels.pop(),o=this.levels.indexOf(t),s=this.levels.get(e?o+1:o-1);if(!s)return this.levels.push(i),null;this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(s));const a=this.nextLevel();return a[r]?(this.levels.push(a),this.singletonFocus(a[r])):(this.setFocus(n),this.levels.push(i),null)}jumpCell_(e,t){this.firstJump?this.virtualize(!1):(this.firstJump=this.getFocus(),this.virtualize(!0));const n=this.currentTable_.id.toString();let r;do{r=this.levels.pop()}while(-1===r.indexOf(n));this.levels.push(r),this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(n)),this.levels.push(this.nextLevel());const i=this.currentTable_.childNodes[e-1];return this.setFocus(this.singletonFocus(i.id.toString())),this.levels.push(this.nextLevel()),this.singletonFocus(i.childNodes[t-1].id.toString())}isLegalJump_(e,t){const n=r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(this.getRebuilt().xml,"id",this.currentTable_.id.toString())[0];if(!n||n.hasAttribute("alternative"))return!1;const i=this.currentTable_.childNodes[e-1];if(!i)return!1;const o=r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(n,"id",i.id.toString())[0];return!(!o||o.hasAttribute("alternative"))&&!(!i||!i.childNodes[t-1])}isInTable_(){let e=this.getFocus().getSemanticPrimary();for(;e;){if(-1!==a.ELIGIBLE_TABLE_TYPES.indexOf(e.type))return this.currentTable_=e,!0;e=e.parent}return!1}}t.TableWalker=a,a.ELIGIBLE_CELL_ROLES=["determinant","rowvector","binomial","squarematrix","multiline","matrix","vector","cases","table"],a.ELIGIBLE_TABLE_TYPES=["multiline","matrix","vector","cases","table"]},8119:function(e,t){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.WalkerState=t.WalkerMoves=void 0,function(e){e.UP="up",e.DOWN="down",e.LEFT="left",e.RIGHT="right",e.REPEAT="repeat",e.DEPTH="depth",e.ENTER="enter",e.EXPAND="expand",e.HOME="home",e.SUMMARY="summary",e.DETAIL="detail",e.ROW="row",e.CELL="cell"}(t.WalkerMoves||(t.WalkerMoves={}));class n{static resetState(e){delete n.STATE[e]}static setState(e,t){n.STATE[e]=t}static getState(e){return n.STATE[e]}}t.WalkerState=n,n.STATE={}},907:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.walkerMapping_=t.walker=void 0;const r=n(4296),i=n(1937),o=n(3531),s=n(4051);t.walker=function(e,n,r,i,o){return(t.walkerMapping_[e.toLowerCase()]||t.walkerMapping_.dummy)(n,r,i,o)},t.walkerMapping_={dummy:(e,t,n,i)=>new r.DummyWalker(e,t,n,i),semantic:(e,t,n,r)=>new i.SemanticWalker(e,t,n,r),syntax:(e,t,n,r)=>new o.SyntaxWalker(e,t,n,r),table:(e,t,n,r)=>new s.TableWalker(e,t,n,r)}},8835:function(e,t,n){Object.defineProperty(t,"__esModule",{value:!0}),t.getBySemanticId=t.getSemanticRoot=t.getAttribute=t.splitAttribute=void 0;const r=n(6671),i=n(8171);t.splitAttribute=function(e){return e?e.split(/,/):[]},t.getAttribute=function(e,t){return e.getAttribute(t)},t.getSemanticRoot=function(e){if(e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.TYPE)&&!e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.PARENT))return e;const t=r.querySelectorAllByAttr(e,i.Attribute.TYPE);for(let e,n=0;e=t[n];n++)if(!e.hasAttribute(i.Attribute.PARENT))return e;return e},t.getBySemanticId=function(e,t){return e.getAttribute(i.Attribute.ID)===t?e:r.querySelectorAllByAttrValue(e,i.Attribute.ID,t)[0]}}},__webpack_module_cache__={};function __webpack_require__(e){var t=__webpack_module_cache__[e];if(void 0!==t)return t.exports;var n=__webpack_module_cache__[e]={exports:{}};return __webpack_modules__[e].call(n.exports,n,n.exports,__webpack_require__),n.exports}__webpack_require__.n=function(e){var t=e&&e.__esModule?function(){return e.default}:function(){return e};return __webpack_require__.d(t,{a:t}),t},__webpack_require__.d=function(e,t){for(var n in t)__webpack_require__.o(t,n)&&!__webpack_require__.o(e,n)&&Object.defineProperty(e,n,{enumerable:!0,get:t[n]})},__webpack_require__.g=function(){if("object"==typeof globalThis)return globalThis;try{return this||new Function("return this")()}catch(e){if("object"==typeof window)return window}}(),__webpack_require__.o=function(e,t){return Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,t)};var __webpack_exports__={};!function(){var e=__webpack_require__(8723),t=__webpack_require__(7306),n=__webpack_require__(8905),r=__webpack_require__.n(n);MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("a11y/sre",t.q,"a11y"),(0,e.r8)({_:{a11y:{sre:n}}});var i=__webpack_require__(1993);if(MathJax.startup){var o=i.GL.resolvePath("[sre]",!1);if("undefined"!=typeof window)window.SREfeature={json:o};else{try{o=MathJax.config.loader.require.resolve(o+"/base.json").replace(/\/base\.json$/,"")}catch(e){}__webpack_require__.g.SREfeature={json:o}}}MathJax.startup&&(("undefined"!=typeof window?window:__webpack_require__.g).SREfeature.custom=function(e){return r().preloadLocales(e)})}()})();��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692426889.043128
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/adaptors/liteDOM.js�����������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000054437�00000000000�021615� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,n,r,o,i,a,l,u,s={244:function(t,e,n){var r,o=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,n=1,r=arguments.length;n0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteElement=void 0;var a=function(t,e,a){var l,u;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===a&&(a=[]),this.kind=t,this.attributes=n({},e),this.children=o([],r(a),!1);try{for(var s=i(this.children),c=s.next();!c.done;c=s.next())c.value.parent=this}catch(t){l={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(u=s.return)&&u.call(s)}finally{if(l)throw l.error}}this.styles=null};e.LiteElement=a},6:function(t,e){var n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var n="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!n)return t;var r,o,i=n.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},r=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},l=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,n=e&&t[e],r=0;if(n)return n.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&r>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteParser=e.PATTERNS=void 0;var u,s=i(n(29)),c=n(946),p=n(735);!function(t){t.TAGNAME="[a-z][^\\s\\n>]*",t.ATTNAME="[a-z][^\\s\\n>=]*",t.VALUE="(?:'[^']*'|\"[^\"]*\"|[^\\s\\n]+)",t.VALUESPLIT="(?:'([^']*)'|\"([^\"]*)\"|([^\\s\\n]+))",t.SPACE="(?:\\s|\\n)+",t.OPTIONALSPACE="(?:\\s|\\n)*",t.ATTRIBUTE=t.ATTNAME+"(?:"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"="+t.OPTIONALSPACE+t.VALUE+")?",t.ATTRIBUTESPLIT="("+t.ATTNAME+")(?:"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"="+t.OPTIONALSPACE+t.VALUESPLIT+")?",t.TAG="(<(?:"+t.TAGNAME+"(?:"+t.SPACE+t.ATTRIBUTE+")*"+t.OPTIONALSPACE+"/?|/"+t.TAGNAME+"|!--[^]*?--|![^]*?)(?:>|$))",t.tag=new RegExp(t.TAG,"i"),t.attr=new RegExp(t.ATTRIBUTE,"i"),t.attrsplit=new RegExp(t.ATTRIBUTESPLIT,"i")}(u=e.PATTERNS||(e.PATTERNS={}));var f=function(){function t(){}return t.prototype.parseFromString=function(t,e,n){void 0===e&&(e="text/html"),void 0===n&&(n=null);for(var r=n.createDocument(),o=n.body(r),i=t.replace(/<\?.*?\?>/g,"").split(u.tag);i.length;){var a=i.shift(),l=i.shift();a&&this.addText(n,o,a),l&&">"===l.charAt(l.length-1)&&("!"===l.charAt(1)?this.addComment(n,o,l):o="/"===l.charAt(1)?this.closeTag(n,o,l):this.openTag(n,o,l,i))}return this.checkDocument(n,r),r},t.prototype.addText=function(t,e,n){return n=s.translate(n),t.append(e,t.text(n))},t.prototype.addComment=function(t,e,n){return t.append(e,new p.LiteComment(n))},t.prototype.closeTag=function(t,e,n){for(var r=n.slice(2,n.length-1).toLowerCase();t.parent(e)&&t.kind(e)!==r;)e=t.parent(e);return t.parent(e)},t.prototype.openTag=function(t,e,n,r){var o=this.constructor.PCDATA,i=this.constructor.SELF_CLOSING,a=n.match(/<(.*?)[\s\n>\/]/)[1].toLowerCase(),l=t.node(a),s=n.replace(/^<.*?[\s\n>]/,"").split(u.attrsplit);return(s.pop().match(/>$/)||s.length<5)&&(this.addAttributes(t,l,s),t.append(e,l),i[a]||n.match(/\/>$/)||(o[a]?this.handlePCDATA(t,l,a,r):e=l)),e},t.prototype.addAttributes=function(t,e,n){for(var r=this.constructor.CDATA_ATTR;n.length;){var o=a(n.splice(0,5),5),i=o[1],l=o[2],u=o[3],c=o[4],p=l||u||c||"";r[i]||(p=s.translate(p)),t.setAttribute(e,i,p)}},t.prototype.handlePCDATA=function(t,e,n,r){for(var o=[],i="",a="";r.length&&a!==i;)o.push(a),o.push(r.shift()),a=r.shift();t.append(e,t.text(o.join("")))},t.prototype.checkDocument=function(t,e){var n,r,o,i,a=this.getOnlyChild(t,t.body(e));if(a){try{for(var u=l(t.childNodes(t.body(e))),s=u.next();!s.done;s=u.next()){if((h=s.value)===a)break;h instanceof p.LiteComment&&h.value.match(/^":">":">".concat(u,""))},t.prototype.serializeInner=function(t,e,n){var r=this;return void 0===n&&(n=!1),this.constructor.PCDATA.hasOwnProperty(e.kind)?t.childNodes(e).map((function(e){return t.value(e)})).join(""):t.childNodes(e).map((function(e){var o=t.kind(e);return"#text"===o?r.protectHTML(t.value(e)):"#comment"===o?e.value:r.serialize(t,e,n)})).join("")},t.prototype.protectAttribute=function(t){return"string"!=typeof t&&(t=String(t)),t.replace(/"/g,""")},t.prototype.protectHTML=function(t){return t.replace(/&/g,"&").replace(//g,">")},t.SELF_CLOSING={area:!0,base:!0,br:!0,col:!0,command:!0,embed:!0,hr:!0,img:!0,input:!0,keygen:!0,link:!0,menuitem:!0,meta:!0,param:!0,source:!0,track:!0,wbr:!0},t.PCDATA={option:!0,textarea:!0,fieldset:!0,title:!0,style:!0,script:!0},t.CDATA_ATTR={style:!0,datafld:!0,datasrc:!0,href:!0,src:!0,longdesc:!0,usemap:!0,cite:!0,datetime:!0,action:!0,axis:!0,profile:!0,content:!0,scheme:!0},t}();e.LiteParser=f},735:function(t,e){var n,r=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteComment=e.LiteText=void 0;var o=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=""),this.value=t}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"#text"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t}();e.LiteText=o;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return r(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"#comment"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e}(o);e.LiteComment=i},492:function(t,e,n){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LiteWindow=void 0;var r=n(946),o=n(877),i=n(6),a=n(246),l=function(){this.DOMParser=a.LiteParser,this.NodeList=i.LiteList,this.HTMLCollection=i.LiteList,this.HTMLElement=r.LiteElement,this.DocumentFragment=i.LiteList,this.Document=o.LiteDocument,this.document=new o.LiteDocument};e.LiteWindow=l},250:function(t,e,n){var r,o=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var n in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,n)&&(t[n]=e[n])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,n=1,r=arguments.length;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[r++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},l=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var n="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!n)return t;var r,o,i=n.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(r=i.next()).done;)a.push(r.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{r&&!r.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},u=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,n){if(n||2===arguments.length)for(var r,o=0,i=e.length;o=0&&t.parent.children.splice(e,1),t.parent=null,t},e.prototype.replace=function(t,e){var n=this.childIndex(e);return n>=0&&(e.parent.children[n]=t,t.parent=e.parent,e.parent=null),e},e.prototype.clone=function(t){var e=this,n=new f.LiteElement(t.kind);return n.attributes=i({},t.attributes),n.children=t.children.map((function(t){if("#text"===t.kind)return new h.LiteText(t.value);if("#comment"===t.kind)return new h.LiteComment(t.value);var r=e.clone(t);return r.parent=n,r})),n},e.prototype.split=function(t,e){var n=new h.LiteText(t.value.slice(e));return t.value=t.value.slice(0,e),t.parent.children.splice(this.childIndex(t)+1,0,n),n.parent=t.parent,n},e.prototype.next=function(t){var e=t.parent;if(!e)return null;var n=this.childIndex(t)+1;return n>=0&&n=0?e.children[n]:null},e.prototype.firstChild=function(t){return t.children[0]},e.prototype.lastChild=function(t){return t.children[t.children.length-1]},e.prototype.childNodes=function(t){return u([],l(t.children),!1)},e.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return t.children[e]},e.prototype.kind=function(t){return t.kind},e.prototype.value=function(t){return"#text"===t.kind?t.value:"#comment"===t.kind?t.value.replace(/^$/,"$2"):""},e.prototype.textContent=function(t){var e=this;return t.children.reduce((function(t,n){return t+("#text"===n.kind?n.value:"#comment"===n.kind?"":e.textContent(n))}),"")},e.prototype.innerHTML=function(t){return this.parser.serializeInner(this,t)},e.prototype.outerHTML=function(t){return this.parser.serialize(this,t)},e.prototype.serializeXML=function(t){return this.parser.serialize(this,t,!0)},e.prototype.setAttribute=function(t,e,n,r){void 0===r&&(r=null),"string"!=typeof n&&(n=String(n)),r&&(e=r.replace(/.*\//,"")+":"+e.replace(/^.*:/,"")),t.attributes[e]=n,"style"===e&&(t.styles=null)},e.prototype.getAttribute=function(t,e){return t.attributes[e]},e.prototype.removeAttribute=function(t,e){delete t.attributes[e]},e.prototype.hasAttribute=function(t,e){return t.attributes.hasOwnProperty(e)},e.prototype.allAttributes=function(t){var e,n,r=t.attributes,o=[];try{for(var i=a(Object.keys(r)),l=i.next();!l.done;l=i.next()){var u=l.value;o.push({name:u,value:r[u]})}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return o},e.prototype.addClass=function(t,e){var n=(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /);n.find((function(t){return t===e}))||(n.push(e),t.attributes.class=n.join(" "))},e.prototype.removeClass=function(t,e){var n=(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /),r=n.findIndex((function(t){return t===e}));r>=0&&(n.splice(r,1),t.attributes.class=n.join(" "))},e.prototype.hasClass=function(t,e){return!!(t.attributes.class||"").split(/ /).find((function(t){return t===e}))},e.prototype.setStyle=function(t,e,n){t.styles||(t.styles=new v.Styles(this.getAttribute(t,"style"))),t.styles.set(e,n),t.attributes.style=t.styles.cssText},e.prototype.getStyle=function(t,e){if(!t.styles){var n=this.getAttribute(t,"style");if(!n)return"";t.styles=new v.Styles(n)}return t.styles.get(e)},e.prototype.allStyles=function(t){return this.getAttribute(t,"style")},e.prototype.insertRules=function(t,e){t.children=[this.text(e.join("\n\n")+"\n\n"+this.textContent(t))]},e.prototype.fontSize=function(t){return 0},e.prototype.fontFamily=function(t){return""},e.prototype.nodeSize=function(t,e,n){return void 0===e&&(e=1),void 0===n&&(n=null),[0,0]},e.prototype.nodeBBox=function(t){return{left:0,right:0,top:0,bottom:0}},e}(s.AbstractDOMAdaptor);e.LiteBase=b;var m=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}((0,c.NodeMixin)(b));e.LiteAdaptor=m,e.liteAdaptor=function(t){return void 0===t&&(t=null),new m(null,t)}},306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},723:function(t,e){MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},857:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=MathJax._.core.DOMAdaptor.AbstractDOMAdaptor},29:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.options=MathJax._.util.Entities.options,e.entities=MathJax._.util.Entities.entities,e.add=MathJax._.util.Entities.add,e.remove=MathJax._.util.Entities.remove,e.translate=MathJax._.util.Entities.translate,e.numeric=MathJax._.util.Entities.numeric},77:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup},878:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Styles=MathJax._.util.Styles.Styles}},c={};function p(t){var e=c[t];if(void 0!==e)return e.exports;var n=c[t]={exports:{}};return s[t].call(n.exports,n,n.exports,p),n.exports}t=p(723),e=p(306),n=p(250),r=p(877),o=p(946),i=p(6),a=p(246),l=p(735),u=p(492),MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("adaptors/liteDOM",e.q,"adaptors"),(0,t.r8)({_:{adaptors:{liteAdaptor:n,lite:{Document:r,Element:o,List:i,Parser:a,Text:l,Window:u}}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.registerConstructor("liteAdaptor",n.liteAdaptor),MathJax.startup.useAdaptor("liteAdaptor",!0))}();���������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000034�00000000000�010212� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������28 mtime=1692426889.0439646
����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/core.js�����������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000652641�00000000000�017434� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,r,n,o,i,a,s,l,u,c,p,f,h,d,y,O,M,E,v,m,b,g,L,N,R,T,S,A,C,_,x,I,w,P,j,D,B,k,X,H,W,F,q,J,z,G,V,U,K,$,Y,Z,Q,tt,et,rt,nt,ot,it,at,st,lt,ut,ct,pt,ft,ht,dt,yt,Ot,Mt,Et,vt,mt,bt,gt,Lt,Nt={444:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLAdaptor=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(e){var r=t.call(this,e.document)||this;return r.window=e,r.parser=new e.DOMParser,r}return o(e,t),e.prototype.parse=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e="text/html"),this.parser.parseFromString(t,e)},e.prototype.create=function(t,e){return e?this.document.createElementNS(e,t):this.document.createElement(t)},e.prototype.text=function(t){return this.document.createTextNode(t)},e.prototype.head=function(t){return t.head||t},e.prototype.body=function(t){return t.body||t},e.prototype.root=function(t){return t.documentElement||t},e.prototype.doctype=function(t){return t.doctype?""):""},e.prototype.tags=function(t,e,r){void 0===r&&(r=null);var n=r?t.getElementsByTagNameNS(r,e):t.getElementsByTagName(e);return Array.from(n)},e.prototype.getElements=function(t,e){var r,n,o=[];try{for(var a=i(t),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;"string"==typeof l?o=o.concat(Array.from(this.document.querySelectorAll(l))):Array.isArray(l)||l instanceof this.window.NodeList||l instanceof this.window.HTMLCollection?o=o.concat(Array.from(l)):o.push(l)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return o},e.prototype.contains=function(t,e){return t.contains(e)},e.prototype.parent=function(t){return t.parentNode},e.prototype.append=function(t,e){return t.appendChild(e)},e.prototype.insert=function(t,e){return this.parent(e).insertBefore(t,e)},e.prototype.remove=function(t){return this.parent(t).removeChild(t)},e.prototype.replace=function(t,e){return this.parent(e).replaceChild(t,e)},e.prototype.clone=function(t){return t.cloneNode(!0)},e.prototype.split=function(t,e){return t.splitText(e)},e.prototype.next=function(t){return t.nextSibling},e.prototype.previous=function(t){return t.previousSibling},e.prototype.firstChild=function(t){return t.firstChild},e.prototype.lastChild=function(t){return t.lastChild},e.prototype.childNodes=function(t){return Array.from(t.childNodes)},e.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return t.childNodes[e]},e.prototype.kind=function(t){var e=t.nodeType;return 1===e||3===e||8===e?t.nodeName.toLowerCase():""},e.prototype.value=function(t){return t.nodeValue||""},e.prototype.textContent=function(t){return t.textContent},e.prototype.innerHTML=function(t){return t.innerHTML},e.prototype.outerHTML=function(t){return t.outerHTML},e.prototype.serializeXML=function(t){return(new this.window.XMLSerializer).serializeToString(t)},e.prototype.setAttribute=function(t,e,r,n){return void 0===n&&(n=null),n?(e=n.replace(/.*\//,"")+":"+e.replace(/^.*:/,""),t.setAttributeNS(n,e,r)):t.setAttribute(e,r)},e.prototype.getAttribute=function(t,e){return t.getAttribute(e)},e.prototype.removeAttribute=function(t,e){return t.removeAttribute(e)},e.prototype.hasAttribute=function(t,e){return t.hasAttribute(e)},e.prototype.allAttributes=function(t){return Array.from(t.attributes).map((function(t){return{name:t.name,value:t.value}}))},e.prototype.addClass=function(t,e){t.classList?t.classList.add(e):t.className=(t.className+" "+e).trim()},e.prototype.removeClass=function(t,e){t.classList?t.classList.remove(e):t.className=t.className.split(/ /).filter((function(t){return t!==e})).join(" ")},e.prototype.hasClass=function(t,e){return t.classList?t.classList.contains(e):t.className.split(/ /).indexOf(e)>=0},e.prototype.setStyle=function(t,e,r){t.style[e]=r},e.prototype.getStyle=function(t,e){return t.style[e]},e.prototype.allStyles=function(t){return t.style.cssText},e.prototype.insertRules=function(t,e){var r,n;try{for(var o=i(e.reverse()),a=o.next();!a.done;a=o.next()){var s=a.value;try{t.sheet.insertRule(s,0)}catch(t){console.warn("MathJax: can't insert css rule '".concat(s,"': ").concat(t.message))}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.fontSize=function(t){var e=this.window.getComputedStyle(t);return parseFloat(e.fontSize)},e.prototype.fontFamily=function(t){return this.window.getComputedStyle(t).fontFamily||""},e.prototype.nodeSize=function(t,e,r){if(void 0===e&&(e=1),void 0===r&&(r=!1),r&&t.getBBox){var n=t.getBBox();return[n.width/e,n.height/e]}return[t.offsetWidth/e,t.offsetHeight/e]},e.prototype.nodeBBox=function(t){var e=t.getBoundingClientRect();return{left:e.left,right:e.right,top:e.top,bottom:e.bottom}},e}(r(5009).AbstractDOMAdaptor);e.HTMLAdaptor=a},6191:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.browserAdaptor=void 0;var n=r(444);e.browserAdaptor=function(){return new n.HTMLAdaptor(window)}},9515:function(t,e,r){var n=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathJax=e.combineWithMathJax=e.combineDefaults=e.combineConfig=e.isObject=void 0;var o=r(3282);function i(t){return"object"==typeof t&&null!==t}function a(t,e){var r,o;try{for(var s=n(Object.keys(e)),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;"__esModule"!==u&&(!i(t[u])||!i(e[u])||e[u]instanceof Promise?null!==e[u]&&void 0!==e[u]&&(t[u]=e[u]):a(t[u],e[u]))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(o=s.return)&&o.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return t}e.isObject=i,e.combineConfig=a,e.combineDefaults=function t(e,r,o){var a,s;e[r]||(e[r]={}),e=e[r];try{for(var l=n(Object.keys(o)),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;i(e[c])&&i(o[c])?t(e,c,o[c]):null==e[c]&&null!=o[c]&&(e[c]=o[c])}}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(s=l.return)&&s.call(l)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return e},e.combineWithMathJax=function(t){return a(e.MathJax,t)},void 0===r.g.MathJax&&(r.g.MathJax={}),r.g.MathJax.version||(r.g.MathJax={version:o.VERSION,_:{},config:r.g.MathJax}),e.MathJax=r.g.MathJax},3282:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.VERSION=void 0,e.VERSION="3.2.2"},5009:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=void 0;var n=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.document=t}return t.prototype.node=function(t,e,n,o){var i,a;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===n&&(n=[]);var s=this.create(t,o);this.setAttributes(s,e);try{for(var l=r(n),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;this.append(s,c)}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(a=l.return)&&a.call(l)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}return s},t.prototype.setAttributes=function(t,e){var n,o,i,a,s,l;if(e.style&&"string"!=typeof e.style)try{for(var u=r(Object.keys(e.style)),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;this.setStyle(t,p.replace(/-([a-z])/g,(function(t,e){return e.toUpperCase()})),e.style[p])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(o=u.return)&&o.call(u)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}if(e.properties)try{for(var f=r(Object.keys(e.properties)),h=f.next();!h.done;h=f.next()){t[p=h.value]=e.properties[p]}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(a=f.return)&&a.call(f)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}try{for(var d=r(Object.keys(e)),y=d.next();!y.done;y=d.next()){"style"===(p=y.value)&&"string"!=typeof e.style||"properties"===p||this.setAttribute(t,p,e[p])}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{y&&!y.done&&(l=d.return)&&l.call(d)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},t.prototype.replace=function(t,e){return this.insert(t,e),this.remove(e),e},t.prototype.childNode=function(t,e){return this.childNodes(t)[e]},t.prototype.allClasses=function(t){var e=this.getAttribute(t,"class");return e?e.replace(/ +/g," ").replace(/^ /,"").replace(/ $/,"").split(/ /):[]},t}();e.AbstractDOMAdaptor=n},3494:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractFindMath=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=function(){function t(t){var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t)}return t.OPTIONS={},t}();e.AbstractFindMath=o},3670:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractHandler=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(r(5722).AbstractMathDocument),a=function(){function t(t,e){void 0===e&&(e=5),this.documentClass=i,this.adaptor=t,this.priority=e}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){return!1},t.prototype.create=function(t,e){return new this.documentClass(t,this.adaptor,e)},t.NAME="generic",t}();e.AbstractHandler=a},805:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HandlerList=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.register=function(t){return this.add(t,t.priority)},e.prototype.unregister=function(t){this.remove(t)},e.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=i(this),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var a=o.value.item;if(a.handlesDocument(t))return a}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}throw new Error("Can't find handler for document")},e.prototype.document=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),this.handlesDocument(t).create(t,e)},e}(r(8666).PrioritizedList);e.HandlerList=a},9206:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractInputJax=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=r(7525),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={}),this.adaptor=null,this.mmlFactory=null;var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.preFilters=new o.FunctionList,this.postFilters=new o.FunctionList}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setAdaptor=function(t){this.adaptor=t},t.prototype.setMmlFactory=function(t){this.mmlFactory=t},t.prototype.initialize=function(){},t.prototype.reset=function(){for(var t=[],e=0;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=e&&s.item.renderDoc(t))return}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.renderMath=function(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===r&&(r=f.STATE.UNPROCESSED);try{for(var a=i(this.items),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(l.priority>=r&&l.item.renderMath(t,e))return}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},e.prototype.renderConvert=function(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===r&&(r=f.STATE.LAST);try{for(var a=i(this.items),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(l.priority>r)return;if(l.item.convert&&l.item.renderMath(t,e))return}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},e.prototype.findID=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=i(this.items),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var a=o.value;if(a.item.id===t)return a.item}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return null},e}(r(8666).PrioritizedList);e.RenderList=y,e.resetOptions={all:!1,processed:!1,inputJax:null,outputJax:null},e.resetAllOptions={all:!0,processed:!0,inputJax:[],outputJax:[]};var O=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.compile=function(t){return null},e}(u.AbstractInputJax),M=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.typeset=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),null},e.prototype.escaped=function(t,e){return null},e}(c.AbstractOutputJax),E=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(p.AbstractMathList),v=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(f.AbstractMathItem),m=function(){function t(e,r,n){var o=this,i=this.constructor;this.document=e,this.options=(0,l.userOptions)((0,l.defaultOptions)({},i.OPTIONS),n),this.math=new(this.options.MathList||E),this.renderActions=y.create(this.options.renderActions),this.processed=new t.ProcessBits,this.outputJax=this.options.OutputJax||new M;var a=this.options.InputJax||[new O];Array.isArray(a)||(a=[a]),this.inputJax=a,this.adaptor=r,this.outputJax.setAdaptor(r),this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.setAdaptor(r)})),this.mmlFactory=this.options.MmlFactory||new h.MmlFactory,this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.setMmlFactory(o.mmlFactory)})),this.outputJax.initialize(),this.inputJax.map((function(t){return t.initialize()}))}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return this.constructor.KIND},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.addRenderAction=function(t){for(var e=[],r=1;r=r&&this.state(r-1),t.renderActions.renderMath(this,t,r)},t.prototype.convert=function(t,r){void 0===r&&(r=e.STATE.LAST),t.renderActions.renderConvert(this,t,r)},t.prototype.compile=function(t){this.state()=e.STATE.INSERTED&&this.removeFromDocument(r),t=e.STATE.TYPESET&&(this.outputData={}),t=e.STATE.COMPILED&&(this.inputData={}),this._state=t),this._state},t.prototype.reset=function(t){void 0===t&&(t=!1),this.state(e.STATE.UNPROCESSED,t)},t}();e.AbstractMathItem=r,e.STATE={UNPROCESSED:0,FINDMATH:10,COMPILED:20,CONVERT:100,METRICS:110,RERENDER:125,TYPESET:150,INSERTED:200,LAST:1e4},e.newState=function(t,r){if(t in e.STATE)throw Error("State "+t+" already exists");e.STATE[t]=r}},9e3:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractMathList=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e.prototype.isBefore=function(t,e){return t.start.i=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.Attributes=e.INHERIT=void 0,e.INHERIT="_inherit_";var n=function(){function t(t,e){this.global=e,this.defaults=Object.create(e),this.inherited=Object.create(this.defaults),this.attributes=Object.create(this.inherited),Object.assign(this.defaults,t)}return t.prototype.set=function(t,e){this.attributes[t]=e},t.prototype.setList=function(t){Object.assign(this.attributes,t)},t.prototype.get=function(t){var r=this.attributes[t];return r===e.INHERIT&&(r=this.global[t]),r},t.prototype.getExplicit=function(t){if(this.attributes.hasOwnProperty(t))return this.attributes[t]},t.prototype.getList=function(){for(var t,e,n=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathMLVisitor=void 0;var a=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.document=null,e}return o(e,t),e.prototype.visitTree=function(t,e){this.document=e;var r=e.createElement("top");return this.visitNode(t,r),this.document=null,r.firstChild},e.prototype.visitTextNode=function(t,e){e.appendChild(this.document.createTextNode(t.getText()))},e.prototype.visitXMLNode=function(t,e){e.appendChild(t.getXML().cloneNode(!0))},e.prototype.visitInferredMrowNode=function(t,e){var r,n;try{for(var o=i(t.childNodes),a=o.next();!a.done;a=o.next()){var s=a.value;this.visitNode(s,e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var r,n,o=this.document.createElement(t.kind);this.addAttributes(t,o);try{for(var a=i(t.childNodes),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;this.visitNode(l,o)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}e.appendChild(o)},e.prototype.addAttributes=function(t,e){var r,n,o=t.attributes,a=o.getExplicitNames();try{for(var s=i(a),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;e.setAttribute(u,o.getExplicit(u).toString())}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=s.return)&&n.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}},e}(r(6325).MmlVisitor);e.MathMLVisitor=a},3909:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlFactory=void 0;var i=r(7860),a=r(6336),s=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"MML",{get:function(){return this.node},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.defaultNodes=a.MML,e}(i.AbstractNodeFactory);e.MmlFactory=s},9007:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.XMLNode=e.TextNode=e.AbstractMmlEmptyNode=e.AbstractMmlBaseNode=e.AbstractMmlLayoutNode=e.AbstractMmlTokenNode=e.AbstractMmlNode=e.indentAttributes=e.TEXCLASSNAMES=e.TEXCLASS=void 0;var l=r(91),u=r(4596);e.TEXCLASS={ORD:0,OP:1,BIN:2,REL:3,OPEN:4,CLOSE:5,PUNCT:6,INNER:7,VCENTER:8,NONE:-1},e.TEXCLASSNAMES=["ORD","OP","BIN","REL","OPEN","CLOSE","PUNCT","INNER","VCENTER"];var c=["","thinmathspace","mediummathspace","thickmathspace"],p=[[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[-1,-1,0,3,0,0,0,1],[2,2,0,0,2,0,0,2],[3,3,0,0,3,0,0,3],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],[1,-1,2,3,1,0,1,1]];e.indentAttributes=["indentalign","indentalignfirst","indentshift","indentshiftfirst"];var f=function(t){function r(e,r,n){void 0===r&&(r={}),void 0===n&&(n=[]);var o=t.call(this,e)||this;return o.prevClass=null,o.prevLevel=null,o.texclass=null,o.arity<0&&(o.childNodes=[e.create("inferredMrow")],o.childNodes[0].parent=o),o.setChildren(n),o.attributes=new l.Attributes(e.getNodeClass(o.kind).defaults,e.getNodeClass("math").defaults),o.attributes.setList(r),o}return o(r,t),r.prototype.copy=function(t){var e,r,n,o;void 0===t&&(t=!1);var s=this.factory.create(this.kind);if(s.properties=i({},this.properties),this.attributes){var l=this.attributes.getAllAttributes();try{for(var u=a(Object.keys(l)),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;("id"!==p||t)&&s.attributes.set(p,l[p])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(r=u.return)&&r.call(u)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}if(this.childNodes&&this.childNodes.length){var f=this.childNodes;1===f.length&&f[0].isInferred&&(f=f[0].childNodes);try{for(var h=a(f),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;y?s.appendChild(y.copy()):s.childNodes.push(null)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(o=h.return)&&o.call(h)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}return s},Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){return this.texclass},set:function(t){this.texclass=t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 1/0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"Parent",{get:function(){for(var t=this.parent;t&&t.notParent;)t=t.Parent;return t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.setChildren=function(e){return this.arity<0?this.childNodes[0].setChildren(e):t.prototype.setChildren.call(this,e)},r.prototype.appendChild=function(e){var r,n,o=this;if(this.arity<0)return this.childNodes[0].appendChild(e),e;if(e.isInferred){if(this.arity===1/0)return e.childNodes.forEach((function(e){return t.prototype.appendChild.call(o,e)})),e;var i=e;(e=this.factory.create("mrow")).setChildren(i.childNodes),e.attributes=i.attributes;try{for(var s=a(i.getPropertyNames()),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;e.setProperty(u,i.getProperty(u))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(n=s.return)&&n.call(s)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}}return t.prototype.appendChild.call(this,e)},r.prototype.replaceChild=function(e,r){return this.arity<0?(this.childNodes[0].replaceChild(e,r),e):t.prototype.replaceChild.call(this,e,r)},r.prototype.core=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreIndex=function(){return 0},r.prototype.childPosition=function(){for(var t,e,r=this,n=r.parent;n&&n.notParent;)r=n,n=n.parent;if(n){var o=0;try{for(var i=a(n.childNodes),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){if(s.value===r)return o;o++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(e=i.return)&&e.call(i)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}}return null},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return this.getPrevClass(t),null!=this.texClass?this:t},r.prototype.updateTeXclass=function(t){t&&(this.prevClass=t.prevClass,this.prevLevel=t.prevLevel,t.prevClass=t.prevLevel=null,this.texClass=t.texClass)},r.prototype.getPrevClass=function(t){t&&(this.prevClass=t.texClass,this.prevLevel=t.attributes.get("scriptlevel"))},r.prototype.texSpacing=function(){var t=null!=this.prevClass?this.prevClass:e.TEXCLASS.NONE,r=this.texClass||e.TEXCLASS.ORD;if(t===e.TEXCLASS.NONE||r===e.TEXCLASS.NONE)return"";t===e.TEXCLASS.VCENTER&&(t=e.TEXCLASS.ORD),r===e.TEXCLASS.VCENTER&&(r=e.TEXCLASS.ORD);var n=p[t][r];return(this.prevLevel>0||this.attributes.get("scriptlevel")>0)&&n>=0?"":c[Math.abs(n)]},r.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&this.coreMO().hasSpacingAttributes()},r.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,n,o){var i,l;void 0===t&&(t={}),void 0===e&&(e=!1),void 0===n&&(n=0),void 0===o&&(o=!1);var u=this.attributes.getAllDefaults();try{for(var c=a(Object.keys(t)),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){var f=p.value;if(u.hasOwnProperty(f)||r.alwaysInherit.hasOwnProperty(f)){var h=s(t[f],2),d=h[0],y=h[1];((r.noInherit[d]||{})[this.kind]||{})[f]||this.attributes.setInherited(f,y)}}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(l=c.return)&&l.call(c)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}void 0===this.attributes.getExplicit("displaystyle")&&this.attributes.setInherited("displaystyle",e),void 0===this.attributes.getExplicit("scriptlevel")&&this.attributes.setInherited("scriptlevel",n),o&&this.setProperty("texprimestyle",o);var O=this.arity;if(O>=0&&O!==1/0&&(1===O&&0===this.childNodes.length||1!==O&&this.childNodes.length!==O))if(O=0&&e!==1/0&&(1===e&&0===this.childNodes.length||1!==e&&this.childNodes.length!==e)&&this.mError('Wrong number of children for "'+this.kind+'" node',t,!0),this.verifyChildren(t)}},r.prototype.verifyAttributes=function(t){var e,r;if(t.checkAttributes){var n=this.attributes,o=[];try{for(var i=a(n.getExplicitNames()),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var l=s.value;"data-"===l.substr(0,5)||void 0!==n.getDefault(l)||l.match(/^(?:class|style|id|(?:xlink:)?href)$/)||o.push(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}o.length&&this.mError("Unknown attributes for "+this.kind+" node: "+o.join(", "),t)}},r.prototype.verifyChildren=function(t){var e,r;try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.verifyTree(t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},r.prototype.mError=function(t,e,r){if(void 0===r&&(r=!1),this.parent&&this.parent.isKind("merror"))return null;var n=this.factory.create("merror");if(n.attributes.set("data-mjx-message",t),e.fullErrors||r){var o=this.factory.create("mtext"),i=this.factory.create("text");i.setText(e.fullErrors?t:this.kind),o.appendChild(i),n.appendChild(o),this.parent.replaceChild(n,this)}else this.parent.replaceChild(n,this),n.appendChild(this);return n},r.defaults={mathbackground:l.INHERIT,mathcolor:l.INHERIT,mathsize:l.INHERIT,dir:l.INHERIT},r.noInherit={mstyle:{mpadded:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,lspace:!0,voffset:!0},mtable:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,align:!0}},maligngroup:{mrow:{groupalign:!0},mtable:{groupalign:!0}}},r.alwaysInherit={scriptminsize:!0,scriptsizemultiplier:!0},r.verifyDefaults={checkArity:!0,checkAttributes:!1,fullErrors:!1,fixMmultiscripts:!0,fixMtables:!0},r}(u.AbstractNode);e.AbstractMmlNode=f;var h=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getText=function(){var t,e,r="";try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i instanceof M&&(r+=i.getText())}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(e=n.return)&&e.call(n)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i;try{for(var s=a(this.childNodes),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;u instanceof f&&u.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,n)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}},e.prototype.walkTree=function(t,e){var r,n;t(this,e);try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;s instanceof f&&s.walkTree(t,e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return e},e.defaults=i(i({},f.defaults),{mathvariant:"normal",mathsize:l.INHERIT}),e}(f);e.AbstractMmlTokenNode=h;var d=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isSpacelike},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isEmbellished},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return-1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.core=function(){return this.childNodes[0]},e.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.childNodes[0].coreMO()},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return t=this.childNodes[0].setTeXclass(t),this.updateTeXclass(this.childNodes[0]),t},e.defaults=f.defaults,e}(f);e.AbstractMmlLayoutNode=d;var y=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return this.childNodes[0].isEmbellished},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.core=function(){return this.childNodes[0]},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.childNodes[0].coreMO()},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var r,n;this.getPrevClass(t),this.texClass=e.TEXCLASS.ORD;var o=this.childNodes[0];o?this.isEmbellished||o.isKind("mi")?(t=o.setTeXclass(t),this.updateTeXclass(this.core())):(o.setTeXclass(null),t=this):t=this;try{for(var i=a(this.childNodes.slice(1)),s=i.next();!s.done;s=i.next()){var l=s.value;l&&l.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return t},r.defaults=f.defaults,r}(f);e.AbstractMmlBaseNode=y;var O=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isToken",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"Parent",{get:function(){return this.parent},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){return e.TEXCLASS.NONE},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"prevClass",{get:function(){return e.TEXCLASS.NONE},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"prevLevel",{get:function(){return 0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return!1},Object.defineProperty(r.prototype,"attributes",{get:function(){return null},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),r.prototype.core=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this},r.prototype.coreIndex=function(){return 0},r.prototype.childPosition=function(){return 0},r.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){return t},r.prototype.texSpacing=function(){return""},r.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){},r.prototype.inheritAttributesFrom=function(t){},r.prototype.verifyTree=function(t){},r.prototype.mError=function(t,e,r){return void 0===r&&(r=!1),null},r}(u.AbstractEmptyNode);e.AbstractMmlEmptyNode=O;var M=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.text="",e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"text"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getText=function(){return this.text},e.prototype.setText=function(t){return this.text=t,this},e.prototype.copy=function(){return this.factory.create(this.kind).setText(this.getText())},e.prototype.toString=function(){return this.text},e}(O);e.TextNode=M;var E=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.xml=null,e.adaptor=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"XML"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.getXML=function(){return this.xml},e.prototype.setXML=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=null),this.xml=t,this.adaptor=e,this},e.prototype.getSerializedXML=function(){return this.adaptor.serializeXML(this.xml)},e.prototype.copy=function(){return this.factory.create(this.kind).setXML(this.adaptor.clone(this.xml))},e.prototype.toString=function(){return"XML data"},e}(O);e.XMLNode=E},3948:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;rthis.childNodes.length&&(t=1),this.attributes.set("selection",t)},e.defaults=i(i({},a.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),{actiontype:"toggle",selection:1}),e}(a.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMaction=s},142:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMfenced=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.texclass=s.TEXCLASS.INNER,e.separators=[],e.open=null,e.close=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mfenced"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){this.getPrevClass(t),this.open&&(t=this.open.setTeXclass(t)),this.childNodes[0]&&(t=this.childNodes[0].setTeXclass(t));for(var e=1,r=this.childNodes.length;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMfrac=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mfrac"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 2},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r;this.getPrevClass(t);try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){(!e||r>0)&&r++,this.childNodes[0].setInheritedAttributes(t,!1,r,n),this.childNodes[1].setInheritedAttributes(t,!1,r,!0)},e.defaults=i(i({},s.AbstractMmlBaseNode.defaults),{linethickness:"medium",numalign:"center",denomalign:"center",bevelled:!1}),e}(s.AbstractMmlBaseNode);e.MmlMfrac=l},3985:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r1&&r.match(e.operatorName)&&"normal"===this.attributes.get("mathvariant")&&void 0===this.getProperty("autoOP")&&void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=a.TEXCLASS.OP,this.setProperty("autoOP",!0)),this},e.defaults=i({},a.AbstractMmlTokenNode.defaults),e.operatorName=/^[a-z][a-z0-9]*$/i,e.singleCharacter=/^[\uD800-\uDBFF]?.[\u0300-\u036F\u1AB0-\u1ABE\u1DC0-\u1DFF\u20D0-\u20EF]*$/,e}(a.AbstractMmlTokenNode);e.MmlMi=s},6405:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMo=void 0;var l=r(9007),u=r(4082),c=r(505),p=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e._texClass=null,e.lspace=5/18,e.rspace=5/18,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"texClass",{get:function(){if(null===this._texClass){var t=this.getText(),e=a(this.handleExplicitForm(this.getForms()),3),r=e[0],n=e[1],o=e[2],i=this.constructor.OPTABLE,s=i[r][t]||i[n][t]||i[o][t];return s?s[2]:l.TEXCLASS.REL}return this._texClass},set:function(t){this._texClass=t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mo"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"hasNewLine",{get:function(){return"newline"===this.attributes.get("linebreak")},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.coreParent=function(){for(var t=this,e=this,r=this.factory.getNodeClass("math");e&&e.isEmbellished&&e.coreMO()===this&&!(e instanceof r);)t=e,e=e.parent;return t},e.prototype.coreText=function(t){if(!t)return"";if(t.isEmbellished)return t.coreMO().getText();for(;((t.isKind("mrow")||t.isKind("TeXAtom")&&t.texClass!==l.TEXCLASS.VCENTER||t.isKind("mstyle")||t.isKind("mphantom"))&&1===t.childNodes.length||t.isKind("munderover"))&&t.childNodes[0];)t=t.childNodes[0];return t.isToken?t.getText():""},e.prototype.hasSpacingAttributes=function(){return this.attributes.isSet("lspace")||this.attributes.isSet("rspace")},Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isAccent",{get:function(){var t=!1,e=this.coreParent().parent;if(e){var r=e.isKind("mover")?e.childNodes[e.over].coreMO()?"accent":"":e.isKind("munder")?e.childNodes[e.under].coreMO()?"accentunder":"":e.isKind("munderover")?this===e.childNodes[e.over].coreMO()?"accent":this===e.childNodes[e.under].coreMO()?"accentunder":"":"";if(r)t=void 0!==e.attributes.getExplicit(r)?t:this.attributes.get("accent")}return t},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e=this.attributes.getList("form","fence"),r=e.form,n=e.fence;return void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.attributes.isSet("lspace")||this.attributes.isSet("rspace"))?null:(n&&this.texClass===l.TEXCLASS.REL&&("prefix"===r&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.OPEN),"postfix"===r&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.CLOSE)),this.adjustTeXclass(t))},e.prototype.adjustTeXclass=function(t){var e=this.texClass,r=this.prevClass;if(e===l.TEXCLASS.NONE)return t;if(t?(!t.getProperty("autoOP")||e!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.REL||(r=t.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD),r=this.prevClass=t.texClass||l.TEXCLASS.ORD,this.prevLevel=this.attributes.getInherited("scriptlevel")):r=this.prevClass=l.TEXCLASS.NONE,e!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN||r!==l.TEXCLASS.NONE&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.OP&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.REL&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.OPEN&&r!==l.TEXCLASS.PUNCT)if(r!==l.TEXCLASS.BIN||e!==l.TEXCLASS.REL&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.CLOSE&&e!==l.TEXCLASS.PUNCT){if(e===l.TEXCLASS.BIN){for(var n=this,o=this.parent;o&&o.parent&&o.isEmbellished&&(1===o.childNodes.length||!o.isKind("mrow")&&o.core()===n);)n=o,o=o.parent;o.childNodes[o.childNodes.length-1]===n&&(this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD)}}else t.texClass=this.prevClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD;else this.texClass=l.TEXCLASS.ORD;return this},e.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(e,r,n,o){void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===r&&(r=!1),void 0===n&&(n=0),void 0===o&&(o=!1),t.prototype.setInheritedAttributes.call(this,e,r,n,o);var i=this.getText();this.checkOperatorTable(i),this.checkPseudoScripts(i),this.checkPrimes(i),this.checkMathAccent(i)},e.prototype.checkOperatorTable=function(t){var e,r,n=a(this.handleExplicitForm(this.getForms()),3),o=n[0],i=n[1],l=n[2];this.attributes.setInherited("form",o);var c=this.constructor.OPTABLE,p=c[o][t]||c[i][t]||c[l][t];if(p){void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=p[2]);try{for(var f=s(Object.keys(p[3]||{})),h=f.next();!h.done;h=f.next()){var d=h.value;this.attributes.setInherited(d,p[3][d])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{h&&!h.done&&(r=f.return)&&r.call(f)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.lspace=(p[0]+1)/18,this.rspace=(p[1]+1)/18}else{var y=(0,u.getRange)(t);if(y){void 0===this.getProperty("texClass")&&(this.texClass=y[2]);var O=this.constructor.MMLSPACING[y[2]];this.lspace=(O[0]+1)/18,this.rspace=(O[1]+1)/18}}},e.prototype.getForms=function(){for(var t=this,e=this.parent,r=this.Parent;r&&r.isEmbellished;)t=e,e=r.parent,r=r.Parent;if(e&&e.isKind("mrow")&&1!==e.nonSpaceLength()){if(e.firstNonSpace()===t)return["prefix","infix","postfix"];if(e.lastNonSpace()===t)return["postfix","infix","prefix"]}return["infix","prefix","postfix"]},e.prototype.handleExplicitForm=function(t){if(this.attributes.isSet("form")){var e=this.attributes.get("form");t=[e].concat(t.filter((function(t){return t!==e})))}return t},e.prototype.checkPseudoScripts=function(t){var e=this.constructor.pseudoScripts;if(t.match(e)){var r=this.coreParent().Parent,n=!r||!(r.isKind("msubsup")&&!r.isKind("msub"));this.setProperty("pseudoscript",n),n&&(this.attributes.setInherited("lspace",0),this.attributes.setInherited("rspace",0))}},e.prototype.checkPrimes=function(t){var e=this.constructor.primes;if(t.match(e)){var r=this.constructor.remapPrimes,n=(0,c.unicodeString)((0,c.unicodeChars)(t).map((function(t){return r[t]})));this.setProperty("primes",n)}},e.prototype.checkMathAccent=function(t){var e=this.Parent;if(void 0===this.getProperty("mathaccent")&&e&&e.isKind("munderover")){var r=e.childNodes[0];if(!r.isEmbellished||r.coreMO()!==this){var n=this.constructor.mathaccents;t.match(n)&&this.setProperty("mathaccent",!0)}}},e.defaults=i(i({},l.AbstractMmlTokenNode.defaults),{form:"infix",fence:!1,separator:!1,lspace:"thickmathspace",rspace:"thickmathspace",stretchy:!1,symmetric:!1,maxsize:"infinity",minsize:"0em",largeop:!1,movablelimits:!1,accent:!1,linebreak:"auto",lineleading:"1ex",linebreakstyle:"before",indentalign:"auto",indentshift:"0",indenttarget:"",indentalignfirst:"indentalign",indentshiftfirst:"indentshift",indentalignlast:"indentalign",indentshiftlast:"indentshift"}),e.MMLSPACING=u.MMLSPACING,e.OPTABLE=u.OPTABLE,e.pseudoScripts=new RegExp(["^[\"'*`","\xaa","\xb0","\xb2-\xb4","\xb9","\xba","\u2018-\u201f","\u2032-\u2037\u2057","\u2070\u2071","\u2074-\u207f","\u2080-\u208e","]+$"].join("")),e.primes=new RegExp(["^[\"'`","\u2018-\u201f","]+$"].join("")),e.remapPrimes={34:8243,39:8242,96:8245,8216:8245,8217:8242,8218:8242,8219:8245,8220:8246,8221:8243,8222:8243,8223:8246},e.mathaccents=new RegExp(["^[","\xb4\u0301\u02ca","`\u0300\u02cb","\xa8\u0308","~\u0303\u02dc","\xaf\u0304\u02c9","\u02d8\u0306","\u02c7\u030c","^\u0302\u02c6","\u2192\u20d7","\u02d9\u0307","\u02da\u030a","\u20db","\u20dc","]$"].join("")),e}(l.AbstractMmlTokenNode);e.MmlMo=p},7238:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlInferredMrow=e.MmlMrow=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e._core=null,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mrow"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isSpacelike",{get:function(){var t,e;try{for(var r=a(this.childNodes),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){if(!n.value.isSpacelike)return!1}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(e=r.return)&&e.call(r)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isEmbellished",{get:function(){var t,e,r=!1,n=0;try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;if(s)if(s.isEmbellished){if(r)return!1;r=!0,this._core=n}else if(!s.isSpacelike)return!1;n++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(e=o.return)&&e.call(o)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.core=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&null!=this._core?this.childNodes[this._core]:this},e.prototype.coreMO=function(){return this.isEmbellished&&null!=this._core?this.childNodes[this._core].coreMO():this},e.prototype.nonSpaceLength=function(){var t,e,r=0;try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i&&!i.isSpacelike&&r++}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(e=n.return)&&e.call(n)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return r},e.prototype.firstNonSpace=function(){var t,e;try{for(var r=a(this.childNodes),n=r.next();!n.done;n=r.next()){var o=n.value;if(o&&!o.isSpacelike)return o}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(e=r.return)&&e.call(r)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return null},e.prototype.lastNonSpace=function(){for(var t=this.childNodes.length;--t>=0;){var e=this.childNodes[t];if(e&&!e.isSpacelike)return e}return null},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r,n,o;if(null!=this.getProperty("open")||null!=this.getProperty("close")){this.getPrevClass(t),t=null;try{for(var i=a(this.childNodes),l=i.next();!l.done;l=i.next()){t=l.value.setTeXclass(t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}null==this.texClass&&(this.texClass=s.TEXCLASS.INNER)}else{try{for(var u=a(this.childNodes),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){t=c.value.setTeXclass(t)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(o=u.return)&&o.call(u)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}this.childNodes[0]&&this.updateTeXclass(this.childNodes[0])}return t},e.defaults=i({},s.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),e}(s.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMrow=l;var u=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"inferredMrow"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"isInferred",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"notParent",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.toString=function(){return"["+this.childNodes.join(",")+"]"},e.defaults=l.defaults,e}(l);e.MmlInferredMrow=u},7265:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMtable=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=r(505),u=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.properties={useHeight:!0},e.texclass=s.TEXCLASS.ORD,e}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mtable"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setInheritedAttributes=function(e,r,n,o){var i,l;try{for(var u=a(s.indentAttributes),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value;e[p]&&this.attributes.setInherited(p,e[p][1]),void 0!==this.attributes.getExplicit(p)&&delete this.attributes.getAllAttributes()[p]}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(l=u.return)&&l.call(u)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}t.prototype.setInheritedAttributes.call(this,e,r,n,o)},e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,s,u;try{for(var c=a(this.childNodes),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){(O=p.value).isKind("mtr")||this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtr"),O).appendChild(O)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(i=c.return)&&i.call(c)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}r=this.getProperty("scriptlevel")||r,e=!(!this.attributes.getExplicit("displaystyle")&&!this.attributes.getDefault("displaystyle")),t=this.addInheritedAttributes(t,{columnalign:this.attributes.get("columnalign"),rowalign:"center"});var f=this.attributes.getExplicit("data-cramped"),h=(0,l.split)(this.attributes.get("rowalign"));try{for(var d=a(this.childNodes),y=d.next();!y.done;y=d.next()){var O=y.value;t.rowalign[1]=h.shift()||t.rowalign[1],O.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,!!f)}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{y&&!y.done&&(u=d.return)&&u.call(d)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},e.prototype.verifyChildren=function(e){for(var r=null,n=this.factory,o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MmlMlabeledtr=e.MmlMtr=void 0;var s=r(9007),l=r(91),u=r(505),c=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mtr"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"linebreakContainer",{get:function(){return!0},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.setChildInheritedAttributes=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,s,l;try{for(var c=a(this.childNodes),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){(y=p.value).isKind("mtd")||this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtd"),y).appendChild(y)}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(i=c.return)&&i.call(c)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}var f=(0,u.split)(this.attributes.get("columnalign"));1===this.arity&&f.unshift(this.parent.attributes.get("side")),t=this.addInheritedAttributes(t,{rowalign:this.attributes.get("rowalign"),columnalign:"center"});try{for(var h=a(this.childNodes),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;t.columnalign[1]=f.shift()||t.columnalign[1],y.setInheritedAttributes(t,e,r,n)}}catch(t){s={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(l=h.return)&&l.call(h)}finally{if(s)throw s.error}}},e.prototype.verifyChildren=function(e){var r,n;if(!this.parent||this.parent.isKind("mtable")){try{for(var o=a(this.childNodes),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var s=i.value;if(!s.isKind("mtd"))this.replaceChild(this.factory.create("mtd"),s).appendChild(s),e.fixMtables||s.mError("Children of "+this.kind+" must be mtd",e)}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}t.prototype.verifyChildren.call(this,e)}else this.mError(this.kind+" can only be a child of an mtable",e,!0)},e.prototype.setTeXclass=function(t){var e,r;this.getPrevClass(t);try{for(var n=a(this.childNodes),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){o.value.setTeXclass(null)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this},e.defaults=i(i({},s.AbstractMmlNode.defaults),{rowalign:l.INHERIT,columnalign:l.INHERIT,groupalign:l.INHERIT}),e}(s.AbstractMmlNode);e.MmlMtr=c;var p=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"mlabeledtr"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"arity",{get:function(){return 1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e}(c);e.MmlMlabeledtr=p},5184:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__assign||function(){return i=Object.assign||function(t){for(var e,r=1,n=arguments.length;r=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.OPTABLE=e.MMLSPACING=e.getRange=e.RANGES=e.MO=e.OPDEF=void 0;var o=r(9007);function i(t,e,r,n){return void 0===r&&(r=o.TEXCLASS.BIN),void 0===n&&(n=null),[t,e,r,n]}e.OPDEF=i,e.MO={ORD:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD11:i(1,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD21:i(2,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD02:i(0,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),ORD55:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),NONE:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.NONE),OP:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0,symmetric:!0}),OPFIXED:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0}),INTEGRAL:i(0,1,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,symmetric:!0}),INTEGRAL2:i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.OP,{largeop:!0,symmetric:!0}),BIN3:i(3,3,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN4:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN01:i(0,1,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),BIN5:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.BIN),TALLBIN:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{stretchy:!0}),BINOP:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{largeop:!0,movablelimits:!0}),REL:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL),REL1:i(1,1,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{stretchy:!0}),REL4:i(4,4,o.TEXCLASS.REL),RELSTRETCH:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{stretchy:!0}),RELACCENT:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{accent:!0}),WIDEREL:i(5,5,o.TEXCLASS.REL,{accent:!0,stretchy:!0}),OPEN:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}),CLOSE:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}),INNER:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.INNER),PUNCT:i(0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT),ACCENT:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{accent:!0}),WIDEACCENT:i(0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{accent:!0,stretchy:!0})},e.RANGES=[[32,127,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[160,191,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[192,591,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[688,879,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[880,6688,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[6832,6911,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[6912,7615,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[7616,7679,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[7680,8191,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[8192,8303,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[8304,8351,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[8448,8527,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[8528,8591,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[8592,8703,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[8704,8959,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,"mo"],[8960,9215,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[9312,9471,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[9472,10223,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[10224,10239,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[10240,10495,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mtext"],[10496,10623,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[10624,10751,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[10752,11007,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,"mo"],[11008,11055,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11056,11087,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[11088,11263,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11264,11744,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[11776,11903,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[11904,12255,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[12272,12351,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[12352,42143,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[42192,43055,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[43056,43071,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[43072,55295,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[63744,64255,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[64256,65023,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[65024,65135,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[65136,65791,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[65792,65935,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[65936,74751,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[74752,74879,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[74880,113823,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normal"],[113824,119391,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[119648,119679,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[119808,120781,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi"],[120782,120831,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mn"],[122624,129023,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[129024,129279,o.TEXCLASS.REL,"mo"],[129280,129535,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mo"],[131072,195103,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,"mi","normnal"]],e.getRange=function(t){var r,o,i=t.codePointAt(0);try{for(var a=n(e.RANGES),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;if(i<=l[1]){if(i>=l[0])return l;break}}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return null},e.MMLSPACING=[[0,0],[1,2],[3,3],[4,4],[0,0],[0,0],[0,3]],e.OPTABLE={prefix:{"(":e.MO.OPEN,"+":e.MO.BIN01,"-":e.MO.BIN01,"[":e.MO.OPEN,"{":e.MO.OPEN,"|":e.MO.OPEN,"||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xac":e.MO.ORD21,"\xb1":e.MO.BIN01,"\u2016":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2018":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0}],"\u201c":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.OPEN,{fence:!0}],"\u2145":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2146":i(2,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),"\u2200":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2202":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2203":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2204":e.MO.ORD21,"\u2207":e.MO.ORD21,"\u220f":e.MO.OP,"\u2210":e.MO.OP,"\u2211":e.MO.OP,"\u2212":e.MO.BIN01,"\u2213":e.MO.BIN01,"\u221a":[1,1,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u221b":e.MO.ORD11,"\u221c":e.MO.ORD11,"\u2220":e.MO.ORD,"\u2221":e.MO.ORD,"\u2222":e.MO.ORD,"\u222b":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222c":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222d":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222e":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u222f":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2230":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2231":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2232":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2233":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u22c0":e.MO.OP,"\u22c1":e.MO.OP,"\u22c2":e.MO.OP,"\u22c3":e.MO.OP,"\u2308":e.MO.OPEN,"\u230a":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2329":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2772":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27e6":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27e8":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ea":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ec":e.MO.OPEN,"\u27ee":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2980":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2983":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2985":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2987":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2989":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298b":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298d":e.MO.OPEN,"\u298f":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2991":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2993":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2995":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2997":e.MO.OPEN,"\u29fc":e.MO.OPEN,"\u2a00":e.MO.OP,"\u2a01":e.MO.OP,"\u2a02":e.MO.OP,"\u2a03":e.MO.OP,"\u2a04":e.MO.OP,"\u2a05":e.MO.OP,"\u2a06":e.MO.OP,"\u2a07":e.MO.OP,"\u2a08":e.MO.OP,"\u2a09":e.MO.OP,"\u2a0a":e.MO.OP,"\u2a0b":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0c":e.MO.INTEGRAL,"\u2a0d":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0e":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a0f":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a10":e.MO.OP,"\u2a11":e.MO.OP,"\u2a12":e.MO.OP,"\u2a13":e.MO.OP,"\u2a14":e.MO.OP,"\u2a15":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a16":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a17":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a18":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a19":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1a":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1b":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2a1c":e.MO.INTEGRAL2,"\u2afc":e.MO.OP,"\u2aff":e.MO.OP},postfix:{"!!":i(1,0),"!":[1,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,null],'"':e.MO.ACCENT,"&":e.MO.ORD,")":e.MO.CLOSE,"++":i(0,0),"--":i(0,0),"..":i(0,0),"...":e.MO.ORD,"'":e.MO.ACCENT,"]":e.MO.CLOSE,"^":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,_:e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"`":e.MO.ACCENT,"|":e.MO.CLOSE,"}":e.MO.CLOSE,"~":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xa8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xaa":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xaf":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\xb0":e.MO.ORD,"\xb2":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb3":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb4":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xb9":e.MO.ACCENT,"\xba":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02c6":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02c7":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02c9":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02ca":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02cb":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02cd":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02d8":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02d9":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02da":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02dc":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u02dd":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u02f7":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0302":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0311":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u03f6":e.MO.REL,"\u2016":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2019":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0}],"\u201a":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201b":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201d":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,{fence:!0}],"\u201e":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u201f":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2032":e.MO.ORD,"\u2033":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2034":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2035":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2036":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2037":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u203e":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u2057":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u20db":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u20dc":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2309":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u230b":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u232a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u23b4":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23b5":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23dc":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23dd":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23de":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23df":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23e0":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u23e1":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u25a0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25a1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25aa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ab":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ad":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25ae":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25af":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u25b2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25be":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c0":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c1":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25ce":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25cf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25d6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25d7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25e6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u266d":e.MO.ORD02,"\u266e":e.MO.ORD02,"\u266f":e.MO.ORD02,"\u2773":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27e7":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27e9":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27eb":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27ed":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u27ef":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2980":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0}],"\u2984":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2986":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2988":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298c":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u298e":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2990":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2992":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2994":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2996":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2998":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u29fd":e.MO.CLOSE},infix:{"!=":e.MO.BIN4,"#":e.MO.ORD,$:e.MO.ORD,"%":[3,3,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,null],"&&":e.MO.BIN4,"":e.MO.ORD,"*":e.MO.BIN3,"**":i(1,1),"*=":e.MO.BIN4,"+":e.MO.BIN4,"+=":e.MO.BIN4,",":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"-":e.MO.BIN4,"-=":e.MO.BIN4,"->":e.MO.BIN5,".":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{separator:!0}],"/":e.MO.ORD11,"//":i(1,1),"/=":e.MO.BIN4,":":[1,2,o.TEXCLASS.REL,null],":=":e.MO.BIN4,";":[0,3,o.TEXCLASS.PUNCT,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"<":e.MO.REL,"<=":e.MO.BIN5,"<>":i(1,1),"=":e.MO.REL,"==":e.MO.BIN4,">":e.MO.REL,">=":e.MO.BIN5,"?":[1,1,o.TEXCLASS.CLOSE,null],"@":e.MO.ORD11,"\\":e.MO.ORD,"^":e.MO.ORD11,_:e.MO.ORD11,"|":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"||":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.BIN,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"|||":[2,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"\xb1":e.MO.BIN4,"\xb7":e.MO.BIN4,"\xd7":e.MO.BIN4,"\xf7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u02b9":e.MO.ORD,"\u0300":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0301":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0303":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0304":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0306":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0307":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0308":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u030c":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u0332":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\u0338":e.MO.REL4,"\u2015":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2017":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2020":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2021":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2022":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2026":e.MO.INNER,"\u2043":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2044":e.MO.TALLBIN,"\u2061":e.MO.NONE,"\u2062":e.MO.NONE,"\u2063":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.NONE,{linebreakstyle:"after",separator:!0}],"\u2064":e.MO.NONE,"\u20d7":e.MO.ACCENT,"\u2111":e.MO.ORD,"\u2113":e.MO.ORD,"\u2118":e.MO.ORD,"\u211c":e.MO.ORD,"\u2190":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2191":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2192":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2193":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2194":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2195":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2196":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2197":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2198":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2199":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u219a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u219b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u219c":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219d":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u219f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a3":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21a7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21a9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21aa":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ab":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ac":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ad":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ae":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21af":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b0":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b2":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b4":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21b6":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21b7":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21b8":e.MO.REL,"\u21b9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ba":e.MO.REL,"\u21bb":e.MO.REL,"\u21bc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21bd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21be":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21bf":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c1":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c2":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c7":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21c8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21c9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ca":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21cb":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21cc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21cd":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21ce":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21cf":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21d0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21d5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d6":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d8":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21d9":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21da":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21db":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21dc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21dd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21de":e.MO.REL,"\u21df":e.MO.REL,"\u21e0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e2":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e4":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e5":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e7":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21e8":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21e9":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ea":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21eb":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ec":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ed":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ee":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21ef":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f0":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21f1":e.MO.REL,"\u21f2":e.MO.REL,"\u21f3":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f4":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f5":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u21f6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21f7":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f8":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21f9":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fa":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fb":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fc":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u21fd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21fe":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u21ff":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2201":i(1,2,o.TEXCLASS.ORD),"\u2205":e.MO.ORD,"\u2206":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2208":e.MO.REL,"\u2209":e.MO.REL,"\u220a":e.MO.REL,"\u220b":e.MO.REL,"\u220c":e.MO.REL,"\u220d":e.MO.REL,"\u220e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2212":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2213":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2214":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2215":e.MO.TALLBIN,"\u2216":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2217":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2218":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2219":e.MO.BIN4,"\u221d":e.MO.REL,"\u221e":e.MO.ORD,"\u221f":e.MO.REL,"\u2223":e.MO.REL,"\u2224":e.MO.REL,"\u2225":e.MO.REL,"\u2226":e.MO.REL,"\u2227":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2228":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2229":e.MO.BIN4,"\u222a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2234":e.MO.REL,"\u2235":e.MO.REL,"\u2236":e.MO.REL,"\u2237":e.MO.REL,"\u2238":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2239":e.MO.REL,"\u223a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u223b":e.MO.REL,"\u223c":e.MO.REL,"\u223d":e.MO.REL,"\u223d\u0331":e.MO.BIN3,"\u223e":e.MO.REL,"\u223f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2240":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2241":e.MO.REL,"\u2242":e.MO.REL,"\u2242\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2243":e.MO.REL,"\u2244":e.MO.REL,"\u2245":e.MO.REL,"\u2246":e.MO.REL,"\u2247":e.MO.REL,"\u2248":e.MO.REL,"\u2249":e.MO.REL,"\u224a":e.MO.REL,"\u224b":e.MO.REL,"\u224c":e.MO.REL,"\u224d":e.MO.REL,"\u224e":e.MO.REL,"\u224e\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u224f":e.MO.REL,"\u224f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2250":e.MO.REL,"\u2251":e.MO.REL,"\u2252":e.MO.REL,"\u2253":e.MO.REL,"\u2254":e.MO.REL,"\u2255":e.MO.REL,"\u2256":e.MO.REL,"\u2257":e.MO.REL,"\u2258":e.MO.REL,"\u2259":e.MO.REL,"\u225a":e.MO.REL,"\u225b":e.MO.REL,"\u225c":e.MO.REL,"\u225d":e.MO.REL,"\u225e":e.MO.REL,"\u225f":e.MO.REL,"\u2260":e.MO.REL,"\u2261":e.MO.REL,"\u2262":e.MO.REL,"\u2263":e.MO.REL,"\u2264":e.MO.REL,"\u2265":e.MO.REL,"\u2266":e.MO.REL,"\u2266\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2267":e.MO.REL,"\u2268":e.MO.REL,"\u2269":e.MO.REL,"\u226a":e.MO.REL,"\u226a\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u226b":e.MO.REL,"\u226b\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u226c":e.MO.REL,"\u226d":e.MO.REL,"\u226e":e.MO.REL,"\u226f":e.MO.REL,"\u2270":e.MO.REL,"\u2271":e.MO.REL,"\u2272":e.MO.REL,"\u2273":e.MO.REL,"\u2274":e.MO.REL,"\u2275":e.MO.REL,"\u2276":e.MO.REL,"\u2277":e.MO.REL,"\u2278":e.MO.REL,"\u2279":e.MO.REL,"\u227a":e.MO.REL,"\u227b":e.MO.REL,"\u227c":e.MO.REL,"\u227d":e.MO.REL,"\u227e":e.MO.REL,"\u227f":e.MO.REL,"\u227f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2280":e.MO.REL,"\u2281":e.MO.REL,"\u2282":e.MO.REL,"\u2282\u20d2":e.MO.REL,"\u2283":e.MO.REL,"\u2283\u20d2":e.MO.REL,"\u2284":e.MO.REL,"\u2285":e.MO.REL,"\u2286":e.MO.REL,"\u2287":e.MO.REL,"\u2288":e.MO.REL,"\u2289":e.MO.REL,"\u228a":e.MO.REL,"\u228b":e.MO.REL,"\u228c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u228f":e.MO.REL,"\u228f\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2290":e.MO.REL,"\u2290\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2291":e.MO.REL,"\u2292":e.MO.REL,"\u2293":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2294":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2295":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2296":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2297":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2298":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2299":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u229f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a0":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a1":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22a2":e.MO.REL,"\u22a3":e.MO.REL,"\u22a4":e.MO.ORD55,"\u22a5":e.MO.REL,"\u22a6":e.MO.REL,"\u22a7":e.MO.REL,"\u22a8":e.MO.REL,"\u22a9":e.MO.REL,"\u22aa":e.MO.REL,"\u22ab":e.MO.REL,"\u22ac":e.MO.REL,"\u22ad":e.MO.REL,"\u22ae":e.MO.REL,"\u22af":e.MO.REL,"\u22b0":e.MO.REL,"\u22b1":e.MO.REL,"\u22b2":e.MO.REL,"\u22b3":e.MO.REL,"\u22b4":e.MO.REL,"\u22b5":e.MO.REL,"\u22b6":e.MO.REL,"\u22b7":e.MO.REL,"\u22b8":e.MO.REL,"\u22b9":e.MO.REL,"\u22ba":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22be":e.MO.BIN3,"\u22bf":e.MO.BIN3,"\u22c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22c8":e.MO.REL,"\u22c9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22ca":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cd":e.MO.REL,"\u22ce":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22cf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d0":e.MO.REL,"\u22d1":e.MO.REL,"\u22d2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u22d4":e.MO.REL,"\u22d5":e.MO.REL,"\u22d6":e.MO.REL,"\u22d7":e.MO.REL,"\u22d8":e.MO.REL,"\u22d9":e.MO.REL,"\u22da":e.MO.REL,"\u22db":e.MO.REL,"\u22dc":e.MO.REL,"\u22dd":e.MO.REL,"\u22de":e.MO.REL,"\u22df":e.MO.REL,"\u22e0":e.MO.REL,"\u22e1":e.MO.REL,"\u22e2":e.MO.REL,"\u22e3":e.MO.REL,"\u22e4":e.MO.REL,"\u22e5":e.MO.REL,"\u22e6":e.MO.REL,"\u22e7":e.MO.REL,"\u22e8":e.MO.REL,"\u22e9":e.MO.REL,"\u22ea":e.MO.REL,"\u22eb":e.MO.REL,"\u22ec":e.MO.REL,"\u22ed":e.MO.REL,"\u22ee":e.MO.ORD55,"\u22ef":e.MO.INNER,"\u22f0":e.MO.REL,"\u22f1":[5,5,o.TEXCLASS.INNER,null],"\u22f2":e.MO.REL,"\u22f3":e.MO.REL,"\u22f4":e.MO.REL,"\u22f5":e.MO.REL,"\u22f6":e.MO.REL,"\u22f7":e.MO.REL,"\u22f8":e.MO.REL,"\u22f9":e.MO.REL,"\u22fa":e.MO.REL,"\u22fb":e.MO.REL,"\u22fc":e.MO.REL,"\u22fd":e.MO.REL,"\u22fe":e.MO.REL,"\u22ff":e.MO.REL,"\u2305":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2306":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2322":e.MO.REL4,"\u2323":e.MO.REL4,"\u2329":e.MO.OPEN,"\u232a":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u23aa":e.MO.ORD,"\u23af":[0,0,o.TEXCLASS.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u23b0":e.MO.OPEN,"\u23b1":e.MO.CLOSE,"\u2500":e.MO.ORD,"\u25b3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25b9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25bf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25c3":e.MO.BIN4,"\u25ef":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2660":e.MO.ORD,"\u2661":e.MO.ORD,"\u2662":e.MO.ORD,"\u2663":e.MO.ORD,"\u2758":e.MO.REL,"\u27f0":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u27f1":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u27f5":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f6":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f7":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f8":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27f9":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fa":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fb":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fc":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fd":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27fe":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u27ff":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2900":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2901":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2902":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2903":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2904":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2905":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2906":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2907":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2908":e.MO.REL,"\u2909":e.MO.REL,"\u290a":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u290b":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u290c":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290d":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u290f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2910":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2911":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2912":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2913":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2914":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2915":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2916":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2917":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2918":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2919":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291e":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u291f":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2920":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2921":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2922":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2923":e.MO.REL,"\u2924":e.MO.REL,"\u2925":e.MO.REL,"\u2926":e.MO.REL,"\u2927":e.MO.REL,"\u2928":e.MO.REL,"\u2929":e.MO.REL,"\u292a":e.MO.REL,"\u292b":e.MO.REL,"\u292c":e.MO.REL,"\u292d":e.MO.REL,"\u292e":e.MO.REL,"\u292f":e.MO.REL,"\u2930":e.MO.REL,"\u2931":e.MO.REL,"\u2932":e.MO.REL,"\u2933":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2934":e.MO.REL,"\u2935":e.MO.REL,"\u2936":e.MO.REL,"\u2937":e.MO.REL,"\u2938":e.MO.REL,"\u2939":e.MO.REL,"\u293a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u293e":e.MO.REL,"\u293f":e.MO.REL,"\u2940":e.MO.REL,"\u2941":e.MO.REL,"\u2942":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2943":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2944":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2945":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2946":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2947":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2948":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2949":e.MO.REL,"\u294a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u294b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u294c":e.MO.REL,"\u294d":e.MO.REL,"\u294e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u294f":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2950":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2951":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2952":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2953":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2954":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2955":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2956":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2957":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2958":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2959":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295a":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295b":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295c":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295d":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u295e":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u295f":e.MO.WIDEREL,"\u2960":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2961":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2962":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2963":e.MO.REL,"\u2964":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2965":e.MO.REL,"\u2966":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2967":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2968":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2969":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u296e":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u296f":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2970":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2971":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2972":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2973":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2974":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2975":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2976":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2977":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2978":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u2979":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297a":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297b":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297c":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297d":e.MO.RELACCENT,"\u297e":e.MO.REL,"\u297f":e.MO.REL,"\u2981":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2982":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2999":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299a":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299b":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299c":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299d":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u299f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a4":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a5":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a6":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a7":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29a9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29aa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ab":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ac":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ad":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ae":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29af":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b4":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b5":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29b6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29b9":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29ba":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bc":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29be":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29bf":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c0":e.MO.REL,"\u29c1":e.MO.REL,"\u29c2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29c3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29c4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c8":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29c9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ca":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cc":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29cd":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ce":e.MO.REL,"\u29cf":e.MO.REL,"\u29cf\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u29d0":e.MO.REL,"\u29d0\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u29d1":e.MO.REL,"\u29d2":e.MO.REL,"\u29d3":e.MO.REL,"\u29d4":e.MO.REL,"\u29d5":e.MO.REL,"\u29d6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29d7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29d8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29d9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29db":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29dc":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29dd":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29de":e.MO.REL,"\u29df":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e1":e.MO.REL,"\u29e2":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29e3":e.MO.REL,"\u29e4":e.MO.REL,"\u29e5":e.MO.REL,"\u29e6":e.MO.REL,"\u29e7":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29e9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ea":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29eb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ec":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ed":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ee":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29ef":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f0":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f1":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f2":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f3":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f4":e.MO.REL,"\u29f5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f7":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29f8":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29f9":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fa":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fb":e.MO.BIN3,"\u29fe":e.MO.BIN4,"\u29ff":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a1d":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a1e":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a1f":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a20":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a21":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2a22":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a23":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a24":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a25":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a26":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a27":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a28":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a29":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a2f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a30":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a31":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a32":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a33":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a34":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a35":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a36":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a37":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a38":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a39":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a3f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a40":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a41":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a42":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a43":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a44":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a45":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a46":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a47":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a48":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a49":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a4f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a50":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a51":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a52":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a53":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a54":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a55":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a56":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a57":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a58":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a59":e.MO.REL,"\u2a5a":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5b":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5c":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5d":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5e":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a5f":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a60":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a61":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a62":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a63":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a64":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a65":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a66":e.MO.REL,"\u2a67":e.MO.REL,"\u2a68":e.MO.REL,"\u2a69":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a6f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a70":e.MO.REL,"\u2a71":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a72":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2a73":e.MO.REL,"\u2a74":e.MO.REL,"\u2a75":e.MO.REL,"\u2a76":e.MO.REL,"\u2a77":e.MO.REL,"\u2a78":e.MO.REL,"\u2a79":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7d\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7e\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2a7f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a80":e.MO.REL,"\u2a81":e.MO.REL,"\u2a82":e.MO.REL,"\u2a83":e.MO.REL,"\u2a84":e.MO.REL,"\u2a85":e.MO.REL,"\u2a86":e.MO.REL,"\u2a87":e.MO.REL,"\u2a88":e.MO.REL,"\u2a89":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a8f":e.MO.REL,"\u2a90":e.MO.REL,"\u2a91":e.MO.REL,"\u2a92":e.MO.REL,"\u2a93":e.MO.REL,"\u2a94":e.MO.REL,"\u2a95":e.MO.REL,"\u2a96":e.MO.REL,"\u2a97":e.MO.REL,"\u2a98":e.MO.REL,"\u2a99":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9a":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9b":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9c":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9d":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9e":e.MO.REL,"\u2a9f":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa0":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa1":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa1\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa2":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa2\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa3":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa4":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa5":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa6":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa7":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa8":e.MO.REL,"\u2aa9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaa":e.MO.REL,"\u2aab":e.MO.REL,"\u2aac":e.MO.REL,"\u2aad":e.MO.REL,"\u2aae":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaf":e.MO.REL,"\u2aaf\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab0\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ab9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aba":e.MO.REL,"\u2abb":e.MO.REL,"\u2abc":e.MO.REL,"\u2abd":e.MO.REL,"\u2abe":e.MO.REL,"\u2abf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ac9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aca":e.MO.REL,"\u2acb":e.MO.REL,"\u2acc":e.MO.REL,"\u2acd":e.MO.REL,"\u2ace":e.MO.REL,"\u2acf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ad9":e.MO.REL,"\u2ada":e.MO.REL,"\u2adb":e.MO.REL,"\u2add":e.MO.REL,"\u2add\u0338":e.MO.REL,"\u2ade":e.MO.REL,"\u2adf":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae0":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae1":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae2":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae3":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae4":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae5":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae6":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae7":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae8":e.MO.REL,"\u2ae9":e.MO.REL,"\u2aea":e.MO.REL,"\u2aeb":e.MO.REL,"\u2aec":e.MO.REL,"\u2aed":e.MO.REL,"\u2aee":e.MO.REL,"\u2aef":e.MO.REL,"\u2af0":e.MO.REL,"\u2af1":e.MO.REL,"\u2af2":e.MO.REL,"\u2af3":e.MO.REL,"\u2af4":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af5":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af6":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2af7":e.MO.REL,"\u2af8":e.MO.REL,"\u2af9":e.MO.REL,"\u2afa":e.MO.REL,"\u2afb":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2afd":e.MO.BIN4,"\u2afe":e.MO.BIN3,"\u2b45":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u2b46":e.MO.RELSTRETCH,"\u3008":e.MO.OPEN,"\u3009":e.MO.CLOSE,"\ufe37":e.MO.WIDEACCENT,"\ufe38":e.MO.WIDEACCENT}},e.OPTABLE.infix["^"]=e.MO.WIDEREL,e.OPTABLE.infix._=e.MO.WIDEREL,e.OPTABLE.infix["\u2adc"]=e.MO.REL},9259:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.SerializedMmlVisitor=e.toEntity=e.DATAMJX=void 0;var s=r(6325),l=r(9007),u=r(450);e.DATAMJX="data-mjx-";e.toEntity=function(t){return"&#x"+t.codePointAt(0).toString(16).toUpperCase()+";"};var c=function(t){function r(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(r,t),r.prototype.visitTree=function(t){return this.visitNode(t,"")},r.prototype.visitTextNode=function(t,e){return this.quoteHTML(t.getText())},r.prototype.visitXMLNode=function(t,e){return e+t.getSerializedXML()},r.prototype.visitInferredMrowNode=function(t,e){var r,n,o=[];try{for(var a=i(t.childNodes),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;o.push(this.visitNode(l,e))}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return o.join("\n")},r.prototype.visitTeXAtomNode=function(t,e){var r=this.childNodeMml(t,e+" ","\n");return e+""+(r.match(/\S/)?"\n"+r+e:"")+""},r.prototype.visitAnnotationNode=function(t,e){return e+""+this.childNodeMml(t,"","")+""},r.prototype.visitDefault=function(t,e){var r=t.kind,n=a(t.isToken||0===t.childNodes.length?["",""]:["\n",e],2),o=n[0],i=n[1],s=this.childNodeMml(t,e+" ",o);return e+"<"+r+this.getAttributes(t)+">"+(s.match(/\S/)?o+s+i:"")+""},r.prototype.childNodeMml=function(t,e,r){var n,o,a="";try{for(var s=i(t.childNodes),l=s.next();!l.done;l=s.next()){var u=l.value;a+=this.visitNode(u,e)+r}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{l&&!l.done&&(o=s.return)&&o.call(s)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}return a},r.prototype.getAttributes=function(t){var e,r,n=[],o=this.constructor.defaultAttributes[t.kind]||{},a=Object.assign({},o,this.getDataAttributes(t),t.attributes.getAllAttributes()),s=this.constructor.variants;a.hasOwnProperty("mathvariant")&&s.hasOwnProperty(a.mathvariant)&&(a.mathvariant=s[a.mathvariant]);try{for(var l=i(Object.keys(a)),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value,p=String(a[c]);void 0!==p&&n.push(c+'="'+this.quoteHTML(p)+'"')}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(r=l.return)&&r.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return n.length?" "+n.join(" "):""},r.prototype.getDataAttributes=function(t){var e={},r=t.attributes.getExplicit("mathvariant"),n=this.constructor.variants;r&&n.hasOwnProperty(r)&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"variant",r),t.getProperty("variantForm")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"alternate","1"),t.getProperty("pseudoscript")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"pseudoscript","true"),!1===t.getProperty("autoOP")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"auto-op","false");var o=t.getProperty("scriptalign");o&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"script-align",o);var i=t.getProperty("texClass");if(void 0!==i){var a=!0;if(i===l.TEXCLASS.OP&&t.isKind("mi")){var s=t.getText();a=!(s.length>1&&s.match(u.MmlMi.operatorName))}a&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"texclass",i<0?"NONE":l.TEXCLASSNAMES[i])}return t.getProperty("scriptlevel")&&!1===t.getProperty("useHeight")&&this.setDataAttribute(e,"smallmatrix","true"),e},r.prototype.setDataAttribute=function(t,r,n){t[e.DATAMJX+r]=n},r.prototype.quoteHTML=function(t){return t.replace(/&/g,"&").replace(//g,">").replace(/\"/g,""").replace(/[\uD800-\uDBFF]./g,e.toEntity).replace(/[\u0080-\uD7FF\uE000-\uFFFF]/g,e.toEntity)},r.variants={"-tex-calligraphic":"script","-tex-bold-calligraphic":"bold-script","-tex-oldstyle":"normal","-tex-bold-oldstyle":"bold","-tex-mathit":"italic"},r.defaultAttributes={math:{xmlns:"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"}},r}(s.MmlVisitor);e.SerializedMmlVisitor=c},2975:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractOutputJax=void 0;var n=r(7233),o=r(7525),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={}),this.adaptor=null;var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,n.userOptions)((0,n.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.postFilters=new o.FunctionList}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"name",{get:function(){return this.constructor.NAME},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setAdaptor=function(t){this.adaptor=t},t.prototype.initialize=function(){},t.prototype.reset=function(){for(var t=[],e=0;e=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractEmptyNode=e.AbstractNode=void 0;var a=function(){function t(t,e,r){var n,o;void 0===e&&(e={}),void 0===r&&(r=[]),this.factory=t,this.parent=null,this.properties={},this.childNodes=[];try{for(var a=i(Object.keys(e)),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value;this.setProperty(l,e[l])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}r.length&&this.setChildren(r)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"kind",{get:function(){return"unknown"},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.setProperty=function(t,e){this.properties[t]=e},t.prototype.getProperty=function(t){return this.properties[t]},t.prototype.getPropertyNames=function(){return Object.keys(this.properties)},t.prototype.getAllProperties=function(){return this.properties},t.prototype.removeProperty=function(){for(var t,e,r=[],n=0;n=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},o=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},i=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLDocument=void 0;var l=r(5722),u=r(7233),c=r(3363),p=r(3335),f=r(5138),h=r(4474),d=function(t){function e(e,r,n){var o=this,i=a((0,u.separateOptions)(n,f.HTMLDomStrings.OPTIONS),2),s=i[0],l=i[1];return(o=t.call(this,e,r,s)||this).domStrings=o.options.DomStrings||new f.HTMLDomStrings(l),o.domStrings.adaptor=r,o.styles=[],o}return o(e,t),e.prototype.findPosition=function(t,e,r,n){var o,i,l=this.adaptor;try{for(var u=s(n[t]),c=u.next();!c.done;c=u.next()){var p=c.value,f=a(p,2),h=f[0],d=f[1];if(e<=d&&"#text"===l.kind(h))return{node:h,n:Math.max(e,0),delim:r};e-=d}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{c&&!c.done&&(i=u.return)&&i.call(u)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return{node:null,n:0,delim:r}},e.prototype.mathItem=function(t,e,r){var n=t.math,o=this.findPosition(t.n,t.start.n,t.open,r),i=this.findPosition(t.n,t.end.n,t.close,r);return new this.options.MathItem(n,e,t.display,o,i)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){var e,r,n,o,i,l,c,p,f;if(!this.processed.isSet("findMath")){this.adaptor.document=this.document,t=(0,u.userOptions)({elements:this.options.elements||[this.adaptor.body(this.document)]},t);try{for(var h=s(this.adaptor.getElements(t.elements,this.document)),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value,O=a([null,null],2),M=O[0],E=O[1];try{for(var v=(n=void 0,s(this.inputJax)),m=v.next();!m.done;m=v.next()){var b=m.value,g=new this.options.MathList;if(b.processStrings){null===M&&(M=(i=a(this.domStrings.find(y),2))[0],E=i[1]);try{for(var L=(l=void 0,s(b.findMath(M))),N=L.next();!N.done;N=L.next()){var R=N.value;g.push(this.mathItem(R,b,E))}}catch(t){l={error:t}}finally{try{N&&!N.done&&(c=L.return)&&c.call(L)}finally{if(l)throw l.error}}}else try{for(var T=(p=void 0,s(b.findMath(y))),S=T.next();!S.done;S=T.next()){R=S.value;var A=new this.options.MathItem(R.math,b,R.display,R.start,R.end);g.push(A)}}catch(t){p={error:t}}finally{try{S&&!S.done&&(f=T.return)&&f.call(T)}finally{if(p)throw p.error}}this.math.merge(g)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{m&&!m.done&&(o=v.return)&&o.call(v)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(r=h.return)&&r.call(h)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.processed.set("findMath")}return this},e.prototype.updateDocument=function(){return this.processed.isSet("updateDocument")||(this.addPageElements(),this.addStyleSheet(),t.prototype.updateDocument.call(this),this.processed.set("updateDocument")),this},e.prototype.addPageElements=function(){var t=this.adaptor.body(this.document),e=this.documentPageElements();e&&this.adaptor.append(t,e)},e.prototype.addStyleSheet=function(){var t=this.documentStyleSheet(),e=this.adaptor;if(t&&!e.parent(t)){var r=e.head(this.document),n=this.findSheet(r,e.getAttribute(t,"id"));n?e.replace(t,n):e.append(r,t)}},e.prototype.findSheet=function(t,e){var r,n;if(e)try{for(var o=s(this.adaptor.tags(t,"style")),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;if(this.adaptor.getAttribute(a,"id")===e)return a}}catch(t){r={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(r)throw r.error}}return null},e.prototype.removeFromDocument=function(t){var e,r;if(void 0===t&&(t=!1),this.processed.isSet("updateDocument"))try{for(var n=s(this.math),o=n.next();!o.done;o=n.next()){var i=o.value;i.state()>=h.STATE.INSERTED&&i.state(h.STATE.TYPESET,t)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{o&&!o.done&&(r=n.return)&&r.call(n)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}return this.processed.clear("updateDocument"),this},e.prototype.documentStyleSheet=function(){return this.outputJax.styleSheet(this)},e.prototype.documentPageElements=function(){return this.outputJax.pageElements(this)},e.prototype.addStyles=function(t){this.styles.push(t)},e.prototype.getStyles=function(){return this.styles},e.KIND="HTML",e.OPTIONS=i(i({},l.AbstractMathDocument.OPTIONS),{renderActions:(0,u.expandable)(i(i({},l.AbstractMathDocument.OPTIONS.renderActions),{styles:[h.STATE.INSERTED+1,"","updateStyleSheet",!1]})),MathList:p.HTMLMathList,MathItem:c.HTMLMathItem,DomStrings:null}),e}(l.AbstractMathDocument);e.HTMLDocument=d},5138:function(t,e,r){var n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLDomStrings=void 0;var o=r(7233),i=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null);var e=this.constructor;this.options=(0,o.userOptions)((0,o.defaultOptions)({},e.OPTIONS),t),this.init(),this.getPatterns()}return t.prototype.init=function(){this.strings=[],this.string="",this.snodes=[],this.nodes=[],this.stack=[]},t.prototype.getPatterns=function(){var t=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.skipHtmlTags),e=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.ignoreHtmlClass),r=(0,o.makeArray)(this.options.processHtmlClass);this.skipHtmlTags=new RegExp("^(?:"+t.join("|")+")$","i"),this.ignoreHtmlClass=new RegExp("(?:^| )(?:"+e.join("|")+")(?: |$)"),this.processHtmlClass=new RegExp("(?:^| )(?:"+r+")(?: |$)")},t.prototype.pushString=function(){this.string.match(/\S/)&&(this.strings.push(this.string),this.nodes.push(this.snodes)),this.string="",this.snodes=[]},t.prototype.extendString=function(t,e){this.snodes.push([t,e.length]),this.string+=e},t.prototype.handleText=function(t,e){return e||this.extendString(t,this.adaptor.value(t)),this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.handleTag=function(t,e){if(!e){var r=this.options.includeHtmlTags[this.adaptor.kind(t)];this.extendString(t,r)}return this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.handleContainer=function(t,e){this.pushString();var r=this.adaptor.getAttribute(t,"class")||"",n=this.adaptor.kind(t)||"",o=this.processHtmlClass.exec(r),i=t;return!this.adaptor.firstChild(t)||this.adaptor.getAttribute(t,"data-MJX")||!o&&this.skipHtmlTags.exec(n)?i=this.adaptor.next(t):(this.adaptor.next(t)&&this.stack.push([this.adaptor.next(t),e]),i=this.adaptor.firstChild(t),e=(e||this.ignoreHtmlClass.exec(r))&&!o),[i,e]},t.prototype.handleOther=function(t,e){return this.pushString(),this.adaptor.next(t)},t.prototype.find=function(t){var e,r;this.init();for(var o=this.adaptor.next(t),i=!1,a=this.options.includeHtmlTags;t&&t!==o;){var s=this.adaptor.kind(t);"#text"===s?t=this.handleText(t,i):a.hasOwnProperty(s)?t=this.handleTag(t,i):s?(t=(e=n(this.handleContainer(t,i),2))[0],i=e[1]):t=this.handleOther(t,i),!t&&this.stack.length&&(this.pushString(),t=(r=n(this.stack.pop(),2))[0],i=r[1])}this.pushString();var l=[this.strings,this.nodes];return this.init(),l},t.OPTIONS={skipHtmlTags:["script","noscript","style","textarea","pre","code","annotation","annotation-xml"],includeHtmlTags:{br:"\n",wbr:"","#comment":""},ignoreHtmlClass:"mathjax_ignore",processHtmlClass:"mathjax_process"},t}();e.HTMLDomStrings=i},3726:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLHandler=void 0;var i=r(3670),a=r(3683),s=function(t){function e(){var e=null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this;return e.documentClass=a.HTMLDocument,e}return o(e,t),e.prototype.handlesDocument=function(t){var e=this.adaptor;if("string"==typeof t)try{t=e.parse(t,"text/html")}catch(t){}return t instanceof e.window.Document||t instanceof e.window.HTMLElement||t instanceof e.window.DocumentFragment},e.prototype.create=function(e,r){var n=this.adaptor;if("string"==typeof e)e=n.parse(e,"text/html");else if(e instanceof n.window.HTMLElement||e instanceof n.window.DocumentFragment){var o=e;e=n.parse("","text/html"),n.append(n.body(e),o)}return t.prototype.create.call(this,e,r)},e}(i.AbstractHandler);e.HTMLHandler=s},3363:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLMathItem=void 0;var i=r(4474),a=function(t){function e(e,r,n,o,i){return void 0===n&&(n=!0),void 0===o&&(o={node:null,n:0,delim:""}),void 0===i&&(i={node:null,n:0,delim:""}),t.call(this,e,r,n,o,i)||this}return o(e,t),Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"adaptor",{get:function(){return this.inputJax.adaptor},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.updateDocument=function(t){if(this.state()=i.STATE.TYPESET){var e=this.adaptor,r=this.start.node,n=e.text("");if(t){var o=this.start.delim+this.math+this.end.delim;if(this.inputJax.processStrings)n=e.text(o);else{var a=e.parse(o,"text/html");n=e.firstChild(e.body(a))}}e.parent(r)&&e.replace(n,r),this.start.node=this.end.node=n,this.start.n=this.end.n=0}},e}(i.AbstractMathItem);e.HTMLMathItem=a},3335:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)});Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.HTMLMathList=void 0;var i=function(t){function e(){return null!==t&&t.apply(this,arguments)||this}return o(e,t),e}(r(9e3).AbstractMathList);e.HTMLMathList=i},5713:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.mathjax=void 0;var n=r(3282),o=r(805),i=r(4542);e.mathjax={version:n.VERSION,handlers:new o.HandlerList,document:function(t,r){return e.mathjax.handlers.document(t,r)},handleRetriesFor:i.handleRetriesFor,retryAfter:i.retryAfter,asyncLoad:null}},9923:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.asyncLoad=void 0;var n=r(5713);e.asyncLoad=function(t){return n.mathjax.asyncLoad?new Promise((function(e,r){var o=n.mathjax.asyncLoad(t);o instanceof Promise?o.then((function(t){return e(t)})).catch((function(t){return r(t)})):e(o)})):Promise.reject("Can't load '".concat(t,"': No asyncLoad method specified"))}},6469:function(t,e,r){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.BBox=void 0;var n=r(6010),o=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t={w:0,h:-n.BIGDIMEN,d:-n.BIGDIMEN}),this.w=t.w||0,this.h="h"in t?t.h:-n.BIGDIMEN,this.d="d"in t?t.d:-n.BIGDIMEN,this.L=this.R=this.ic=this.sk=this.dx=0,this.scale=this.rscale=1,this.pwidth=""}return t.zero=function(){return new t({h:0,d:0,w:0})},t.empty=function(){return new t},t.prototype.empty=function(){return this.w=0,this.h=this.d=-n.BIGDIMEN,this},t.prototype.clean=function(){this.w===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.w=0),this.h===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.h=0),this.d===-n.BIGDIMEN&&(this.d=0)},t.prototype.rescale=function(t){this.w*=t,this.h*=t,this.d*=t},t.prototype.combine=function(t,e,r){void 0===e&&(e=0),void 0===r&&(r=0);var n=t.rscale,o=e+n*(t.w+t.L+t.R),i=r+n*t.h,a=n*t.d-r;o>this.w&&(this.w=o),i>this.h&&(this.h=i),a>this.d&&(this.d=a)},t.prototype.append=function(t){var e=t.rscale;this.w+=e*(t.w+t.L+t.R),e*t.h>this.h&&(this.h=e*t.h),e*t.d>this.d&&(this.d=e*t.d)},t.prototype.updateFrom=function(t){this.h=t.h,this.d=t.d,this.w=t.w,t.pwidth&&(this.pwidth=t.pwidth)},t.fullWidth="100%",t.StyleAdjust=[["borderTopWidth","h"],["borderRightWidth","w"],["borderBottomWidth","d"],["borderLeftWidth","w",0],["paddingTop","h"],["paddingRight","w"],["paddingBottom","d"],["paddingLeft","w",0]],t}();e.BBox=o},6751:function(t,e){var r,n=this&&this.__extends||(r=function(t,e){return r=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},r(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function n(){this.constructor=t}r(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(n.prototype=e.prototype,new n)}),o=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},i=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},a=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o",gtdot:"\u22d7",harrw:"\u21ad",hbar:"\u210f",hellip:"\u2026",hookleftarrow:"\u21a9",hookrightarrow:"\u21aa",imath:"\u0131",infin:"\u221e",intcal:"\u22ba",iota:"\u03b9",jmath:"\u0237",kappa:"\u03ba",kappav:"\u03f0",lEg:"\u2a8b",lambda:"\u03bb",lap:"\u2a85",larrlp:"\u21ab",larrtl:"\u21a2",lbrace:"{",lbrack:"[",le:"\u2264",leftleftarrows:"\u21c7",leftthreetimes:"\u22cb",lessdot:"\u22d6",lmoust:"\u23b0",lnE:"\u2268",lnap:"\u2a89",lne:"\u2a87",lnsim:"\u22e6",longmapsto:"\u27fc",looparrowright:"\u21ac",lowast:"\u2217",loz:"\u25ca",lt:"<",ltimes:"\u22c9",ltri:"\u25c3",macr:"\xaf",malt:"\u2720",mho:"\u2127",mu:"\u03bc",multimap:"\u22b8",nLeftarrow:"\u21cd",nLeftrightarrow:"\u21ce",nRightarrow:"\u21cf",nVDash:"\u22af",nVdash:"\u22ae",natur:"\u266e",nearr:"\u2197",nharr:"\u21ae",nlarr:"\u219a",not:"\xac",nrarr:"\u219b",nu:"\u03bd",nvDash:"\u22ad",nvdash:"\u22ac",nwarr:"\u2196",omega:"\u03c9",omicron:"\u03bf",or:"\u2228",osol:"\u2298",period:".",phi:"\u03c6",phiv:"\u03d5",pi:"\u03c0",piv:"\u03d6",prap:"\u2ab7",precnapprox:"\u2ab9",precneqq:"\u2ab5",precnsim:"\u22e8",prime:"\u2032",psi:"\u03c8",quot:'"',rarrtl:"\u21a3",rbrace:"}",rbrack:"]",rho:"\u03c1",rhov:"\u03f1",rightrightarrows:"\u21c9",rightthreetimes:"\u22cc",ring:"\u02da",rmoust:"\u23b1",rtimes:"\u22ca",rtri:"\u25b9",scap:"\u2ab8",scnE:"\u2ab6",scnap:"\u2aba",scnsim:"\u22e9",sdot:"\u22c5",searr:"\u2198",sect:"\xa7",sharp:"\u266f",sigma:"\u03c3",sigmav:"\u03c2",simne:"\u2246",smile:"\u2323",spades:"\u2660",sub:"\u2282",subE:"\u2ac5",subnE:"\u2acb",subne:"\u228a",supE:"\u2ac6",supnE:"\u2acc",supne:"\u228b",swarr:"\u2199",tau:"\u03c4",theta:"\u03b8",thetav:"\u03d1",tilde:"\u02dc",times:"\xd7",triangle:"\u25b5",triangleq:"\u225c",upsi:"\u03c5",upuparrows:"\u21c8",veebar:"\u22bb",vellip:"\u22ee",weierp:"\u2118",xi:"\u03be",yen:"\xa5",zeta:"\u03b6",zigrarr:"\u21dd",nbsp:"\xa0",rsquo:"\u2019",lsquo:"\u2018"};var i={};function a(t,r){if("#"===r.charAt(0))return s(r.slice(1));if(e.entities[r])return e.entities[r];if(e.options.loadMissingEntities){var a=r.match(/^[a-zA-Z](fr|scr|opf)$/)?RegExp.$1:r.charAt(0).toLowerCase();i[a]||(i[a]=!0,(0,n.retryAfter)((0,o.asyncLoad)("./util/entities/"+a+".js")))}return t}function s(t){var e="x"===t.charAt(0)?parseInt(t.slice(1),16):parseInt(t);return String.fromCodePoint(e)}e.add=function(t,r){Object.assign(e.entities,t),i[r]=!0},e.remove=function(t){delete e.entities[t]},e.translate=function(t){return t.replace(/&([a-z][a-z0-9]*|#(?:[0-9]+|x[0-9a-f]+));/gi,a)},e.numeric=s},7525:function(t,e,r){var n,o=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},a=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},s=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0&&o[o.length-1])||6!==i[0]&&2!==i[0])){a=0;continue}if(3===i[0]&&(!o||i[1]>o[0]&&i[1]0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.LinkedList=e.ListItem=e.END=void 0,e.END=Symbol();var a=function(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.next=null,this.prev=null,this.data=t};e.ListItem=a;var s=function(){function t(){for(var t=[],r=0;r1;){var u=o.shift(),c=o.shift();u.merge(c,e),o.push(u)}return o.length&&(this.list=o[0].list),this},t.prototype.merge=function(t,r){var o,i,a,s,l;void 0===r&&(r=null),null===r&&(r=this.isBefore.bind(this));for(var u=this.list.next,c=t.list.next;u.data!==e.END&&c.data!==e.END;)r(c.data,u.data)?(o=n([u,c],2),c.prev.next=o[0],u.prev.next=o[1],i=n([u.prev,c.prev],2),c.prev=i[0],u.prev=i[1],a=n([t.list,this.list],2),this.list.prev.next=a[0],t.list.prev.next=a[1],s=n([t.list.prev,this.list.prev],2),this.list.prev=s[0],t.list.prev=s[1],u=(l=n([c.next,u],2))[0],c=l[1]):u=u.next;return c.data!==e.END&&(this.list.prev.next=t.list.next,t.list.next.prev=this.list.prev,t.list.prev.next=this.list,this.list.prev=t.list.prev,t.list.next=t.list.prev=t.list),this},t}();e.LinkedList=s},7233:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;oe.length}}}},t.prototype.add=function(e,r){void 0===r&&(r=t.DEFAULTPRIORITY);var n=this.items.length;do{n--}while(n>=0&&r=0&&this.items[e].item!==t);e>=0&&this.items.splice(e,1)},t.DEFAULTPRIORITY=5,t}();e.PrioritizedList=r},4542:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.retryAfter=e.handleRetriesFor=void 0,e.handleRetriesFor=function(t){return new Promise((function e(r,n){try{r(t())}catch(t){t.retry&&t.retry instanceof Promise?t.retry.then((function(){return e(r,n)})).catch((function(t){return n(t)})):t.restart&&t.restart.isCallback?MathJax.Callback.After((function(){return e(r,n)}),t.restart):n(t)}}))},e.retryAfter=function(t){var e=new Error("MathJax retry");throw e.retry=t,e}},4139:function(t,e){var r=this&&this.__values||function(t){var e="function"==typeof Symbol&&Symbol.iterator,r=e&&t[e],n=0;if(r)return r.call(t);if(t&&"number"==typeof t.length)return{next:function(){return t&&n>=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.CssStyles=void 0;var n=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=null),this.styles={},this.addStyles(t)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"cssText",{get:function(){return this.getStyleString()},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.addStyles=function(t){var e,n;if(t)try{for(var o=r(Object.keys(t)),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;this.styles[a]||(this.styles[a]={}),Object.assign(this.styles[a],t[a])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}},t.prototype.removeStyles=function(){for(var t,e,n=[],o=0;o=t.length&&(t=void 0),{value:t&&t[n++],done:!t}}};throw new TypeError(e?"Object is not iterable.":"Symbol.iterator is not defined.")},n=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var n,o,i=r.call(t),a=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},o=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o1;)e.shift(),r.push(e.shift());return r}function l(t){var e,n,o=s(this.styles[t]);0===o.length&&o.push(""),1===o.length&&o.push(o[0]),2===o.length&&o.push(o[0]),3===o.length&&o.push(o[1]);try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var l=a.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,l),o.shift())}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}function u(t){var e,n,o=v.connect[t].children,i=[];try{for(var a=r(o),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value,u=this.styles[t+"-"+l];if(!u)return void delete this.styles[t];i.push(u)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(n=a.return)&&n.call(a)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}i[3]===i[1]&&(i.pop(),i[2]===i[0]&&(i.pop(),i[1]===i[0]&&i.pop())),this.styles[t]=i.join(" ")}function c(t){var e,n;try{for(var o=r(v.connect[t].children),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,a),this.styles[t])}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(n=o.return)&&n.call(o)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}}function p(t){var e,i,a=o([],n(v.connect[t].children),!1),s=this.styles[this.childName(t,a.shift())];try{for(var l=r(a),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;if(this.styles[this.childName(t,c)]!==s)return void delete this.styles[t]}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(i=l.return)&&i.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}this.styles[t]=s}var f=/^(?:[\d.]+(?:[a-z]+)|thin|medium|thick|inherit|initial|unset)$/,h=/^(?:none|hidden|dotted|dashed|solid|double|groove|ridge|inset|outset|inherit|initial|unset)$/;function d(t){var e,n,o,i,a={width:"",style:"",color:""};try{for(var l=r(s(this.styles[t])),u=l.next();!u.done;u=l.next()){var c=u.value;c.match(f)&&""===a.width?a.width=c:c.match(h)&&""===a.style?a.style=c:a.color=c}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{u&&!u.done&&(n=l.return)&&n.call(l)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}try{for(var p=r(v.connect[t].children),d=p.next();!d.done;d=p.next()){var y=d.value;this.setStyle(this.childName(t,y),a[y])}}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(i=p.return)&&i.call(p)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}}function y(t){var e,n,o=[];try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.styles[this.childName(t,s)];l&&o.push(l)}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(n=i.return)&&n.call(i)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}o.length?this.styles[t]=o.join(" "):delete this.styles[t]}var O={style:/^(?:normal|italic|oblique|inherit|initial|unset)$/,variant:new RegExp("^(?:"+["normal|none","inherit|initial|unset","common-ligatures|no-common-ligatures","discretionary-ligatures|no-discretionary-ligatures","historical-ligatures|no-historical-ligatures","contextual|no-contextual","(?:stylistic|character-variant|swash|ornaments|annotation)\\([^)]*\\)","small-caps|all-small-caps|petite-caps|all-petite-caps|unicase|titling-caps","lining-nums|oldstyle-nums|proportional-nums|tabular-nums","diagonal-fractions|stacked-fractions","ordinal|slashed-zero","jis78|jis83|jis90|jis04|simplified|traditional","full-width|proportional-width","ruby"].join("|")+")$"),weight:/^(?:normal|bold|bolder|lighter|[1-9]00|inherit|initial|unset)$/,stretch:new RegExp("^(?:"+["normal","(?:(?:ultra|extra|semi)-)?condensed","(?:(?:semi|extra|ulta)-)?expanded","inherit|initial|unset"].join("|")+")$"),size:new RegExp("^(?:"+["xx-small|x-small|small|medium|large|x-large|xx-large|larger|smaller","[d.]+%|[d.]+[a-z]+","inherit|initial|unset"].join("|")+")(?:/(?:normal|[d.+](?:%|[a-z]+)?))?$")};function M(t){var e,o,i,a,l=s(this.styles[t]),u={style:"",variant:[],weight:"",stretch:"",size:"",family:"","line-height":""};try{for(var c=r(l),p=c.next();!p.done;p=c.next()){var f=p.value;u.family=f;try{for(var h=(i=void 0,r(Object.keys(O))),d=h.next();!d.done;d=h.next()){var y=d.value;if((Array.isArray(u[y])||""===u[y])&&f.match(O[y]))if("size"===y){var M=n(f.split(/\//),2),E=M[0],m=M[1];u[y]=E,m&&(u["line-height"]=m)}else""===u.size&&(Array.isArray(u[y])?u[y].push(f):u[y]=f)}}catch(t){i={error:t}}finally{try{d&&!d.done&&(a=h.return)&&a.call(h)}finally{if(i)throw i.error}}}}catch(t){e={error:t}}finally{try{p&&!p.done&&(o=c.return)&&o.call(c)}finally{if(e)throw e.error}}!function(t,e){var n,o;try{for(var i=r(v.connect[t].children),a=i.next();!a.done;a=i.next()){var s=a.value,l=this.childName(t,s);if(Array.isArray(e[s])){var u=e[s];u.length&&(this.styles[l]=u.join(" "))}else""!==e[s]&&(this.styles[l]=e[s])}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(o=i.return)&&o.call(i)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}}(t,u),delete this.styles[t]}function E(t){}var v=function(){function t(t){void 0===t&&(t=""),this.parse(t)}return Object.defineProperty(t.prototype,"cssText",{get:function(){var t,e,n=[];try{for(var o=r(Object.keys(this.styles)),i=o.next();!i.done;i=o.next()){var a=i.value,s=this.parentName(a);this.styles[s]||n.push(a+": "+this.styles[a]+";")}}catch(e){t={error:e}}finally{try{i&&!i.done&&(e=o.return)&&e.call(o)}finally{if(t)throw t.error}}return n.join(" ")},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),t.prototype.set=function(e,r){for(e=this.normalizeName(e),this.setStyle(e,r),t.connect[e]&&!t.connect[e].combine&&(this.combineChildren(e),delete this.styles[e]);e.match(/-/)&&(e=this.parentName(e),t.connect[e]);)t.connect[e].combine.call(this,e)},t.prototype.get=function(t){return t=this.normalizeName(t),this.styles.hasOwnProperty(t)?this.styles[t]:""},t.prototype.setStyle=function(e,r){this.styles[e]=r,t.connect[e]&&t.connect[e].children&&t.connect[e].split.call(this,e),""===r&&delete this.styles[e]},t.prototype.combineChildren=function(e){var n,o,i=this.parentName(e);try{for(var a=r(t.connect[e].children),s=a.next();!s.done;s=a.next()){var l=s.value,u=this.childName(i,l);t.connect[u].combine.call(this,u)}}catch(t){n={error:t}}finally{try{s&&!s.done&&(o=a.return)&&o.call(a)}finally{if(n)throw n.error}}},t.prototype.parentName=function(t){var e=t.replace(/-[^-]*$/,"");return t===e?"":e},t.prototype.childName=function(e,r){return r.match(/-/)?r:(t.connect[e]&&!t.connect[e].combine&&(r+=e.replace(/.*-/,"-"),e=this.parentName(e)),e+"-"+r)},t.prototype.normalizeName=function(t){return t.replace(/[A-Z]/g,(function(t){return"-"+t.toLowerCase()}))},t.prototype.parse=function(t){void 0===t&&(t="");var e=this.constructor.pattern;this.styles={};for(var r=t.replace(e.comment,"").split(e.style);r.length>1;){var o=n(r.splice(0,3),3),i=o[0],a=o[1],s=o[2];if(i.match(/[^\s\n]/))return;this.set(a,s)}},t.pattern={style:/([-a-z]+)[\s\n]*:[\s\n]*((?:'[^']*'|"[^"]*"|\n|.)*?)[\s\n]*(?:;|$)/g,comment:/\/\*[^]*?\*\//g},t.connect={padding:{children:i,split:l,combine:u},border:{children:i,split:c,combine:p},"border-top":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-right":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-bottom":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-left":{children:a,split:d,combine:y},"border-width":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},"border-style":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},"border-color":{children:i,split:l,combine:null},font:{children:["style","variant","weight","stretch","line-height","size","family"],split:M,combine:E}},t}();e.Styles=v},6010:function(t,e){Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.px=e.emRounded=e.em=e.percent=e.length2em=e.MATHSPACE=e.RELUNITS=e.UNITS=e.BIGDIMEN=void 0,e.BIGDIMEN=1e6,e.UNITS={px:1,in:96,cm:96/2.54,mm:96/25.4},e.RELUNITS={em:1,ex:.431,pt:.1,pc:1.2,mu:1/18},e.MATHSPACE={veryverythinmathspace:1/18,verythinmathspace:2/18,thinmathspace:3/18,mediummathspace:4/18,thickmathspace:5/18,verythickmathspace:6/18,veryverythickmathspace:7/18,negativeveryverythinmathspace:-1/18,negativeverythinmathspace:-2/18,negativethinmathspace:-3/18,negativemediummathspace:-4/18,negativethickmathspace:-5/18,negativeverythickmathspace:-6/18,negativeveryverythickmathspace:-7/18,thin:.04,medium:.06,thick:.1,normal:1,big:2,small:1/Math.sqrt(2),infinity:e.BIGDIMEN},e.length2em=function(t,r,n,o){if(void 0===r&&(r=0),void 0===n&&(n=1),void 0===o&&(o=16),"string"!=typeof t&&(t=String(t)),""===t||null==t)return r;if(e.MATHSPACE[t])return e.MATHSPACE[t];var i=t.match(/^\s*([-+]?(?:\.\d+|\d+(?:\.\d*)?))?(pt|em|ex|mu|px|pc|in|mm|cm|%)?/);if(!i)return r;var a=parseFloat(i[1]||"1"),s=i[2];return e.UNITS.hasOwnProperty(s)?a*e.UNITS[s]/o/n:e.RELUNITS.hasOwnProperty(s)?a*e.RELUNITS[s]:"%"===s?a/100*r:a*r},e.percent=function(t){return(100*t).toFixed(1).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"%"},e.em=function(t){return Math.abs(t)<.001?"0":t.toFixed(3).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"em"},e.emRounded=function(t,e){return void 0===e&&(e=16),t=(Math.round(t*e)+.05)/e,Math.abs(t)<.001?"0em":t.toFixed(3).replace(/\.?0+$/,"")+"em"},e.px=function(t,r,n){return void 0===r&&(r=-e.BIGDIMEN),void 0===n&&(n=16),t*=n,r&&t0)&&!(n=i.next()).done;)a.push(n.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return a},n=this&&this.__spreadArray||function(t,e,r){if(r||2===arguments.length)for(var n,o=0,i=e.length;o0)&&!(n=s.next()).done;)r.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return r};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AsciiMath=void 0;var o=i(309),l=i(406),u=i(77),h=i(577),p=function(t){function e(i){var n=this,a=r((0,u.separateOptions)(i,h.FindAsciiMath.OPTIONS,e.OPTIONS),3),s=a[1],o=a[2];return(n=t.call(this,o)||this).findAsciiMath=n.options.FindAsciiMath||new h.FindAsciiMath(s),n}return a(e,t),e.prototype.compile=function(t,e){return l.LegacyAsciiMath.Compile(t.math,t.display)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){return this.findAsciiMath.findMath(t)},e.NAME="AsciiMath",e.OPTIONS=s(s({},o.AbstractInputJax.OPTIONS),{FindAsciiMath:null}),e}(o.AbstractInputJax);e.AsciiMath=p},577:function(t,e,i){"use strict";var n,a=this&&this.__extends||(n=function(t,e){return n=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var i in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,i)&&(t[i]=e[i])},n(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function i(){this.constructor=t}n(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(i.prototype=e.prototype,new i)}),s=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var i="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!i)return t;var n,a,s=i.call(t),r=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(n=s.next()).done;)r.push(n.value)}catch(t){a={error:t}}finally{try{n&&!n.done&&(i=s.return)&&i.call(s)}finally{if(a)throw a.error}}return r};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.FindAsciiMath=void 0;var r=i(649),o=i(720),l=i(769),u=function(t){function e(e){var i=t.call(this,e)||this;return i.getPatterns(),i}return a(e,t),e.prototype.getPatterns=function(){var t=this,e=this.options,i=[];this.end={},e.delimiters.forEach((function(e){return t.addPattern(i,e,!1)})),this.start=new RegExp(i.join("|"),"g"),this.hasPatterns=i.length>0},e.prototype.addPattern=function(t,e,i){var n=s(e,2),a=n[0],r=n[1];t.push((0,o.quotePattern)(a)),this.end[a]=[r,i,new RegExp((0,o.quotePattern)(r),"g")]},e.prototype.findEnd=function(t,e,i,n){var a=s(n,3),r=a[1],o=a[2],u=o.lastIndex=i.index+i[0].length,h=o.exec(t);return h?(0,l.protoItem)(i[0],t.substr(u,h.index-u),h[0],e,i.index,h.index+h[0].length,r):null},e.prototype.findMathInString=function(t,e,i){var n,a;for(this.start.lastIndex=0;n=this.start.exec(i);)(a=this.findEnd(i,e,n,this.end[n[0]]))&&(t.push(a),this.start.lastIndex=a.end.n)},e.prototype.findMath=function(t){var e=[];if(this.hasPatterns)for(var i=0,n=t.length;i1&&(t=2===arguments.length&&"function"!=typeof arguments[0]&&arguments[0]instanceof Object&&"number"==typeof arguments[1]?[].slice.call(t,e):[].slice.call(arguments,0)),t instanceof Array&&1===t.length&&(t=t[0]),"function"==typeof t)return t.execute===i.prototype.execute?t:i({hook:t});if(t instanceof Array){if("string"==typeof t[0]&&t[1]instanceof Object&&"function"==typeof t[1][t[0]])return i({hook:t[1][t[0]],object:t[1],data:t.slice(2)});if("function"==typeof t[0])return i({hook:t[0],data:t.slice(1)});if("function"==typeof t[1])return i({hook:t[1],object:t[0],data:t.slice(2)})}else{if("string"==typeof t)return s&&s(),i({hook:a,data:[t]});if(t instanceof Object)return i(t);if(void 0===t)return i({})}throw Error("Can't make callback from given data")},o=function(t,e){(t=r(t)).called||(p(t,e),e.pending++)},l=function(){var t=this.signal;delete this.signal,this.execute=this.oldExecute,delete this.oldExecute;var e=this.execute.apply(this,arguments);if(n(e)&&!e.called)p(e,t);else for(var i=0,a=t.length;i0&&e=0;t--)this.hooks.splice(t,1);this.remove=[]}}),f=e.Object.Subclass({Init:function(){this.pending=this.running=0,this.queue=[],this.Push.apply(this,arguments)},Push:function(){for(var t,e=0,i=arguments.length;e=this.timeout?(t(this.STATUS.ERROR),1):0},file:function(t,i){i<0?e.Ajax.loadTimeout(t):e.Ajax.loadComplete(t)},execute:function(){this.hook.call(this.object,this,this.data[0],this.data[1])},checkSafari2:function(t,e,i){t.time(i)||(c.styleSheets.length>e&&c.styleSheets[e].cssRules&&c.styleSheets[e].cssRules.length?i(t.STATUS.OK):setTimeout(t,t.delay))},checkLength:function(t,i,n){if(!t.time(n)){var a=0,s=i.sheet||i.styleSheet;try{(s.cssRules||s.rules||[]).length>0&&(a=1)}catch(t){(t.message.match(/protected variable|restricted URI/)||t.message.match(/Security error/))&&(a=1)}a?setTimeout(e.Callback([n,t.STATUS.OK]),0):setTimeout(t,t.delay)}}},loadComplete:function(t){t=this.fileURL(t);var i=this.loading[t];return i&&!i.preloaded?(e.Message.Clear(i.message),i.timeout&&clearTimeout(i.timeout),i.script&&(0===a.length&&setTimeout(s,0),a.push(i.script)),this.loaded[t]=i.status,delete this.loading[t],this.addHook(t,i.callback)):(i&&delete this.loading[t],this.loaded[t]=this.STATUS.OK,i={status:this.STATUS.OK}),this.loadHooks[t]?this.loadHooks[t].Execute(i.status):null},loadTimeout:function(t){this.loading[t].timeout&&clearTimeout(this.loading[t].timeout),this.loading[t].status=this.STATUS.ERROR,this.loadError(t),this.loadComplete(t)},loadError:function(t){e.Message.Set(["LoadFailed","File failed to load: %1",t],null,2e3),e.Hub.signal.Post(["file load error",t])},Styles:function(t,i){var n=this.StyleString(t);if(""===n)(i=e.Callback(i))();else{var a=c.createElement("style");a.type="text/css",this.head=(this.head,null),this.head.appendChild(a),a.styleSheet&&void 0!==a.styleSheet.cssText?a.styleSheet.cssText=n:a.appendChild(c.createTextNode(n)),i=this.timer.create.call(this,i,a)}return i},StyleString:function(t){if("string"==typeof t)return t;var e,i,n="";for(e in t)if(t.hasOwnProperty(e))if("string"==typeof t[e])n+=e+" {"+t[e]+"}\n";else if(t[e]instanceof Array)for(var a=0;a="0"&&r<="9")s[n]=e[s[n]-1],"number"==typeof s[n]&&(s[n]=this.number(s[n]));else if("{"===r)if((r=s[n].substr(1))>="0"&&r<="9")s[n]=e[s[n].substr(1,s[n].length-2)-1],"number"==typeof s[n]&&(s[n]=this.number(s[n]));else{var o=s[n].match(/^\{([a-z]+):%(\d+)\|(.*)\}$/);if(o)if("plural"===o[1]){var l=e[o[2]-1];if(void 0===l)s[n]="???";else{l=this.plural(l)-1;var u=o[3].replace(/(^|[^%])(%%)*%\|/g,"$1$2%\uefef").split(/\|/);l>=0&&l=3?i.push([s[0],s[1],this.processSnippet(t,s[2])]):i.push(e[n])}else i.push(e[n]);return i},markdownPattern:/(%.)|(\*{1,3})((?:%.|.)+?)\2|(`+)((?:%.|.)+?)\4|\[((?:%.|.)+?)\]\(([^\s\)]+)\)/,processMarkdown:function(t,e,i){for(var n,a=[],s=t.split(this.markdownPattern),r=s[0],o=1,l=s.length;o0||this.Get("scriptlevel")>0)&&n>=0?"":this.TEXSPACELENGTH[Math.abs(n)]},TEXSPACELENGTH:["",t.LENGTH.THINMATHSPACE,t.LENGTH.MEDIUMMATHSPACE,t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE],TEXSPACE:[[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[-1,-1,0,3,0,0,0,1],[2,2,0,0,2,0,0,2],[3,3,0,0,3,0,0,3],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,-1,2,3,0,0,0,1],[1,1,0,1,1,1,1,1],[1,-1,2,3,1,0,1,1]],autoDefault:function(t){return""},isSpacelike:function(){return!1},isEmbellished:function(){return!1},Core:function(){return this},CoreMO:function(){return this},childIndex:function(t){if(null!=t)for(var e=0,i=this.data.length;e=55296&&i.charCodeAt(0)<56320?t.VARIANT.ITALIC:t.VARIANT.NORMAL}return""},setTeXclass:function(e){this.getPrevClass(e);var i=this.data.join("");return i.length>1&&i.match(/^[a-z][a-z0-9]*$/i)&&this.texClass===t.TEXCLASS.ORD&&(this.texClass=t.TEXCLASS.OP,this.autoOP=!0),this}}),t.mn=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mn",isToken:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,defaults:{mathvariant:t.INHERIT,mathsize:t.INHERIT,mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT}}),t.mo=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mo",isToken:!0,defaults:{mathvariant:t.INHERIT,mathsize:t.INHERIT,mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT,form:t.AUTO,fence:t.AUTO,separator:t.AUTO,lspace:t.AUTO,rspace:t.AUTO,stretchy:t.AUTO,symmetric:t.AUTO,maxsize:t.AUTO,minsize:t.AUTO,largeop:t.AUTO,movablelimits:t.AUTO,accent:t.AUTO,linebreak:t.LINEBREAK.AUTO,lineleading:t.INHERIT,linebreakstyle:t.AUTO,linebreakmultchar:t.INHERIT,indentalign:t.INHERIT,indentshift:t.INHERIT,indenttarget:t.INHERIT,indentalignfirst:t.INHERIT,indentshiftfirst:t.INHERIT,indentalignlast:t.INHERIT,indentshiftlast:t.INHERIT,texClass:t.AUTO},defaultDef:{form:t.FORM.INFIX,fence:!1,separator:!1,lspace:t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE,rspace:t.LENGTH.THICKMATHSPACE,stretchy:!1,symmetric:!1,maxsize:t.SIZE.INFINITY,minsize:"0em",largeop:!1,movablelimits:!1,accent:!1,linebreak:t.LINEBREAK.AUTO,lineleading:"1ex",linebreakstyle:"before",indentalign:t.INDENTALIGN.AUTO,indentshift:"0",indenttarget:"",indentalignfirst:t.INDENTALIGN.INDENTALIGN,indentshiftfirst:t.INDENTSHIFT.INDENTSHIFT,indentalignlast:t.INDENTALIGN.INDENTALIGN,indentshiftlast:t.INDENTSHIFT.INDENTSHIFT,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.REL},SPACE_ATTR:{lspace:1,rspace:2,form:4},useMMLspacing:7,autoDefault:function(e,i){var n=this.def;if(!n){if("form"===e)return this.useMMLspacing&=~this.SPACE_ATTR.form,this.getForm();for(var a=this.data.join(""),s=[this.Get("form"),t.FORM.INFIX,t.FORM.POSTFIX,t.FORM.PREFIX],r=0,o=s.length;r=55296&&i<56320&&(i=(i-55296<<10)+(e.charCodeAt(1)-56320)+65536);for(var n=0,a=this.RANGES.length;n=0;t--)if(this.data[0]&&!this.data[t].isSpacelike())return this.data[t];return null},Core:function(){return this.isEmbellished()&&void 0!==this.core?this.data[this.core]:this},CoreMO:function(){return this.isEmbellished()&&void 0!==this.core?this.data[this.core].CoreMO():this},toString:function(){return this.inferred?"["+this.data.join(",")+"]":this.SUPER(arguments).toString.call(this)},setTeXclass:function(e){var i,n=this.data.length;if(!this.open&&!this.close||e&&e.fnOP){for(i=0;i0)&&e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t==this.den||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses}),t.msqrt=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"msqrt",inferRow:!0,linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses,adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return!0}}),t.mroot=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mroot",linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,adjustChild_displaystyle:function(t){return 1!==t&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel");return 1===t&&(e+=2),e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return 0===t||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setSeparateTeXclasses}),t.mstyle=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mstyle",isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,inferRow:!0,defaults:{scriptlevel:t.INHERIT,displaystyle:t.INHERIT,scriptsizemultiplier:Math.sqrt(.5),scriptminsize:"8pt",mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,dir:t.INHERIT,infixlinebreakstyle:t.LINEBREAKSTYLE.BEFORE,decimalseparator:"."},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.scriptlevel;if(null==e)e=this.Get("scriptlevel");else if(String(e).match(/^ *[-+]/)){e=this.Get("scriptlevel",null,!0)+parseInt(e)}return e},inheritFromMe:!0,noInherit:{mpadded:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,lspace:!0,voffset:!0},mtable:{width:!0,height:!0,depth:!0,align:!0}},getRemoved:{fontfamily:"fontFamily",fontweight:"fontWeight",fontstyle:"fontStyle",fontsize:"fontSize"},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.merror=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"merror",inferRow:!0,linebreakContainer:!0,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD}),t.mpadded=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mpadded",inferRow:!0,isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,width:"",height:"",depth:"",lspace:0,voffset:0},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.mphantom=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mphantom",texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,inferRow:!0,isSpacelike:t.mbase.childrenSpacelike,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,setTeXclass:t.mbase.setChildTeXclass}),t.mfenced=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mfenced",defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,open:"(",close:")",separators:","},addFakeNodes:function(){var e=this.getValues("open","close","separators");if(e.open=e.open.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),e.close=e.close.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),e.separators=e.separators.replace(/[ \t\n\r]/g,""),""!==e.open&&(this.SetData("open",t.mo(e.open).With({fence:!0,form:t.FORM.PREFIX,texClass:t.TEXCLASS.OPEN})),this.data.open.useMMLspacing=0),""!==e.separators){for(;e.separators.length0)&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel");return t>0&&e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t===this.sub||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setBaseTeXclasses}),t.msub=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"msub"}),t.msup=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"msup",sub:2,sup:1}),t.mmultiscripts=t.msubsup.Subclass({type:"mmultiscripts",adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return t%2==1||this.Get("texprimestyle")}}),t.mprescripts=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mprescripts"}),t.none=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"none"}),t.munderover=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"munderover",base:0,under:1,over:2,sub:1,sup:2,ACCENTS:["","accentunder","accent"],linebreakContainer:!0,isEmbellished:t.mbase.childEmbellished,Core:t.mbase.childCore,CoreMO:t.mbase.childCoreMO,defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,accent:t.AUTO,accentunder:t.AUTO,align:t.ALIGN.CENTER,texClass:t.AUTO,subscriptshift:"",superscriptshift:""},autoDefault:function(e){return"texClass"===e?this.isEmbellished()?this.CoreMO().Get(e):t.TEXCLASS.ORD:"accent"===e&&this.data[this.over]?this.data[this.over].CoreMO().Get("accent"):!("accentunder"!==e||!this.data[this.under])&&this.data[this.under].CoreMO().Get("accent")},adjustChild_displaystyle:function(t){return!(t>0)&&this.Get("displaystyle")},adjustChild_scriptlevel:function(t){var e=this.Get("scriptlevel"),i=this.data[this.base]&&!this.Get("displaystyle")&&this.data[this.base].CoreMO().Get("movablelimits");return t!=this.under||!i&&this.Get("accentunder")||e++,t!=this.over||!i&&this.Get("accent")||e++,e},adjustChild_texprimestyle:function(t){return!(t!==this.base||!this.data[this.over])||this.Get("texprimestyle")},setTeXclass:t.mbase.setBaseTeXclasses}),t.munder=t.munderover.Subclass({type:"munder"}),t.mover=t.munderover.Subclass({type:"mover",over:1,under:2,sup:1,sub:2,ACCENTS:["","accent","accentunder"]}),t.mtable=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"mtable",defaults:{mathbackground:t.INHERIT,mathcolor:t.INHERIT,align:t.ALIGN.AXIS,rowalign:t.ALIGN.BASELINE,columnalign:t.ALIGN.CENTER,groupalign:"{left}",alignmentscope:!0,columnwidth:t.WIDTH.AUTO,width:t.WIDTH.AUTO,rowspacing:"1ex",columnspacing:".8em",rowlines:t.LINES.NONE,columnlines:t.LINES.NONE,frame:t.LINES.NONE,framespacing:"0.4em 0.5ex",equalrows:!1,equalcolumns:!1,displaystyle:!1,side:t.SIDE.RIGHT,minlabelspacing:"0.8em",texClass:t.TEXCLASS.ORD,useHeight:1},adjustChild_displaystyle:function(){return null!=this.displaystyle?this.displaystyle:this.defaults.displaystyle},inheritFromMe:!0,noInherit:{mover:{align:!0},munder:{align:!0},munderover:{align:!0},mtable:{align:!0,rowalign:!0,columnalign:!0,groupalign:!0,alignmentscope:!0,columnwidth:!0,width:!0,rowspacing:!0,columnspacing:!0,rowlines:!0,columnlines:!0,frame:!0,framespacing:!0,equalrows:!0,equalcolumns:!0,displaystyle:!0,side:!0,minlabelspacing:!0,texClass:!0,useHeight:1}},linebreakContainer:!0,Append:function(){for(var e=0,i=arguments.length;e>10),56320+(1023&t)))}}),t.xml=t.mbase.Subclass({type:"xml",Init:function(){return this.div=document.createElement("div"),this.SUPER(arguments).Init.apply(this,arguments)},Append:function(){for(var t=0,e=arguments.length;t":i.REL,"?":[1,1,e.CLOSE],"\\":i.ORD,"^":i.ORD11,_:i.ORD11,"|":[2,2,e.ORD,{fence:!0,stretchy:!0,symmetric:!0}],"#":i.ORD,$:i.ORD,".":[0,3,e.PUNCT,{separator:!0}],"\u02b9":i.ORD,"\u0300":i.ACCENT,"\u0301":i.ACCENT,"\u0303":i.WIDEACCENT,"\u0304":i.ACCENT,"\u0306":i.ACCENT,"\u0307":i.ACCENT,"\u0308":i.ACCENT,"\u030c":i.ACCENT,"\u0332":i.WIDEACCENT,"\u0338":i.REL4,"\u2015":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2017":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u2020":i.BIN3,"\u2021":i.BIN3,"\u20d7":i.ACCENT,"\u2111":i.ORD,"\u2113":i.ORD,"\u2118":i.ORD,"\u211c":i.ORD,"\u2205":i.ORD,"\u221e":i.ORD,"\u2305":i.BIN3,"\u2306":i.BIN3,"\u2322":i.REL4,"\u2323":i.REL4,"\u2329":i.OPEN,"\u232a":i.CLOSE,"\u23aa":i.ORD,"\u23af":[0,0,e.ORD,{stretchy:!0}],"\u23b0":i.OPEN,"\u23b1":i.CLOSE,"\u2500":i.ORD,"\u25ef":i.BIN3,"\u2660":i.ORD,"\u2661":i.ORD,"\u2662":i.ORD,"\u2663":i.ORD,"\u3008":i.OPEN,"\u3009":i.CLOSE,"\ufe37":i.WIDEACCENT,"\ufe38":i.WIDEACCENT}}},{OPTYPES:i});var n=t.mo.prototype.OPTABLE;n.infix["^"]=i.WIDEREL,n.infix._=i.WIDEREL,n.prefix["\u2223"]=i.OPEN,n.prefix["\u2225"]=i.OPEN,n.postfix["\u2223"]=i.CLOSE,n.postfix["\u2225"]=i.CLOSE}(MathJax.ElementJax.mml),MathJax.ElementJax.mml.loadComplete("jax.js")},315:function(){MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath=MathJax.InputJax({id:"AsciiMath",version:"2.7.2",directory:MathJax.InputJax.directory+"/AsciiMath",extensionDir:MathJax.InputJax.extensionDir+"/AsciiMath",config:{fixphi:!0,useMathMLspacing:!0,displaystyle:!0,decimalsign:"."}}),MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath.Register("math/asciimath"),MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath.loadComplete("config.js")},247:function(){var t,e;!function(t){var e,i=MathJax.Object.Subclass({firstChild:null,lastChild:null,Init:function(){this.childNodes=[]},appendChild:function(t){return t.parent&&t.parent.removeChild(t),this.lastChild&&(this.lastChild.nextSibling=t),this.firstChild||(this.firstChild=t),this.childNodes.push(t),t.parent=this,this.lastChild=t,t},removeChild:function(t){for(var e=0,i=this.childNodes.length;e=n-1&&(this.lastChild=t),this.childNodes[i]=t,t.nextSibling=e.nextSibling,e.nextSibling=e.parent=null,e},hasChildNodes:function(t){return this.childNodes.length>0},toString:function(){return"{"+this.childNodes.join("")+"}"}}),n={getElementById:!0,createElementNS:function(i,n){var a=e[n]();return"mo"===n&&t.config.useMathMLspacing&&(a.useMMLspacing=128),a},createTextNode:function(t){return e.chars(t).With({nodeValue:t})},createDocumentFragment:function(){return i()}},a={appName:"MathJax"},s="blue",r=!0,o=!0,l=".",u="Microsoft"==a.appName.slice(0,9);function h(t){return u?n.createElement(t):n.createElementNS("http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml",t)}var p="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML";function c(t){return u?n.createElement("m:"+t):n.createElementNS(p,t)}function d(t,e){var i;return i=u?n.createElement("m:"+t):n.createElementNS(p,t),e&&i.appendChild(e),i}var m=["\ud835\udc9c","\u212c","\ud835\udc9e","\ud835\udc9f","\u2130","\u2131","\ud835\udca2","\u210b","\u2110","\ud835\udca5","\ud835\udca6","\u2112","\u2133","\ud835\udca9","\ud835\udcaa","\ud835\udcab","\ud835\udcac","\u211b","\ud835\udcae","\ud835\udcaf","\ud835\udcb0","\ud835\udcb1","\ud835\udcb2","\ud835\udcb3","\ud835\udcb4","\ud835\udcb5","\ud835\udcb6","\ud835\udcb7","\ud835\udcb8","\ud835\udcb9","\u212f","\ud835\udcbb","\u210a","\ud835\udcbd","\ud835\udcbe","\ud835\udcbf","\ud835\udcc0","\ud835\udcc1","\ud835\udcc2","\ud835\udcc3","\u2134","\ud835\udcc5","\ud835\udcc6","\ud835\udcc7","\ud835\udcc8","\ud835\udcc9","\ud835\udcca","\ud835\udccb","\ud835\udccc","\ud835\udccd","\ud835\udcce","\ud835\udccf"],f=["\ud835\udd04","\ud835\udd05","\u212d","\ud835\udd07","\ud835\udd08","\ud835\udd09","\ud835\udd0a","\u210c","\u2111","\ud835\udd0d","\ud835\udd0e","\ud835\udd0f","\ud835\udd10","\ud835\udd11","\ud835\udd12","\ud835\udd13","\ud835\udd14","\u211c","\ud835\udd16","\ud835\udd17","\ud835\udd18","\ud835\udd19","\ud835\udd1a","\ud835\udd1b","\ud835\udd1c","\u2128","\ud835\udd1e","\ud835\udd1f","\ud835\udd20","\ud835\udd21","\ud835\udd22","\ud835\udd23","\ud835\udd24","\ud835\udd25","\ud835\udd26","\ud835\udd27","\ud835\udd28","\ud835\udd29","\ud835\udd2a","\ud835\udd2b","\ud835\udd2c","\ud835\udd2d","\ud835\udd2e","\ud835\udd2f","\ud835\udd30","\ud835\udd31","\ud835\udd32","\ud835\udd33","\ud835\udd34","\ud835\udd35","\ud835\udd36","\ud835\udd37"],g=["\ud835\udd38","\ud835\udd39","\u2102","\ud835\udd3b","\ud835\udd3c","\ud835\udd3d","\ud835\udd3e","\u210d","\ud835\udd40","\ud835\udd41","\ud835\udd42","\ud835\udd43","\ud835\udd44","\u2115","\ud835\udd46","\u2119","\u211a","\u211d","\ud835\udd4a","\ud835\udd4b","\ud835\udd4c","\ud835\udd4d","\ud835\udd4e","\ud835\udd4f","\ud835\udd50","\u2124","\ud835\udd52","\ud835\udd53","\ud835\udd54","\ud835\udd55","\ud835\udd56","\ud835\udd57","\ud835\udd58","\ud835\udd59","\ud835\udd5a","\ud835\udd5b","\ud835\udd5c","\ud835\udd5d","\ud835\udd5e","\ud835\udd5f","\ud835\udd60","\ud835\udd61","\ud835\udd62","\ud835\udd63","\ud835\udd64","\ud835\udd65","\ud835\udd66","\ud835\udd67","\ud835\udd68","\ud835\udd69","\ud835\udd6a","\ud835\udd6b"],y=0,E=1,x=2,T=3,C=4,b=5,S=6,I=7,N=8,A=9,v=10,R=15,O={input:'"',tag:"mtext",output:"mbox",tex:null,ttype:v},L=[{input:"alpha",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"beta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b2",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"chi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c7",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"delta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Delta",tag:"mo",output:"\u0394",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"epsi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b5",tex:"epsilon",ttype:y},{input:"varepsilon",tag:"mi",output:"\u025b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"eta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b7",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"gamma",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Gamma",tag:"mo",output:"\u0393",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"iota",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"kappa",tag:"mi",output:"\u03ba",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lambda",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Lambda",tag:"mo",output:"\u039b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lamda",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Lamda",tag:"mo",output:"\u039b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"mu",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bc",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"nu",tag:"mi",output:"\u03bd",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"omega",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Omega",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a9",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"phi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03d5",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"varphi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Phi",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"pi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Pi",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"psi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Psi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03a8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"rho",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"sigma",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Sigma",tag:"mo",output:"\u03a3",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"tau",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"theta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b8",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"vartheta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03d1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Theta",tag:"mo",output:"\u0398",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"upsilon",tag:"mi",output:"\u03c5",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"xi",tag:"mi",output:"\u03be",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"Xi",tag:"mo",output:"\u039e",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"zeta",tag:"mi",output:"\u03b6",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"*",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c5",tex:"cdot",ttype:y},{input:"**",tag:"mo",output:"\u2217",tex:"ast",ttype:y},{input:"***",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c6",tex:"star",ttype:y},{input:"//",tag:"mo",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"\\\\",tag:"mo",output:"\\",tex:"backslash",ttype:y},{input:"setminus",tag:"mo",output:"\\",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"xx",tag:"mo",output:"\xd7",tex:"times",ttype:y},{input:"|><",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c9",tex:"ltimes",ttype:y},{input:"><|",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ca",tex:"rtimes",ttype:y},{input:"|><|",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c8",tex:"bowtie",ttype:y},{input:"-:",tag:"mo",output:"\xf7",tex:"div",ttype:y},{input:"divide",tag:"mo",output:"-:",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"@",tag:"mo",output:"\u2218",tex:"circ",ttype:y},{input:"o+",tag:"mo",output:"\u2295",tex:"oplus",ttype:y},{input:"ox",tag:"mo",output:"\u2297",tex:"otimes",ttype:y},{input:"o.",tag:"mo",output:"\u2299",tex:"odot",ttype:y},{input:"sum",tag:"mo",output:"\u2211",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"prod",tag:"mo",output:"\u220f",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"^^",tag:"mo",output:"\u2227",tex:"wedge",ttype:y},{input:"^^^",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c0",tex:"bigwedge",ttype:I},{input:"vv",tag:"mo",output:"\u2228",tex:"vee",ttype:y},{input:"vvv",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c1",tex:"bigvee",ttype:I},{input:"nn",tag:"mo",output:"\u2229",tex:"cap",ttype:y},{input:"nnn",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c2",tex:"bigcap",ttype:I},{input:"uu",tag:"mo",output:"\u222a",tex:"cup",ttype:y},{input:"uuu",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c3",tex:"bigcup",ttype:I},{input:"!=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2260",tex:"ne",ttype:y},{input:":=",tag:"mo",output:":=",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"lt",tag:"mo",output:"<",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"<=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2264",tex:"le",ttype:y},{input:"lt=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2264",tex:"leq",ttype:y},{input:"gt",tag:"mo",output:">",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:">=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2265",tex:"ge",ttype:y},{input:"gt=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2265",tex:"geq",ttype:y},{input:"-<",tag:"mo",output:"\u227a",tex:"prec",ttype:y},{input:"-lt",tag:"mo",output:"\u227a",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:">-",tag:"mo",output:"\u227b",tex:"succ",ttype:y},{input:"-<=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2aaf",tex:"preceq",ttype:y},{input:">-=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2ab0",tex:"succeq",ttype:y},{input:"in",tag:"mo",output:"\u2208",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"!in",tag:"mo",output:"\u2209",tex:"notin",ttype:y},{input:"sub",tag:"mo",output:"\u2282",tex:"subset",ttype:y},{input:"sup",tag:"mo",output:"\u2283",tex:"supset",ttype:y},{input:"sube",tag:"mo",output:"\u2286",tex:"subseteq",ttype:y},{input:"supe",tag:"mo",output:"\u2287",tex:"supseteq",ttype:y},{input:"-=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2261",tex:"equiv",ttype:y},{input:"~=",tag:"mo",output:"\u2245",tex:"cong",ttype:y},{input:"~~",tag:"mo",output:"\u2248",tex:"approx",ttype:y},{input:"~",tag:"mo",output:"\u223c",tex:"sim",ttype:y},{input:"prop",tag:"mo",output:"\u221d",tex:"propto",ttype:y},{input:"and",tag:"mtext",output:"and",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"or",tag:"mtext",output:"or",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"not",tag:"mo",output:"\xac",tex:"neg",ttype:y},{input:"=>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d2",tex:"implies",ttype:y},{input:"if",tag:"mo",output:"if",tex:null,ttype:S},{input:"<=>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d4",tex:"iff",ttype:y},{input:"AA",tag:"mo",output:"\u2200",tex:"forall",ttype:y},{input:"EE",tag:"mo",output:"\u2203",tex:"exists",ttype:y},{input:"_|_",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a5",tex:"bot",ttype:y},{input:"TT",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a4",tex:"top",ttype:y},{input:"|--",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a2",tex:"vdash",ttype:y},{input:"|==",tag:"mo",output:"\u22a8",tex:"models",ttype:y},{input:"(",tag:"mo",output:"(",tex:"left(",ttype:C},{input:")",tag:"mo",output:")",tex:"right)",ttype:b},{input:"[",tag:"mo",output:"[",tex:"left[",ttype:C},{input:"]",tag:"mo",output:"]",tex:"right]",ttype:b},{input:"{",tag:"mo",output:"{",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:"}",tag:"mo",output:"}",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"|",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:A},{input:":|:",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"|:",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:":|",tag:"mo",output:"|",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"(:",tag:"mo",output:"\u2329",tex:"langle",ttype:C},{input:":)",tag:"mo",output:"\u232a",tex:"rangle",ttype:b},{input:"<<",tag:"mo",output:"\u2329",tex:null,ttype:C},{input:">>",tag:"mo",output:"\u232a",tex:null,ttype:b},{input:"{:",tag:"mo",output:"{:",tex:null,ttype:C,invisible:!0},{input:":}",tag:"mo",output:":}",tex:null,ttype:b,invisible:!0},{input:"int",tag:"mo",output:"\u222b",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"dx",tag:"mi",output:"{:d x:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dy",tag:"mi",output:"{:d y:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dz",tag:"mi",output:"{:d z:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"dt",tag:"mi",output:"{:d t:}",tex:null,ttype:N},{input:"oint",tag:"mo",output:"\u222e",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"del",tag:"mo",output:"\u2202",tex:"partial",ttype:y},{input:"grad",tag:"mo",output:"\u2207",tex:"nabla",ttype:y},{input:"+-",tag:"mo",output:"\xb1",tex:"pm",ttype:y},{input:"-+",tag:"mo",output:"\u2213",tex:"mp",ttype:y},{input:"O/",tag:"mo",output:"\u2205",tex:"emptyset",ttype:y},{input:"oo",tag:"mo",output:"\u221e",tex:"infty",ttype:y},{input:"aleph",tag:"mo",output:"\u2135",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"...",tag:"mo",output:"...",tex:"ldots",ttype:y},{input:":.",tag:"mo",output:"\u2234",tex:"therefore",ttype:y},{input:":'",tag:"mo",output:"\u2235",tex:"because",ttype:y},{input:"/_",tag:"mo",output:"\u2220",tex:"angle",ttype:y},{input:"/_\\",tag:"mo",output:"\u25b3",tex:"triangle",ttype:y},{input:"'",tag:"mo",output:"\u2032",tex:"prime",ttype:y},{input:"tilde",tag:"mover",output:"~",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"\\ ",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"frown",tag:"mo",output:"\u2322",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"quad",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"qquad",tag:"mo",output:"\xa0\xa0\xa0\xa0",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"cdots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ef",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"vdots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22ee",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"ddots",tag:"mo",output:"\u22f1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"diamond",tag:"mo",output:"\u22c4",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"square",tag:"mo",output:"\u25a1",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"|__",tag:"mo",output:"\u230a",tex:"lfloor",ttype:y},{input:"__|",tag:"mo",output:"\u230b",tex:"rfloor",ttype:y},{input:"|~",tag:"mo",output:"\u2308",tex:"lceiling",ttype:y},{input:"~|",tag:"mo",output:"\u2309",tex:"rceiling",ttype:y},{input:"CC",tag:"mo",output:"\u2102",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"NN",tag:"mo",output:"\u2115",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"QQ",tag:"mo",output:"\u211a",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"RR",tag:"mo",output:"\u211d",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"ZZ",tag:"mo",output:"\u2124",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"f",tag:"mi",output:"f",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"g",tag:"mi",output:"g",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lim",tag:"mo",output:"lim",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"Lim",tag:"mo",output:"Lim",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"sin",tag:"mo",output:"sin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cos",tag:"mo",output:"cos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"tan",tag:"mo",output:"tan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sinh",tag:"mo",output:"sinh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cosh",tag:"mo",output:"cosh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"tanh",tag:"mo",output:"tanh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"cot",tag:"mo",output:"cot",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sec",tag:"mo",output:"sec",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"csc",tag:"mo",output:"csc",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arcsin",tag:"mo",output:"arcsin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arccos",tag:"mo",output:"arccos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"arctan",tag:"mo",output:"arctan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"coth",tag:"mo",output:"coth",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"sech",tag:"mo",output:"sech",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"csch",tag:"mo",output:"csch",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"exp",tag:"mo",output:"exp",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"abs",tag:"mo",output:"abs",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["|","|"]},{input:"norm",tag:"mo",output:"norm",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u2225","\u2225"]},{input:"floor",tag:"mo",output:"floor",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u230a","\u230b"]},{input:"ceil",tag:"mo",output:"ceil",tex:null,ttype:E,rewriteleftright:["\u2308","\u2309"]},{input:"log",tag:"mo",output:"log",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"ln",tag:"mo",output:"ln",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"det",tag:"mo",output:"det",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"dim",tag:"mo",output:"dim",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"mod",tag:"mo",output:"mod",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"gcd",tag:"mo",output:"gcd",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lcm",tag:"mo",output:"lcm",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"lub",tag:"mo",output:"lub",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"glb",tag:"mo",output:"glb",tex:null,ttype:y},{input:"min",tag:"mo",output:"min",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"max",tag:"mo",output:"max",tex:null,ttype:I},{input:"Sin",tag:"mo",output:"Sin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cos",tag:"mo",output:"Cos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Tan",tag:"mo",output:"Tan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arcsin",tag:"mo",output:"Arcsin",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arccos",tag:"mo",output:"Arccos",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Arctan",tag:"mo",output:"Arctan",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Sinh",tag:"mo",output:"Sinh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cosh",tag:"mo",output:"Cosh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Tanh",tag:"mo",output:"Tanh",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Cot",tag:"mo",output:"Cot",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Sec",tag:"mo",output:"Sec",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Csc",tag:"mo",output:"Csc",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Log",tag:"mo",output:"Log",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Ln",tag:"mo",output:"Ln",tex:null,ttype:E,func:!0},{input:"Abs",tag:"mo",output:"abs",tex:null,ttype:E,notexcopy:!0,rewriteleftright:["|","|"]},{input:"uarr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2191",tex:"uparrow",ttype:y},{input:"darr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2193",tex:"downarrow",ttype:y},{input:"rarr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2192",tex:"rightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"->",tag:"mo",output:"\u2192",tex:"to",ttype:y},{input:">->",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a3",tex:"rightarrowtail",ttype:y},{input:"->>",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a0",tex:"twoheadrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:">->>",tag:"mo",output:"\u2916",tex:"twoheadrightarrowtail",ttype:y},{input:"|->",tag:"mo",output:"\u21a6",tex:"mapsto",ttype:y},{input:"larr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2190",tex:"leftarrow",ttype:y},{input:"harr",tag:"mo",output:"\u2194",tex:"leftrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"rArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d2",tex:"Rightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"lArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d0",tex:"Leftarrow",ttype:y},{input:"hArr",tag:"mo",output:"\u21d4",tex:"Leftrightarrow",ttype:y},{input:"sqrt",tag:"msqrt",output:"sqrt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"root",tag:"mroot",output:"root",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"frac",tag:"mfrac",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"/",tag:"mfrac",output:"/",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"stackrel",tag:"mover",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"overset",tag:"mover",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"underset",tag:"munder",output:"stackrel",tex:null,ttype:x},{input:"_",tag:"msub",output:"_",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"^",tag:"msup",output:"^",tex:null,ttype:T},{input:"hat",tag:"mover",output:"^",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"bar",tag:"mover",output:"\xaf",tex:"overline",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"vec",tag:"mover",output:"\u2192",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"dot",tag:"mover",output:".",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ddot",tag:"mover",output:"..",tex:null,ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"overarc",tag:"mover",output:"\u23dc",tex:"overparen",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ul",tag:"munder",output:"\u0332",tex:"underline",ttype:E,acc:!0},{input:"ubrace",tag:"munder",output:"\u23df",tex:"underbrace",ttype:R,acc:!0},{input:"obrace",tag:"mover",output:"\u23de",tex:"overbrace",ttype:R,acc:!0},{input:"text",tag:"mtext",output:"text",tex:null,ttype:v},{input:"mbox",tag:"mtext",output:"mbox",tex:null,ttype:v},{input:"color",tag:"mstyle",ttype:x},{input:"id",tag:"mrow",ttype:x},{input:"class",tag:"mrow",ttype:x},{input:"cancel",tag:"menclose",output:"cancel",tex:null,ttype:E},O,{input:"bb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"bold",output:"bb",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathbf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"bold",output:"mathbf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"sf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"sans-serif",output:"sf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathsf",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"sans-serif",output:"mathsf",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"bbb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"double-struck",output:"bbb",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:g},{input:"mathbb",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"double-struck",output:"mathbb",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:g},{input:"cc",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"script",output:"cc",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:m},{input:"mathcal",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"script",output:"mathcal",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:m},{input:"tt",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"monospace",output:"tt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"mathtt",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"monospace",output:"mathtt",tex:null,ttype:E},{input:"fr",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"fraktur",output:"fr",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:f},{input:"mathfrak",tag:"mstyle",atname:"mathvariant",atval:"fraktur",output:"mathfrak",tex:null,ttype:E,codes:f}];function M(t,e){return t.input>e.input?1:-1}var k,D,P,H=[];function w(){var t,e=L.length;for(t=0;t>1]=H[a];if(D=P,""!=s)return P=L[e].ttype,L[e];P=y,a=1,i=t.slice(0,1);for(var u=!0;"0"<=i&&i<="9"&&a<=t.length;)i=t.slice(a,a+1),a++;if(i==l&&"0"<=(i=t.slice(a,a+1))&&i<="9")for(u=!1,a++;"0"<=i&&i<="9"&&a<=t.length;)i=t.slice(a,a+1),a++;return u&&a>1||a>2?(i=t.slice(0,a-1),n="mn"):(a=2,n=("A">(i=t.slice(0,1))||i>"Z")&&("a">i||i>"z")?"mo":"mi"),"-"==i&&" "!==t.charAt(1)&&D==T?(P=T,{input:i,tag:n,output:i,ttype:E,func:!0}):{input:i,tag:n,output:i,ttype:y}}function j(t){var e;t.hasChildNodes()&&(!t.firstChild.hasChildNodes()||"mrow"!=t.nodeName&&"M:MROW"!=t.nodeName||"("!=(e=t.firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue)&&"["!=e&&"{"!=e||t.removeChild(t.firstChild),!t.lastChild.hasChildNodes()||"mrow"!=t.nodeName&&"M:MROW"!=t.nodeName||")"!=(e=t.lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue)&&"]"!=e&&"}"!=e||t.removeChild(t.lastChild))}function B(t){var e,i,a,s,r,o=n.createDocumentFragment();if(null==(e=U(t=J(t,0)))||e.ttype==b&&k>0)return[null,t];switch(e.ttype==N&&(e=U(t=e.output+J(t,e.input.length))),e.ttype){case I:case y:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];case C:return k++,a=G(t=J(t,e.input.length),!0),k--,"boolean"==typeof e.invisible&&e.invisible?i=d("mrow",a[0]):(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),(i=d("mrow",i)).appendChild(a[0])),[i,a[1]];case v:return e!=O&&(t=J(t,e.input.length)),-1==(s="{"==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf("}"):"("==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf(")"):"["==t.charAt(0)?t.indexOf("]"):e==O?t.slice(1).indexOf('"')+1:0)&&(s=t.length)," "==(r=t.slice(1,s)).charAt(0)&&((i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i)),o.appendChild(d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(r)))," "==r.charAt(r.length-1)&&((i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i)),t=J(t,s+1),[d("mrow",o),t];case R:case E:if(null==(a=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0])return[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];if("boolean"==typeof e.func&&e.func)return"^"==(r=t.charAt(0))||"_"==r||"/"==r||"|"==r||","==r||1==e.input.length&&e.input.match(/\w/)&&"("!=r?[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t]:((i=d("mrow",d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)))).appendChild(a[0]),[i,a[1]]);if(j(a[0]),"sqrt"==e.input)return[d(e.tag,a[0]),a[1]];if(void 0!==e.rewriteleftright)return(i=d("mrow",d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.rewriteleftright[0])))).appendChild(a[0]),i.appendChild(d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.rewriteleftright[1]))),[i,a[1]];if("cancel"==e.input)return(i=d(e.tag,a[0])).setAttribute("notation","updiagonalstrike"),[i,a[1]];if("boolean"==typeof e.acc&&e.acc){i=d(e.tag,a[0]);var l=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output));return"vec"==e.input&&("mrow"==a[0].nodeName&&1==a[0].childNodes.length&&null!==a[0].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue&&1==a[0].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue.length||null!==a[0].firstChild.nodeValue&&1==a[0].firstChild.nodeValue.length)&&l.setAttribute("stretchy",!1),i.appendChild(l),[i,a[1]]}if(!u&&void 0!==e.codes)for(s=0;s64&&r.charCodeAt(p)<91?h+=e.codes[r.charCodeAt(p)-65]:r.charCodeAt(p)>96&&r.charCodeAt(p)<123?h+=e.codes[r.charCodeAt(p)-71]:h+=r.charAt(p);"mi"==a[0].nodeName?a[0]=d("mo").appendChild(n.createTextNode(h)):a[0].replaceChild(d("mo").appendChild(n.createTextNode(h)),a[0].childNodes[s])}return(i=d(e.tag,a[0])).setAttribute(e.atname,e.atval),[i,a[1]];case x:if(null==(a=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0])return[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.input)),t];j(a[0]);var c=B(a[1]);return null==c[0]?[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.input)),t]:(j(c[0]),["color","class","id"].indexOf(e.input)>=0?("{"==t.charAt(0)?s=t.indexOf("}"):"("==t.charAt(0)?s=t.indexOf(")"):"["==t.charAt(0)&&(s=t.indexOf("]")),r=t.slice(1,s),i=d(e.tag,c[0]),"color"===e.input?i.setAttribute("mathcolor",r):"class"===e.input?i.setAttribute("class",r):"id"===e.input&&i.setAttribute("id",r),[i,c[1]]):("root"!=e.input&&"stackrel"!=e.output||o.appendChild(c[0]),o.appendChild(a[0]),"frac"==e.input&&o.appendChild(c[0]),[d(e.tag,o),c[1]]));case T:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),t];case S:return t=J(t,e.input.length),(i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i),o.appendChild(d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output))),(i=d("mspace")).setAttribute("width","1ex"),o.appendChild(i),[d("mrow",o),t];case A:return k++,a=G(t=J(t,e.input.length),!1),k--,r="",null!=a[0].lastChild&&(r=a[0].lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue),"|"==r&&","!==t.charAt(0)?(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode(e.output)),(i=d("mrow",i)).appendChild(a[0]),[i,a[1]]):(i=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u2223")),[i=d("mrow",i),t]);default:return t=J(t,e.input.length),[d(e.tag,n.createTextNode(e.output)),t]}}function F(t){var e,i,a,s,r,o;if(i=U(t=J(t,0)),s=(r=B(t))[0],(e=U(t=r[1])).ttype==T&&"/"!=e.input){if(null==(r=B(t=J(t,e.input.length)))[0]?r[0]=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u25a1")):j(r[0]),t=r[1],o=i.ttype==I||i.ttype==R,"_"==e.input)if("^"==(a=U(t)).input){var l=B(t=J(t,a.input.length));j(l[0]),t=l[1],(s=d(o?"munderover":"msubsup",s)).appendChild(r[0]),s.appendChild(l[0]),s=d("mrow",s)}else(s=d(o?"munder":"msub",s)).appendChild(r[0]);else"^"==e.input&&o?(s=d("mover",s)).appendChild(r[0]):(s=d(e.tag,s)).appendChild(r[0]);void 0!==i.func&&i.func&&(a=U(t)).ttype!=T&&a.ttype!=b&&(i.input.length>1||a.ttype==C)&&(r=F(t),(s=d("mrow",s)).appendChild(r[0]),t=r[1])}return[s,t]}function G(t,e){var i,a,s,r,o=n.createDocumentFragment();do{a=(s=F(t=J(t,0)))[0],(i=U(t=s[1])).ttype==T&&"/"==i.input?(null==(s=F(t=J(t,i.input.length)))[0]?s[0]=d("mo",n.createTextNode("\u25a1")):j(s[0]),t=s[1],j(a),(a=d(i.tag,a)).appendChild(s[0]),o.appendChild(a),i=U(t)):null!=a&&o.appendChild(a)}while((i.ttype!=b&&(i.ttype!=A||e)||0==k)&&null!=i&&""!=i.output);if(i.ttype==b||i.ttype==A){var l=o.childNodes.length;if(l>0&&"mrow"==o.childNodes[l-1].nodeName&&o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild&&o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild.firstChild){var u=o.childNodes[l-1].lastChild.firstChild.nodeValue;if(")"==u||"]"==u){var h=o.childNodes[l-1].firstChild.firstChild.nodeValue;if("("==h&&")"==u&&"}"!=i.output||"["==h&&"]"==u){var p=[],c=!0,m=o.childNodes.length;for(r=0;c&&r1&&(c=p[r].length==p[r-2].length)}var g=[];if(c=c&&(p.length>1||p[0].length>0)){var y,E,x,C,S=n.createDocumentFragment();for(r=0;r2&&(o.removeChild(o.firstChild),o.removeChild(o.firstChild)),S.appendChild(d("mtr",y))}(a=d("mtable",S)).setAttribute("columnlines",g.join(" ")),"boolean"==typeof i.invisible&&i.invisible&&a.setAttribute("columnalign","left"),o.replaceChild(a,o.firstChild)}}}}t=J(t,i.input.length),"boolean"==typeof i.invisible&&i.invisible||(a=d("mo",n.createTextNode(i.output)),o.appendChild(a))}return[o,t]}function V(t,e){var i;return k=0,i=d("mstyle",G((t=(t=(t=t.replace(/ /g,"")).replace(/>/g,">")).replace(/</g,"<")).replace(/^\s+/g,""),!1)[0]),""!=s&&i.setAttribute("mathcolor",s),""!=z&&(i.setAttribute("fontsize",z),i.setAttribute("mathsize",z)),""!=W&&(i.setAttribute("fontfamily",W),i.setAttribute("mathvariant",W)),r&&i.setAttribute("displaystyle","true"),i=d("math",i),o&&i.setAttribute("title",t.replace(/\s+/g," ")),i}o=!1;var W="",z=(s="","");!function(){for(var t=0,e=L.length;t=n-1&&(this.lastChild=t),this.SetData(i,t),t.nextSibling=e.nextSibling,e.nextSibling=e.parent=null,e},hasChildNodes:function(t){return this.childNodes.length>0},setAttribute:function(t,e){this[t]=e}}),w()},Augment:function(t){for(var e in t)if(t.hasOwnProperty(e)){switch(e){case"displaystyle":r=t[e];break;case"decimal":decimal=t[e];break;case"parseMath":V=t[e];break;case"parseExpr":G=t[e];break;case"parseIexpr":F=t[e];break;case"parseSexpr":B=t[e];break;case"removeBrackets":j=t[e];break;case"getSymbol":U=t[e];break;case"position":X=t[e];break;case"removeCharsAndBlanks":J=t[e];break;case"createMmlNode":d=t[e];break;case"createElementMathML":c=t[e];break;case"createElementXHTML":h=t[e];break;case"initSymbols":w=t[e];break;case"refreshSymbols":_=t[e];break;case"compareNames":M=t[e]}this[e]=t[e]}},parseMath:V,parseExpr:G,parseIexpr:F,parseSexr:B,removeBrackets:j,getSymbol:U,position:X,removeCharsAndBlanks:J,createMmlNode:d,createElementMathML:c,createElementXHTML:h,initSymbols:w,refreshSymbols:_,compareNames:M,createDocumentFragment:i,document:n,define:function(t,e){L.push({input:t,tag:"mo",output:e,tex:null,ttype:N}),_()},newcommand:function(t,e){L.push({input:t,tag:"mo",output:e,tex:null,ttype:N}),_()},newsymbol:function(t){L.push(t),_()},symbols:L,names:H,TOKEN:{CONST:y,UNARY:E,BINARY:x,INFIX:T,LEFTBRACKET:C,RIGHTBRACKET:b,SPACE:S,UNDEROVER:I,DEFINITION:N,LEFTRIGHT:A,TEXT:v,UNARYUNDEROVER:R}}})}(MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath),(t=MathJax.InputJax.AsciiMath).Augment({sourceMenuTitle:["AsciiMathInput","AsciiMath Input"],annotationEncoding:"text/x-asciimath",prefilterHooks:MathJax.Callback.Hooks(!0),postfilterHooks:MathJax.Callback.Hooks(!0),Translate:function(t){var i,n=MathJax.HTML.getScript(t),a={math:n,script:t},s=this.prefilterHooks.Execute(a);if(s)return s;n=a.math;try{i=this.AM.parseMath(n)}catch(t){if(!t.asciimathError)throw t;i=this.formatError(t,n)}return a.math=e(i),this.postfilterHooks.Execute(a),this.postfilterHooks.Execute(a)||a.math},formatError:function(t,i,n){var a=t.message.replace(/\n.*/,"");return MathJax.Hub.signal.Post(["AsciiMath Jax - parse error",a,i,n]),e.Error(a)},Error:function(t){throw MathJax.Hub.Insert(Error(t),{asciimathError:!0})},Startup:function(){e=MathJax.ElementJax.mml,this.AM.Init()}}),t.loadComplete("jax.js")},723:function(t,e){"use strict";MathJax._.components.global.isObject,MathJax._.components.global.combineConfig,MathJax._.components.global.combineDefaults,e.r8=MathJax._.components.global.combineWithMathJax,MathJax._.components.global.MathJax},649:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractFindMath=MathJax._.core.FindMath.AbstractFindMath},309:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.AbstractInputJax=MathJax._.core.InputJax.AbstractInputJax},769:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.protoItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.protoItem,e.AbstractMathItem=MathJax._.core.MathItem.AbstractMathItem,e.STATE=MathJax._.core.MathItem.STATE,e.newState=MathJax._.core.MathItem.newState},806:function(t,e){"use strict";e.g=MathJax._.core.MmlTree.MmlFactory.MmlFactory},77:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.isObject=MathJax._.util.Options.isObject,e.APPEND=MathJax._.util.Options.APPEND,e.REMOVE=MathJax._.util.Options.REMOVE,e.OPTIONS=MathJax._.util.Options.OPTIONS,e.Expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.Expandable,e.expandable=MathJax._.util.Options.expandable,e.makeArray=MathJax._.util.Options.makeArray,e.keys=MathJax._.util.Options.keys,e.copy=MathJax._.util.Options.copy,e.insert=MathJax._.util.Options.insert,e.defaultOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.defaultOptions,e.userOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.userOptions,e.selectOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptions,e.selectOptionsFromKeys=MathJax._.util.Options.selectOptionsFromKeys,e.separateOptions=MathJax._.util.Options.separateOptions,e.lookup=MathJax._.util.Options.lookup},720:function(t,e){"use strict";Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.sortLength=MathJax._.util.string.sortLength,e.quotePattern=MathJax._.util.string.quotePattern,e.unicodeChars=MathJax._.util.string.unicodeChars,e.unicodeString=MathJax._.util.string.unicodeString,e.isPercent=MathJax._.util.string.isPercent,e.split=MathJax._.util.string.split}},e={};function i(n){var a=e[n];if(void 0!==a)return a.exports;var s=e[n]={exports:{}};return t[n].call(s.exports,s,s.exports,i),s.exports}i.g=function(){if("object"==typeof globalThis)return globalThis;try{return this||new Function("return this")()}catch(t){if("object"==typeof window)return window}}(),function(){"use strict";var t=i(723),e=i(306),n=i(884),a=i(577);MathJax.loader&&MathJax.loader.checkVersion("input/asciimath",e.q,"input"),(0,t.r8)({_:{input:{asciimath_ts:n,asciimath:{FindAsciiMath:a}}}}),MathJax.startup&&(MathJax.startup.registerConstructor("asciimath",n.AsciiMath),MathJax.startup.useInput("asciimath"))}()}();����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������././@PaxHeader��������������������������������������������������������������������������������������0000000�0000000�0000000�00000000033�00000000000�010211� x����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������27 mtime=1692426889.044968
�����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������opencv_pg-1.0.2/src/opencv_pg/docs/js/mathjax/input/mml.js������������������������������������������0000644�0000000�0000000�00000034367�00000000000�020427� 0����������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������ustar�00�������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������������!function(){"use strict";var t,e,r,a,o,i={306:function(t,e){e.q=void 0,e.q="3.2.2"},236:function(t,e,r){var a,o=this&&this.__extends||(a=function(t,e){return a=Object.setPrototypeOf||{__proto__:[]}instanceof Array&&function(t,e){t.__proto__=e}||function(t,e){for(var r in e)Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(e,r)&&(t[r]=e[r])},a(t,e)},function(t,e){if("function"!=typeof e&&null!==e)throw new TypeError("Class extends value "+String(e)+" is not a constructor or null");function r(){this.constructor=t}a(t,e),t.prototype=null===e?Object.create(e):(r.prototype=e.prototype,new r)}),i=this&&this.__read||function(t,e){var r="function"==typeof Symbol&&t[Symbol.iterator];if(!r)return t;var a,o,i=r.call(t),n=[];try{for(;(void 0===e||e-- >0)&&!(a=i.next()).done;)n.push(a.value)}catch(t){o={error:t}}finally{try{a&&!a.done&&(r=i.return)&&r.call(i)}finally{if(o)throw o.error}}return n};Object.defineProperty(e,"__esModule",{value:!0}),e.MathML=void 0;var n=r(309),s=r(77),l=r(898),c=r(794),h=r(332),p=function(t){function e(e){void 0===e&&(e={});var r=this,a=i((0,s.separateOptions)(e,c.FindMathML.OPTIONS,h.MathMLCompile.OPTIONS),3),o=a[0],n=a[1],p=a[2];return(r=t.call(this,o)||this).findMathML=r.options.FindMathML||new c.FindMathML(n),r.mathml=r.options.MathMLCompile||new h.MathMLCompile(p),r.mmlFilters=new l.FunctionList,r}return o(e,t),e.prototype.setAdaptor=function(e){t.prototype.setAdaptor.call(this,e),this.findMathML.adaptor=e,this.mathml.adaptor=e},e.prototype.setMmlFactory=function(e){t.prototype.setMmlFactory.call(this,e),this.mathml.setMmlFactory(e)},Object.defineProperty(e.prototype,"processStrings",{get:function(){return!1},enumerable:!1,configurable:!0}),e.prototype.compile=function(t,e){var r=t.start.node;if(!r||!t.end.node||this.options.forceReparse||"#text"===this.adaptor.kind(r)){var a=this.executeFilters(this.preFilters,t,e,(t.math||"").trim()),o=this.checkForErrors(this.adaptor.parse(a,"text/"+this.options.parseAs)),i=this.adaptor.body(o);1!==this.adaptor.childNodes(i).length&&this.error("MathML must consist of a single element"),r=this.adaptor.remove(this.adaptor.firstChild(i)),"math"!==this.adaptor.kind(r).replace(/^[a-z]+:/,"")&&this.error("MathML must be formed by a  ## Installation
Currently tested with python 3.8.10/3.10.0 and opencv-contrib-python-headless 4.8.0.76 on an M1 Mac.
From PyPi:
```shell
pip install opencv-pg
```
From Github Repo:
```shell
pip install git+https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
```
### Note for Linux Users
**NOTE:** I no longer have access to anything but a Mac (as of `1.0.2`), so I can't confirm if the below still stands. It did in `1.0.1`.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (others currently untested), there may be missing links to xcb related shared objects.
tldr;
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
------
**Digging Deeper**
If you see errors about xcb, you can perform the following to help troubleshoot. In your terminal, make the following export:
```shell
export QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS=1
```
Run opencvpg again and validate the output. The final lines will likely mention details about files not found. Likely `libxcb-xinerama.so.0`.
Run the following:
```shell
cd your_venv/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/PySide2/Qt/plugins/platforms/
ldd libqxcb.so | grep "not found"
```
This will print any missing links. In our case, `libxcb-xinerama.so.0` showed up a couple times. Reinstalling the package as follows resolved the issue:
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
Once it’s working, you may want to disable that `QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS` env variable so it doesn’t throw extra garbage in your output.
## Usage
### Playground
To launch the OpenCV Playground with:
* The built-in image:
```shell
opencvpg
```
* An image of your choice:
```shell
opencvpg --image
## Installation
Currently tested with python 3.8.10/3.10.0 and opencv-contrib-python-headless 4.8.0.76 on an M1 Mac.
From PyPi:
```shell
pip install opencv-pg
```
From Github Repo:
```shell
pip install git+https://github.com/opencv-pg/opencv-pg
```
### Note for Linux Users
**NOTE:** I no longer have access to anything but a Mac (as of `1.0.2`), so I can't confirm if the below still stands. It did in `1.0.1`.
On Ubuntu 16.04 (others currently untested), there may be missing links to xcb related shared objects.
tldr;
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
------
**Digging Deeper**
If you see errors about xcb, you can perform the following to help troubleshoot. In your terminal, make the following export:
```shell
export QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS=1
```
Run opencvpg again and validate the output. The final lines will likely mention details about files not found. Likely `libxcb-xinerama.so.0`.
Run the following:
```shell
cd your_venv/lib/pythonX.X/site-packages/PySide2/Qt/plugins/platforms/
ldd libqxcb.so | grep "not found"
```
This will print any missing links. In our case, `libxcb-xinerama.so.0` showed up a couple times. Reinstalling the package as follows resolved the issue:
```shell
sudo apt-get install --reinstall libxcb-xinerama0
```
Once it’s working, you may want to disable that `QT_DEBUG_PLUGINS` env variable so it doesn’t throw extra garbage in your output.
## Usage
### Playground
To launch the OpenCV Playground with:
* The built-in image:
```shell
opencvpg
```
* An image of your choice:
```shell
opencvpg --image